Work and Heat. Internal Energy Physical Chemistry
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Work of Expansion
Wsurr=mgh=(mg/A)=Ah=Pex∆V
(mg/A) = Pexternal
Ah= ∆V
Wsys=-Wsurr=-P∆V
Wsys=-P∆V
Sign Conventions Wsys<0 expansion, Wsys>0 contraction, W=0 ∆V=0 work of expansion is 0
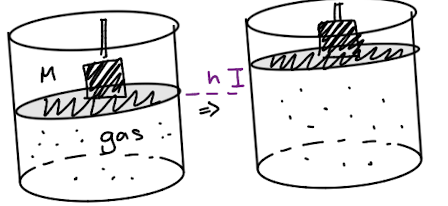
Quasistatic process
also known as a quasi-equilibrium process
a thermodynamic process that occurs slowly enough for the system to remain in internal thermodynamic equilibrium.
Quasistatic expansion and maximum work
Force of the gas is initially slightly larger than the force external
Pex≤ Pgas
Wsurr=Pex∆V≤Pg∆V → maximum when Pgas=Pex
(Wsurr)max=Pgas∆V
(Wsurr)rev=P∆V
Wrev=-Psys∆V
Reversible work of expansion = work in a quasistatic process
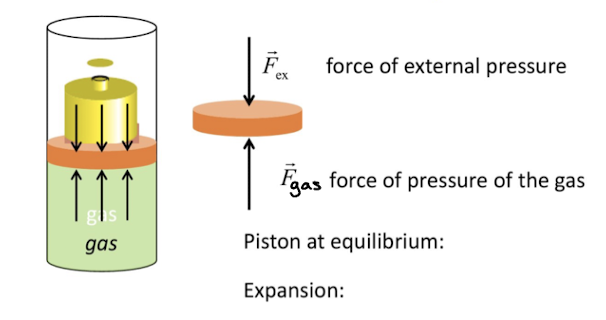
Isothermal quasistatic expansion of an ideal gas
every word matters for the application of this formula
ideal gas: PV=nRT
∆W=-Pex∆V=-Peye∆V (b/c quasistatic)
Isothermal: thermal bath temp to maintain temperature, and allow heat energy to maintain expansion.
Due to P vs V graph differentials taken to form final equation
Volume is a true differential due to it being a state funtion where as work is not a state function.
Wrev= -nRT x In (Vf/Vi)
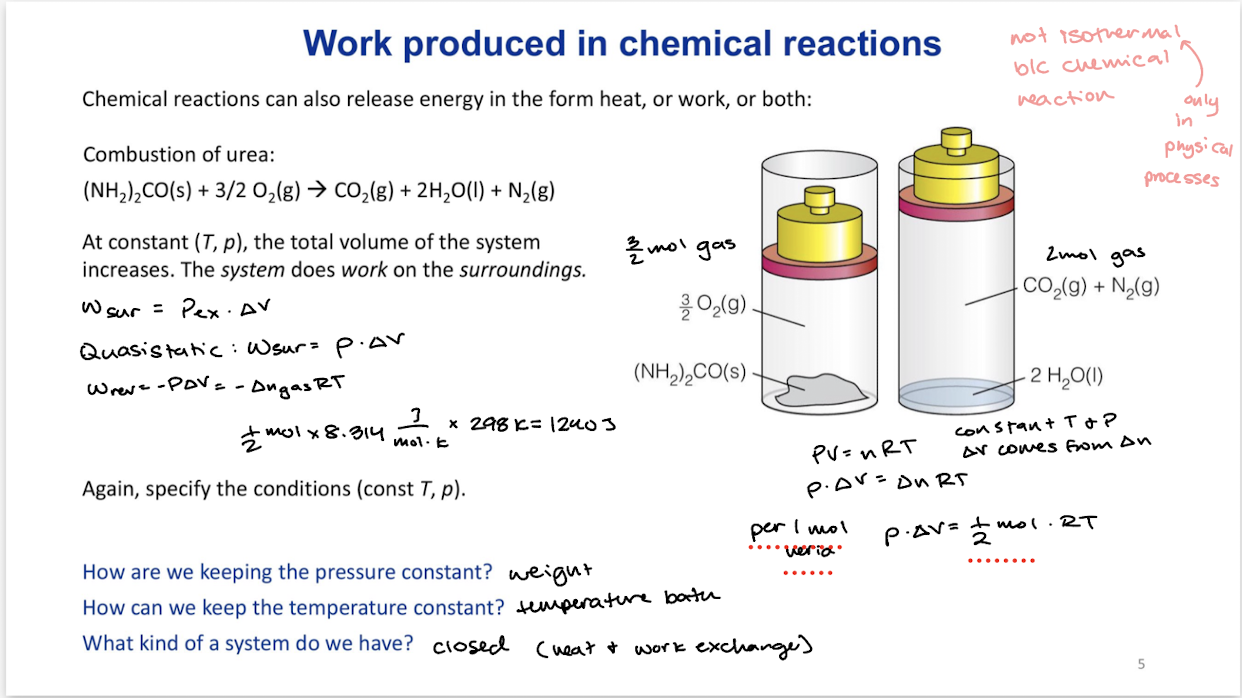
Work produced in chemical reactions
Chemical reactions can also release energy in the form of heat, or work, or both.
Not considered isothermal even if temperature is held constant due to it being a chemical reaction rather than a physical process
The measurement of heat
Heat capacity is heat absorbed by the system that raises its temperature by 1K (or 1˚C)
C=(q/∆t) units: J/K or J/˚C (extensive depends on the amount of substance)
intensive does not depend on the amount of substance (tabulated)
Specific Heat Capacity: Cs=(q/m∆T) units: J/KgK
Molar Heat Capacity: Cm=(q/n∆T) units: J/molK
Heat Capacity depends on the process in which the system recieves heat.
Constant V: Cmv=Cv= (qv/n∆T) heat added at constant V
Constant P: Cmp=Cp=(qp/n∆T) heat added at constant P