AP Human Geography Test Preparation Flashcards
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
sequent occupance
the notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place (shown clearly in Rome)
cultural landscape
the essence of how humans interact with nature; often leaving a visible imprint on the earth's surface
arithmetic density
total population/total land area
physiological density
total population/unit of arable land
agricultural density
# of farmers/unit of arable land- highest in LDCs
hearth
the region from which ideas originate
5 Major: Mesopotamia, Indus River Valley, Nile River Valley, Huang He/Yellow River, Mesoamerica
diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from place to place
relocation diffusion
the spread of an idea through physical movement of people from one place to another
hierarchal diffusion
type of expansion diffusion: looks random but is not, usually related to modern technology, space time compression (if an area is connected, space/time/distance is no longer an issue)
contagious diffusion
type of expansion diffusion: RAPID, UNIFORM spread, leads to distance decay
distribution
the arrangement of something across Earth's surface
environmental determinism
the idea that physical environment causes human activity-humans must adapt to their environment/cannot change it
environmental possibilism
the idea that physical environment may limit some human activity, but generally humans are able to alter their environment to suit their needs
site
the physical character of a place; what is there, why it is significant
situation
the location of a place relative to other places
scale
representation of a real-world phenomenon at a certain level of generalization or reduction
formal region
everyone shares in common one or more distinct characteristics; clear, defined boundary lines
perceptual or vernacular region
fuzzy boundary lines- everyone's perception of the region is different
functional or nodal region
An area that has a node, such as an airport or stadium
geographic information systems
allows geographers to map, analyze, store, and model spatial data
thematic maps
maps that tell stories, typically showing the degree of some attribute
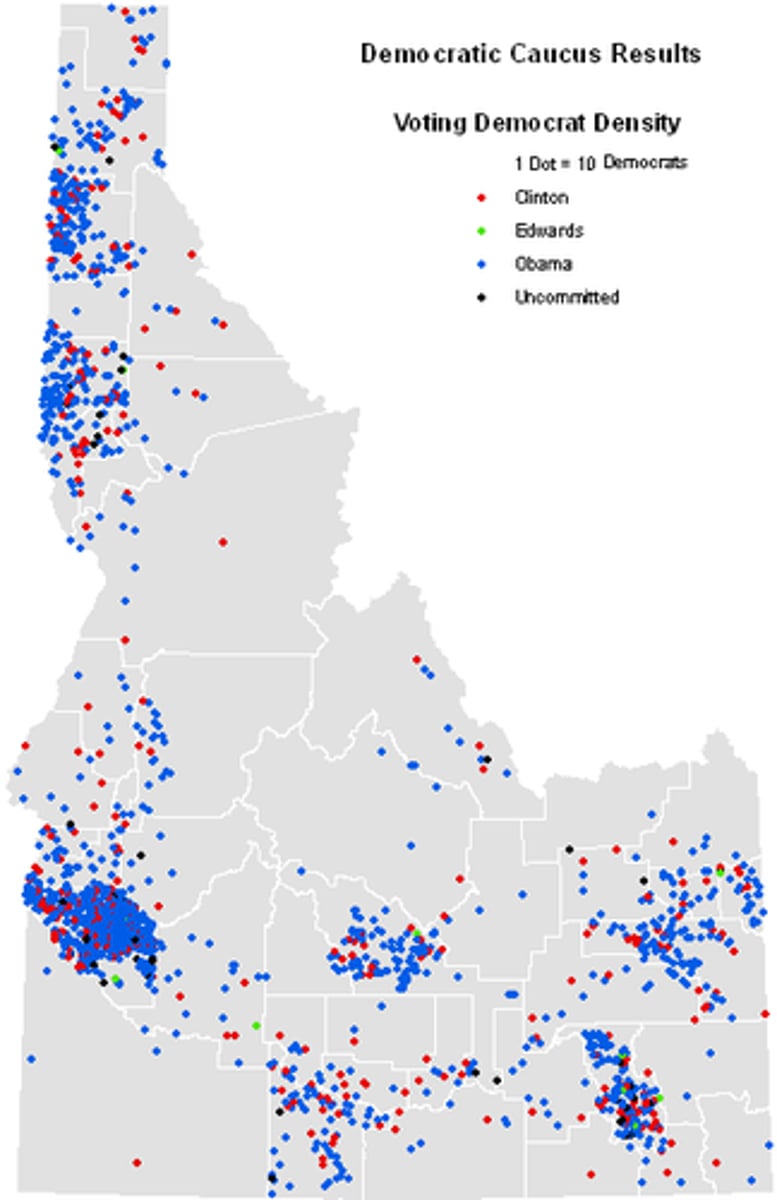
dot map
thematic map: dot on a map represents some frequency of the mapped variable
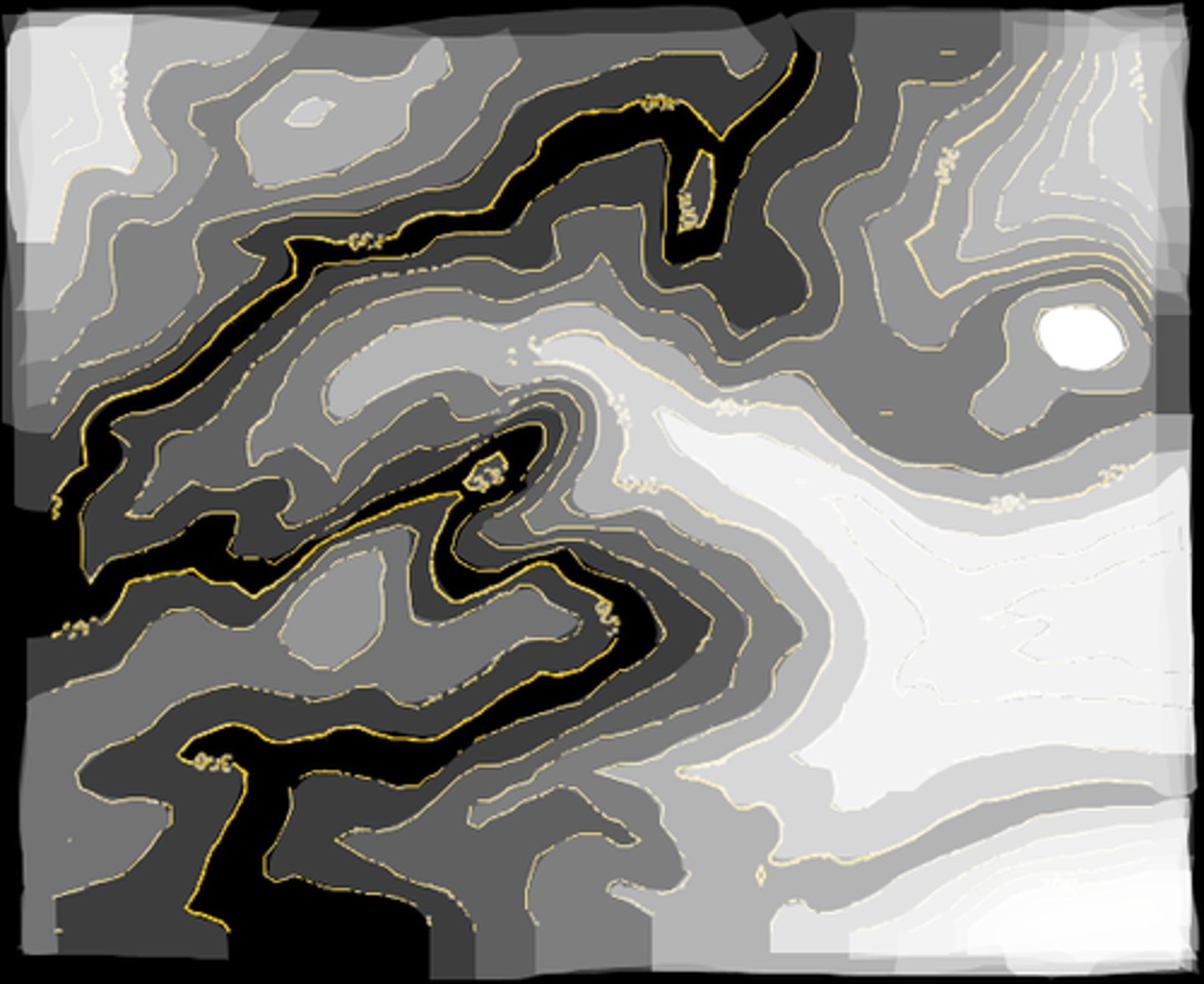
isoline map
thematic map: uses lines of equal value to represent data like elevation, barometer pressure, temperature, or migration
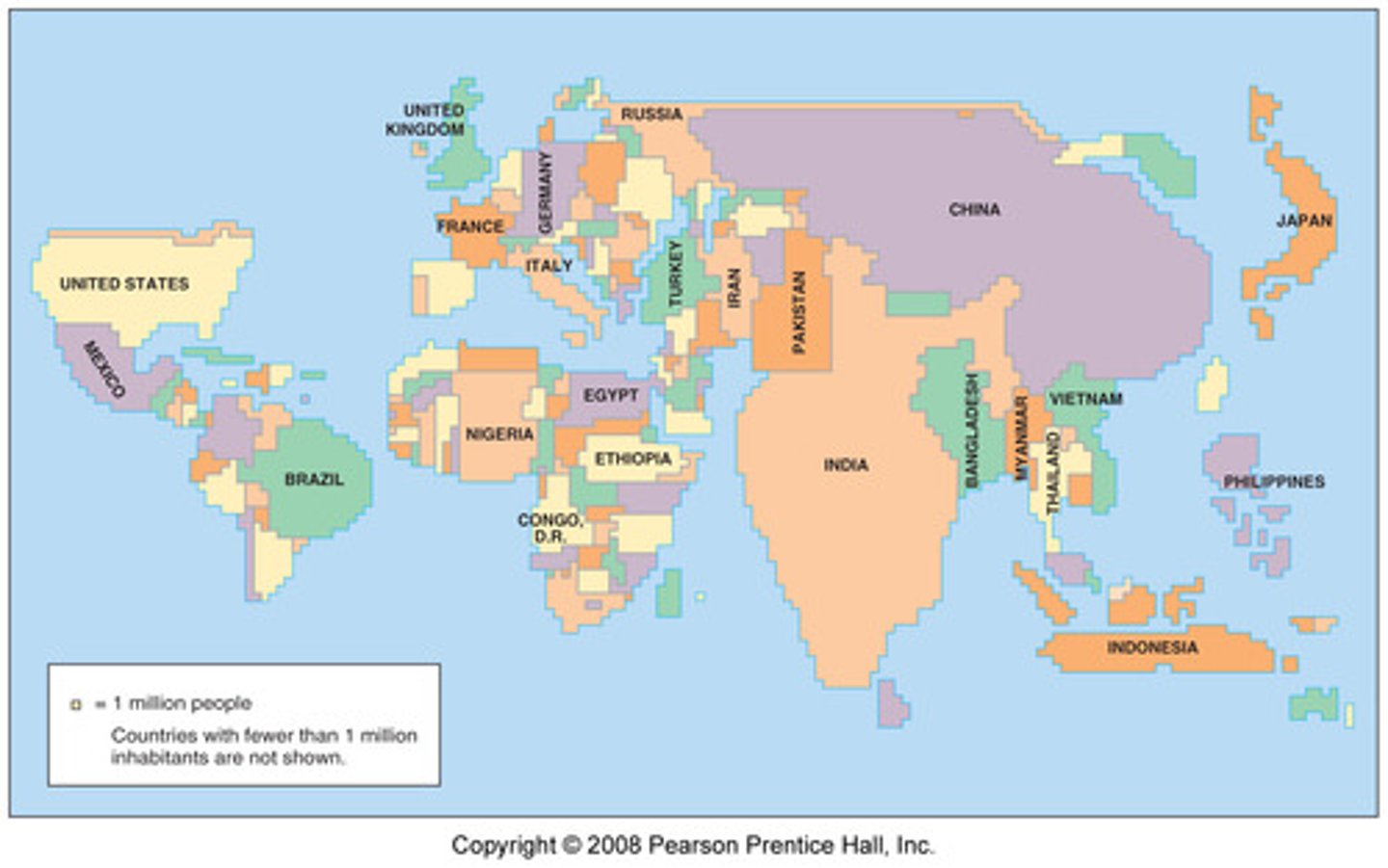
cartogram
thematic map: uses relative size of political units to convey a value
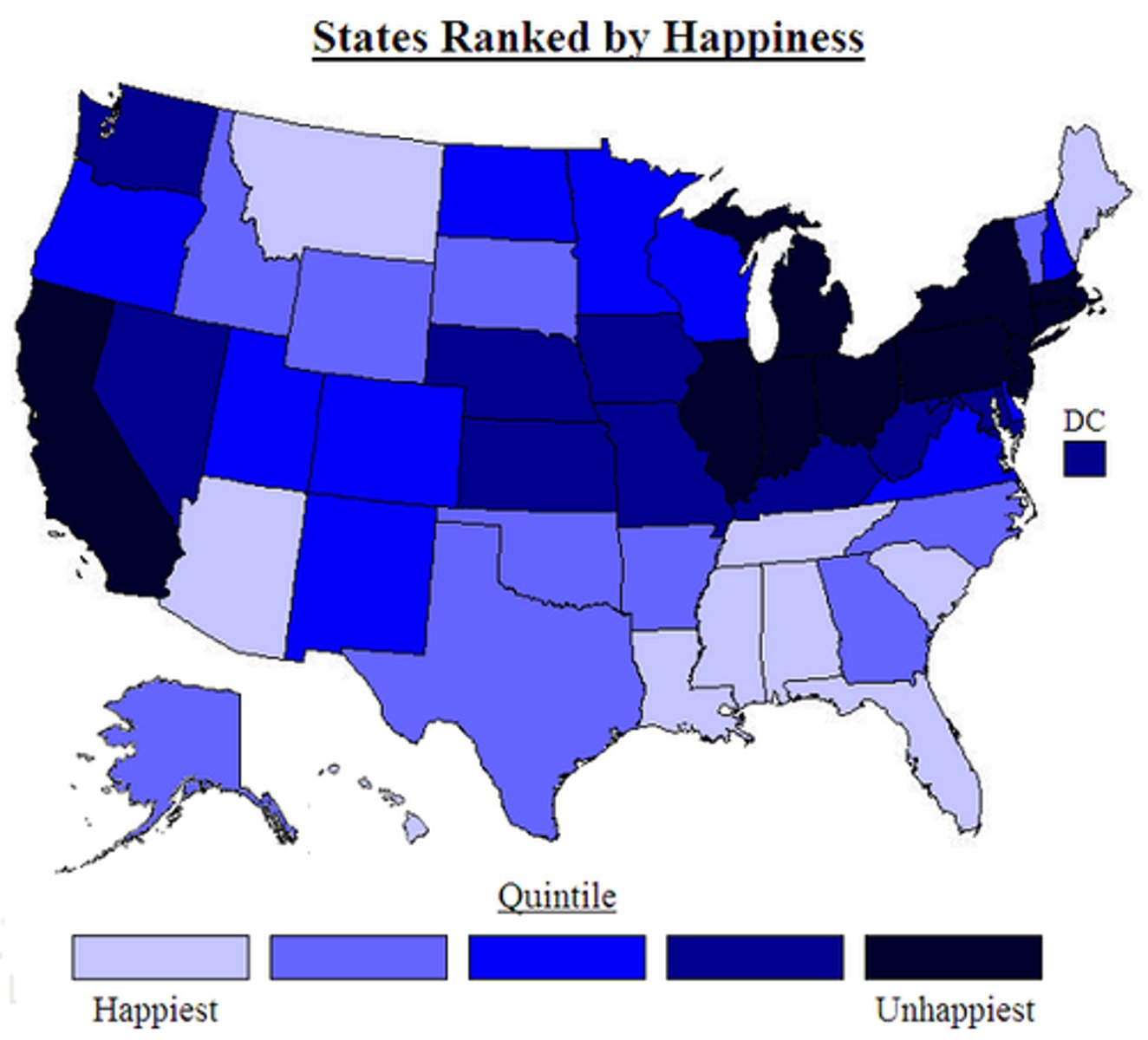
choropleth map
thematic map: a variable is depicted with shading patterns or colors
proportional symbol map
