Principles and Protocols of Exercise Tolerance Testing in Cardiology
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is the primary purpose of exercise testing?
To assess cardiovascular fitness and identify any abnormalities during physical exertion.
What are the key indications for conducting an ETT?
Chest pain, stable angina, post-myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, pacemaker function, cardiac failure, and valvular disease.
What should be confirmed before a patient is referred for an ETT?
The patient must be able to perform the test, have a complete clinical history, and no absolute contraindications.
What are the pre-test instructions for patients undergoing ETT?
Patients should eat only a light meal, wear comfortable shoes, avoid strenuous exercise for 4 hours prior, and minimize smoking for 24 hours prior.
What is the significance of the exercise room environment?
It should be well-lit, clean, well-ventilated, and large enough to accommodate equipment and personnel.
What emergency equipment must be checked before each ETT session?
Resuscitation equipment, including a defibrillator, arrest drugs, oxygen, and suction.
What is the Bruce Protocol in ETT?
A widely used exercise testing protocol that involves changes in speed and slope every 3 minutes, with an exercise intensity of 2-3 METS per stage.
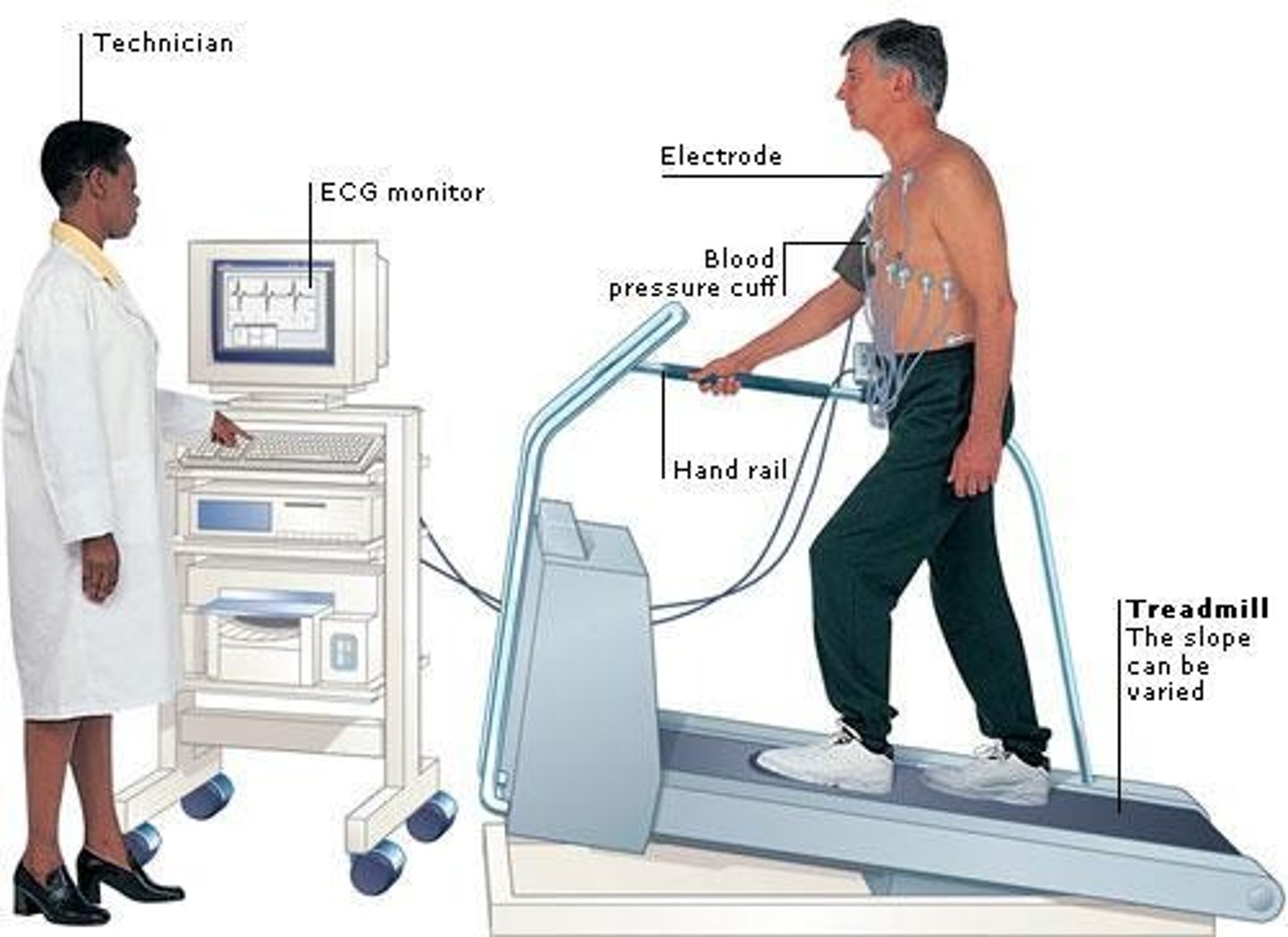
What are METs in the context of exercise testing?
