Economics Growth Models: Solow, Romer, and GDP Frameworks
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What does the Solow diagram illustrate?
The dynamics of capital per worker (k), showing diminishing returns to capital.
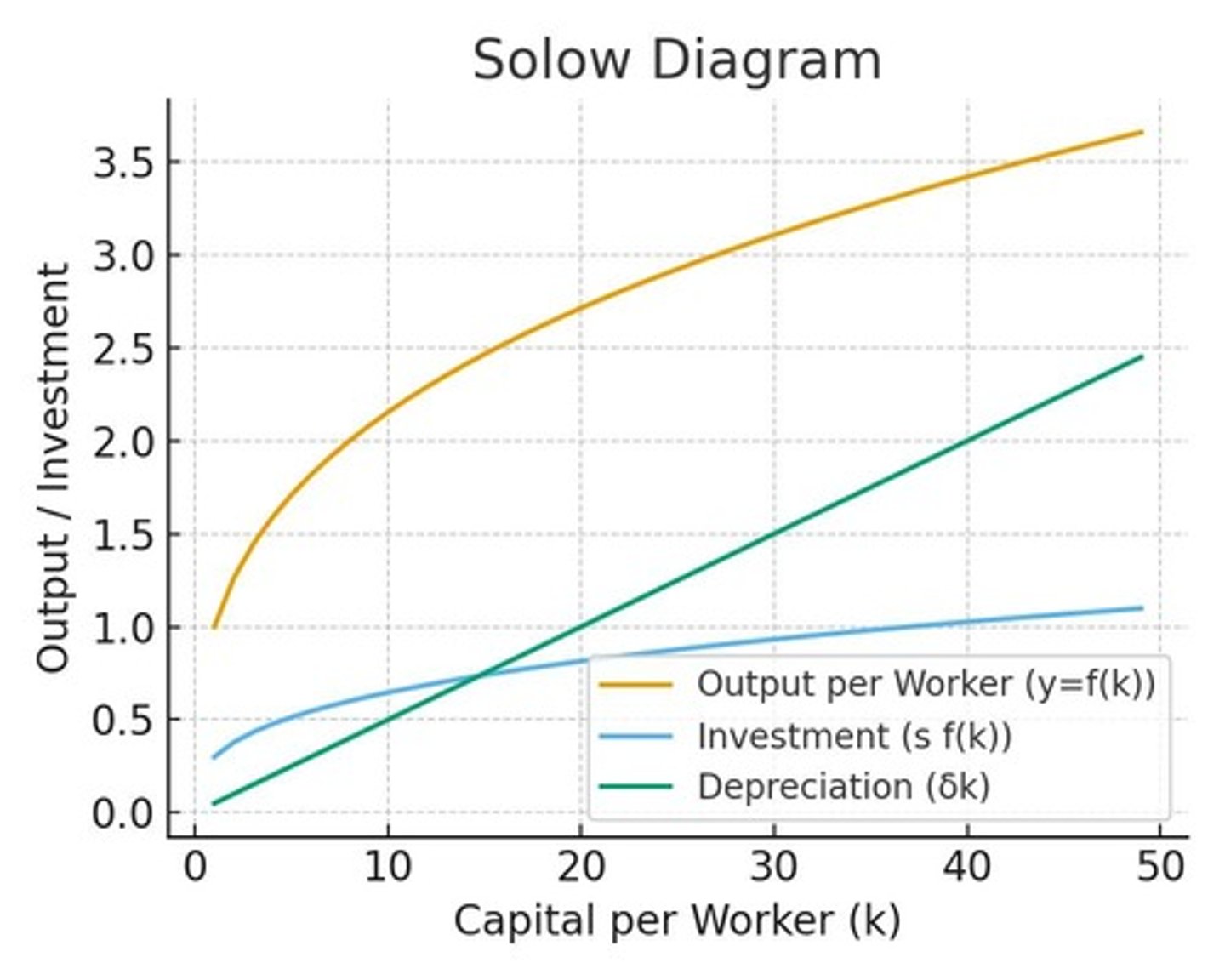
What determines the steady state in the Solow model?
The point where investment equals depreciation, determining long-run output per worker.
How does the investment curve in the Solow model behave?
It depends on the savings rate and is represented as s f(k).
What is the growth behavior of the stock of ideas in the Romer model?
It grows exponentially over time as researchers create new knowledge.
