Specific Responses - antibodies
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What is the key responses in specific reponse
Anything, Immunoglobins, lymphocytes
Antibody mediated immunity
Humoral
Plasma cells secrete
antibodies that circulate in the blood, bind to antigens, clear antigens from body
Cell mediated immunity
Specific T cells are activated that attack and kill spraying pathogens and infected cells
Antigen
A molecule or molecular structure, such as may be present at the outside of a pathogen that can be bound to an antigen-specific antibody or an antigen receptor and is capable of triggering immune reactions
Epitope
the precise molecular group of an antigen that defines it specificity and triggers the immune response
The immune system wont usually react to… under normal homeostatic conditions due to… of T cells in the…
self-antigens under normal homeostatic conditions due to negative selection of T cells in the thymus
Gene segments
encode for receptors on the surface of T and B cells and variable region on antibodies
Gene segments are… leads to…
rearranged extensively which leads to huge assortment of receptors on T and B cells and antibodies
What do each T and B lymphocyte have in combine?
They contain a protein receptor of a unique configuration. It’s specific and reactor to a specific antigen
What occurs during the development of B cells
A complete coding sequence for each of the two antibody Charmaine to be synthesized and assembled by the site specific genetic recombination
V(D)J recombination
is the unique mechanism of genetic recombination that occurs one in developing lymphocytes during the early stages of T and B cells maturation. Resulting in highly diverse repertoire of antibodies/immunoglobulins (IGs) and T cell receptors (TCRs) found on B cells and T cells
Clone
each genetically unique line of lymphocytes arising from the gene segment rearrangement
Each T and B cells that are generating will respond to how many specific antigens?
one
Where do T and B cells migrate
lymphoid tissues
Thymus
Location of T lymphocyte maturation, this specialized organ has T cells attack the body’s own proteins and eliminate them
Thymosin
polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus that controls the T cell maturation
Each T cell …. Substance which it identifies with its receptor
attacks a specific foreign substance
How are T cell receptors generated
via random shuffling of gene segments
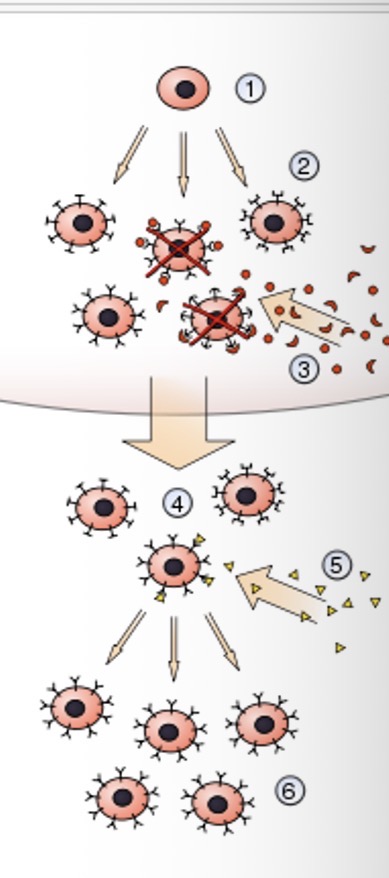
What is the first step of clonal selection theory?
A hematopoietic stem cell undergoes differentiation and genetic rearrangement to produce immature lymphocytes
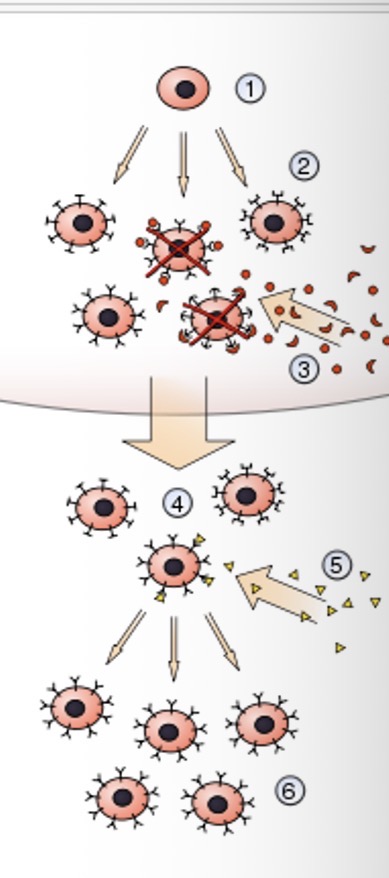
What is the second step of clonal selection theory?
