AP Biology Final Review: Cell Structure, Macromolecules, Enzymes, and Energy
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
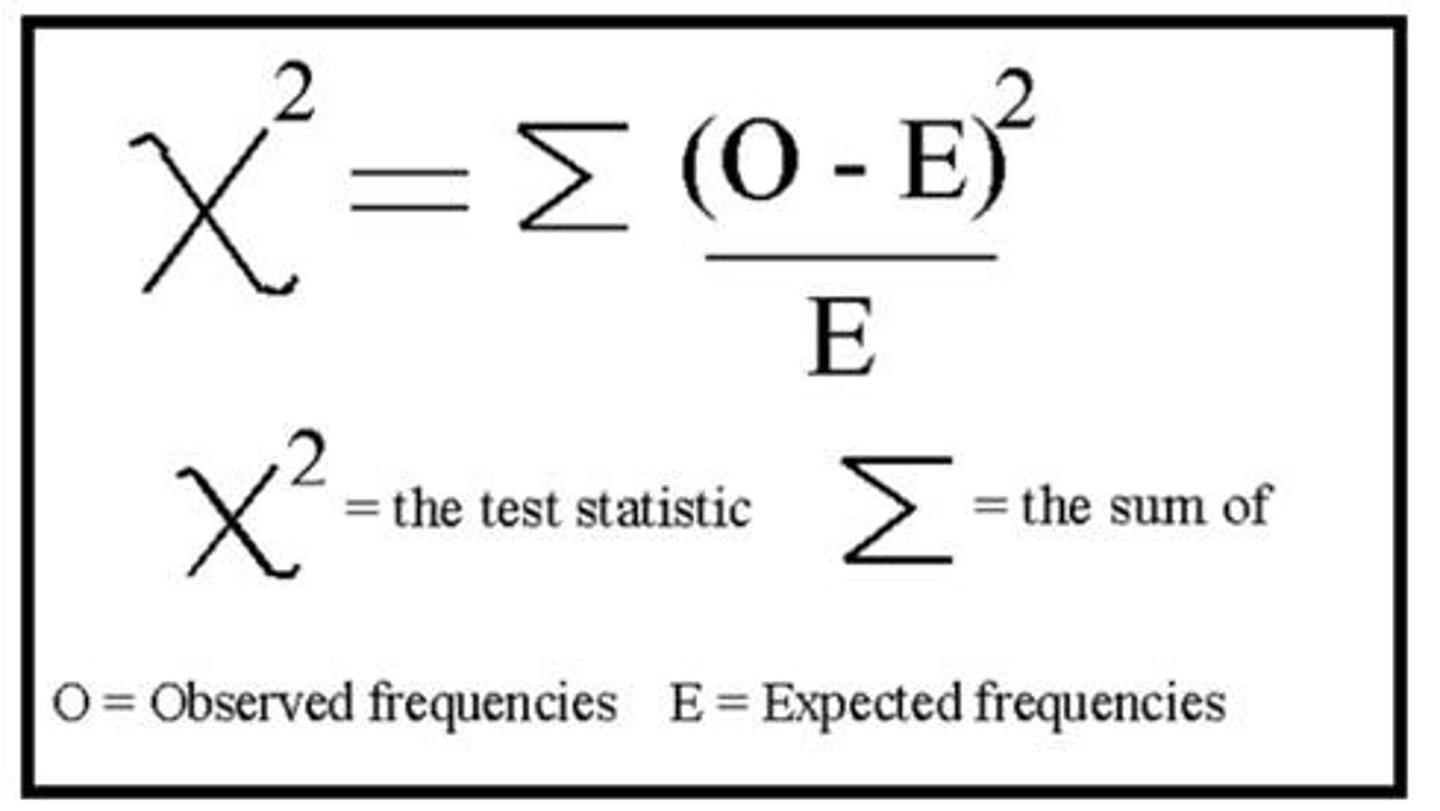
What is a Chi Square analysis used for?
To analyze categorical data.
What should be included in a good graph?
Title, x-axis and y-axis titles with units, and consistent numbers.
What is the difference between a bar graph and a line graph?
A bar graph is for categorical data; a line graph shows trends over time.
What is tested in science?
Hypotheses.
What do positive feedback loops do?
Amplify a change.
