Chem 24/10/25 Bronsted Lowry theory
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Arrhenius theory
An acid dissociates in water to produce H+ ions
A base disassociates in water to produce OH- ions
Bronsted Lowry acids and bases (theory)
An acid is a proton donor
A base is a proton acceptor
This model allows the classification of both acids and bases
Proton donor
different acids can donate amounts of protons i.e. monoprotic = donate one proton e.g. HCL, HF
Polyprotic acids
Can donate more than one proton in steps e.g. HCL
Diprotic e.g. h2so4
Triprotic e.g. h3po4
Conjugate acid-base pairs
When an acid donates a proton, it forms its conjugate acid
when a base accepts a proton, it forms its conjugate acid
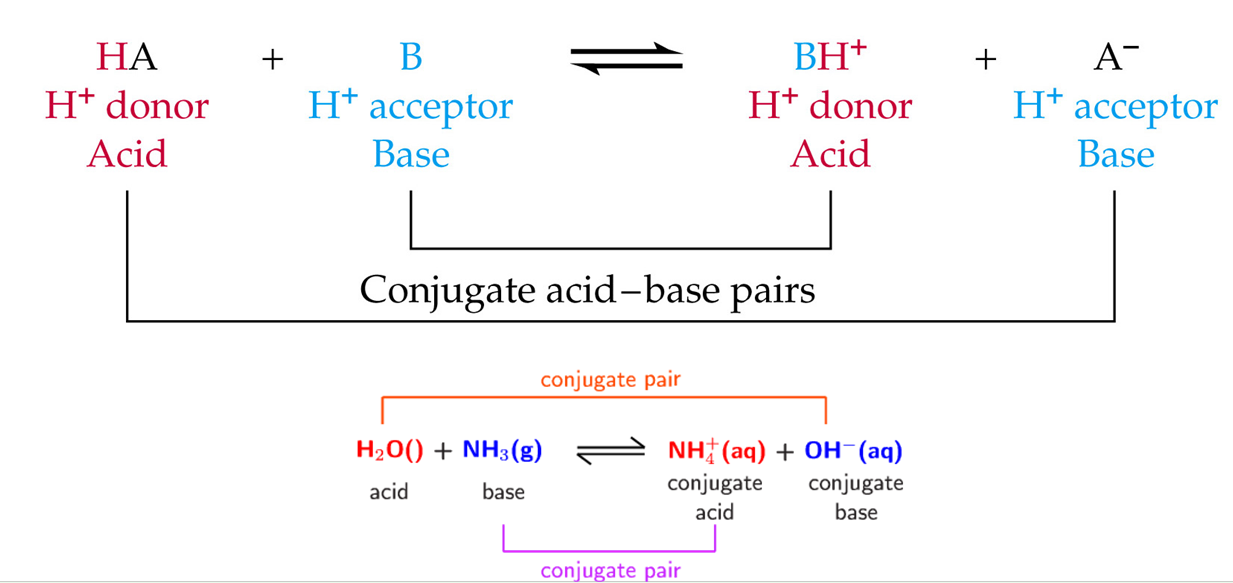
Amphiprotic
Amphiprotic species are amphoteric (Meaning they can act as either an acid or a base) e.g. Water (Amphiprotic)
HCO3- is amphiprotic
H2PO4 and HPO4 2- are amphiprotic