Ch 4 Cell Metabolism Vet Tech A&P1 (Material NOT on Ch 3, 4 exam has been removed in this version)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Normal Hydration
Consuming the same amount of water that is lost.
Metabolic water
Water made inside of cells during chemical reactions.
Insensible water loss
Water lost through breathing.
Intracellular fluid
Fluid located inside cells.
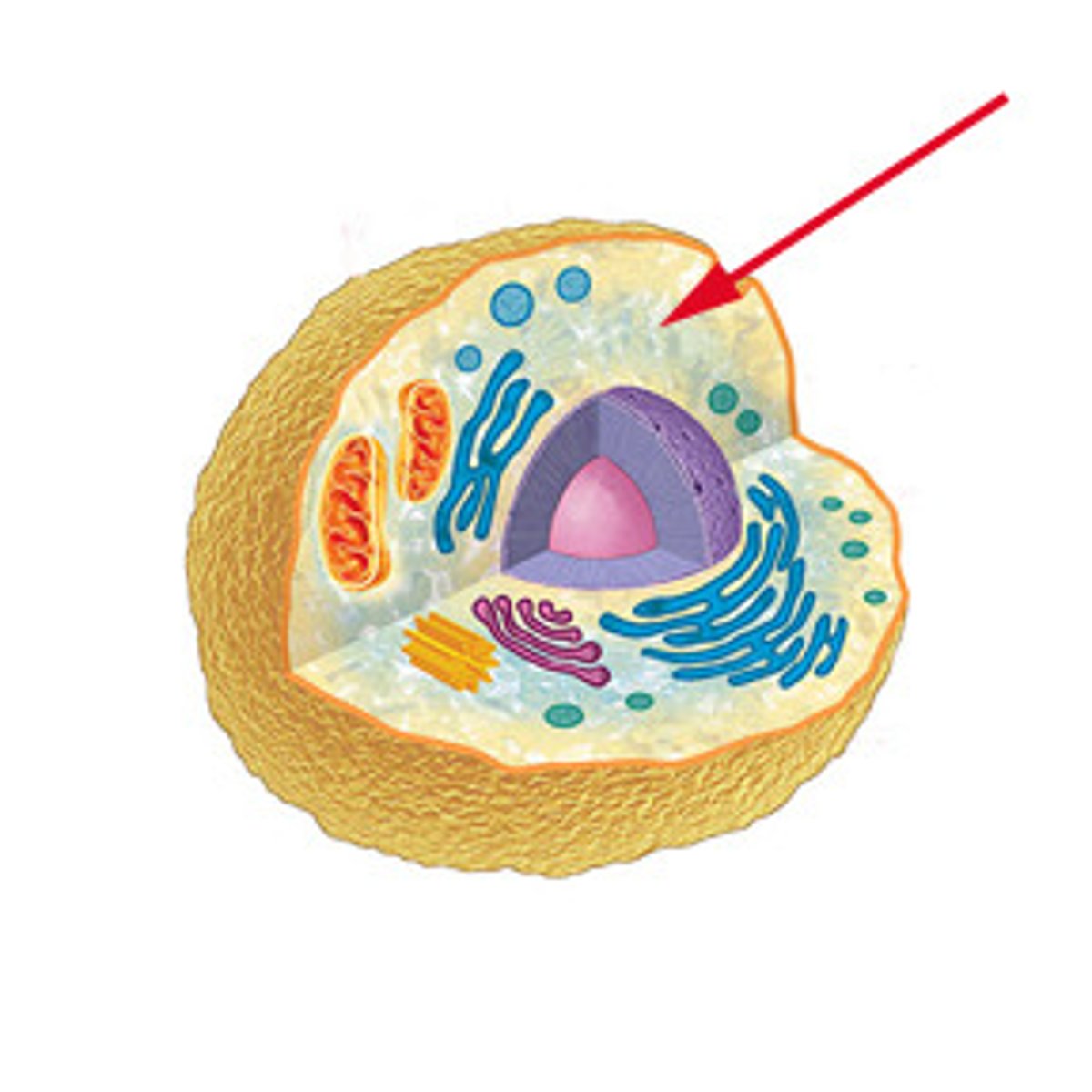
Extracellular fluid
Fluid located outside cells.