thematic map: size of a symbol varies in proportion to the intensity of the mapped variable
projection
transferring data from the globe to a flat surface: distortions will occur
reference maps
literal maps, tell what a place looks like
absolute distance
exact measurement of space between two places
relative distance
approximate measurement of the physical space between two places
carrying capacity
the population level that can be supported, given the quantity of food, habitat, water, and other infrastructure present
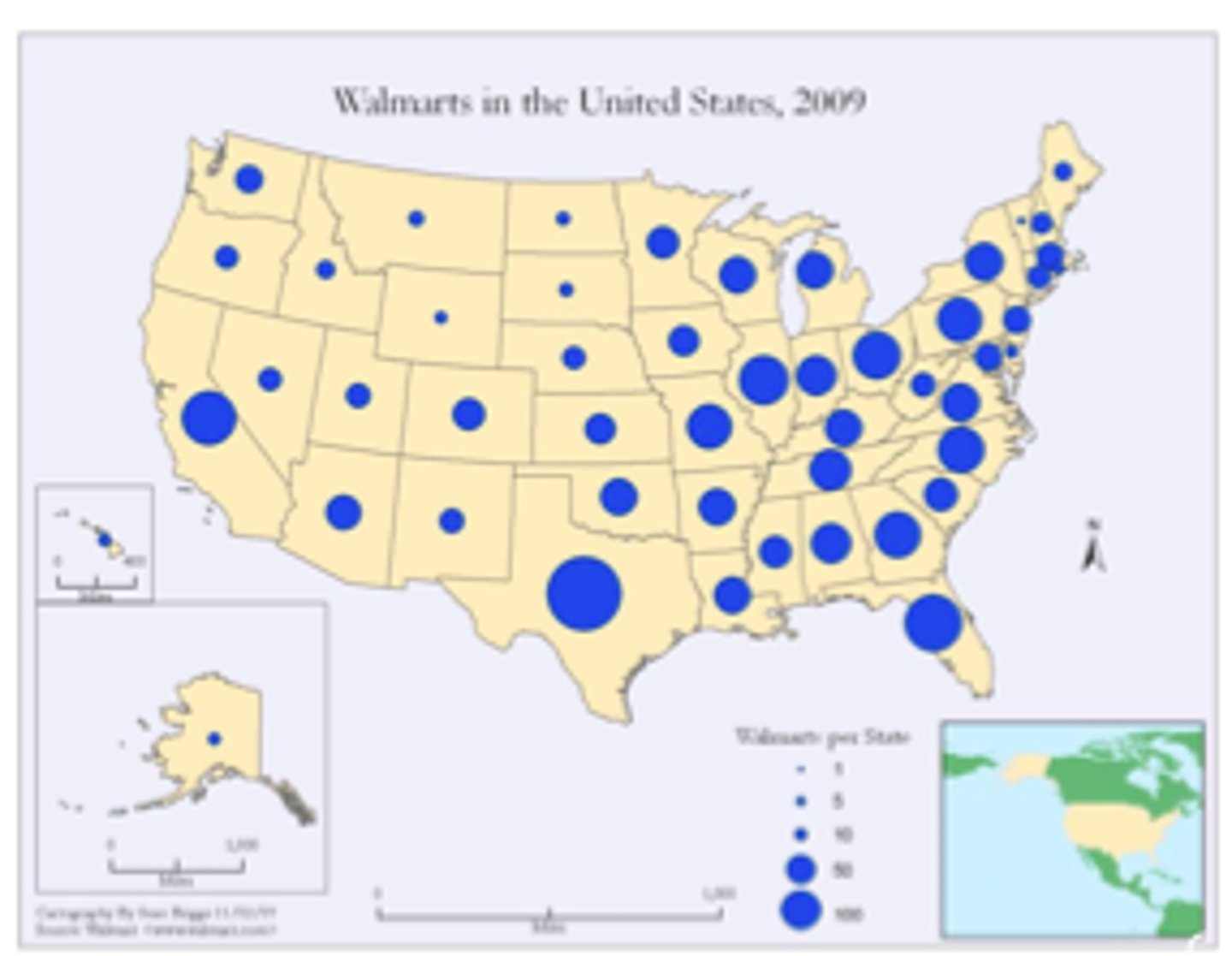
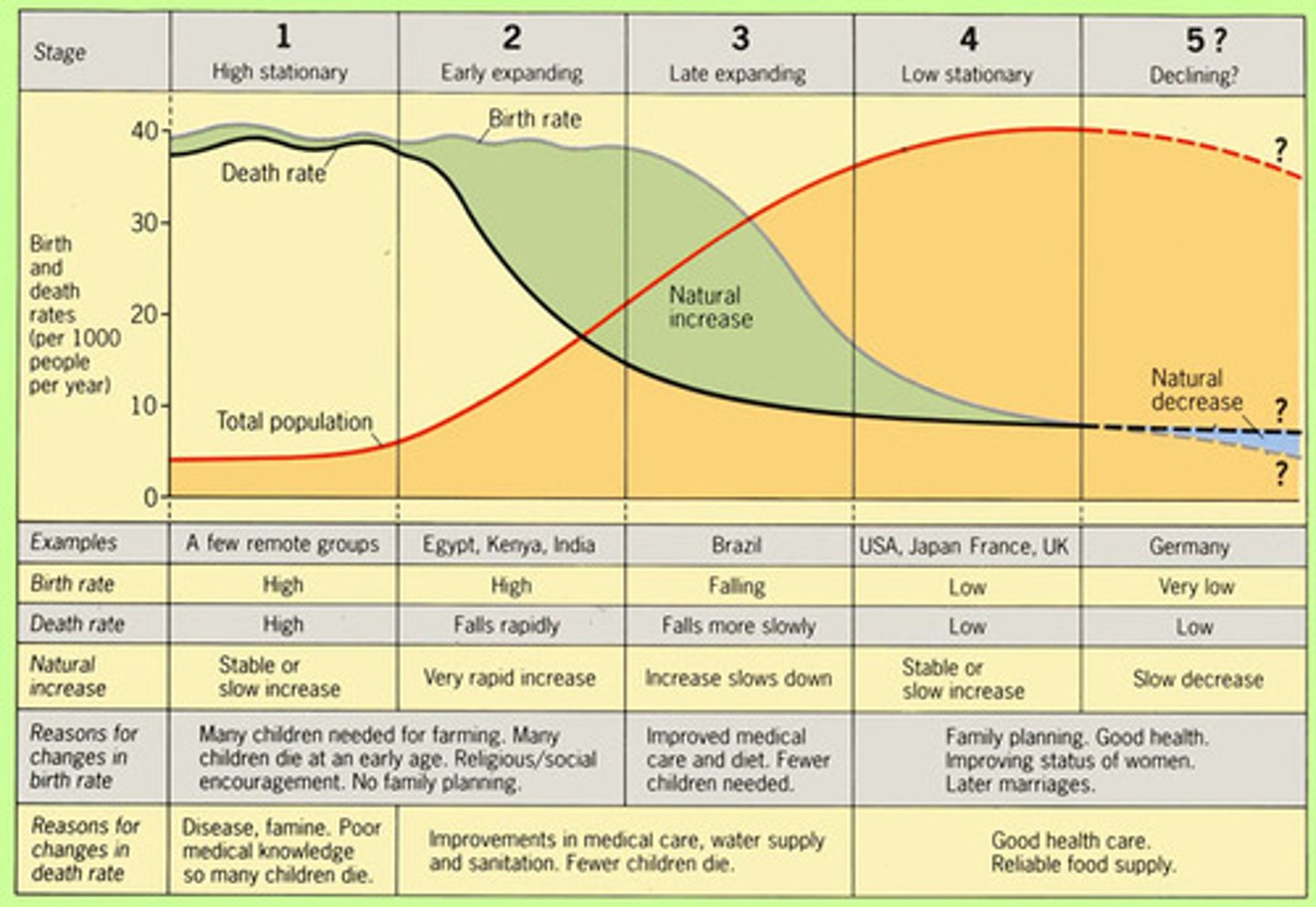
demographic transition model
shows 5 stages of population growth
dependency ratio
the number of people who are too young or old to work compared to the number of people in their productive years
ecumene
parts of earth's surface occupied by human settlement
epidemiological transition model
shows distinctive cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model
j curve
when population projection shows exponential growth
Thomas Malthus
argued that the world's rate of population increase was far outrunning food production (determinism)
Esther Boserup
viewed population growth as a positive force driving agricultural innovations that could support more people (possibilism)
neo-malthusian
person who argues that population growth in LDCs and outstripping of resources other than food will create long term problems for the earth
population distributions
