AP Psychology Unit 3: Development
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Psychoactive Drug
a chemical substance that alters perceptions and moods
Tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug's effect
Addiction
compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences
Withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
Physical Dependance
a physiological need for a drug, marked by unpleasant withdrawal symptoms when the drug is discontinued
Psychological Dependence
a psychological need to use a drug, such as to relieve negative emotions
Depressants
drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
Alcohol Dependence (Alcoholism)
alcohol use marked by tolerance, withdrawal if suspended, and a drive to continue use
Barbiturates
drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgement
Opiates
opium and its derivatives, such as morphine and heroin; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Stimulants
drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
Amphetamines
drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing speeded-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes
Nicotine
a stimulating and highly addictive psychoactive drug in tobacco
Methamphetamine
a powerfully addictive drug that stimulates the central nervous system, with speeded-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes; over time, appears to reduce baseline dopamine levels
Ecstacy
a synthetic stimulant and mild hallucinogen. Produces euphoria and social intimacy, but with short-term health risks and longer-term harm to serotonin-producing neurons and to mood and cognition.
Hallucinogens
psychedelic ("mind-manifesting") drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
LSD
a powerful hallucinogenic drug; also known as acid
Near-death experience
an altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death (such as through cardiac arrest); often similar to drug-induced hallucinations
Marijuana
dried leaves and flowers of the hemp plant, and has the characteristics of a stimulant, depressant, and hallucinogen
THC
the major active ingredient in marijuana; triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations
Agonist
a chemical that mimics the action of a neurotransmitter.
Antagonist
a chemical that opposes the action of a neurotransmitter
Blood-brain barrier
a mechanism that prevents certain molecule from entering the brain but allows others to cross
Reverse tolerance
a condition in which less and less alcohol causes intoxication
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
DNA
a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
