quiz energy enzymes and cell resp.
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
energy
capacity to cause change or do work
Kinetic energy
energy associated with motion
thermal energy
kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms and moleucles
(heat energy - thermal energy in transfer between objects
potential energy
energy that matter possesses bc of its location and structure
Chemical energy
potential energy that can be released during a chemical reaction
Conservation of E / First law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but converted from one form to another
Thermodynamics
study of energy and transformations
Closed system
unable to exchange energy or matter with its surroundings
cannot reach equilibrium
open system
can exchange E and matter w surroundings
cells and organisms are open systems
Second law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer increases entropy (disorder) in the universe
Entropy
Measure of molecular disorder, randomness (heat has the most)
Free energy
energy that can do work when temp and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell
chem reactions are going to proceed in direction that causes a loss of free E
more free E is less stable but has greater work capacity
Potential e →
Kinetic E (thermal, kinetic)
Exergonic
proceeds with a net release of free E and is spontaneous
is favorable
need exergonic for endogonic
Endergonic/Endogonic
absorbs free energy from surroundings - non spontaneous
unfavored and requires energy to be done
Metabolism
combined catabolic and anabolic pathways
Catabolic
break apart
Anabolic
link together
three types of work cells do
chemical work
transport work
mechanical work
ATP
cells energy shuttle, makes RNA
made of ribose, adenine, and 3 phosphate groups'
breaks down glucose
ATP hydrolysis
breaks phosphate group off from energy, can be undone/added back
Enzymes
end in -ase
helps with reaction, catalyst, does NOT get used up during reaction, (reused)
Catalysis
reaction enabled by a catalyst
Substrate
reactant that enzyme binds to (The thing that goes INTO the enzyme, the thing that changes during reaction)
