4.6 Amines
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Primary Amine
where nitrogen bonded to only one carbon atom
Secondary Amine
where nitrogen bonded to two carbon atoms
Tertiary Amine
where nitrogen bonded to three carbon atoms
What is an amine group
Reactants and conditions for the formation of primary amines from halogenoalkanes
halogenoalkane and ammonia dissolved in water/ethanol.
sealed tube to avoid escape of ammonia, which is used in excess
What kind of reaction is the formation of primary amines from halogenoalkanes
Nucleophilic Substitution
Mechanism for formation of primary amines from halogenoalkanes
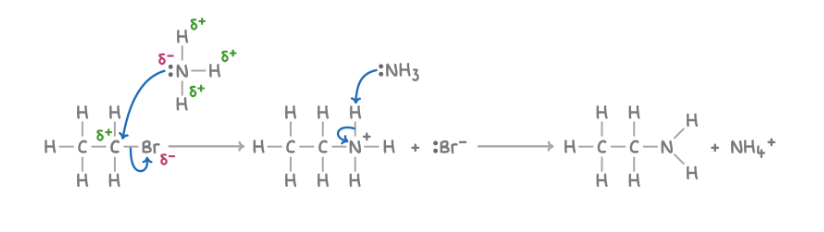
Additional products of the formation of primary amines from halogenoalkanes
HBr
If excess halogenoalkane is added with ammonia dissolved in water/ethanol
Further substitution takes place and a secondary amine is formed

Describe the formation of primary amines from nitriles
produced by reduction of nitriles using LiAlH4
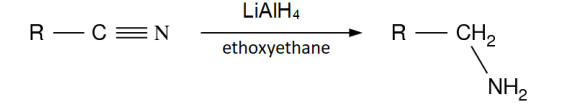
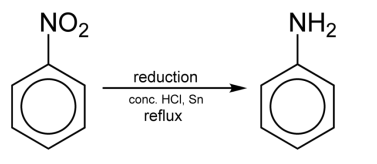
Describe the formation of aromatic amines from nitrobenzenes
Reducing agent = Iron in HCl or Hydrogen with a nickel catalyst
Reflux
Forms phenylamine
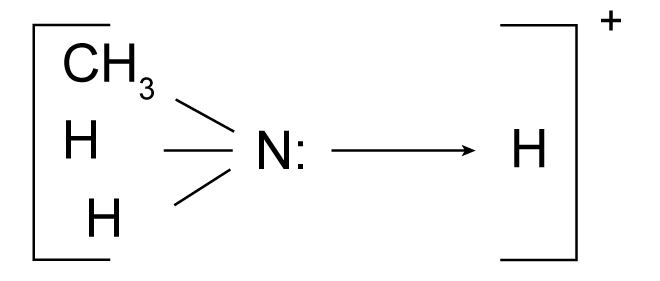
What allows amines to accept a proton
Amines, like ammonia, have a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom.
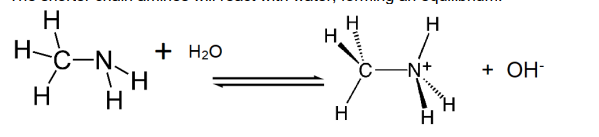
What will shorter chain amines react with
water forming an equilibrium
Equilibrium lies well over to the left
What is a test for amines
Red litmus paper-- red to blue
How are alkylamines stronger bases than ammonia
the alkyl groups ‘push’ electrons more onto the nitrogen atom, making it more δ- when compared with ammonia’s nitrogen.
Why are longer alkylamines stronger bases
The longer the chain the more significant the effect of the push of electrons
Why are phenylamines a weaker base than ammonia and alkylamines
the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen becomes part of the delocalised π-electron system of the benzene ring. This makes the nitrogen relatively less δ-.
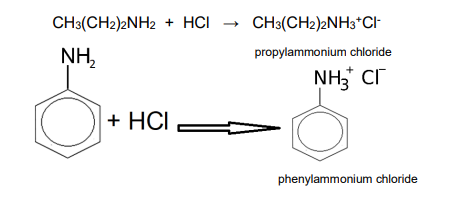
All …. react with acid to make a salt
amines
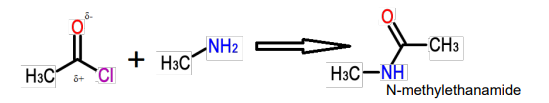
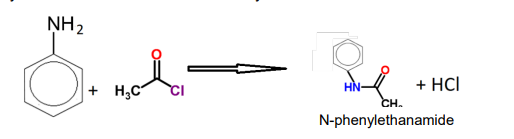
Describe the ethanoylation of primary amines using ethanoyl Chloride
Amines can act as nucleophiles due to the nitrogen lone pair. They attack the δ+ carbon of the carbonyl group in an acid chloride
Reaction of phenylamine and ethanoyl chloride
How is nitrous acid made
reacting sodium nitrate(III) (sodium nitrite) with dilute HCl.
Why does nitrous acid have to be made in situ
instability
What does the reaction of nitrous acid with aromatic and aliphatic amines form at room temp
alcohol, water and N2 gas
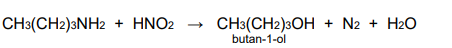
What does the reaction of primary aromatic amines with nitric acid form at 10 degrees
benzenediazonium chloride
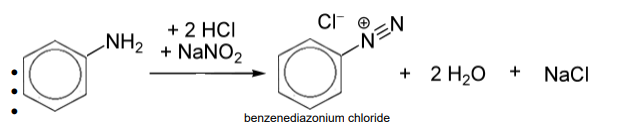
Why must there be excess nitric acid in the reaction
so that all the amine is converted.
Benzenediazonium chloride can couple with unused phenylamine
Why is the product not isolated
pure benzenediazonium is explosively unstable
How are diazonium compounds useful as intermediates in the synthesis of organic compounds
1) If aqueous benzenediazonium chloride is warmed above 10 degrees a phenol is formed
2) Iodobenzene is formed when aqueous benzenediazonium chloride is warmed with aqueous potassium iodide
How to identify Nitrogen gas
Put lit splint in and nothing happens
What does the reaction of benzenediazonium chloride with phenols and amines form
coloured compounds called azodydes