Genes
DNA segments that serve as the key functional units in hereditary transmission
Genome
the complete instructions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes
Monozygotic twins
identical twins formed when one zygote splits into two separate masses of cells, each of which develops into a separate embryo
Dizygotic twins
fraternal twins who are produced when two separate ova are fertilized by two separate sperm at roughly the same time
Temperament
a person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
Molecular genetics
the subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of genes
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
X Chromosome
the sex chromosome that is present in both sexes: singly in males and doubly in females
Y Chromosome
the sex chromosome found only in males
Gender Role
a set of expected behaviors for males or for females
Social Learning Theory
the theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
Gender identity
our sense of being male or female
Gender typing
the process of developing the behaviors, thoughts, and emotions associated with a particular gender
Zygote
fertilized egg
Embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
Fetus
the developing human organism from 9 weeks after conception to birth
Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
physical and cognitive abnormalities in children caused by a pregnant woman's heavy drinking
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
Maturation
biological growth processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience
Critical Period
an optimal period shortly after birth when an organism's exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces proper development
Infantile Amnesia
inability to remember events before age 3
Cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
Assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
Accommodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
Object Permanence
a sensorimotor child developes the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
Egocentrism
the preoperational child's difficulty taking another's point of view
Artificialism
the belief of the preoperational child that all objects are made by people
Conservation
the principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
Metacognition
thinking about thinking
Theory of Mind
ability to reason about what other people know or believe (empathy)
Animistic Thought
giving non living objects their own feelings and thoughts
Zones of Proximal Development (ZPD)
