Buffers and Extrations
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lab 1 Chem 241
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Buffers
Mixture of weak acid and weak conjugate base.
Ex: acetic acid/acetate, ammonium
equation: henderson hasselbalch
If acid=base then it is log(1)=0.
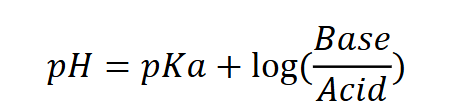
Henderson Hasselbalch
Can be used when we know the concentration of both acid/basic components to calculate pH
Ex: acetic acid has a pKa of 4.5. if you mix together 1M acetic acid and 3M acetate, what is the pH of the buffer solution
pH= 4.5+log(3/1) = 5.0
Can also be used when given a defined ph what is the acid/base ratio?
Ex: An acetic acid/acetate buffer has a pH of 4.2, how much of each component?
4.2 = 4.5 + log(base/acid)
log(base/acid) = -0.3 and base/acid= 0.5
0.4 M acetate and 0.8 M acetic acid.
grignard reagants
RMgX, strong nucleophile and bases and extremely basic can react w/ any proton source
highly reactive compounds used to form new C-C compounds
carbonyl compounds reactive with aldeyhes/ketones to create alcohols
Grignard reagents are destroyed by acids
grignard product mixture
mix depends on type of electrophile that it was reacted with and conditions
mixture used for: drying, evaporating, extraction
used to isolate desired product
Ex: Connecting Buffers and Grignard
How much base do we need to add to get all sodium benzoate that is water soluble?
Need buffer with 99% base and 1% acid, Henderson-Hasselbalch equation specifies we need 2 pH unit above pKa to obtain that goal. So if benzoic acid has pKa of 4.5 we would need pH to be 6.5 or higher.
acid neeeded to neutralize benzoic acid to make it perticipate would have to be a lower pH about 2.5.
NMR
exceptions to the symmetry rule are cis/trans H’s are different from each other (diastereotopic)
Ex: alkenes and cycloalkanes and chiral systems
cycloalkanes and symmetry:
Ex: CH4 environments: 1 C and 1 H
TLC Plates
lower Rf is more polar
Higher Rf is less polar
diethyl ether in TLC plate
How do you know which compnent has a high or low boiling point in GC based off resutls?
high retention = high b.p.
low retention time = low b.p.
Those with low retention time and low b.p. will come first in a simple/fractional distillation
How can you tell 2 components are present in the same amount in GC results?
Same area and different retention time
S vs. R
How did we use green chemistry for alkene bromination
using a safe brominating reagent.
How did we use green chemistry in Friedal-Crafts acylation of ferrocene?
avoiding solvent in the reaction.
How did we use green chemistry in barbier reaction?
using water as a co-solvent
repalcing highly reactive magnesium metal with zinc
How was green chemistry used in green oxidation?
using copper instead of more harmful chromium
using a catalytic metal instead of stoichiometric
what are 2 structural features of an azo dye that will impact its color?
amount of conjugated bonds
charge of functional groups
exact substituents present
How do you know whether or not a primary amine has been fully converted into diazonium salt?
starch-iodine paper would tell whether or not extra sodium nitrate was present which we could infer meant that the diazonium was formed
STARCH PAPER
In the aromatic bromination experiment we used NBS instead of liquid bromine. Why did this NOT change the major product.
NBS generates Br2, helps carry out the standard reaction.
Why do none of the reactants give meta as a major product?
They all have lone pairs which cause stabilization through ortho/para intermediates
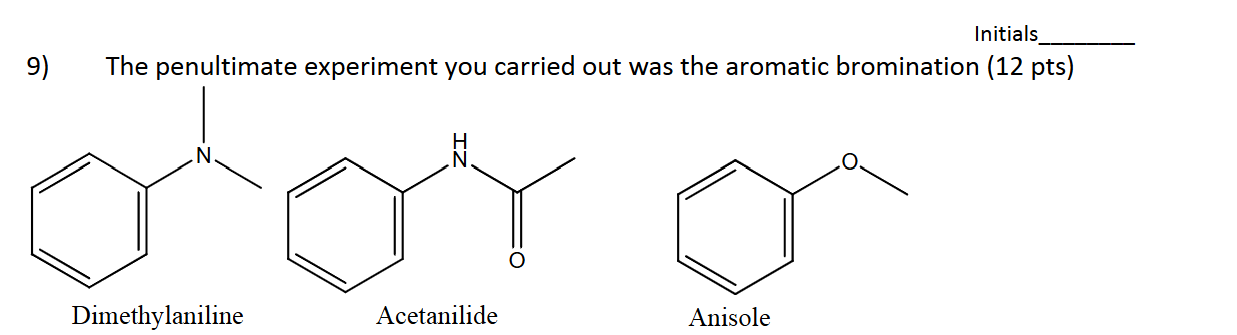
In the Friedal-Crafts Acylation, if acetylation occurred twice did the major product have the acetyl groups on the same ring or different rings?