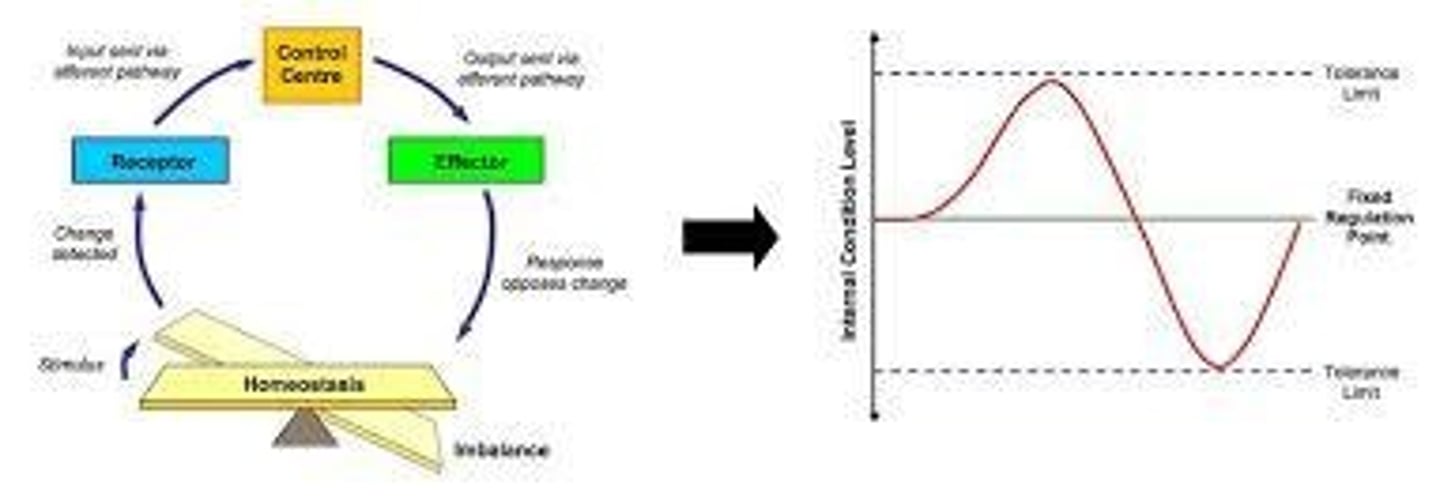
What do negative feedback loops do?
Counteract a change to maintain stability.
What are covalent bonds?
Strong bonds formed by the sharing of electrons.
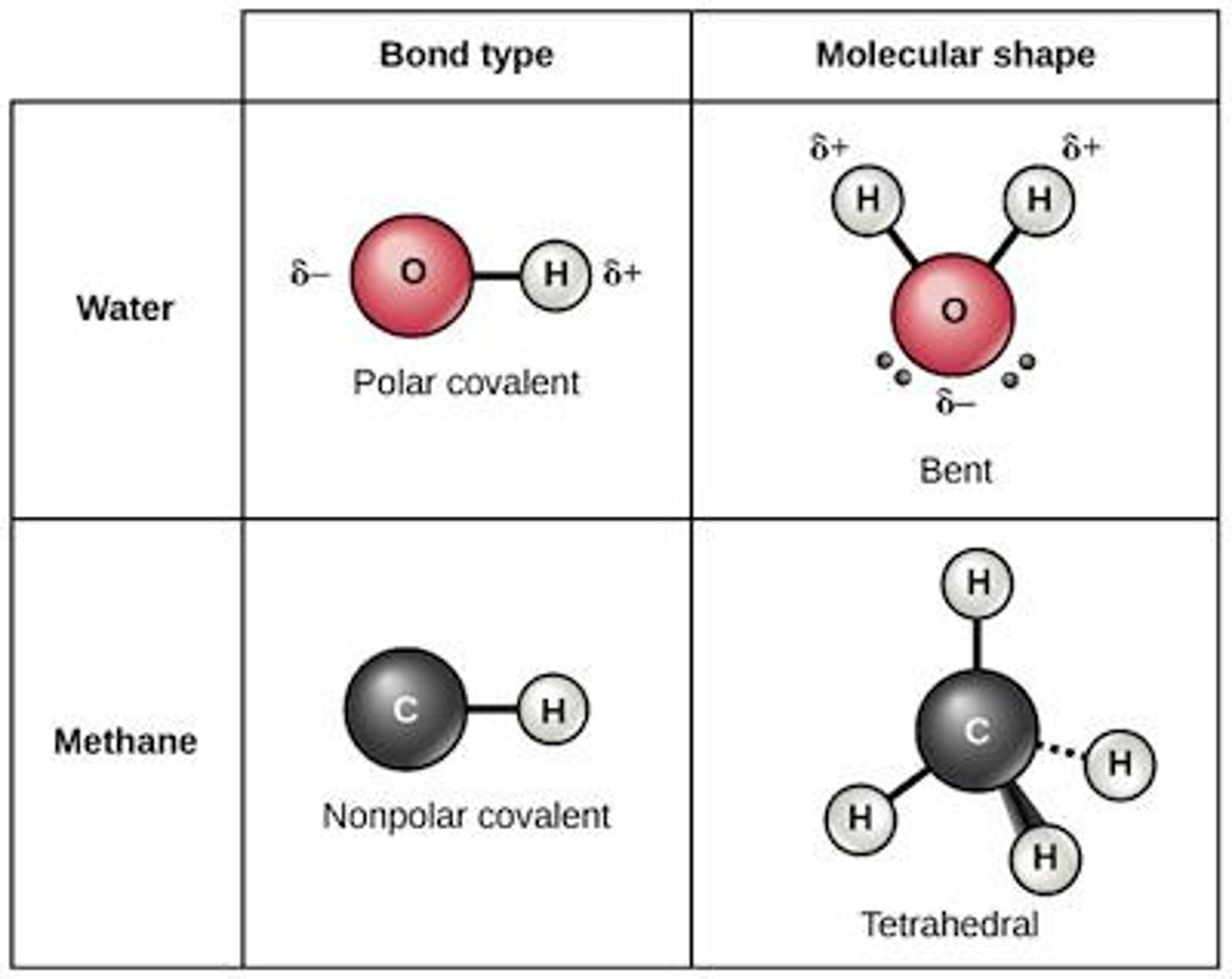
What is a nonpolar covalent bond?