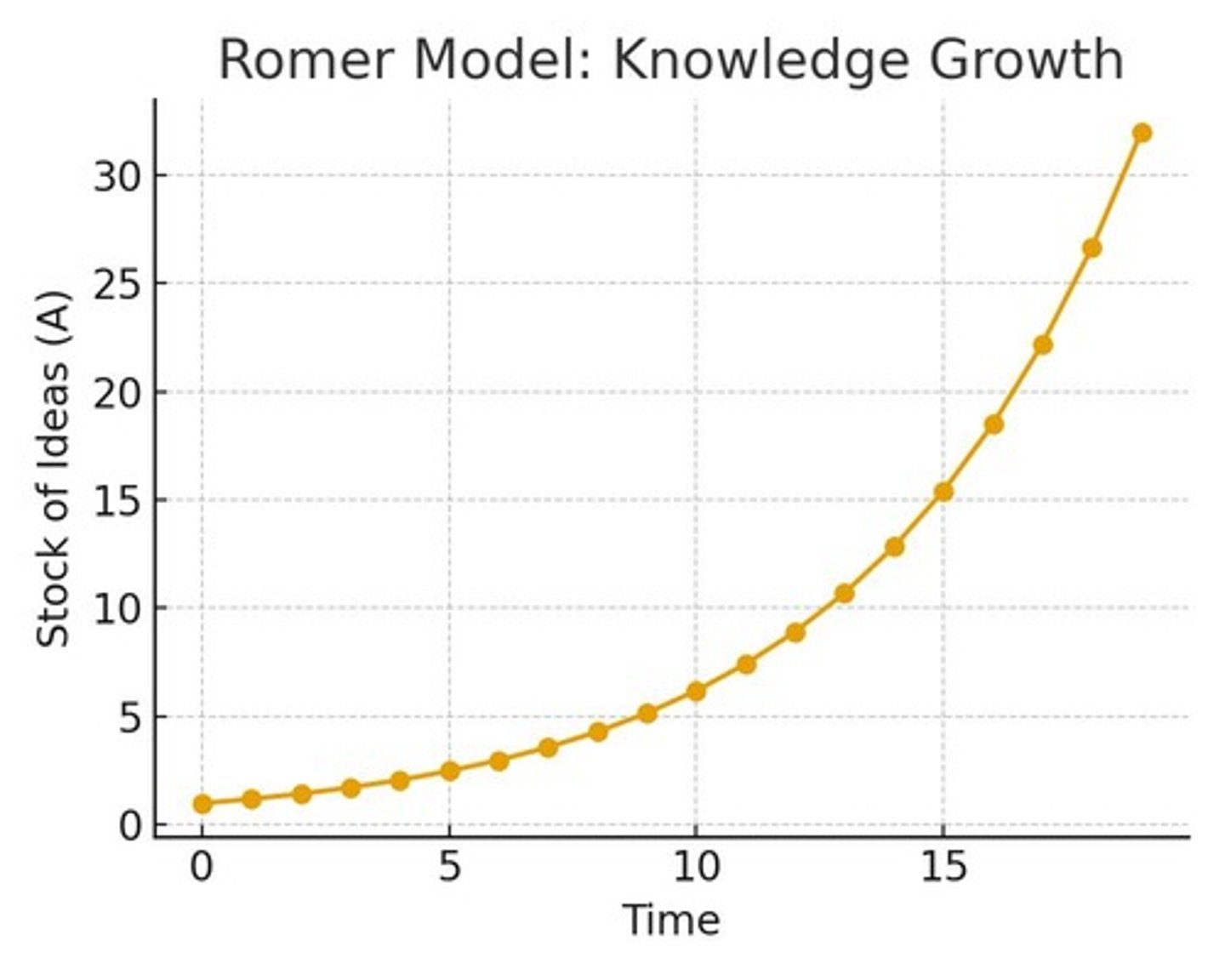
Why are ideas considered nonrival in the Romer model?
Because they can be used by multiple people simultaneously without being depleted.
What are the four components of GDP in the expenditure approach?
Consumption (C), Investment (I), Government spending (G), and Net Exports (NX).