The immature lymphocytes are bonded to different antigens receptors
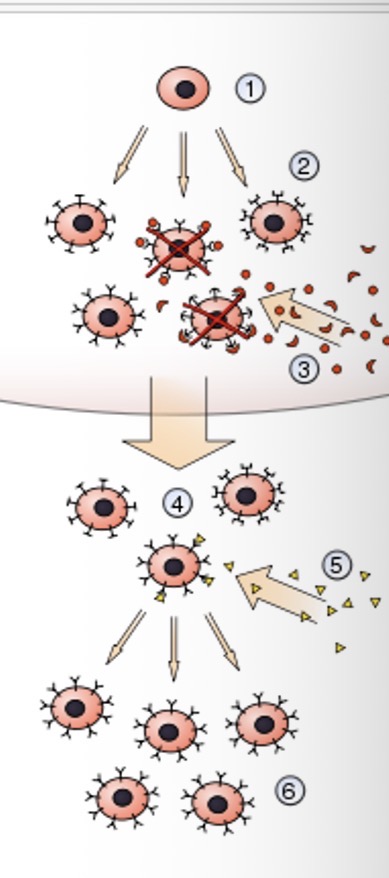
What is the third step of clonal selection theory?
Those that bind to styling from red board own tissues ARE DESTROYED
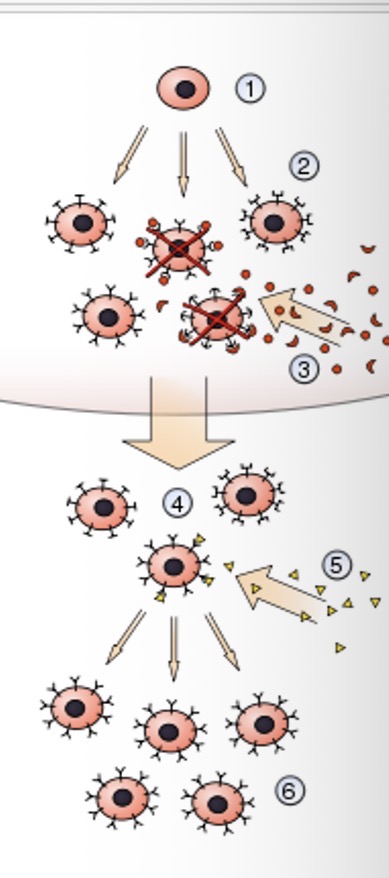
What is the fourth step of clonal selection theory?
Those that bond with different tissues become mature into inactive lymphocytes
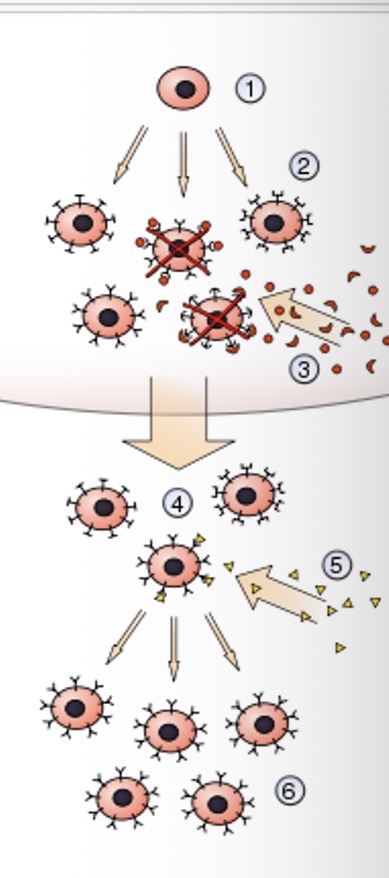
What is the fifth step of clonal selection theory?