Metabolic equivalents, where 1 MET equals the resting metabolic rate of 3.5 ml O2/kg/min.
What should be monitored continuously during an ETT?
ECG, arrhythmias, ST segment changes, blood pressure, and the patient's physical condition.
What actions should be taken during the post-exercise recovery period?
Ensure all physiological measurements return to near normal baseline and monitor for symptoms and ECG changes.
What are the responsibilities of the supervising cardiac physiologist during ETT?
To ensure patient safety, interpret data, provide accurate reports, and check all protocols are followed.
What is the role of skin preparation in ETT?
To lower resistance and decrease noise by removing the superficial layer of skin.
What should be done if a patient exhibits abnormal responses during recovery?
Monitor for mechanical dysfunction and electrophysiological abnormalities, which may persist and be significant.
What constitutes a positive ETT result?
Indications of ischemia such as ST segment depression or elevation during exercise.
What constitutes a negative ETT result?
No significant ST segment changes or symptoms during the test.
What are the advantages of using a bicycle for exercise testing?
Bicycles are cheaper, smaller, less noisy, and better for patients with mobility problems.
What are the disadvantages of using a treadmill for exercise testing?
Treadmills are expensive, noisy, require a large area, and patients must be able to walk.
What should be done if a patient requests to stop the test?
The test should be stopped immediately for patient safety.
What is the minimum frequency for measuring ECG and blood pressure during ETT?
Measurements should be taken supine and standing prior to the test, immediately before each progression, at peak exercise, and at 3-minute intervals in recovery.
What are the safety statistics for ETT post-myocardial infarction?
Fatal cardiac events are 0.03%, serious cardiac events are 0.09%, and complex arrhythmias are 1.4%.
What should be done if significant results are obtained during ETT?
Results should be reported immediately to the supervising consultant.
What is the importance of comparing computerized ST analysis to raw data?
It ensures accuracy and reliability of the test results.
What are some common end points for terminating an ETT?
Patient request, moderate-to-severe angina, dyspnea, signs of poor perfusion, and abnormal blood pressure responses.
What is the role of the named medic during an ETT session?
To be responsible for the session and immediately contactable in case of emergencies.
What is the purpose of the warm-up stage in ETT protocols?
To prepare the patient for exercise and reduce the risk of injury.
What is exercise-induced hypotension?
A drop in blood pressure during exercise.
What does significant ST depression indicate during exercise?
It may suggest myocardial ischemia.
What are common symptoms that indicate negative ETT results?
Fatigue, dyspnoea, sweating, and flushing.
What happens to the P wave during exercise in a normal ECG response?
The magnitude increases slightly inferiorly.
How does the PR interval change during exercise?
It shortens and slopes downwards inferiorly.
What does the QRS complex do at maximum exercise?
The Q wave can become more negative, R wave decreases in height, and S wave increases in height.
What is the ischemic cascade?
A sequence of events in the myocardium following ischemia, starting with changes in mechanical function, followed by ECG changes, and then symptoms.
Where is the J point located on an ECG?
At the junction between the termination of the QRS complex and the beginning of the ST segment.
What is the significance of ST depression measured after the J point?
It indicates potential ischemia and is measured as the difference from the isoelectric line.
