Reactions of alkenes
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mechanism of electrophylic addition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Addition of a halogen
Non-polar halogen molecule
Induced dipole in halogen
Halogen acts as electrophile
Pi bond of C=C bond breaks
Forms dative covalent bond with positive end of Br molecule
Br-Br bond breaks - heterolytic fission
Carbocation intermediate formed
Lone pair of electrons on bromide ion forms dative covalent bond with the C of carbocation
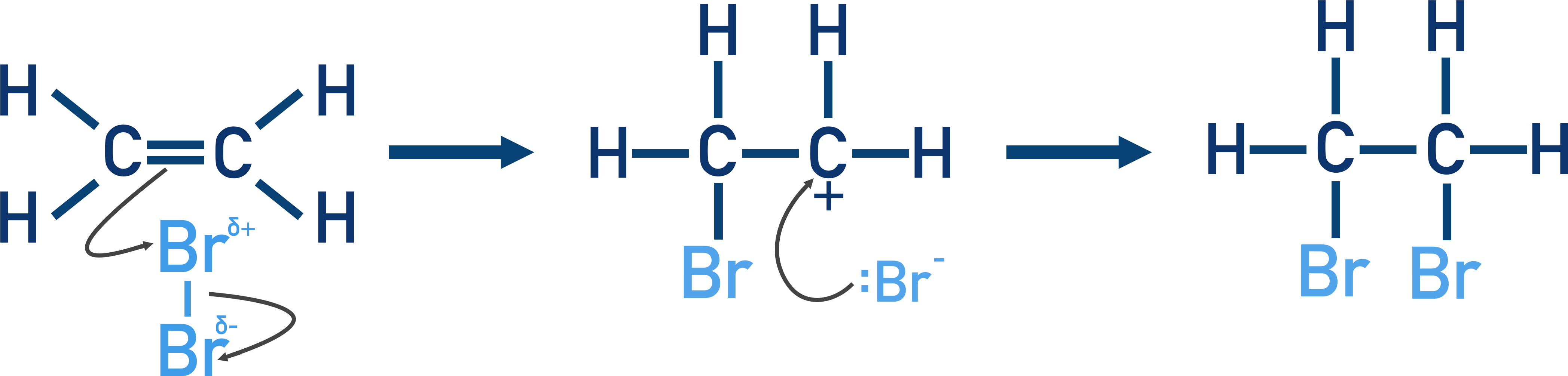
Addition of a hydrogen halide (symmetrical alkene)
Permanent dipole in HBr
Pi bond of breaks
Forms dative covalent bond with H
HBr bond breaks - heterolytic fission
Carbocation intermediate
Lone pair of electrons on Br- forms dative covalent bond with C of carbocation
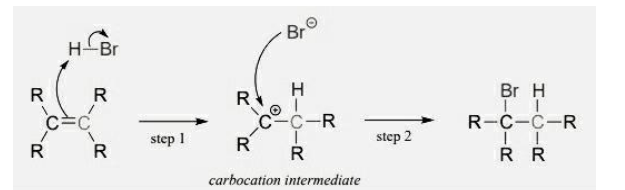
Addition of a hydrogen halide (unsymmetrical alkene)
Same as symmetrical alkene except there are two possible carbocation intermediates
This means a major and a minor product is formed
Major product is formed from the most stable carbocation
How to determine stability of carbocation intermediate
The more alkyl groups the C is bonded to, the more stable
Primary carbocation = C+ bonded to 1 alkyl group
Secondary carbocation = C+ bonded to 2 alkyl groups
Tertiary carbocation = C+ bonded to 3 alkyl groups
What is the most stable type of carbocation?
Tertiary
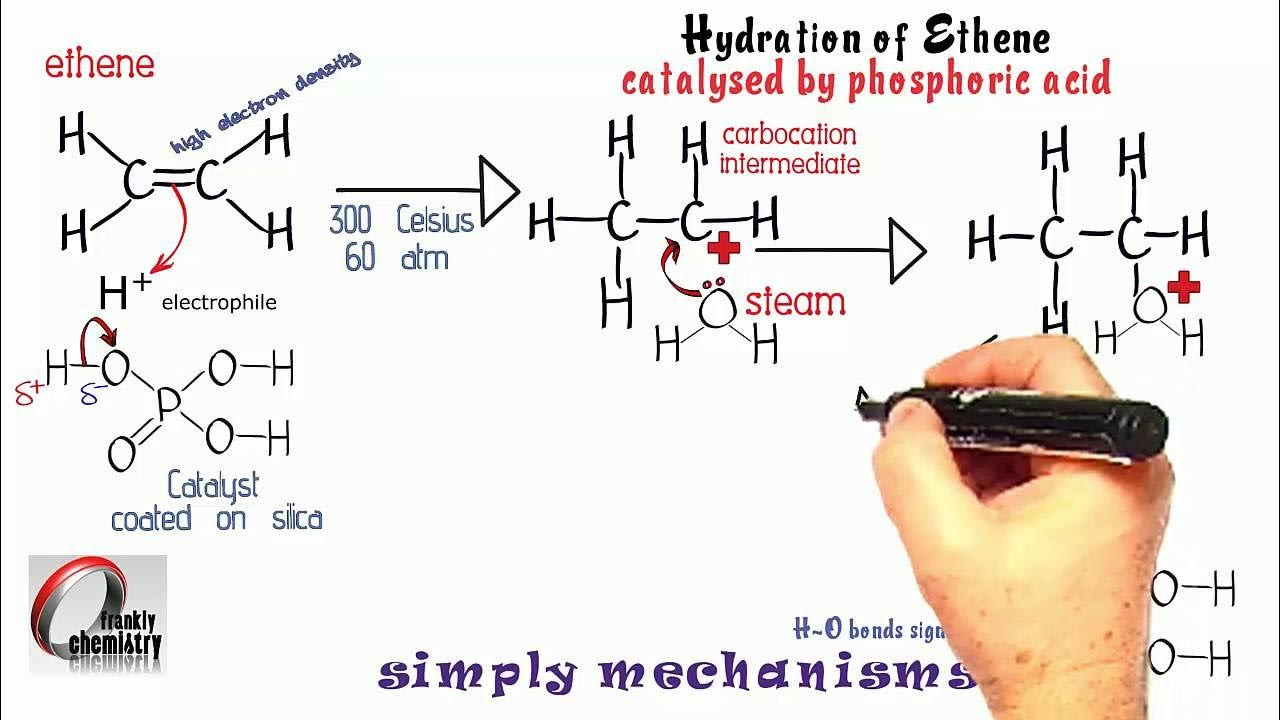
Addition of steam to form alcohols
Conditions = 330*C, 200 atm, H2O(g), phosphoric acid catalyst
H+ from H3PO4
Pi bond breaks
Forms dative covalent bond with H+
Carbocation intermediate
Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of H2O forms dative covalent bond with C of carbocation
Heterolytic fission of O-H bond
H+ catalyst is regenerated