the difference between two levels of linguistic (cognitive) performance--that which the student can do independently and that which he or she can do with the help of an adult or more capable peers
Sensorimotor Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
Pre-operational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic, are egocentric, and believes in artificialism
Concrete Operational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events and understand conservation
Formal Operational Stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts and metacognition
Rooting Reflex
a baby's tendency, when touched on the cheek, to turn toward the touch
Sucking Reflex
reflex that causes a newborn to make sucking motions when a finger or nipple if placed in the mouth
Grasping Reflex
an infant's clinging response to a touch on the palm of his or her hand
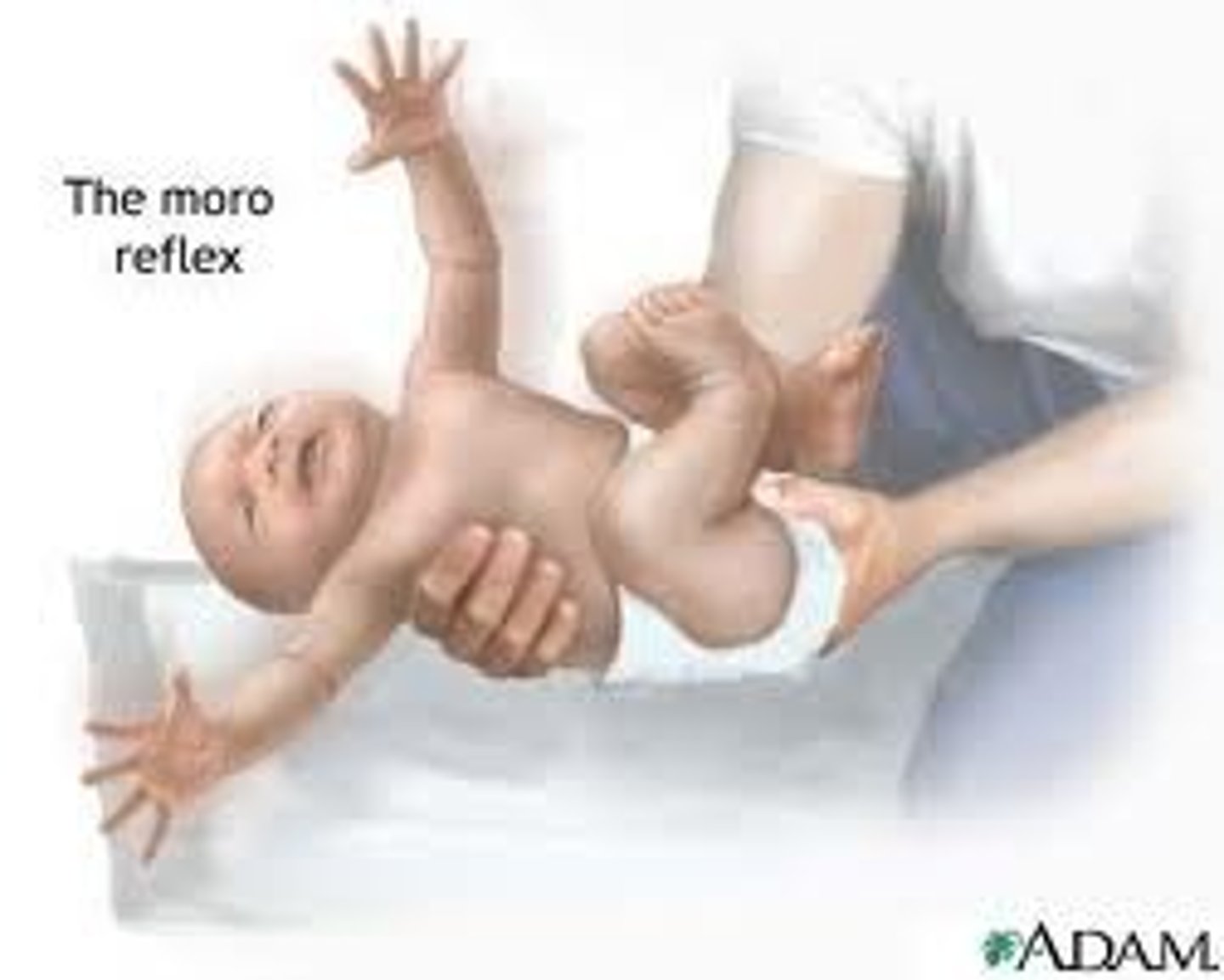
Moro reflex
reflex in which a newborn strectches out the arms and legs and cries in response to a loud noise or an abrupt change in the environment
Babinski reflex
reflex in which a newborn fans out the toes when the sole of the foot is touched

Pre-conventional morality
first level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development in which the child's behavior is governed by the consequences of the behavior
Conventional morality
second level of Kohlberg's stages of moral development in which the child's behavior is governed by conforming to the society's norms of behavior
Post-conventional morality
Kohlberg's highest stage of morality: occurs late in life and is a personal morality, developed by the adult and which supersedes society's rules, laws, and restrictions
Stranger anxiety
the fear of strangers that infants commonly display, beginning by about 8 months of age
Attachment
an emotional tie with another person; shown in young children by their seeking closeness to the caregiver and showing distress on separation
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
Self-concept
our understanding and evaluation of who we are
Adolescence
the transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence
Puberty
the period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
Identity
our sense of self; according to Erikson, the adolescent's task is to solidify a sense of self by testing and integrating various roles
Intimacy
in Erikson's theory, the ability to form close, loving relationships; a primary developmental task in late adolescence and early adulthood
The Heinz Dilemma
stealing a drug he cannot afford in order to save his wife's life
Internalization