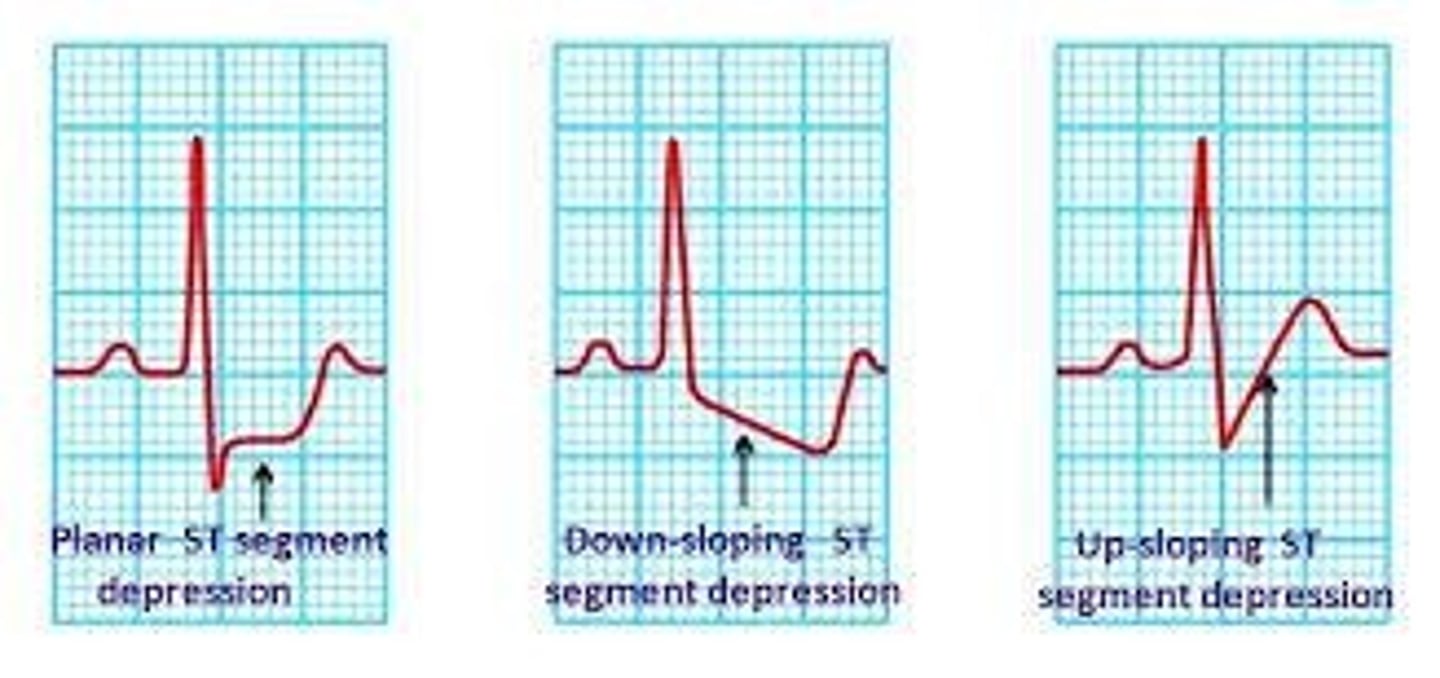
What does upsloping ST depression indicate?
It can be a normal variant and usually resolves quickly.
What does horizontal ST depression indicate?
It can be a stronger indicator of ischemic heart disease (IHD).