Equal sharing of electrons.
What is a polar covalent bond?
Unequal sharing of electrons, resulting in partial charges.
What are ionic bonds?
Bonds formed by the transfer of electrons.
What are hydrogen bonds?
Weak attractions between a positively charged hydrogen atom and a negatively charged atom.
What is the equation for water disassociating into ions?
2H₂O ⇌ H⁺ + OH⁻
What makes a solution acidic?
The presence of H+ ions.
What makes a solution basic?
The presence of OH- ions.
What are anabolic reactions?
Reactions that build complex molecules and require energy.
What are catabolic reactions?
Reactions that break down molecules and release energy.
What role do carbohydrates play in photosynthesis?
They are the product for energy storage (glucose).
What role do carbohydrates play in cellular respiration?
They are the reactant that is broken down (glucose).
What are the main components of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
What is denaturation in proteins?
The loss of structure and function due to environmental factors.
How are proteins made?
By linking amino acids through peptide bonds.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
To store, transmit, and express genetic information.
What is DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid; a double helix structure.
What is selective permeability in cell membranes?
The ability of membranes to control what enters and exits the cell.
What is the structure of the phospholipid bilayer?
It has a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails, creating selective permeability.
What types of molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Small nonpolar molecules can pass through; others need protein channels.
What do channel proteins do?
They allow certain molecules to move across the membrane.
How do carrier proteins function?
They bind to specific molecules, change shape, and transport them across the membrane, often using energy (active transport) or following gradients (facilitated diffusion).
What role do peripheral proteins play?
They help maintain the structure of the cell membrane.
What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
It reduces permeability and helps maintain fluidity.
What is facilitated diffusion?
It is the movement of molecules from high to low concentration without energy.
What is active transport?
It is the movement of molecules from low to high concentration that requires energy.
What is endocytosis?
It is the process where the membrane wraps around molecules, pinches off, and allows them to enter the cell.
What is exocytosis?
It is the process where molecules are packaged in the ER, form a vesicle, and are released from the cell.
What is the relationship between endosymbiotic organelles and their free-living ancestors?
Certain bacteria engulfed other bacteria, leading to the formation of eukaryotic cells, with organelles like chloroplasts and mitochondria having their own DNA.
What does the 1st Law of Thermodynamics state?
Energy can be transferred or transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
What does the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics state?
Each energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
How does entropy relate to usable energy?
Higher entropy means energy is more spread out and less available for doing useful work.
What is an exergonic reaction?
An energy-releasing reaction.
What is an endergonic reaction?
An energy-absorbing reaction.