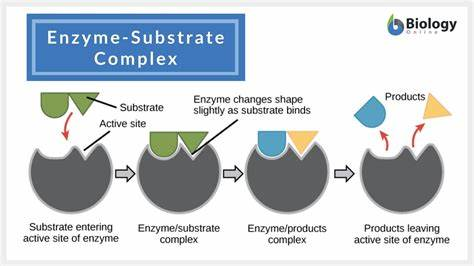
Active site
WHERE the substrate bonds to the enzyme
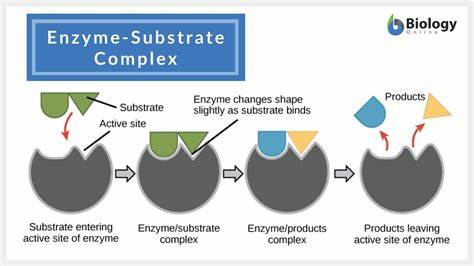
An active site can lower an energy barrier by
Orienting substrate correctly
straining substrate bonds
providing a favorable microenvironment
covalently bonding to the substrate (CHARGES HAVE TO LINE UP)
Enzyme activity can be affected by
temp
pH
chemicals like cofactors and inhibitors
Cofactors
non protein enyzme helper
may be inorganic (metal in ionic form) or organic
organic ones are called coenzymes (vitamins)
Competitive inhibitors
bind to active site, making reaction impossible
noncompetitive inhibitors
binds to another parts of enzyme causing indirect impacts to reaction
Allosteric regulation
is good and bad
may either inhibit or stimulate an enzymes activity
occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects the proteins function at another site
cooperativity
a form of allosteric regulation that can amplify enzyme activity
simplified image
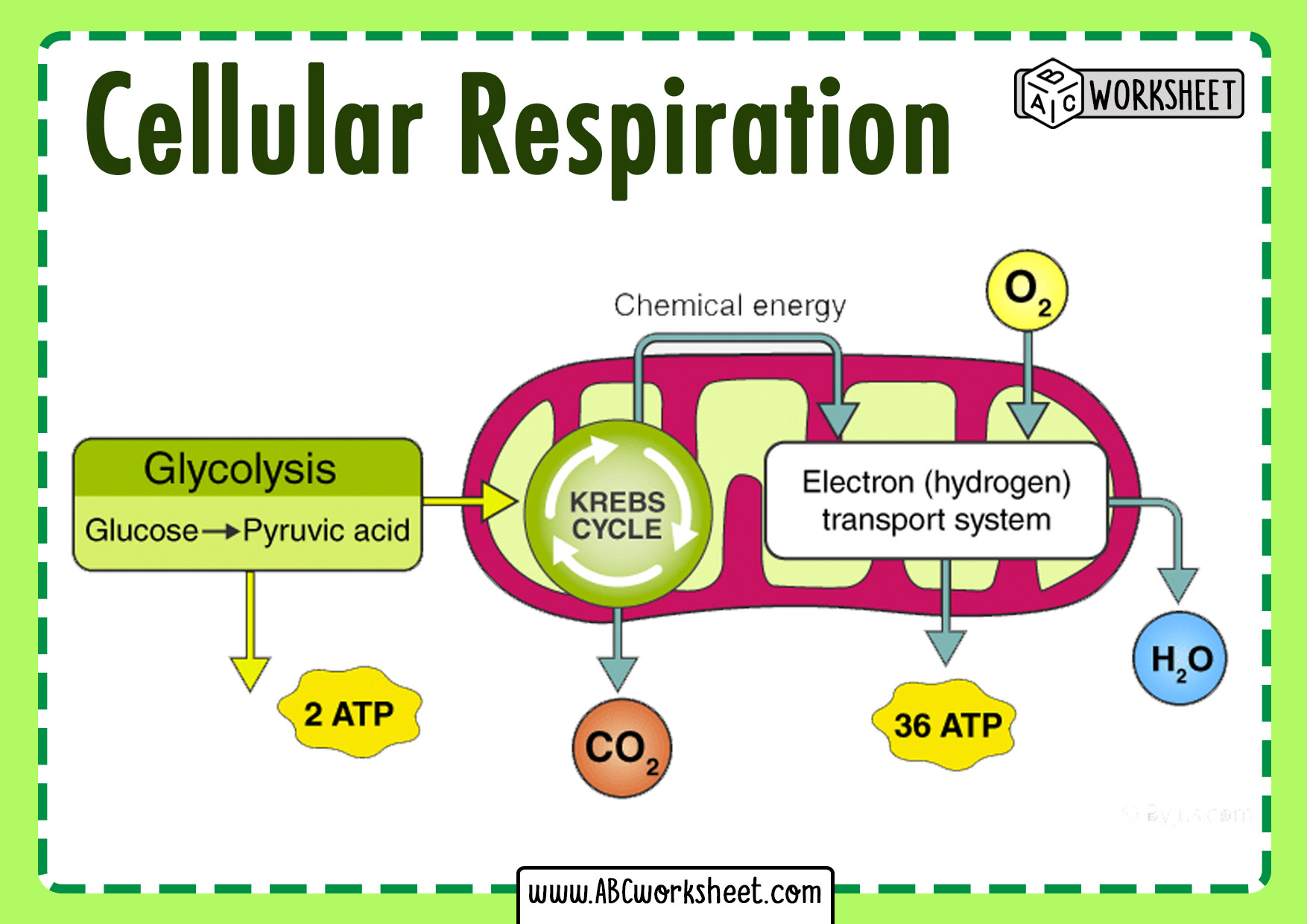
balanced chem eq. for cell respiration
Glucose + 6O2 → 6h2o + 6co2 + atp
O2 is reduced (gains e-)
glucose is oxidized (loses e-)
inputs and outputs glycolysis
input - glucose, 2 NAD+, 2 ATP, 4 ADP,
output - 2 (3 carbon) pyruvates, 2 NADH, 4ATP
Important details - G3P is in the middle of the glucose to pyruvate transformation lol
Input and output of pyruvate oxidation
inputs: 2 pyruvates, 2 NAD+, 2 coA
outputs: 2 acetly coA, 2 co2, 2 NADH
NO ATP!
inputs n outies for citric acid cycle
inputs: 2 acetly coA, 3NAD+, 1 FAD, 1 ADP
outies: 2 CO2, 3NADH, 1 FADH2, 1ATP, protons released to make gradient
Oxaloacetate + Acetyl group = ?
citric acid
activated carriers and their groups carried
ATP - phosphate groups
NADH, NADPH, FADH2 - electrons and hydrogens
Acetly Co-enzyme A - acetyl group
kinase
catalyzes the addition of a phosphate group to substrate
isomerase
rearranges chemical bonds by changing isomer
dehydrogenase
removes a hydrogen
mutase
moves chemical functional group
Where are the electrons in the ETC from?