Intravascular fluid
Fluid located inside blood vessels.
Interstitial fluid
Fluid directly surrounding cells.
Solutes
Solids that are dissolved in water.
Electrolytes
Particles in body fluids capable of conducting an electrical current.
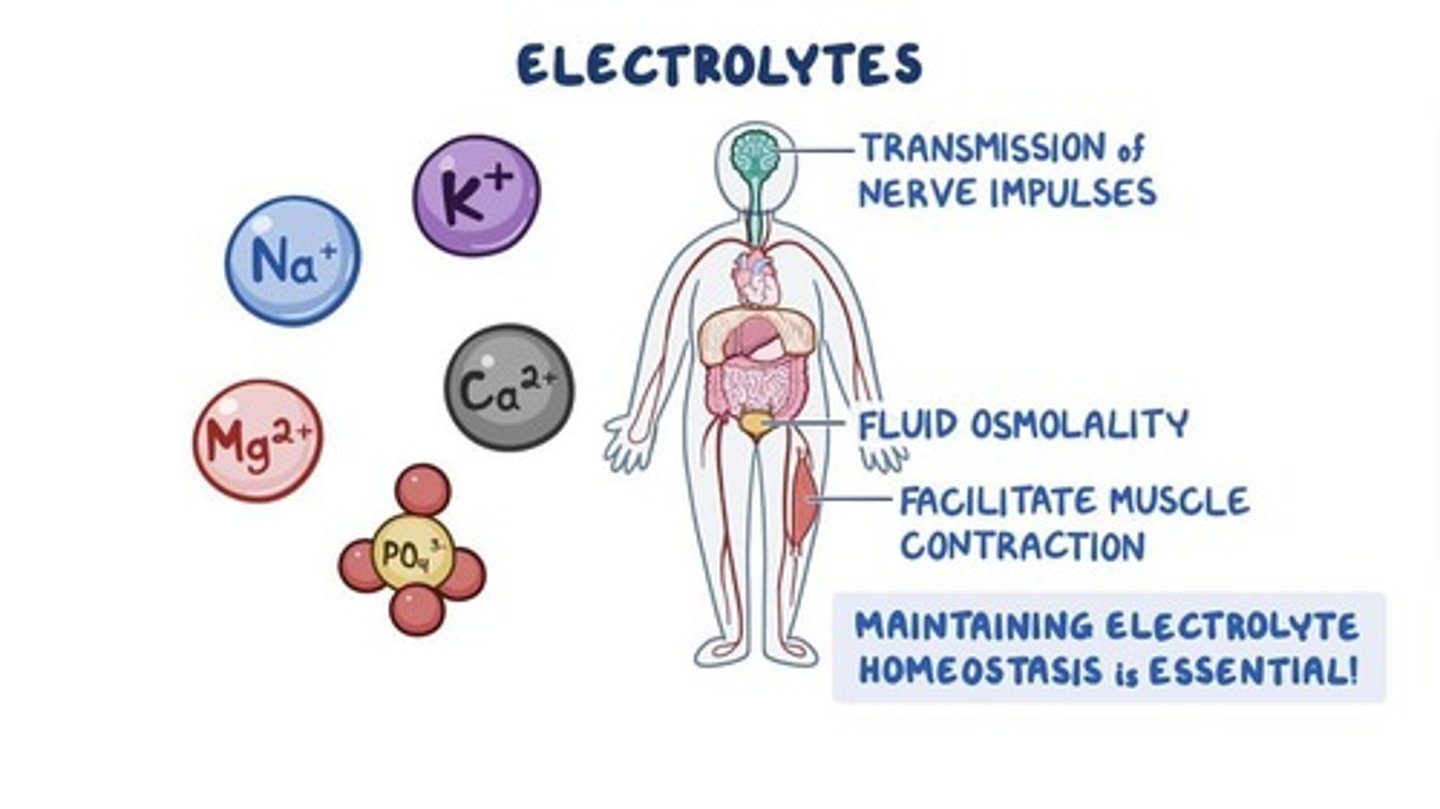
Cations
Positively charged ions.
