ch 22 iontropic receptor signaling
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
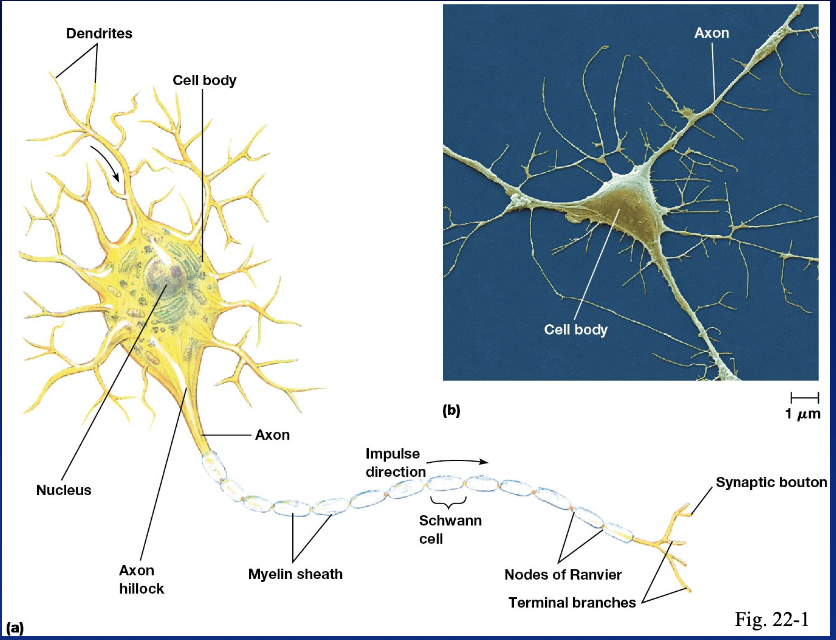
parts of a neuron
dendrites, cell body, nucleus, axon hillock, axon, myelin sheath, terminal branches
Na+/K+-ATPase establishes electrochemical gradients of
sodium and potassium
The k+ leak channel ____ the potassium permeability and potassium travels ___ the concentration gradient making (out of the cell)
increases, down
at resting membrane potential the amount of potassium in the cell is ___ than the amount of ___ and viceversa
higher, sodium
acetylcholine is an example of an ___ ____
excitatory neurotransmitter
acetylcholine binds to the nicotinic receptor which is a
ligand-gated ion channel
nicotine receptor is activated by ___. it allows ___ to go into the cell
nicotine, sodium
neurons have two types of voltage gated channels
sodium and potassium
sodium voltage gated channel is made of ___ polypeptide subunits
single
the potassium voltage gated channels is made of ____ polypeptides subunits
4 separate
when the membrane potential depolarizes to -50mv voltage gated channels change their conformation causing the channel to
open
sodium and potassium are surrounded by
water
describe how oxygen helps sodium and potassium get through the channel
to shed the hydration shell of the sodium and the potassium the oxygen atoms in the amino acids channel interacts with their ions and they shed the water allowing them to pass through
sodium and potassium cannot pass though each other’s channel due to ___. they also cannot she enough water to fit in each other’s channel
size
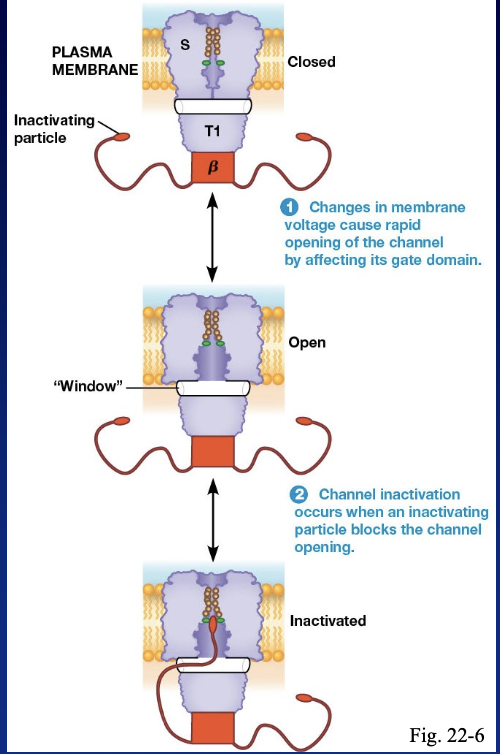
To prevent a channel of opening too quick…
the inactivating particle portion of the protein blocks the channel and after a millisecond it returns to it’s original conformation
describe action potential
resting state: sodium and potassium gates are closed and the resting potential is at about -60mV
depolarizing phase: sodium channels open and action potential begins when the neuron is depolarized by about 20 mV to its threshold potential. potential reaches +40 mV very rapidly