the arrangement of people according to density, concentration, and/or pattern
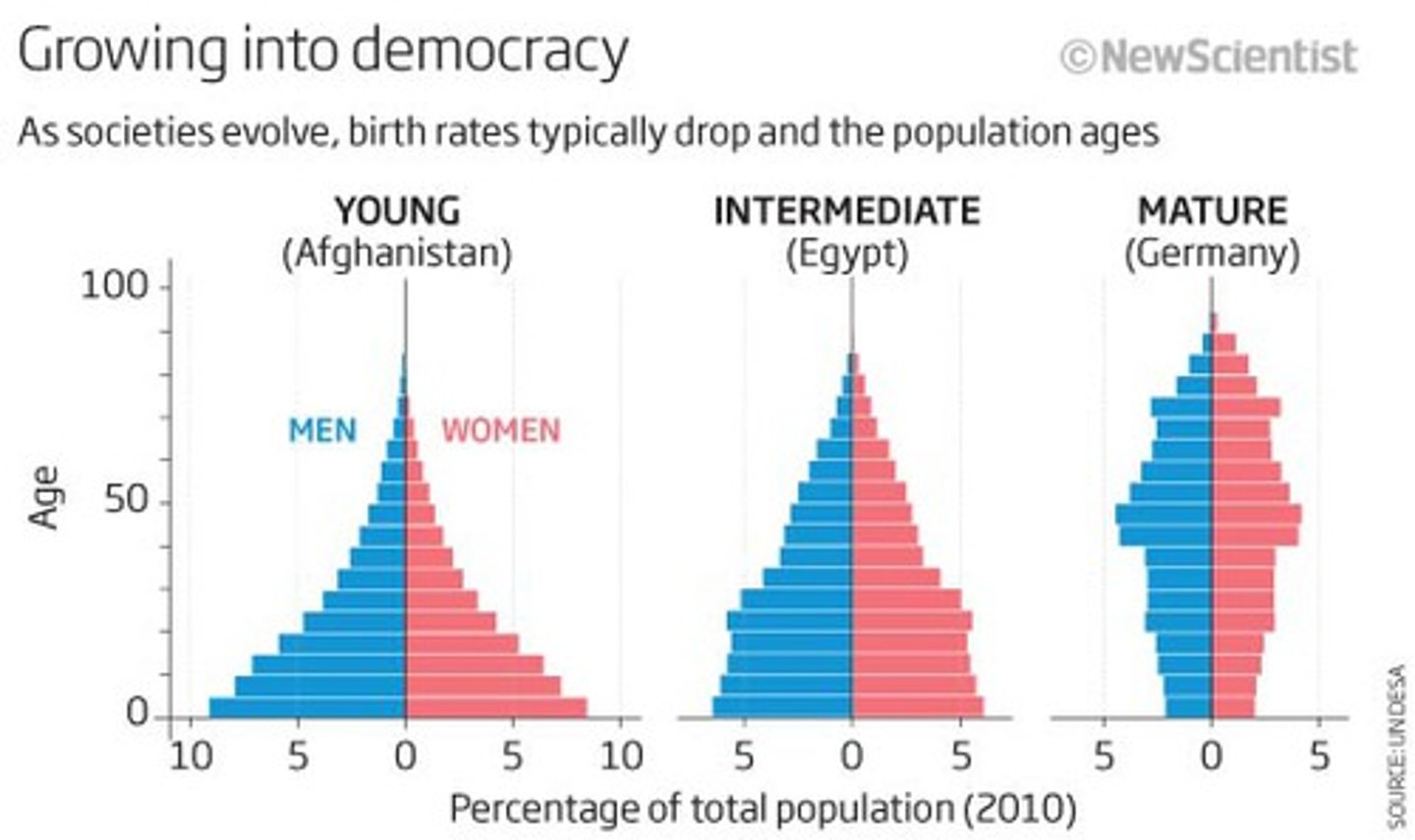
population pyramid
population displayed by age and gender on a bar graph- closer to rectangle shape is best
rate of natural increase
the percentage by which a population grows each year
s curve
population projection that predicts zero population growth at some point
distance decay
when contact between two groups diminishes because of distance between them
gravity model
created by Hotelling, predicts that optimal location of a service is directly related to number of people in the area and inversely related to the distance people must travel to access it
push factor
something that causes people to leave their old residence and move to new places (environmental disaster, bad economy, famine, etc)
pull factor
causes people to move into a new place (job opportunities, good weather, family)
refugee
someone forced to leave their home country, and crosses international boundary lines
displaced person
someone forced to leave home, but stays within international boundary lines
time space compression
the idea that distance between some places is actually shrinking due to technology
chain migration
people move to places where they have family or people who share their beliefs
step migration
people must go to multiple places before arriving at their final location
periodic migration