Anions
Negatively charged ions.
Electrolyte concentrations
Expressed in meq/L.
Acidity
More free H+ ions in a solution equals more acidity.
pH of pure water
7 (neutral).
pH of blood
7.4.
pH of gastric juice
Below 7 (pH 2).
Alkalinity
More free OH- ions in a solution, the more basic or alkaline.
pH of bleach
Above 7.
Osmolality
Measurement of solute concentration in fluid.
High osmolality
Indicates high concentration of solutes.
Serum osmolality tests
Used to assess hydration status.
Hyperglycemia
High blood glucose, sugar, simple blood test
Isotonic Fluid
Same solute level as normal blood; extracellular fluid has same concentration of dissolved substances as intracellular fluid
Example of Isotonic Fluid
0.9% NaCl (normal saline)
Hypotonic Fluid
Solute level is less than that of blood; cytoplasm of the cell is more concentrated (more solute) than the extracellular fluid
Osmolality in Hypotonic Fluid
Osmolality is greater than that of blood cells; extracellular fluid is more concentrated than the cytoplasm
Movement of Water in Hypotonic Fluid
Water flows to the area with most solute, into the cell, causing it to swell and possibly to break
Edema
Abnormal, excess accumulation of fluid in tissue; common sign of abnormal movement of fluid from vascular space into interstitial space
Pulmonary Edema
Fluid moves into lungs
Cutaneous Edema
Fluid moves into interstitial space, generally into gravity-dependent areas or into the abdomen
Crystalloid
Composed of sterile water rich with electrolytes; isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic; solutes are small and able to cross vascular wall
Colloid
Heavy molecules suspended in isotonic crystalloid; solutes too large to cross vascular wall
Fluid therapy phases
Administered in three phases: Resuscitation during shock, Replacement when dehydrated, Maintenance during elective surgical procedures
Membrane Processes
Absorption of nutrients or excretion of waste through plasma membrane may occur with or without using energy (ATP) from the cell
Passive processes
Does NOT use ATP
Active processes
DOES use ATP
Membrane permeability
Freely permeable (small, hydrophobic, moves quickly through), Selectively permeable (allows some things through but not others), Impermeable (not permeable, needs a protein 'doorway')
Passive Diffusion
Movement of molecules from higher to lower concentration; moves WITH the concentration gradient
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of molecules from higher to lower concentration; moves WITH the concentration gradient
Selective carrier proteins
Assist in movement of molecules from higher to lower concentration.
Factors determining molecule passage
Molecular size (small), lipid solubility (hydrophobic), molecular charge (neutral).
Osmosis
Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from dilute solution to a more concentrated one.
Osmotic pressure
The pressure required to prevent the flow of water across a semipermeable membrane.
Equilibrium
Objective is for movement of water to achieve the same concentration on both sides of a semipermeable membrane.
Oncotic Pressure
The difference between osmotic pressure of blood and osmotic pressure of interstitial fluid or lymph.
Filtration
Based on a pressure gradient; liquids may be pushed through a membrane if pressure on one side is greater.
Active membrane processes
Movement of molecules from low concentration to high concentration across the cell membrane using energy (ATP).
Active transport
Some amino acids and ions rely on a carrier protein and energy (ATP) to move through the plasma membrane.