Foreign antigens are presented and some may bind
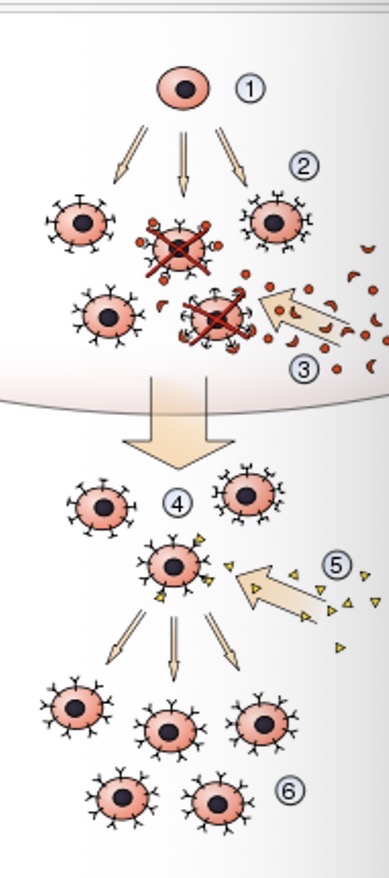
What is the sixth step of clonal selection theory?
Those that bind with the antigens are activated and produce many clones of themselves
Hematopoietic stem cell can give rise to…
all the other blood cells through teh process of haematopoiesis in the red bone marrow
Immunoglobulin
Contains large glycoprotein molecules that serve as a antibodies and a specific receptor to B cells
Immunoglobin is secreted by… which reside in the..
plasma cells which reside in the blood plasma
IgD
Membrane receptor for mature B cells
Allergy to IgE
A hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system → red eyes and itchiness wtvH
Hives
Also known as urticaria, its an outbreak of swollen and pale red bumps on the skin as a result of the body’s reaction to certain allergens
Allergic reactions are
distinctive because of excessive activation of certain white blood cells by a type of antibody - IgE →inflammatory response which can range from uncomfortable to danergous
Which white blood cells are over activated during an allergic reaction
mast cells and basophils → histamine
The body is able to produce milling of different antibodies because…
it combines different segments of the same gene and removing different introns for different antibodies
Genetic rearrangements in developing B cells… into genes encoding light and heavy chains
combine gene segments
What are light and heavy chain genes transcribed to?
precursor mRNA → processed into finished mRNAs or translated into antibody polypeptides
What generates the capability needed to respond to numerous antigens?
The differentiation of B cells and the random C and J DNA segments joining with C to form light chain genes and the assembly of heavy chains for T cell receptor formation
Dendritic Cells
A type of Antigen presenting cell (APC) that is located in tissues which are in contact with the external environment - i.e skin, lining of nose, lungs, stomach, intestines
When dendritic cells are activated, where do they migrate?
lymph nodes
When the dendritic cells aer in the lymph nodes they interact with…
T cells and B cells to initiate adaptive immune response
What is the role of a helper T cell?
They trigger a humoral and cell mediated response (CMI)
Cytokines from help T cells..
initiate antibody production and fabricate T cells to kill infected cells
What two conditions must be met before the T cell can activate the adaptive immune response
An antigen fragment must be displayed in the APC
The antigen must bind to the T cell receptor on the helper T cell
Antigen presenting cell (APC) examples
Dendritic cells, macrophages, or B cells
What makes APCs so special ?