people migrate for a certain period of time, and plan to return to their home at some point. ex: migration to college or old people going to florida for the winter
cyclical migration
people migrate daily to work or school
acculturation
process of only adopting certain customs of a culture to suit one's lifestyle
assimilation
less dominant culture loses their culture to a more dominant culture
Buddhism
universalizing religion: system of beliefs that seeks to explain ultimate realities of all people- originated in N. India and Nepal
Christianity
universalizing religion: monotheistic religion centered on the life and teachings of Jesus, originated in SW Asia (split into three branches: Eastern Orthodox, Roman Catholic, and Protestant)
Confucianism
ethnic: complex system of moral, social, political, and religious thought that has influenced Chinese civilization
ethnic religion
a religion that does not seek converts
universalizing religion
a religion that seeks converts
fundamentalism
literal interpretation and strict adherence to basic principles of a religion
lingua franca
universal language, used for quick and efficient communication: previously Latin, now English
secularism
belief that religion and government should be separate
Sino Tibetan language family
language area that spreads through most of SE Asia and China
geopolitics
the study of the interplay between political relations and the territorial context in which they occur
Apartheid
segregation of blacks in S. Africa from 1948 to 1994
centrifugal force
a factor that causes a country to be forced apart (religious differences, environmental disaster, bad leader)
centripetal force
a factor that pulls a country together (common enemy, good economy, charismatic leader)
city-state
a sovereign state that comprises a town and the surrounding countryside
decolonization
the movement of European colonies gaining independence
devolution
decentralization of a government from a unitary to a federal system or fracturing of a government: worked in UK with Scotland, not in Yugoslavia
domino theory
the idea that political destabilization in one country can lead to collapse of political stability in neighboring countries
east/west divide
iron curtain: geographic separation between the largely democratic and free market countries of the west and communist and socialist countries of the east
enclave
a country or part of a country that is mostly or completely surrounded by the territory of another country (Lesotho)
exclave
a country which is geographically separated from the main part by a surrounding alien territory
exclusive economic zone
a sea zone over which a state has special rights over the exploration and use of marine resources
federalism
opposite of unitary: system of government in which power is distributed among certain geographical territories rather than concentrated within a central government