Opposite rings since ketone stabilizes the ring through resonance and acts as a deactivator.
In Friedal Crafts, one of the variables we tested was stirring. What trend would you have expected to see for the product yield vs stirring. And why did the class not see a trend at all?
Stirring = more proudct
stirring = hard to accomplish with little solvent so there was no effectiveness accomplished with stirring
Friedal Crafts - Why is ferrocene more reactive than benzene in Friedal craft reactions.
more ionic than neutral
less aromatic
Friedal Crafts, we used a gradient elution from 10% —> 20% —> 50% acetone. Why would it not have been effective to use 50% acetone?
all 3 compounds would elude very fast and wouldn’t separate from each other.
TLC with green oxidation, which was the limting reactant and which was in excess.
the alcohol was excess because oxygen is limited by how much air is present.
TLC green oxidation, We used 0.1 eq. of copper in this reaction. State 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of using 0.1 eq. rather than 1 equivalent.
advantage: saves material, less cost and waste
disadvantage: reaction would go faster with more copper
TLC Green oxidation, 4 of the 6 reactant alcohols were solids, while 4 of the 6 product aldehyes were liquids. Why were a larger number of aldehydes liquids compared to alcohols?
alcohols are more polar due to H bonding = higher melting points and be solid
alcohls more polar (partial credit)
TLC green oxidation, the color changed several times over the course of this experiment. What happened during the final color change to make it useful while the initial color changes were not?
Inital color changes are as the catalytic complex formed
final color change is when catalytic cycle stopped
Marked TLC with pencil, why bad when using pen?
the ink could dissolve in the organic solvent
“Like dissolves like. Therefore the polar solvent will make polar compounds move faster while a nonpolar solvent will make nonpolar compounds move faster.” Why is this wrong?
What matters is how well the solvent pulls against silica and polar solvents pull better.
a polar solvent will make all compounds move faster whether they are polar or nonpolar
If you took a break and came back to find the solvent had reached the top of your TLC plate, why would that ruin your analysis?
even after the solvent reached the top, the compounds could keep moving, so we wouldn’t have an accurate Rf.
Alkyl halide reaction - Why did methoxide give mostly 2-heptene while tert-butoxide gave mostly 1-heptene? You must explicity discuss each base.
Methoxide is a small base, so it is able to grab an H form the center of the molecule
Tert-butoxide is a large base, so it’s limited to grabbing an H from the outside
1-heptene and 2-heptene both ahve the same MW. How did the GC-MS software distinguish between them?
it compared the fragmentation pattern of the MS with its database
In Alkyl halide reaction was that only E2 and SN2 reactions could happen. how come we rules out E1 and SN1 reactions out as a possibility?
if there is a strong base present, E2 would outcompete E1/SN1 and likewise for strong nucleophiles and SN2.
Barbier reaction, Why is the barbier reaction useful to synthetic organic chemists?
any reaction taht can reliably make new C-C bonds is powerful.
greener, simpler, and effeicient in building complex molecules
Why was it important to quench the unreacted zinc with aqueous HCl before disposing of it?
The zinc would eventually react with water to product H2 gas, which would not be safe if generated in a waste container.
Why didn’t we use NMR to analyze the cinnamic acid bromination you carried out in lab?
The NMR spectra of the diastereomers are too similar to tell apart.
Cinnamic acid contains 4 C double bonded to C bonds. How come only the indicated bond is the only one that gets brominated?
benzene is more stable than alkenes so only alkene reacts.
Explain this statement: “distillation is a purification technique while GC is an analytic technique.”
distillation is large scale, so it help isolate each compouds after they are seperated
GC is a small scale, so no material will be gained back after seperation
Name the compound that we use to set the Oppm point of the chemical shift scale.