They contain both the MHC class I and MHC class II proteins where as other cells only have MHC I protein
What can activate a helper T cell?
macrophage or dendritic cell
When B cells are activated by the T cell, they give rise to?
antibody secreting cells - plasma cells
Antibodies can unite with the antigen via
opsonization where the virus or pathogen is coated
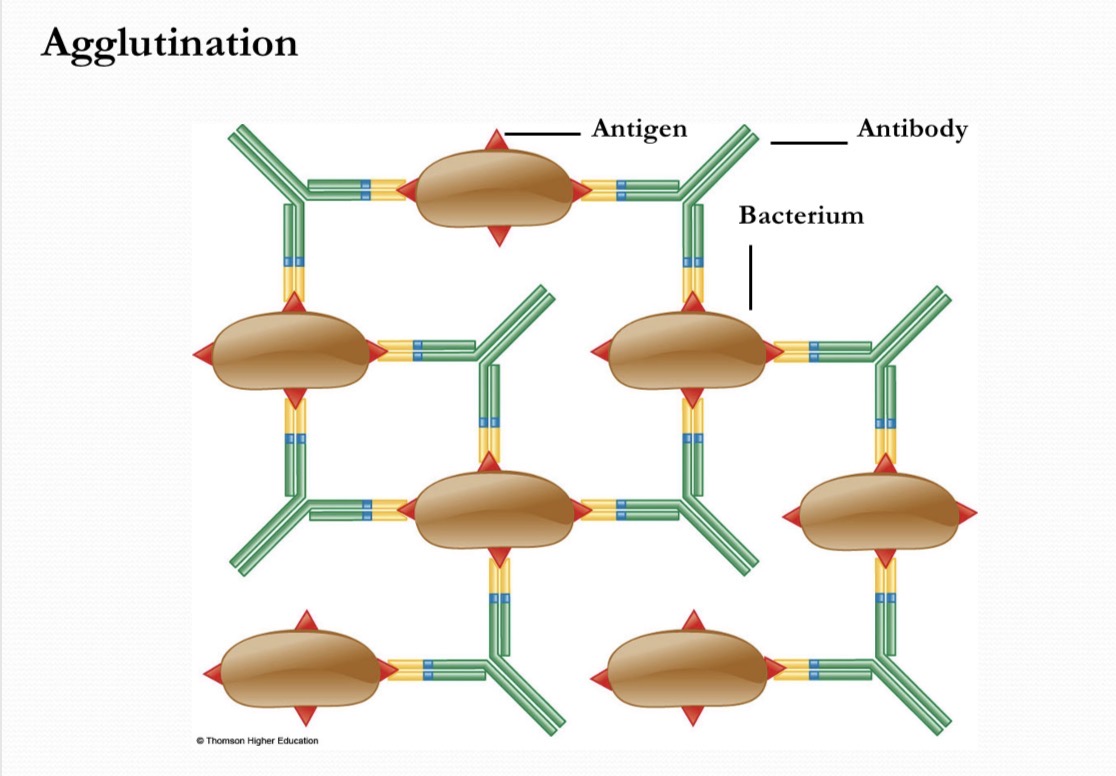
Antibodies can immobilize with the antigen via
aggutinate where antibodies can cross-link
Antibodies can call attention to the antigen via
binding of Ab enhancing phagocytotic recognition so wbc can engulf the pathogen
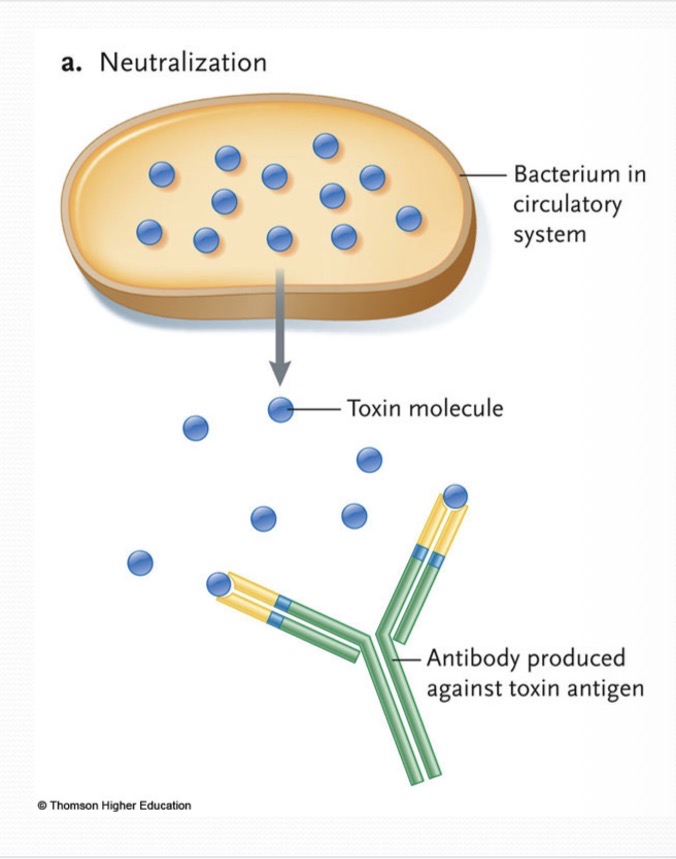
Antibodies can neutralize the antigen via
Ab filling receptor site on the virus to prevent attachment to the host cell
Antibodies can destroy the antigen via
interaction of Ab with complement fixation to rupture some viruses
What are the ways Antibodies can kill invading bacteria?