the e-s come from NADH and FADH2, which is very important for phosphorylation oxidation
phosphorylation oxidation (i cant be bothered to type it out rn)
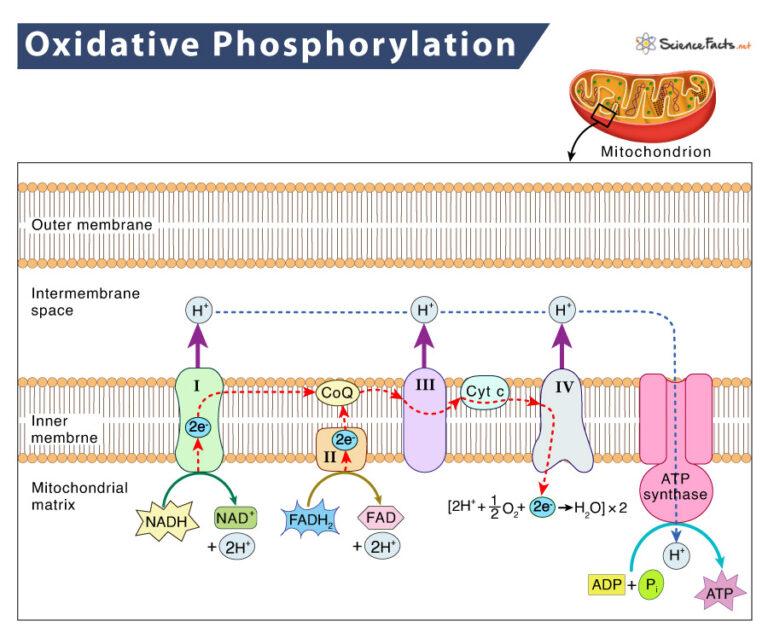
THE LASt electron acceptor issssssss?
O2 to make H2O 🥳
proton pumping
produces a steep electrochemical proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane
ATP synthase
enzyme, Uses energy stored in electrochem. gradient to make ATP
chemiosmosis
the use of energy in a proton gradient to drive cellular work
this is important
glucose → NADH → electrons to the ETC → proton motive force → ATP
Overall how much ATP per glucose?
Around 32 ATP per glucose, but about 34% of the energy in a glucose molecule is transferred to ATP during cell resp. the rest is lost as heat ☹
Aerobic respiration
consumes organic molecules and O2 to yield ATP
Fermentation
Partial degradation of sugars that occurs without O2 (anaerobic)
Anaerobic resp.
consumes compounds other than o2
When is O2 used in the cell respiration cycle?
It is only used in the last step in the ETC chain to turn the 6o2 into water (the glucose makes CO2)
Which step of cell resp. is not in the mitochondria?
Glycolysis - it is in the cytoplasm
Where is pyruvate oxidation?
mitochondrial matrix
Where is citric acid cycle?
Mito. matrix
Where is Oxidative phosphorylation
in the mitochondria inner membrane
What is the point of fermentation
It is to regenerate NADH to NAD+ for glycolysis
How is photosynthesis a cycle?
Light Energy → photosynthesis → organic molecules and O2 → cellular respiration → CO2 + H2O which then gets released back into ecosystem
know how to draw diagrams on a mitochondrion, chloroplast, and the diagram for cell resp. and photosynthesis
hehe
Light reactions in thylakoid (membrane)
Split h2o !!!!!!
release o2
reduce the e- acceptor NADP+ to NADPH
Generate ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
The ‘captured’ Energy from light reactions used by carbon fixation
PSII
Absorbs light to take apart water
Transfers e- through proton pump (makes concen gradient)
ATP synthase brings protons back to stroma
Stroma → thylakoid space
PSI
On membrane thylakoid
Absorbs light
e- passed through pumps and gets added to NADP+→NADPH
Calvin cycle
Uses the CO2 to make glucose (or other organic compounds)
Inputs 3CO2 per cycle
there is 6ATP and 6 NADPH to phosphoglycerate
1 G3P is immediate output of cycle
9 ATP used altogether
Rubisco
enzyme that puts the CO2 onto molecules in calvin cycle
G3P in photosyn. why important
It can be used to start cellular respiration since G3P is a crucial step in glycolysis
Gases move freely in chloroplasts becasue?
simple diffusion
How do gasses get to cells deep within the leaf?
Cells can separate their pore-guard cells, they breathe
What happens if CO2 isnt avaliable for calvin cycle?
The cell will input O2 into the calvin cycle, but it can’t make G3P with O2, so it is a waste of energy and O2
C4 plants
made of 4c molecule, minimize the cost of photorespiration by incorporating CO2 into four Carbon compounds
Pep carboxylase
make the 4carbon compounds that can be converted to pyruvate + CO2
CAM Plants/Crassulacean acid metabolism
take in compounds in a time sensitive way
They only open their stomata at night, meaning they only breathe in CO2 at night, so H2O doesn’t get evaporated
has stomata closed during the day