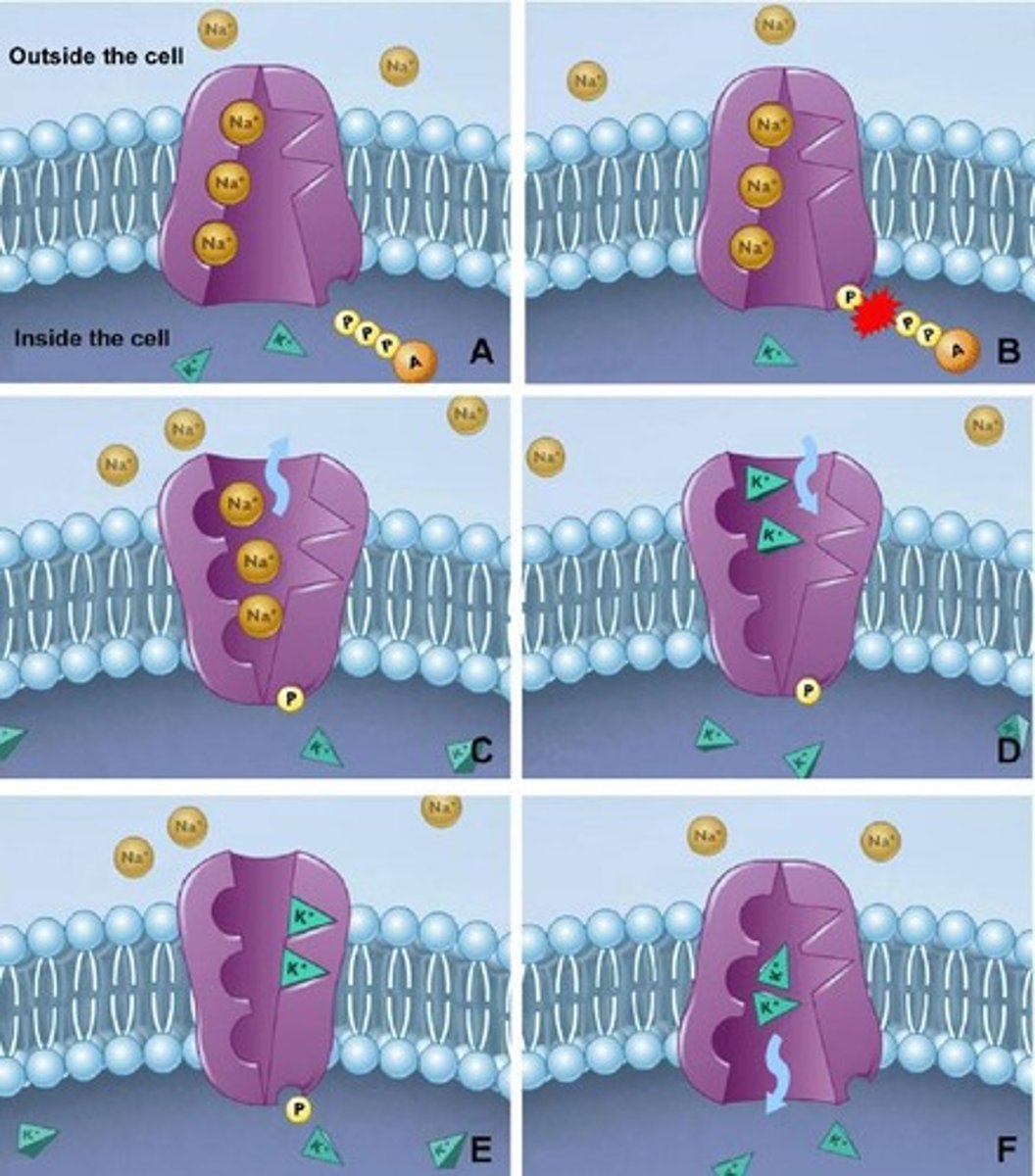
Na/K Pump
An example of active transport that moves sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane.
Cytosis
Mechanism for bringing nutrients into the cell and ejecting waste.