agglutination of bacteria into a clump preventing potential infections
stimulations of complement
enhancing phagocytosis
initiate membrane response complexes via innate immune responses
Whats the main distinction between B and T cells?
Antigen receptors of T cells will only bind to antigens that are displayed and antigen receptors of B cells bind to epitopes of intact antigens on pathogens or circulating free in body fluids
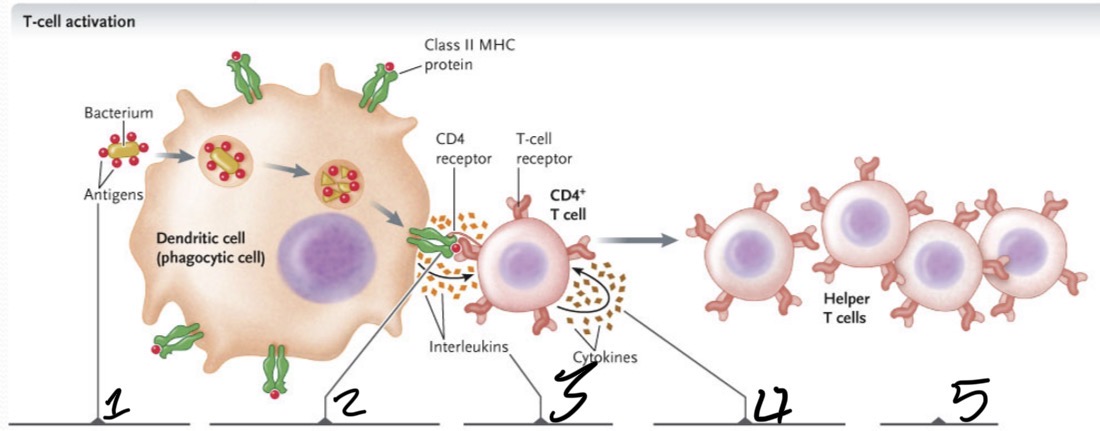
What occurs at 1?
The bacterium is taken up by phagocytosis and degraded in a lyosome
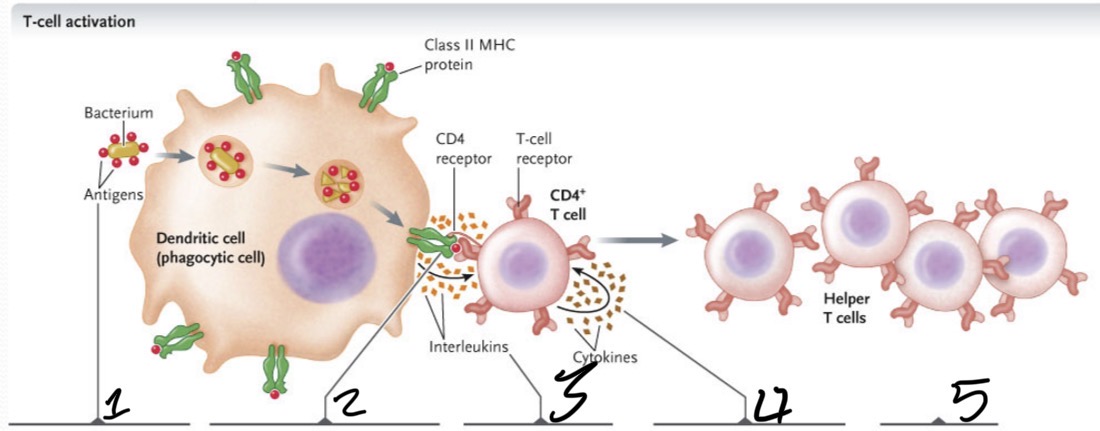
What occurs at 2?