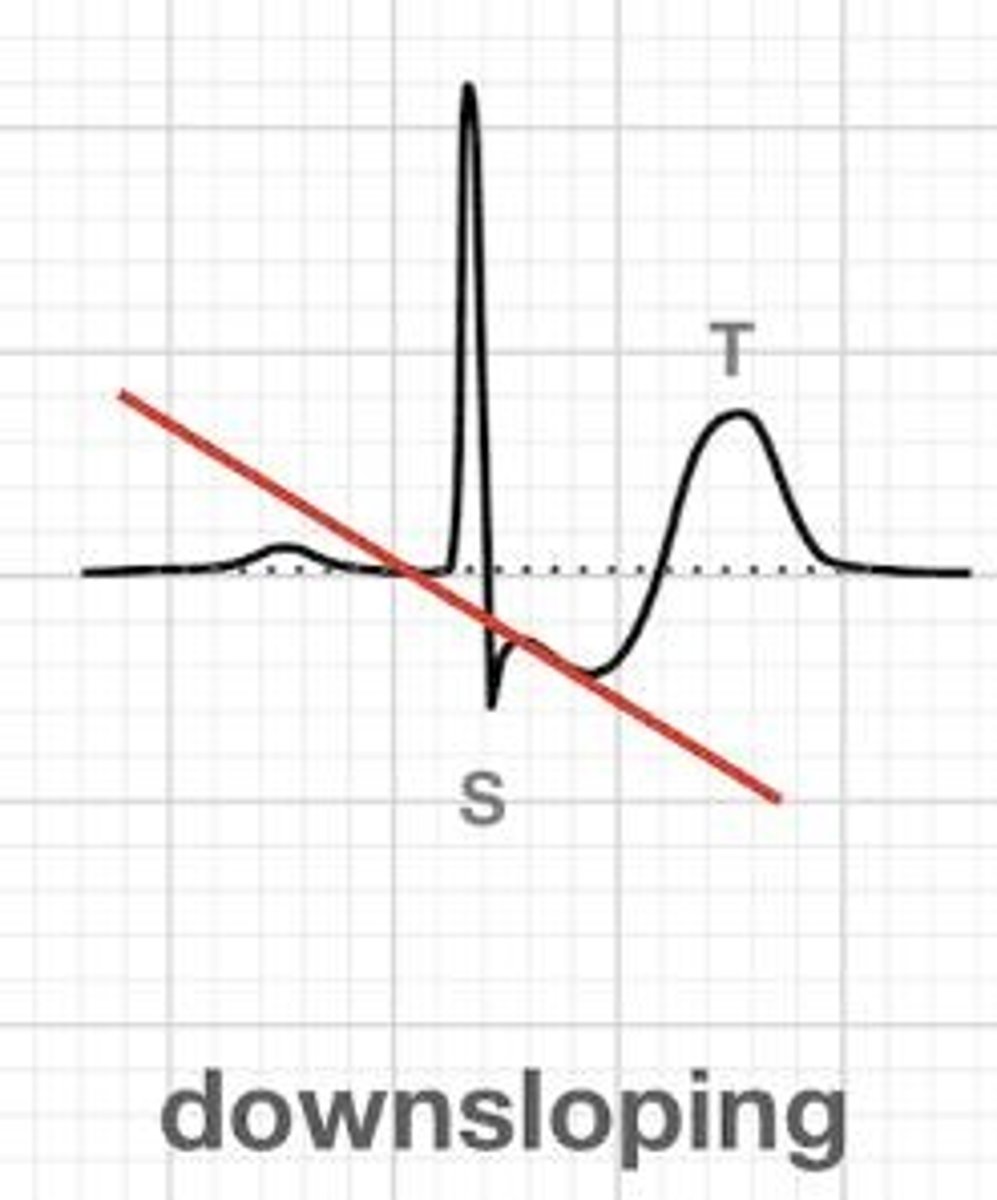
What is the strongest indicator of IHD on an ECG?
Downsloping ST depression.
What is Prinzmetal angina?
A type of angina caused by temporary vasospasm, leading to a marked but transient reduction in lumen diameter.
What demographic is most affected by Prinzmetal angina?
Predominantly younger females with no cardiovascular risk factors, except smoking.
What is the role of exercise testing in diagnosing Prinzmetal angina?
ETT is of no value in its diagnosis as it is not demand-induced.
What happens to ST elevation post Q wave infarction?
It is relatively common, with 30% in anterior MI and 15% in inferior MI.
What are absolute contraindications for exercise testing?
Severe angina, unstable angina, recent MI, uncontrolled hypertension, and history of ventricular arrhythmias.
What is the importance of LBBB during ETT?
ST depression usually occurs but is not indicative of ischemia; onset of LBBB during ETT is an indication to stop the test.