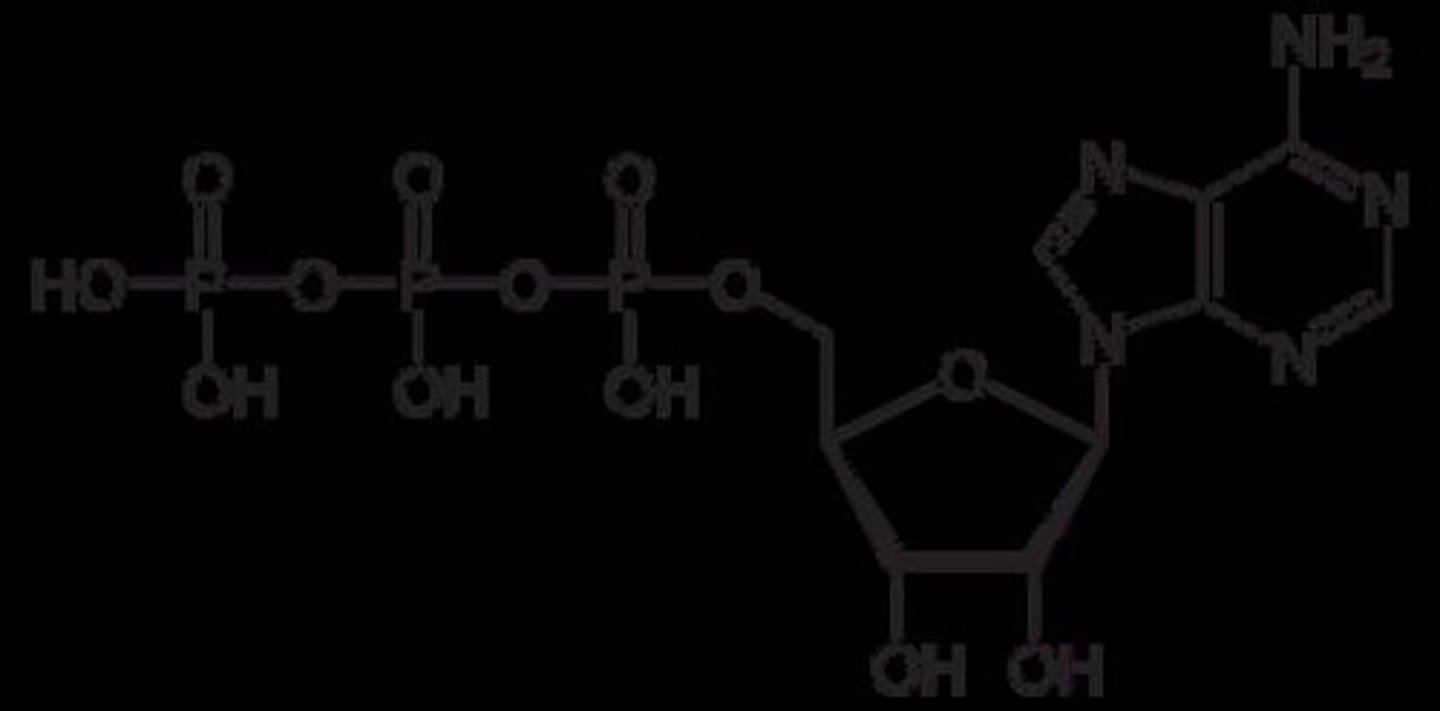
What is the structure of ATP?
ATP consists of three phosphate groups, and energy is stored within the bonds between them.
What is the induced fit model in enzyme activity?
It describes how an enzyme changes shape to better catalyze a reaction when a substrate binds.
What factors affect enzyme function?
Temperature and pH can affect enzyme activity, potentially slowing down reactions.
What are competitive inhibitors?
Molecules that resemble the natural substrate and compete for the enzyme's active site.
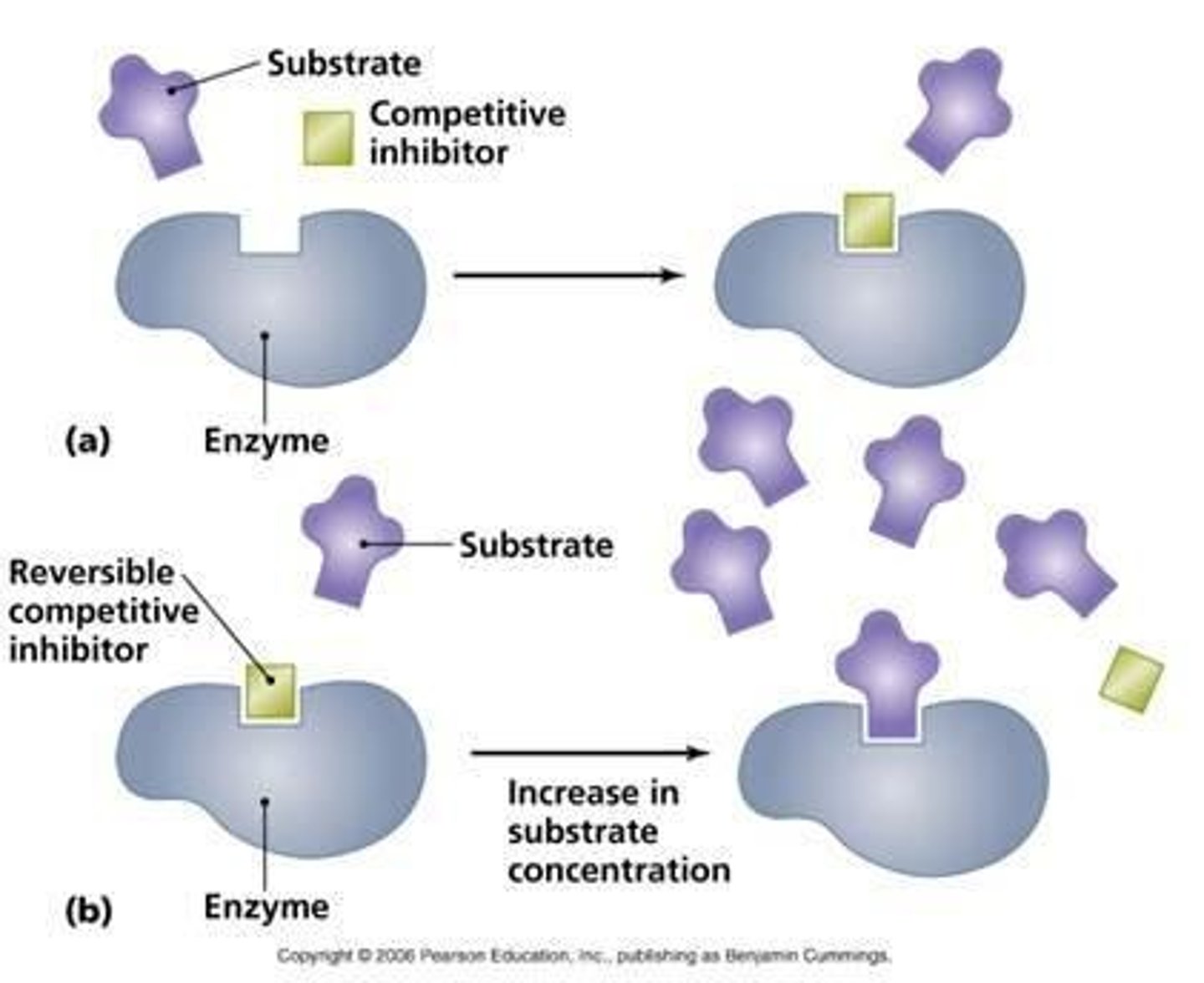
What are non-competitive inhibitors?
Molecules that bind to an enzyme at an allosteric site, changing its shape and reducing its activity.
What is cooperativity in enzymes?
It is a phenomenon where the binding of a substrate to one active site affects the binding of additional substrates to other active sites.
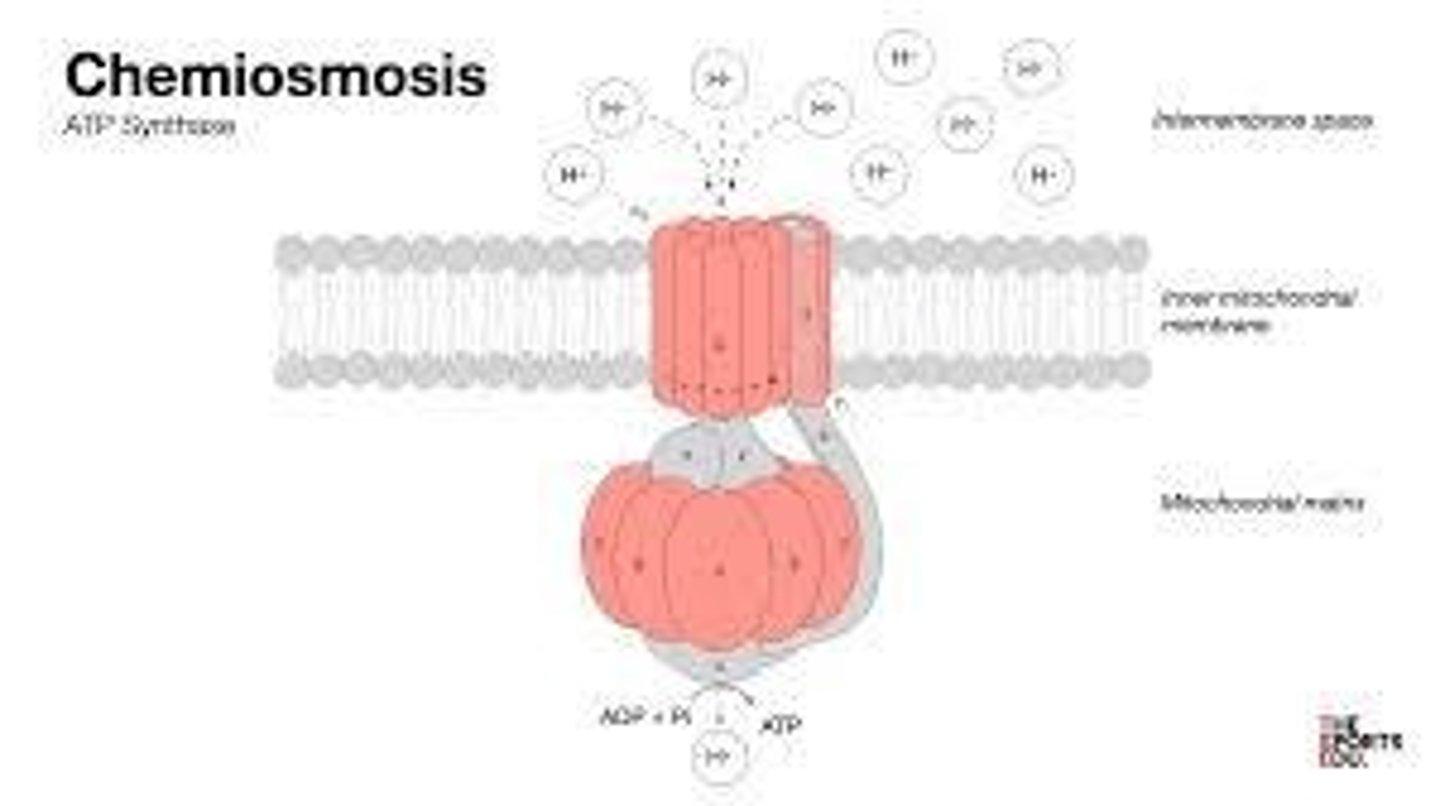
What is the role of NAD+/NADH and FAD/FADH2 in cellular respiration?
They carry electrons or release electrons to energize different molecules.
What is the function of oxygen in cellular respiration?
It acts as the final electron acceptor.
Where does glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm.
What is the benefit of fermentation?
It allows for energy release when oxygen is not present, despite not producing ATP.
What happens to NADH when O2 is present?
It is converted to NAD+ for glycolysis to occur again.
What occurs when O2 isn't present?
