Biology S1 Final Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Last updated 8:20 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Biology
Study of life
2
New cards
Cell
Smallest unit of life
3
New cards
Levels of organization in living things
Cells, Tissue, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism
4
New cards
Homeostasis
Process of keeping a stable internal environment
5
New cards
Scientific Method
Observe, Predict, Experiment, Analyze, Interpret
6
New cards
Hypothesis
A possible explanation/prediction validated/invalidated by experiments
7
New cards
Hypothesis Example
***IF*** I study, ***THEN*** I will pass this final.
8
New cards
Variable
Numbers found through experiments then used to graph
9
New cards
Independent Variable
Variable that is __altered by the scientist__
10
New cards
Dependent Variable
Variable that is __affected by the variable__ set by the scientest
11
New cards
Controlled Experiment
Tested under programmed conditions
12
New cards
Competition Factors
Food, Water, Shelter
13
New cards
Symbiotic Relationship
Relationship between **two** animals that **interact** with each other
14
New cards
Types of Symbiotic Relationships
Mutualism, Commensalism, Parisitism
15
New cards
Mutualism
Both animals **benefit**
16
New cards
Commensalism
One animal **benefits**, the other remains **neutral**
17
New cards
Parisitism
One animal **benefits** by **harming** the other
18
New cards
Niche
The __**role**__ of a species within an ecosystem
19
New cards
Habitat
The **location** of where species live
20
New cards
Difference between **Niche** and **Habitat**
**Niche** is a __role__; **Habitat** is a location
21
New cards
Autotroph
Organism that **makes** its own food (plants)
22
New cards
Heterotroph
Organisms that **consume** others (animals)
23
New cards
Carnivore
Animal that only eats **meat** (Wolf)
24
New cards
Omnivore
Animal that eats both **meat and plants** (Human)
25
New cards
Herbivore
Animal that only eats **plants** (Caterpillar)
26
New cards
Sun
Ultimate **energy** source
27
New cards
Proton
Subatomic particle with a **positive** charge
28
New cards
Electron
Subatomic particle with a **negative** charge
29
New cards
Neutron
Subatomic particle with **no** charge
30
New cards
Nucleus (Atom)
**Location** of protons and neutrons
31
New cards
Electron Cloud
**Location** of electrons
32
New cards
Atomic Number
**Equal** to the number of **protons**; **defines** the element on the **periodic table**
33
New cards
Mass Number
Protons + Neutrons = ________
34
New cards
Ionic Bonds
**Metallic** element **bonded** to a **nonmetal** element through the **transfer** of electrons
35
New cards
Covalent Bonds
**Two Nonmetals** bonded to each other through the **sharing** of electrons
36
New cards
Cell Theory
Cell is the basic **unit of life**, Cells come from **pre-existing cells**, **All** organisms are **made** out of cells
37
New cards
Prokaryote
Cells with __no__ membrane-bound nucleus or organelle (Bacteria)
38
New cards
Eukaryote
Cells __with__ __membrane__-bound nucleus and organelles (Plant/Animal Cells)
39
New cards
Difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have a nucleus while Prokaryotes don’t
40
New cards
Functions of Nucleus
Stores **DNA**, maintain **integrity**, facilitate **transcription** and **replication**
41
New cards
Mitochondria
Create **ATP**
42
New cards
Cytoplasm
**Fluid** filling the inside of the cell
43
New cards
Chloroplast
Only in **plants**; carries out photosynthesis to make energy for the plant
44
New cards
Golgi Apparatus
Prepares large molecules for **storage** in the cell or for secretion out of the cell
45
New cards
Ribosome
Make **proteins** for the cell
46
New cards
Cell Membrane
Thin layer of **lipids** and **proteins** **separating** the cell’s contents from the environment
47
New cards
Smooth ER
**Functions** in making **lipids**, processes **carbohydrates**, and modifies chemicals **toxic** to the cell; Smooth due to the absence of **ribosomes**
48
New cards
Rough ER
Helps synthesize **proteins** & manufacture new **cell membrane**; Smooth due to presence of **ribosomes**
49
New cards
Difference between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have **cell walls** and **chloroplasts**
50
New cards
Solvent
**Liquid** that **DIS**__**SOLVE**__**S** the substance
51
New cards
Solute
Substance that __**is**__ dissolved
52
New cards
Example of a Solution
When making hot chocolate, the milk is the **solvent** and the chocolate powder is the **solute**. The milk **dissolves** the powder.