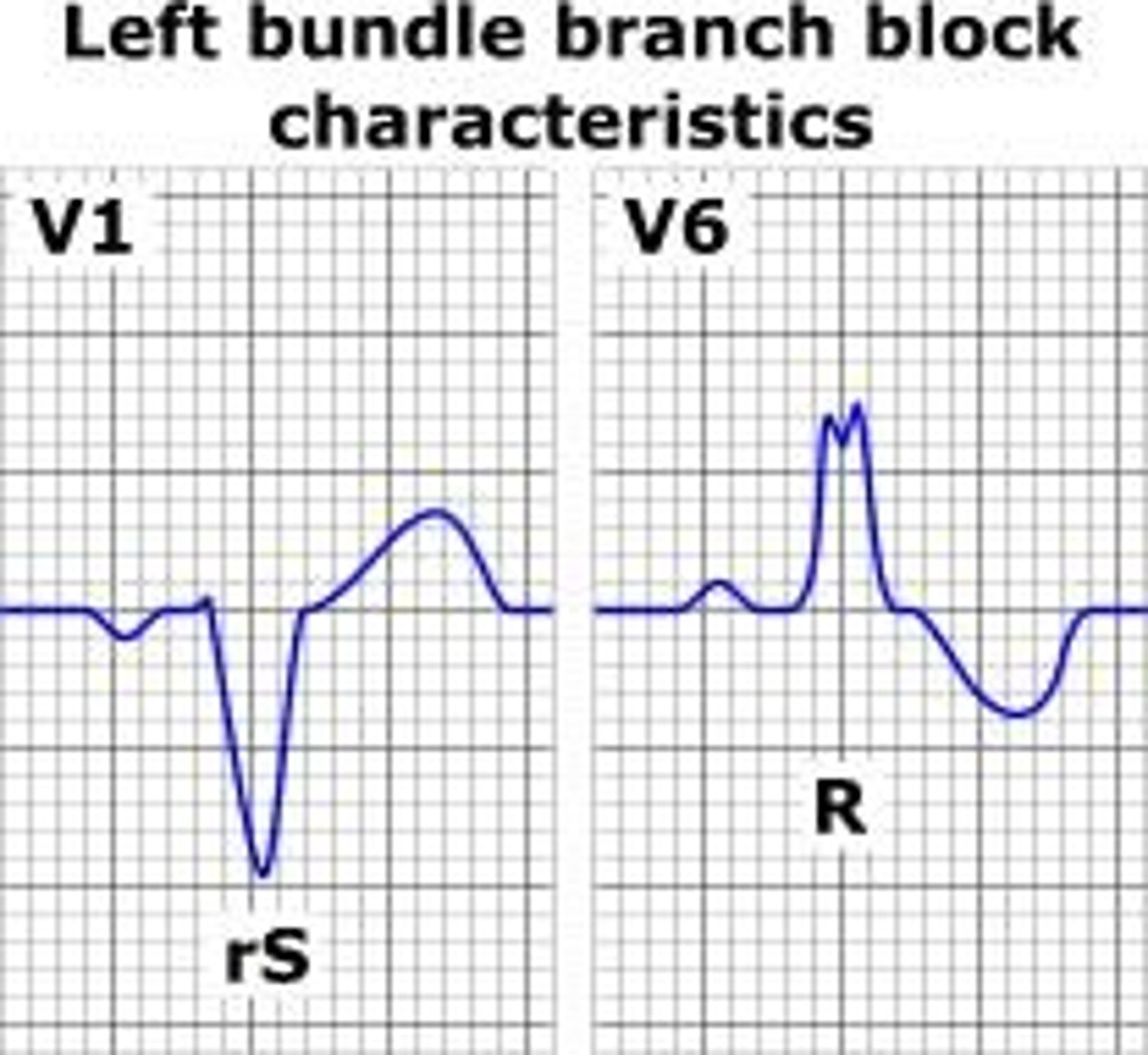
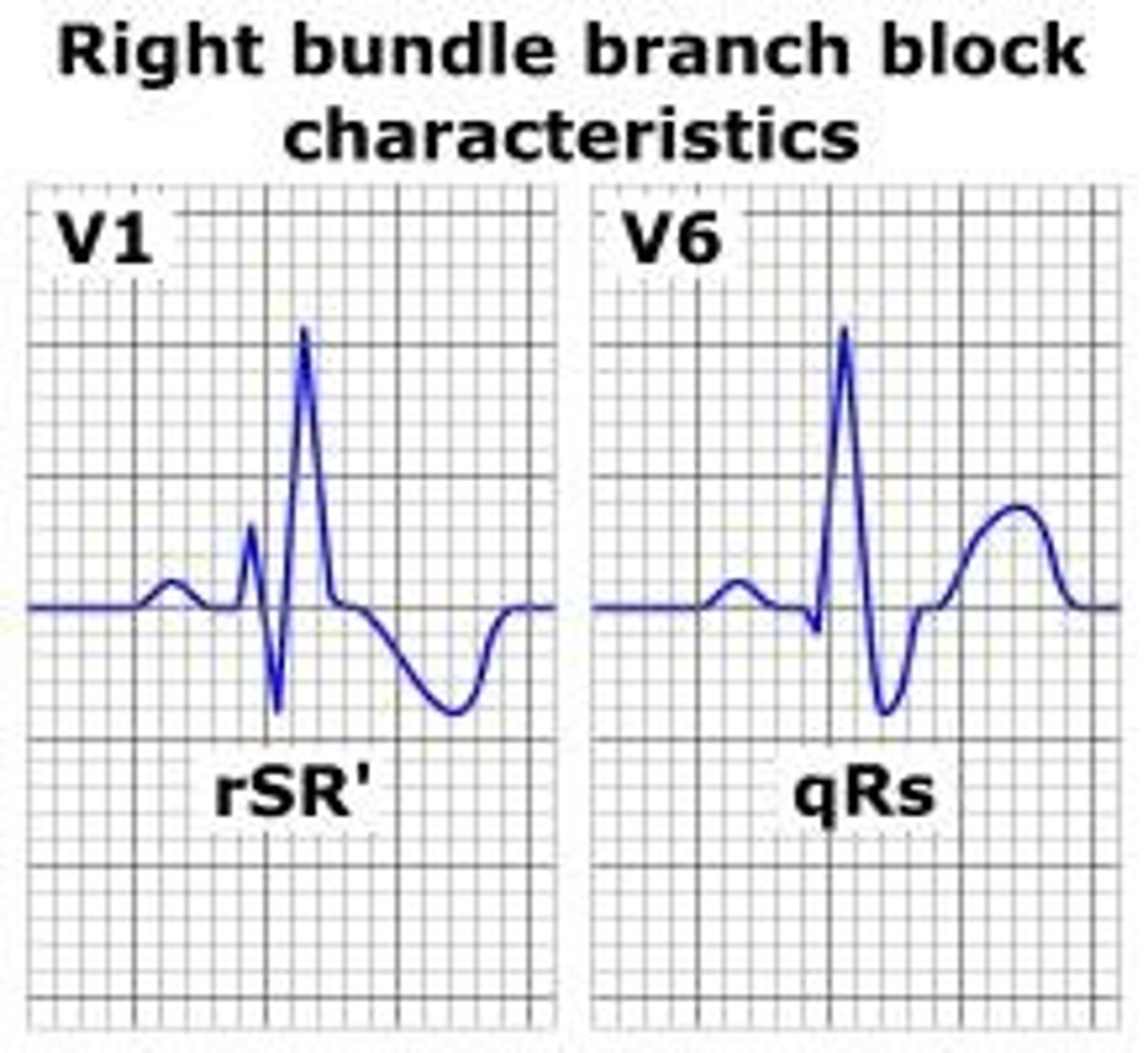
What should be done if RBBB occurs during ETT?
The test should be stopped as ST depression in leads V1-V3 is not associated with ischemia.
What is the first-line test for patients with suspected coronary artery disease?
64-slice CT coronary angiography.
What is the recommended exercise testing protocol post-MI?
Sub-maximal testing with a predetermined endpoint of 70% of predicted maximum heart rate.
What is the role of beta blockers in ETT?
They are not omitted but can mask symptoms and ST changes.
What is the responsibility of the cardiac physiologist during ETT?
To postpone a test or seek further information as appropriate.
What should be included in an ETT report?
An accurate account of events and a concise narrative of the test.
What is the significance of ST segment changes during ETT?
They can indicate myocardial ischemia and guide further management.
What is the expected recovery of T wave height after exercise?
T wave height usually normalizes within 1 minute of recovery.
What does a shortening of the QT interval indicate during exercise?
It is a normal response to exercise.
What are the implications of ST elevation without Q waves?
It is rare and usually results from spasm, being very arrhythmogenic.