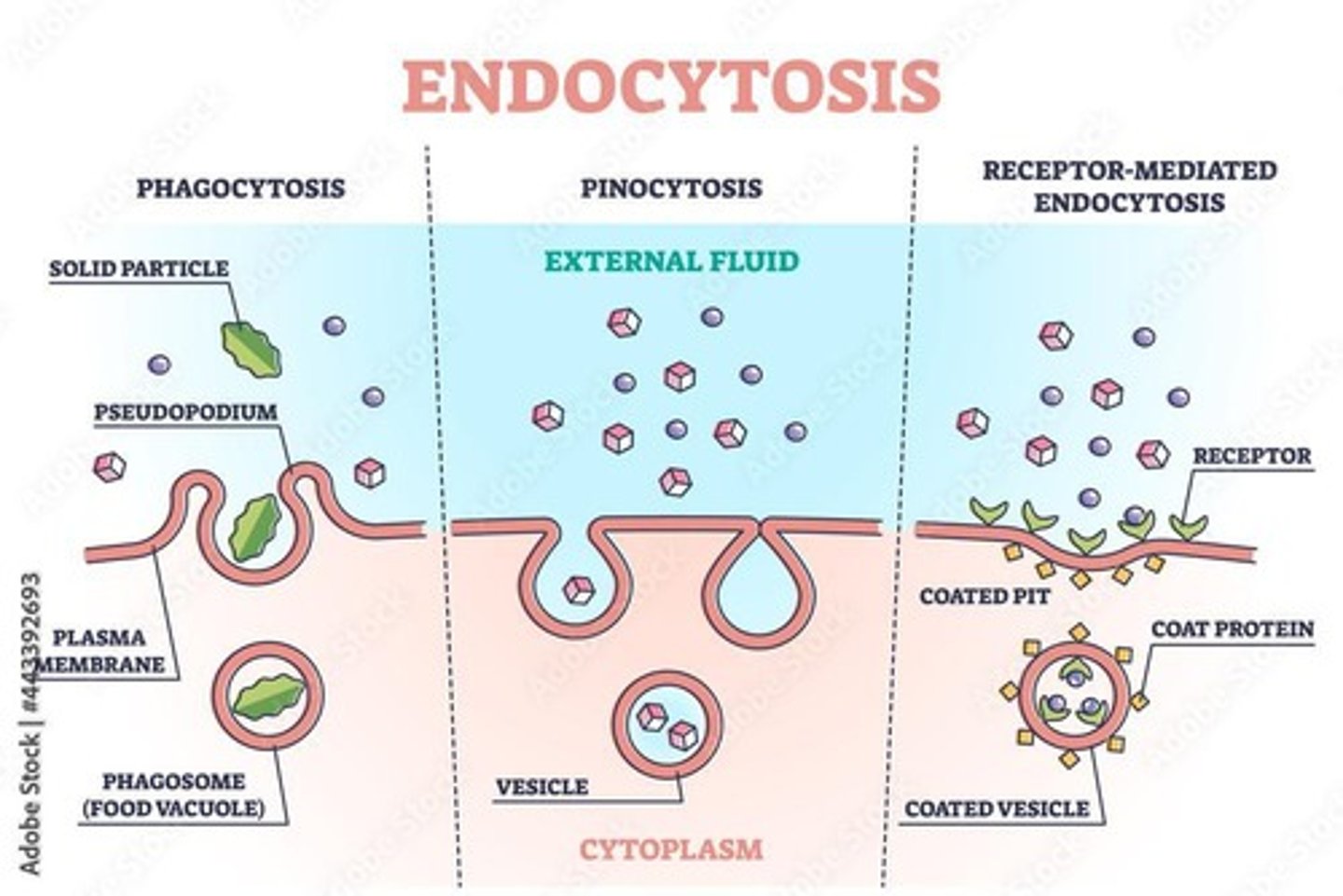
Endocytosis
Transports large particles or liquids into the cell by engulfing them.
Exocytosis
Cells export intracellular substances into the extracellular space.
Phagocytosis
Cell 'eats'; cells engulf solid material.
Pinocytosis
Cell 'drinks'; cells engulf liquid material.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A very specific process where ligands bind to specific receptors, forming a vesicle.
Hydrostatic pressure
The pressure exerted by a fluid at equilibrium due to the force of gravity.
Subcutaneous edema
Swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues.
Ascites
Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity.
Vesicles
Substances packaged by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi body for transport.