Bacterial antigens are displayed on the APC cell surface bound to class II MHC proteins and presented to CD4+ T cells with TCRs that recognize the antigen
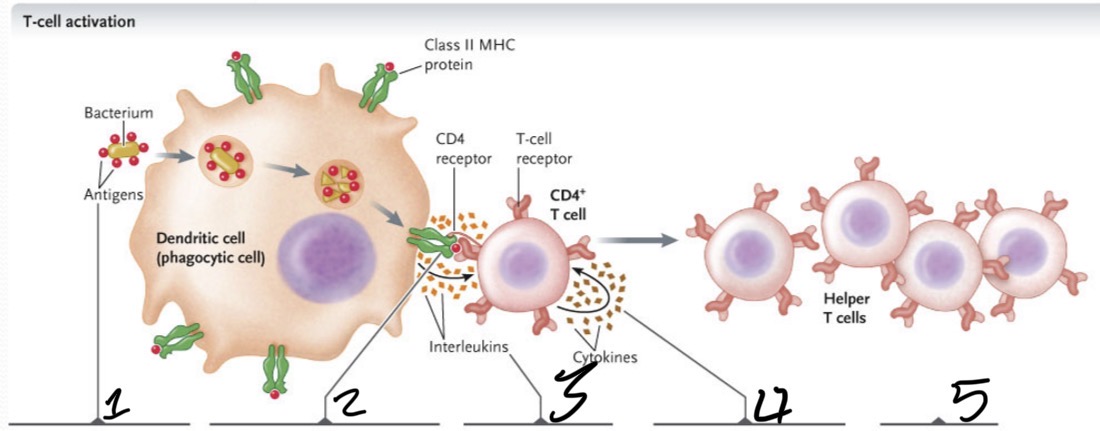
What occurs 3?
The APC secretes an interleukin which activates the T cell
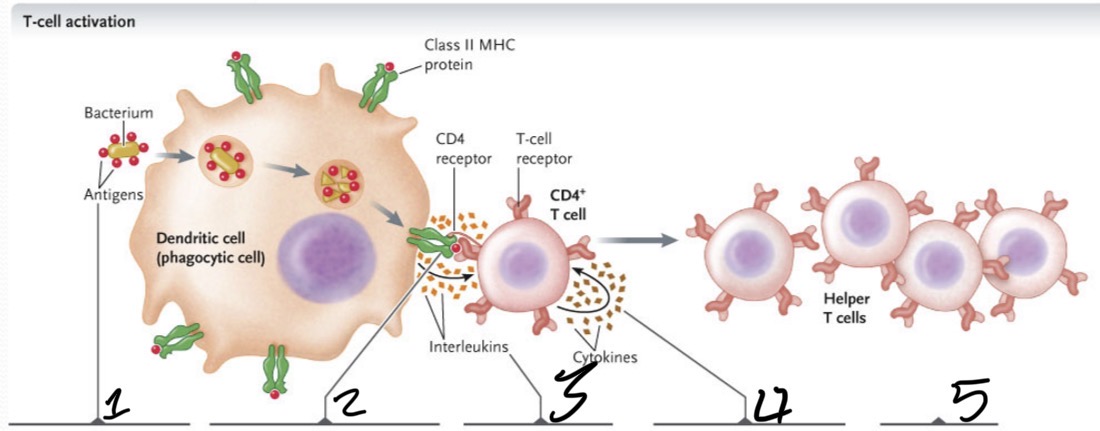
What occurs 4?