repolarizing phase: sodium channels inactivate and potassium channels open. once the cell reaches its peak positive potential, it repolarizes and returning to a negative membrane potential
hyperpolarizing phase: potassium channels remain open and sodium channels close. Often the membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting potential
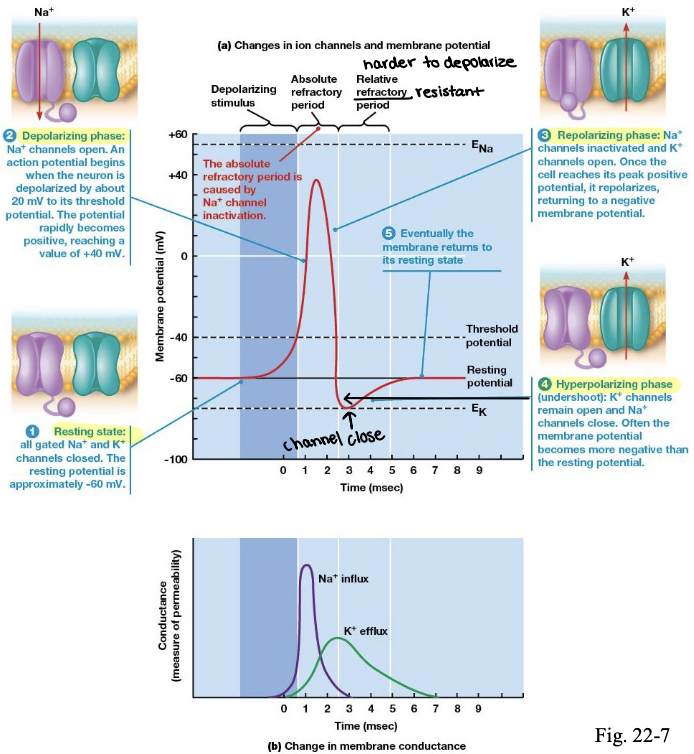
action potential moves one way due to the
refractory period
myelin is surrounded by ___ ___ that wrap their plasma membrane around the axons of peripheral neurons
schwann cells
the small gaps between the patches of myelin are called
nodes of ranvier
The myelin insulated the axon’s ___ and ion exchange only occurs at the ___
membrane, nodes
the action potention thorugh myelin skips from node to node and that is called
saltatory conduction
___ ___ speeds up the rate of action potential 10x
saltatory conduction
electrical synapse is a physical connection and the presynaptic and post synaptic cells are directly connected by
gap junction
in electrical synapses sodium diffuses directly from the presynaptic neuron to the post synaptic neuron causing
depolarization
in chemical synapse the presynaptic and post synaptic cells are separated by the
synaptic cleft
formation of the binding between synapses
neurotransmission is a form of regulated transmission. When the action potential reaches the synaptic terminal volted gated Ca++ channels open. Ca++ diffuses rapidly into presynaptic neuron acting as secondary messenger causing vesicles filled with neurotransmitters to fuse with the plasma membrane. Neurotransmitter is released and diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds receptors on the postsynaptic neuron
synaptic vesicles dock at the plasma membrane with
VSNARE and T SNARE
___ inputs open sodium channels generating excitatory postsynaptic potential
excitatory
___ inputs open potassium channel or chloride channels and generate the postsynaptic potential
inhibitory
there is no voltage gated channels in the ___ ___ only past axon hillock
cell body
the neurotransmitter can be
diffused degraded or retaken
action potential can only be generated if the
membrane potential reaches threshold at the axon hillock