Fermentation takes place to regenerate NAD+ for glycolysis.
How much ATP is formed in Glycolysis?
About 2 ATP.
How much ATP is formed in the Krebs cycle?
About 2 ATP.
How much ATP is formed in the ETC/oxidative phosphorylation?
30+ ATP.
How much ATP is produced during fermentation?
No ATP, but it allows glycolysis to continue.
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Autotrophs produce their own food; heterotrophs must consume others for energy.
Why is understanding photosynthesis important?
It is essential for life as it provides oxygen for animals.
What does it mean to phosphorylate ADP?
To add a phosphate group to make ATP.
What role does H2O play in photosynthesis?
It is split to release high-energy electrons.
What role does CO2 play in photosynthesis?
It is the final electron acceptor.
What occurs during the light-dependent reactions?
Electrons flow, producing NADPH and ATP.
What are the main stages of the Calvin Cycle?
Carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of RuBP.
What is the difference between C3, C4, and CAM plants?
They differ in how they capture and utilize CO2.
What indicates an exergonic reaction?
More reactants than products and a negative free energy change.
What indicates an endergonic reaction?
More products than reactants and a positive free energy change.
What is activation energy?
The energy needed to start and complete a reaction.
What happens to chemical bonds during reactions?
Activation energy weakens bonds, allowing rearrangement into products.
What are the characteristics of enzymes?
They have an active site, are proteins, reduce activation energy, can be reused, and work best at specific pH and temperatures.
What is a substrate in enzyme reactions?
The molecule that binds to the enzyme and is transformed.
What is the enzyme-substrate complex?
The combination of enzyme and substrate during a reaction.
What is induced fit in enzyme reactions?
The enzyme changes shape slightly to better fit the substrate.
How do environmental factors affect enzyme reactions?
pH, temperature, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration influence reaction rates.
What is a noncompetitive inhibitor?
An inhibitor that binds to a different site on the enzyme, changing its shape.
What is a competitive inhibitor?
An inhibitor that binds to the active site of the enzyme.
What is allosteric regulation?
Regulation of enzyme activity through binding at sites other than the active site.
What is a stimulatory factor in enzyme activity?
A factor that affects the enzyme (but not the active site) that speeds up reactions.
What is an inhibitory factor in enzyme activity?
A factor that affects the enzyme (but not the active site) that slows down or stops reactions.
What is cooperativity in enzyme activity?
It occurs when something binds allosterically and helps the enzyme be more productive.
What is feedback inhibition in enzyme reactions?
A process where the product of a reaction inhibits an earlier step in the pathway to regulate the reaction.