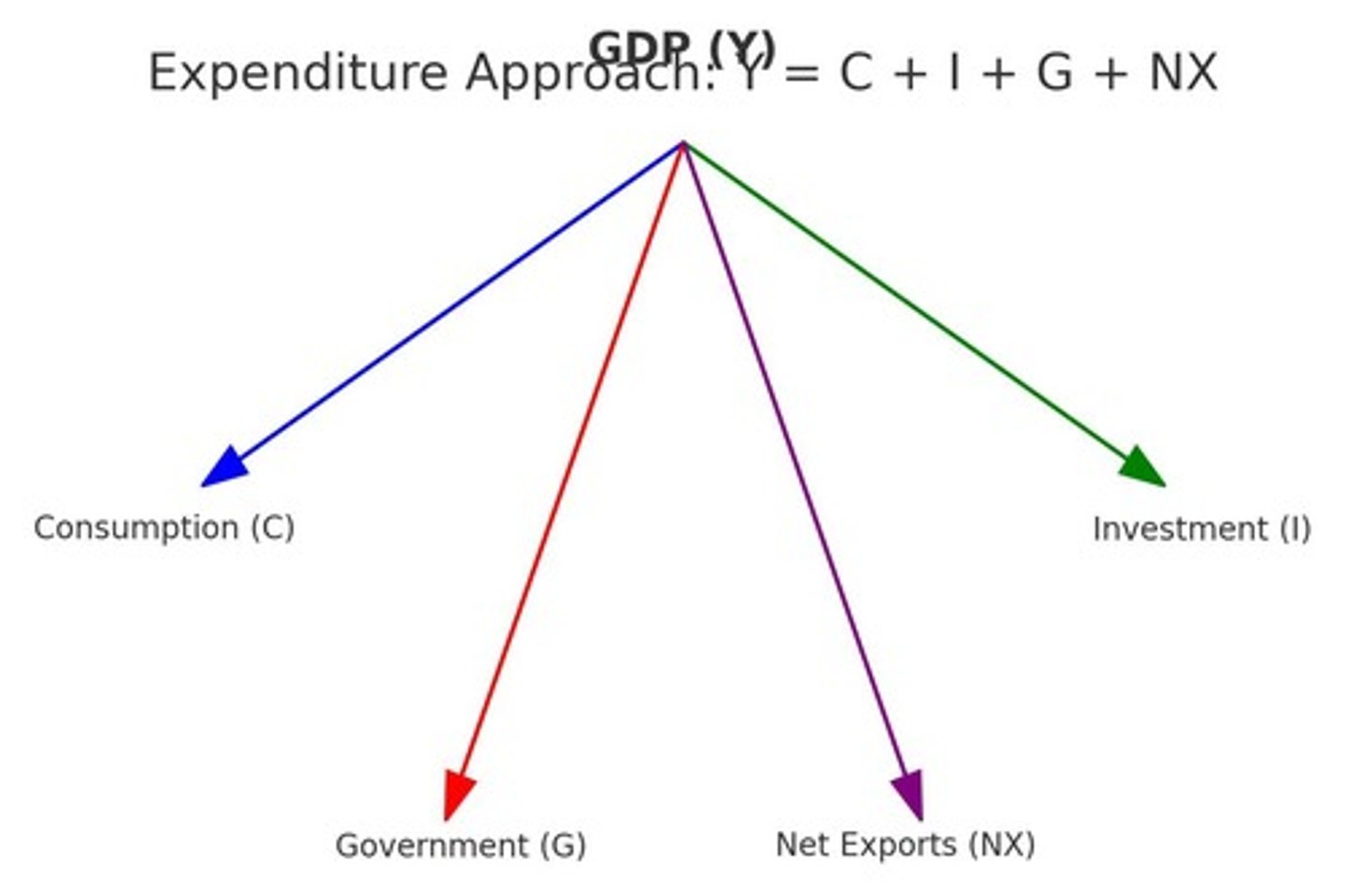
What is the equation for GDP using the expenditure approach?
Y = C + I + G + NX.
What does the labor market equilibrium equation represent?
The point where labor supply (Ls) equals labor demand (Ld).
What is the formula for nominal GDP?
Yt = Σ (Pit × Qit).
How is real GDP calculated?
Yt = Σ (Pi,t-1 × Qit).
What is the GDP deflator formula?
Price Level = Nominal GDP / Real GDP.
What does the Constant Growth Rule state?
x_t = x_0 (1 + g)^t.
How is the doubling time estimated using the Rule of 70?
Doubling Time ≈ 70 / g.
What is the production function in the context of economic growth?
Y = A K^(1/3) L^(2/3).
What does the general Cobb-Douglas production function represent?
Y = K^α L^(1-α).
What are the marginal products of capital (MPK) and labor (MPL)?
MPK = ∂Y/∂K and MPL = ∂Y/∂L.
What is the equation for Solow capital accumulation?
K_(t+1) = K_t + I_t - δK_t.
What does the per capita capital dynamics equation represent?
∆k = s y - δk.
What is the steady state condition in the Solow model?
s f(k) = δ k.
What does the Romer idea production equation indicate?
∆A = z L_A A.
What is the resource constraint in the Romer model?
L = L_Y + L_A.
What is the growth accounting equation?
g_Y = g_A + α g_K + (1-α) g_L.