Activated T cell secretes cytokines, which stimulate the T cell to proliferate to produce a clone of cells
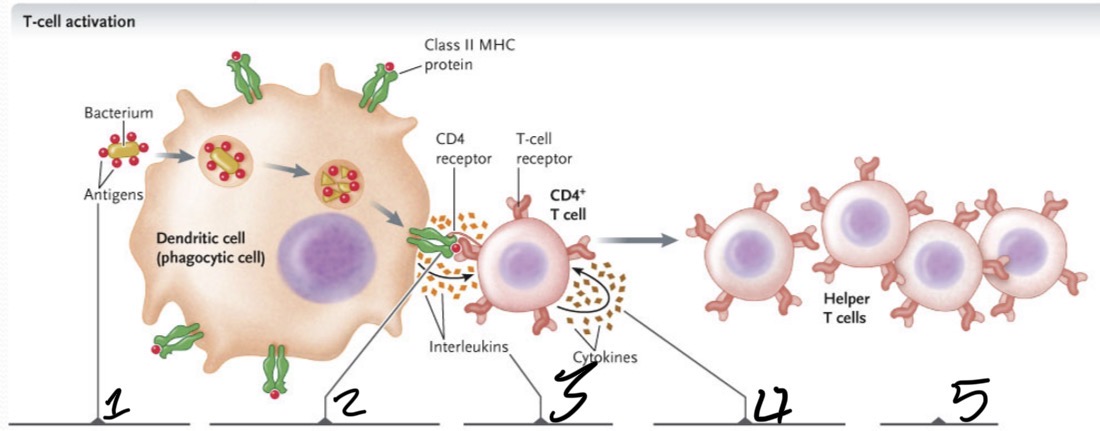
What occurs at 5?
The cloned cells differentiate into helper T cells
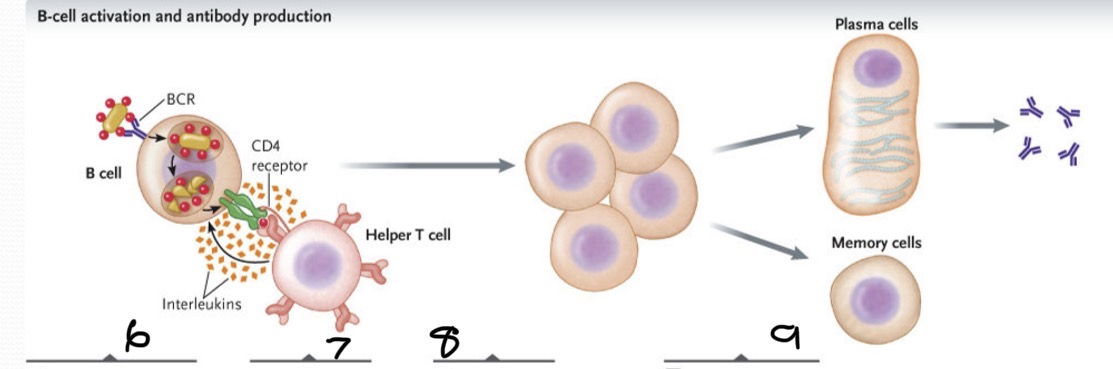
What occurs at 6?