53
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of particles from **high to low** concentration (__no energy__ required as it is a passive transport)
54
New cards
Facilitated diffusion
Diffusion but using a **carrier molecule** (__no energy__ required as it is a passive transport)
55
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of **water** from high to low concentration (__no energy__ required as it is a passive transport)
56
New cards
Active Transport
Movement of particles **against** the gradient otherwise known as LOW to HIGH concentration (**REQUIRES** energy)
57
New cards
DNA
Double Helix structure that stores genetic code; Universal Code; Double-Stranded, Deoxyribose sugars, has Thymine
58
New cards
Replication
The process by which DNA is copied; Occurs in the S phase of Interphase prior to cell division
59
New cards
First step of Replication
Helicase unzips DNA
60
New cards
Second step of Replication
Bases pair up and find their complementary bases with the help of DNA polymerase
61
New cards
Third step of Replication
Backbone bonds the sugar - phosphate backbone is assembled to complete strand
62
New cards
2 DNA strands each have ONE new and ONE old
This results after DNA replication occurs
63
New cards
Guanine
Cytosine pairs with
64
New cards
Adenine (DNA)
Thymine pairs with
65
New cards
Adenine (RNA)
Uracil
66
New cards
Codon
Three base section of mRNA that carries a code for a specific amino acid
67
New cards
AUG
This Codon means STOP
68
New cards
Translation
This process occurs in the Ribosomes and has three steps: Initiation, Elongation, and Termination
69
New cards
Initiation
Step in translation when the mRNA attaches to ribosomes
70
New cards
Elongation
Step in translation when tRNA matches up to mRNA with anitcodons
71
New cards
Termination
Step in translation when ribosome reaches a stop codon and protein is released
72
New cards
Protein Synthesis
Transcription and Translation make up this process
73
New cards
Transcription
Process by which genetic info. from DNA is copied to mRNA
74
New cards
RNA polymerase
Binds unattached RNA bases to complementary bases on DNA strand
75
New cards
RNA
Single-Stranded, Ribose sugar group, has Uracil; Called Ribonucleic Acid
76
New cards
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
This type of RNA makes up Ribosomes
77
New cards
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
This type of RNA carries DNA info to ribosomes
78
New cards
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Carries amino acids to ribosome
79
New cards
Frameshift
The deletion or addition of nucleotides resulting in the disruption of codons
80
New cards
Inversion
Chromosome breaks in two places resulting in a piece of DNA that is reversed and re-inserted into the chromosome
81
New cards
Translocation
When a chromosome breaks and the two fragmented pieces re-attach to different chromosomes
82
New cards
Mitosis
This process occurs in somatic cells (body cells) and its objective is to make identical cells with identical chromosomes
83
New cards
Prophase
First phase of Mitosis; Chromosomes condense and are visible, nucleus disappears, spindle fibers form
84
New cards
Metaphase
Second phase of Mitosis; Chromosomes pulled to center of cell
85
New cards
Anaphase
Third phase of Mitosis; Centromeres divide and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell by Spindle Fibers
86
New cards
Telophase
Nucleus reforms around 2 new identical sets of chromosomes and chromosomes uncoil back to chromatin
87
New cards
Plants
Cell division is different in ______ due to the cell walls denying pinching off so cell wall forms between new cells
88
New cards
Meiosis
Create gametes (sperm) for sexual reproduction
89
New cards
Haploid (n)
One set of chromosomes, randomly distributed to gametes
90
New cards
Diploid (2n)
One pair of chromosomes, one set from each parent
91
New cards
Gametes
Sperm
92
New cards
Crossing Over
Happens in Meiosis, Prophase I, results in new gene combos on chromosomes that will produce unique gametes
93
New cards
ATP structure
\
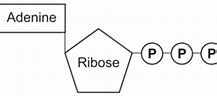
94
New cards
Photosynthesis Equation
6CO2 + 6H20 + (light energy) → C6H12O6 + 6O2
95
New cards
Thylakoid
An individual disk of a grana, contains chlorophyll
96
New cards
Chlorophyll
Pigment reflecting green light making plants appear green and allows for photosynthesis
97
New cards
Chloroplast
Organelle in which Photosynthesis occurs
98
New cards
Cellular Respiration Equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H20 + (ATP)
99
New cards
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis → Kreb’s Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle) → Electron Transport Chain
100
New cards
Anaerobic Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis → Fermentation (Lactic - Animals, Alcohol - Bacteria/Yeast)