forward capital
a symbolically relocated capital usually because of either economic or strategic reasons (ex: Brasilia)
frontier
a zone where no state exercises complete political control
gerrymandering
redrawing legislative boundary lines to benefit the political party in power
Heartland Theory
Mackinder's theory that any political power based in the heart of Eurasia could gain enough strength to dominate the world
imperialism
a country has control over a territory already occupied by an indigenous society
microstate
a state or territory that is small in both population and area
NAFTA
allows the opening of trade borders between Mexico, Canada, and the US
nation-state
country whose population possesses a substantial degree of cultural homogeneity and unity- territory corresponds to that occupied by a particular ethnicity that has been transformed into a nationality
Rimland Theory
Spykman's theory that the domination of the coastal fringes of Eurasia would provide the base for world conquest
sovereignty
supreme or independent political power
World Systems Theory
theory developed by Immanuel Wallerstein that explains the emergence of a core, periphery, and semi-periphery in terms of economic and political connections
Balkanization
the process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities (Yugoslavia)
agribusiness
the set of economic and political relationships that organize food production for commercial purposes- companies control everything from "seed to store"
desertification
the process by which formally fertile lands become increasingly arid (happening in between the sahara and sub-saharan Africa bc of goat grazing)
extensive agriculture
an agricultural system characterized by low inputs of labor per unit land area
feedlots
places where livestock are concentrated in a very small area and raised on hormones and hearty grains to prepare them for slaughter
GMOs
foods that are mostly products of organisms that had their genes altered in a laboratory
Green Revolution
1970s-1980s: the development of higher yield and faster growing crops through increased technology and fertilizers- developed strategies in an attempt to make LDCs as productive as MDCs-created large economic gap between rich and poor
intensive cultivation
agricultural activity that involves effective and efficient use of labor on small plots of land to maximize crop yield- wet rice production
livestock ranching
extensive commercial agriculture that includes the grazing of livestock
market gardening
the small scale production of fruits, vegetable, and flowers sold directly to local consumers
mediterranean agriculture
an agricultural system in which the climate provides moist and moderate winters; ideal for grapes, olives, and nuts