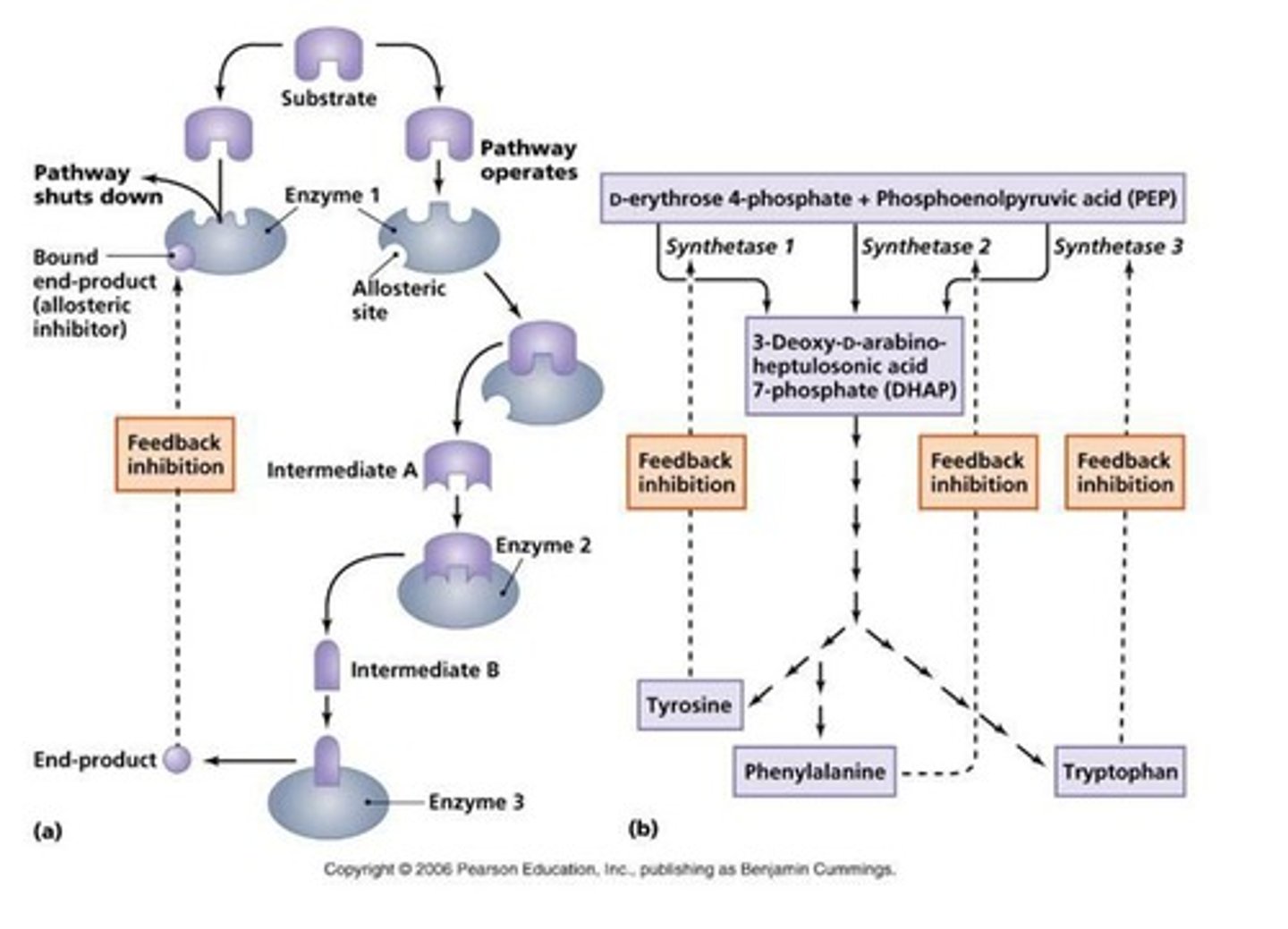
How can enzymes evolve?
Enzymes can evolve through changes in DNA that alter protein structure for better or worse.