TMS
tetramethylsilane
Si(CH3)4
State 1 advantage of simple distillation and 1 advtange of fractional distillations
simple: can be done quicker
fractional: better purity
Why is percent revovery after recrystillization never 100%?
some of the compound will remain dissolved in the solvent
Why are melting poitns reported as ranges rather than single point?
it takes time to fully melt, during which the temperature keeps increasing
How do you know whether or not the sodium has fully dried the organic layer?
if some of the sodium sulfate is powdery and not clumped then there isn’t any water left.
What is the main safety hazard of the catalyst in the Fischer esterification?
sulfuric acid is corrosive and very reactive
How should leftover Mg metal be quenched safely?
in the fume hood by adding HCl to form MgCl2
TLC plate at not at completion
if we see both reactant and product in the crude reaction mixture, the reaction made some product but did not go to completion
Give two properties of a good crystallization solvent, as specifically related to the crystallization process.
all impurities should be soluble in the solvent at all temperatures
product should be soluble in hot solvent and insoluble in cold solvent
What is the purpose of using the 2 condenser tubes? Why are they used for and how do they differ?
vertical condenser tube allows the vapor to condense helping separate the two components based on the B.P.
The more horizontal condenser is cooled with water and allows the product vapors to condense into a liquid and flow into the collection vessel
How will a fractional distillation compare to a simple distillation in effectiveness at serrating a mixture of 2 solvents?
Fractional is more effective than simple distillation
Graph a distillation temperature vs. volume
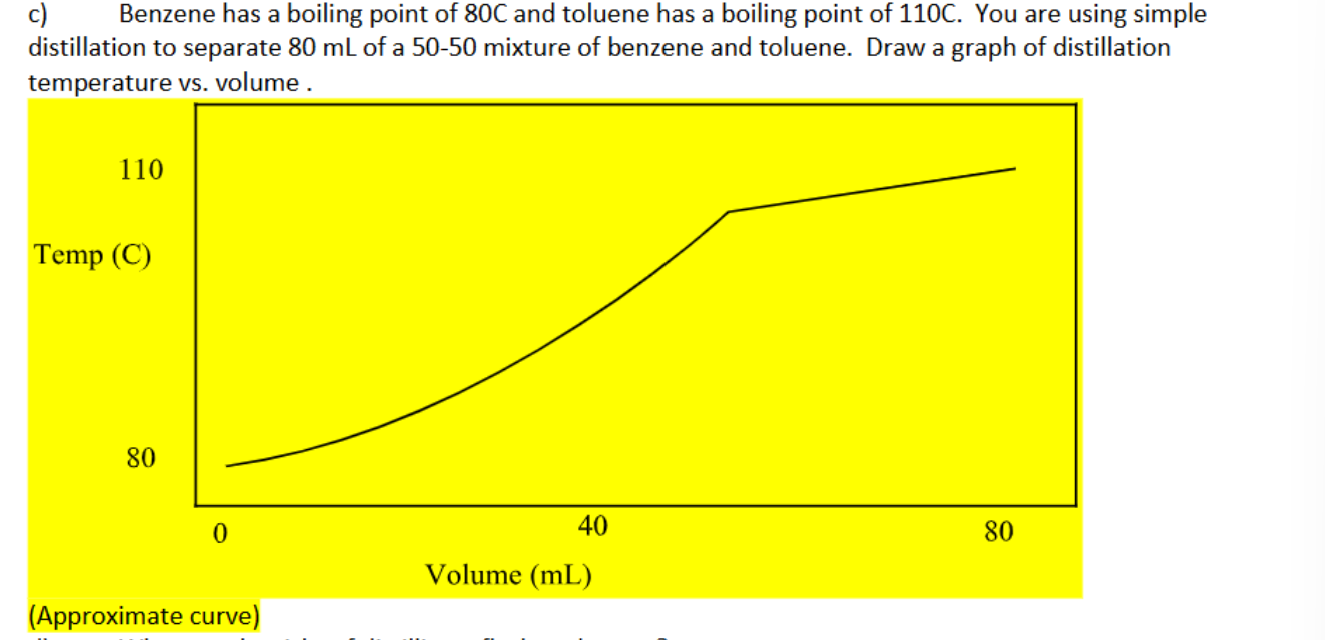
What are the risks of distilling a flask to dryness?
any residue in the flask may overheat and polymerize
may product unwanted byproducts and make flask difficult to clean
Acid-Base Extractions
neutral uncharged molecules prefer the organic layer
charged (ionized) forms prefer the aqueous layer