BCR binds to antigen on the bacterium. The bacterium is engulfed and its macromolecules degraded. The antigens produced are displayed on cell surface bound to class II MHC proteins
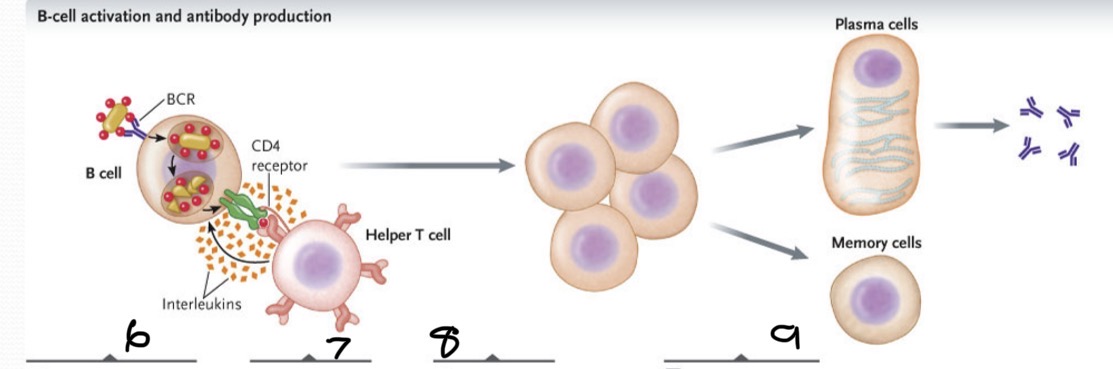
What occurs at 7
The TCR of a helper T cell recognizes the specific antigen on the B cells bind and link the two cells together
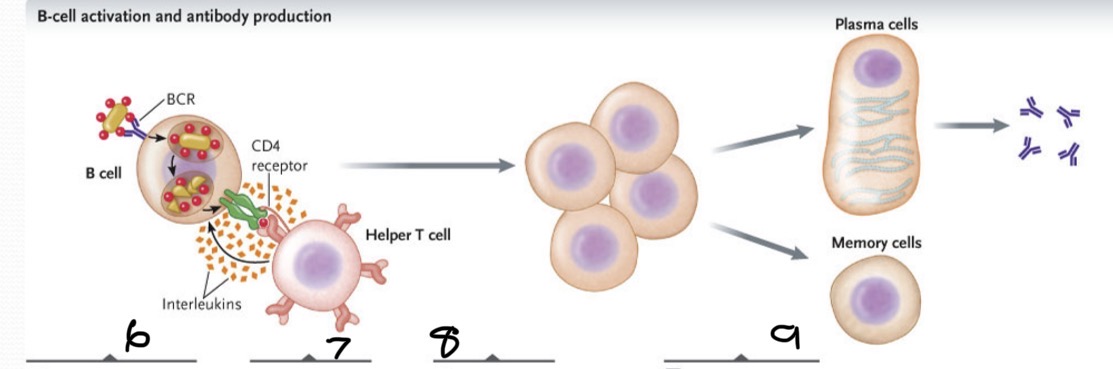
What occurs at 8?
Interleukins stimulate B-cells proliferation to produce a clone of cells
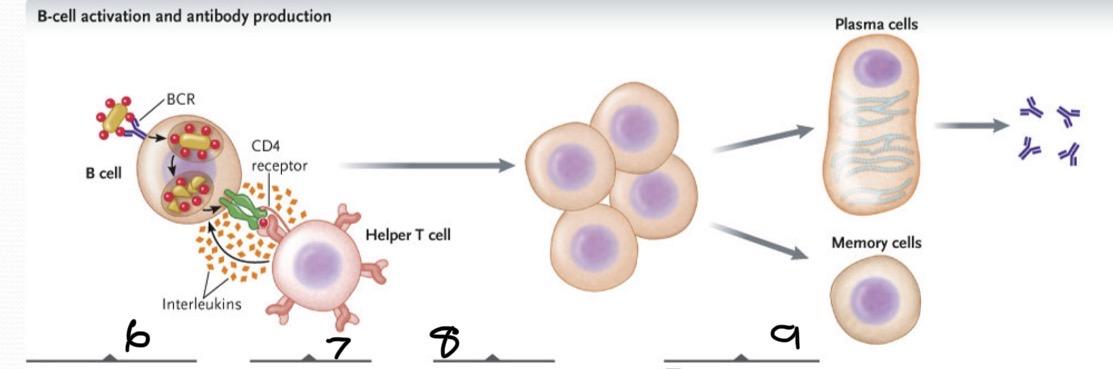
What occurs at 9?
Some cloned B cells differentiate into plasma cells, which secrete antibodies specific for the antigen while a few differentiate into memory B cells