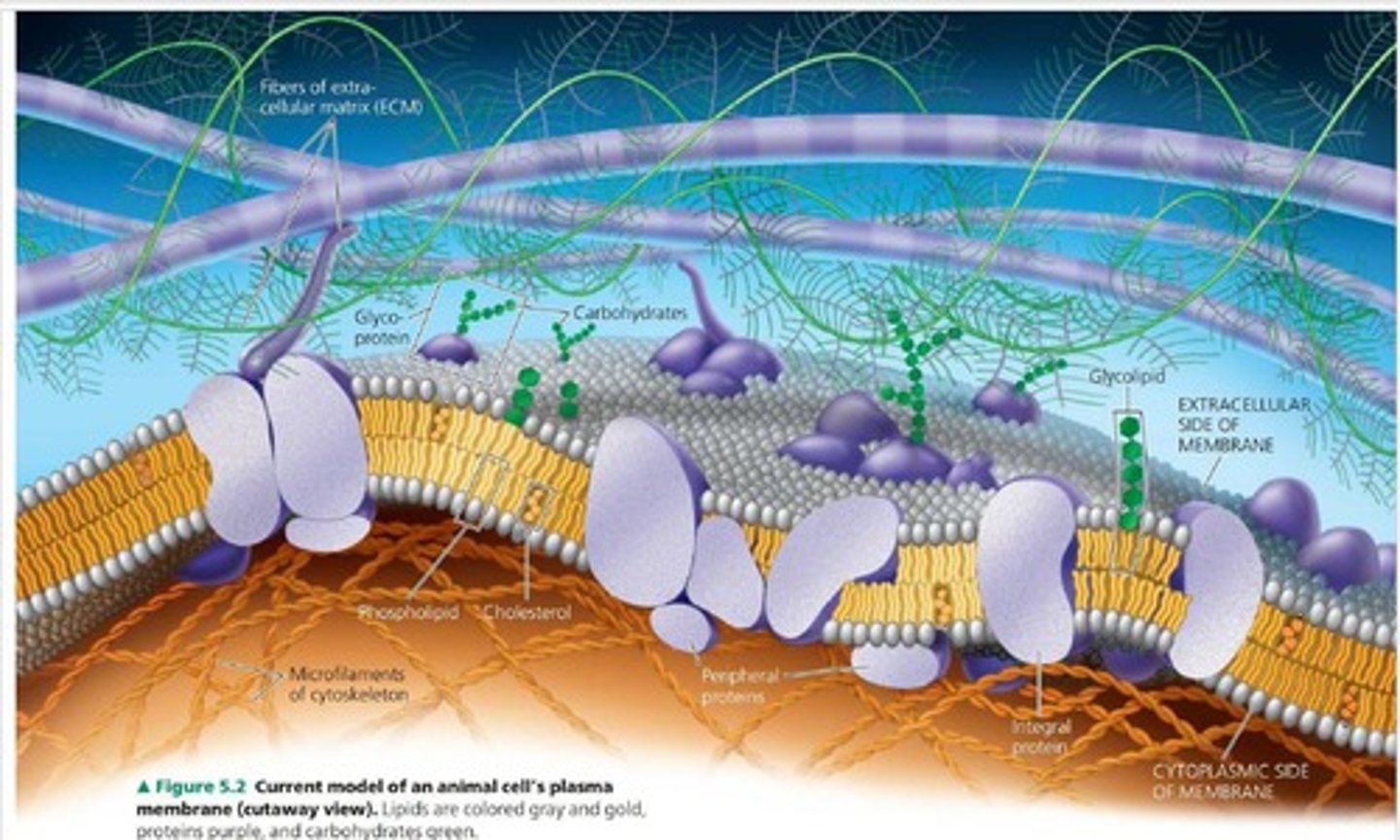
What is the structure of the cell membrane?
A phospholipid bilayer that is semi-permeable and contains various proteins.
What role do proteins play in the cell membrane?
They help regulate the entry and exit of certain molecules.
How does the structure of biological membranes influence selective permeability?
Embedded proteins allow nonpolar molecules through, while polar molecules require specific transport.
What mechanisms do organisms use to maintain solute and water balance?
Active transport, specialized organs, hormonal control, and structural adaptations.
What are the mechanisms for transporting large molecules across the plasma membrane?
Endocytosis and exocytosis.
How does the structure of a molecule affect its ability to pass through the cell membrane?
Small polar or uncharged molecules can pass, while larger or charged molecules need channel proteins.
How do concentration gradients affect molecular movement across membranes?
Molecules usually move from high to low concentration; low to high requires a carrier protein.
What is osmoregulation?
The process of balancing internal water and salt levels to prevent cell dehydration or swelling.
What is passive transport?
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without using cellular energy.
What are the functions of subcellular components and organelles?
They contribute to various cellular functions, including metabolism, energy production, and waste removal.
How do internal membranes and membrane-bound organelles contribute to eukaryotic cell functions?
They compartmentalize cellular functions, allowing for specialized environments and processes.
What are the similarities and differences in compartmentalization between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
What are cellular membranes made of?
Lipids and proteins
What is selective permeability in membranes?
The ability of membranes to allow certain substances to pass while blocking others.
What are the two types of bulk transport across membranes?
Exocytosis and endocytosis.
What is the primary function of mitochondria?
To change energy from one form to another.
What is the role of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells?
To carry out genetic instructions housed in the nucleus.
What are the four macromolecules of life?
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.