process by which a norm becomes a part of an individual's personality, thereby conditioning the individual to conform to society's expectations
Scaffolding
the support for learning and problem solving that encourages independence and growth (Vygotsky)
Zones of Proximal Development
(Vygotsky) distance between what an individaul can accomplish on independently and what he or she can accomplish with the guidance and encouragement of a more skilled partner (develop quickly or slowly depends on these zones)
Cross-sectional Study
a study in which people of different ages are compared with one another
Longitudinal Study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
Terminal Decline
acceleration in deterioration of cognitive functioning 4 years before death
Social Clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Stage of Grief and Loss
responses to death and loss: denial, anger, bargaining, depression, acceptance
Death Deferral
the phenomenon that death rate increases when people reach their birthdays
Albert Bandura
pioneer in observational learning (AKA social learning), stated that people profit from the mistakes/successes of others; Studies: Bobo Dolls-adults demonstrated 'appropriate' play with dolls, children mimicked play
Jean Piaget
researcher on cognitive development
Mary Ainsworth
developmental psychology; compared effects of maternal separation, devised patterns of attachment; "The Strange Situation": observation of parent/child attachment

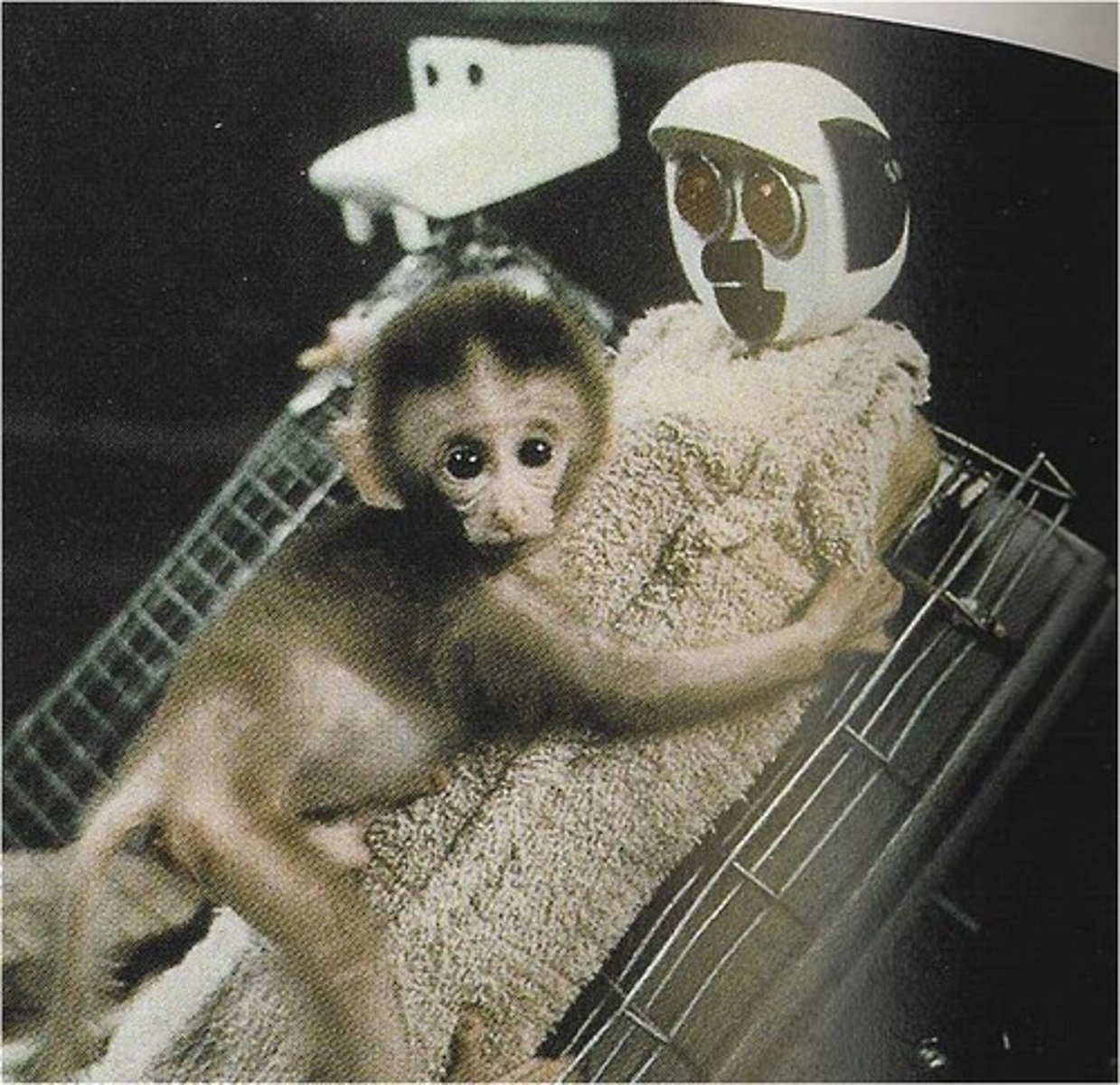
Harry Harlow
development, contact comfort, attachment; experimented with baby rhesus monkeys and presented them with cloth or wire "mothers;" showed that the monkeys became attached to the cloth mothers because of contact comfort

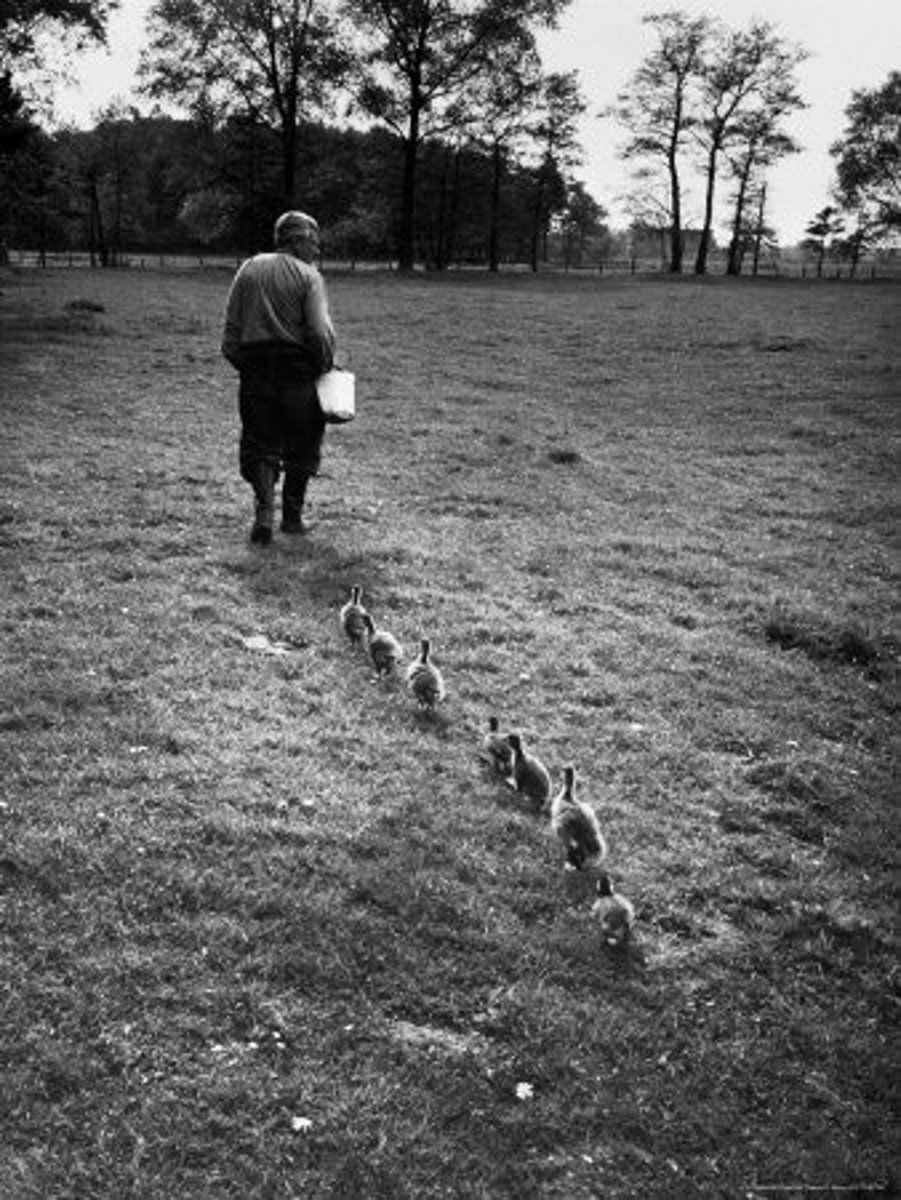
Konrad Lorenz
researcher who focused on critical attachment periods in baby birds, a concept he called imprinting

Erik Erikson
neo-Freudian, humanistic; 8 psychosocial stages of development: theory shows how people evolve through the life span
G. Stanley Hall
American psychologist who established the first psychology research laboratory in the United States and founded the American Psychological Association
Lawrence Kohlberg
moral development; most famous moral dilemma is "Heinz" who has an ill wife and cannot afford the medication. Should he steal the medication and why?
Carol Gilligan
Presented feminist critique of Kolhberg's moral development theory; believed women's moral sense guided by relationships, while men's are more rigid
Lev Vygotsky
child development; investigated how culture & interpersonal communication guide development; zone of proximal development; play research