2 OMFS (Exam2): Advanced Maxillofacial Imaging
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
-Facial trauma
-Infection
-Neoplasms
-Surgical Planning
What are some indications for getting a CT for the head and neck:
Muti-detector Computed Tomography
What does MDCT stand for?
axial
A CT produces images of the body that are in _____ cuts
- saggital
- coronal
- axial
Hounsfield values
CT uses ________ to measure attenuation of radiation through tissue, assigns a gray scaled image
- saggital
- coronal
- axial
What are the planes of view available to visualize in a CT?
fan
A CT captures images in a ________ - shaped geometry
coronal
ID the plane of view:
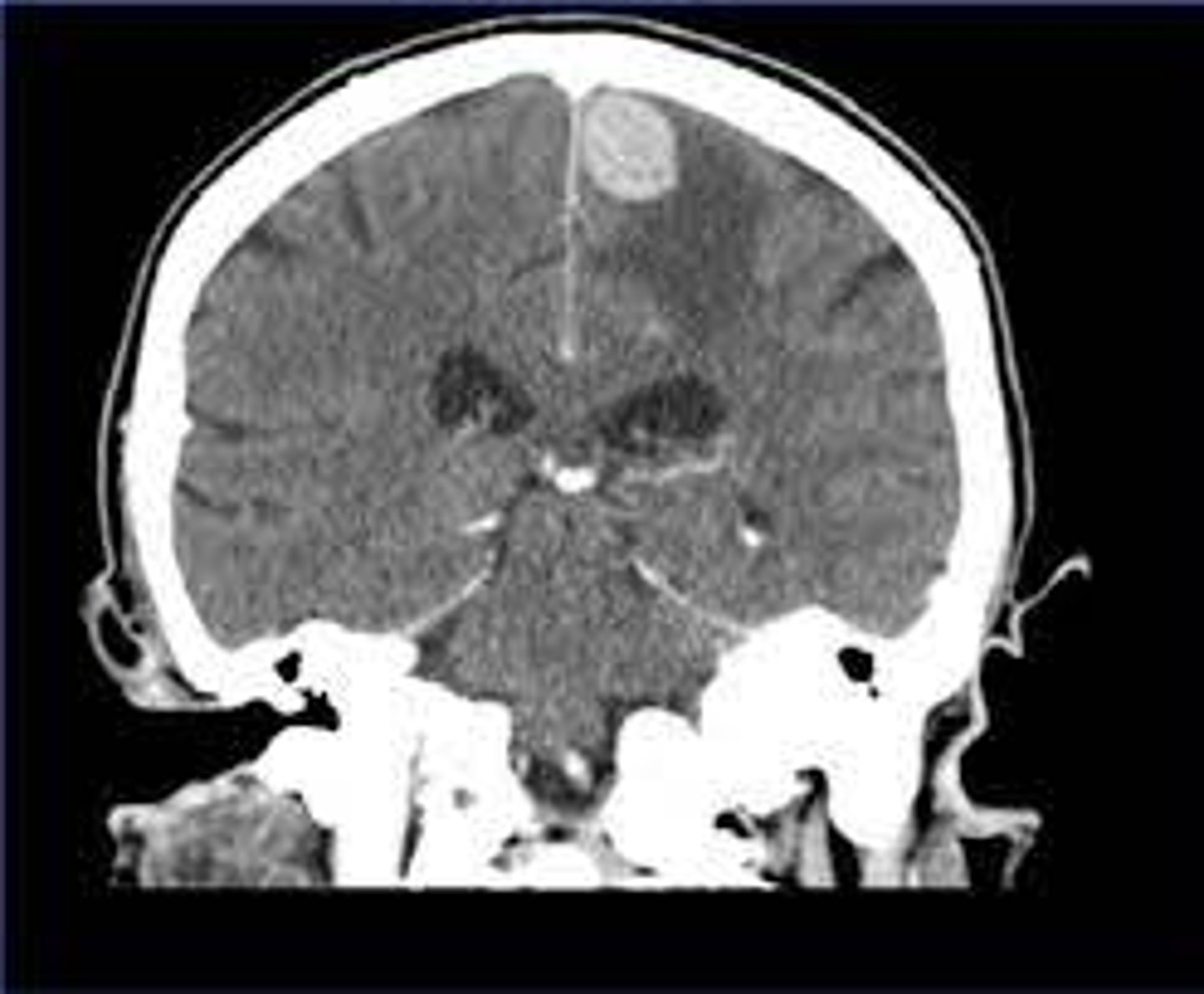
saggital
ID the plane of view:
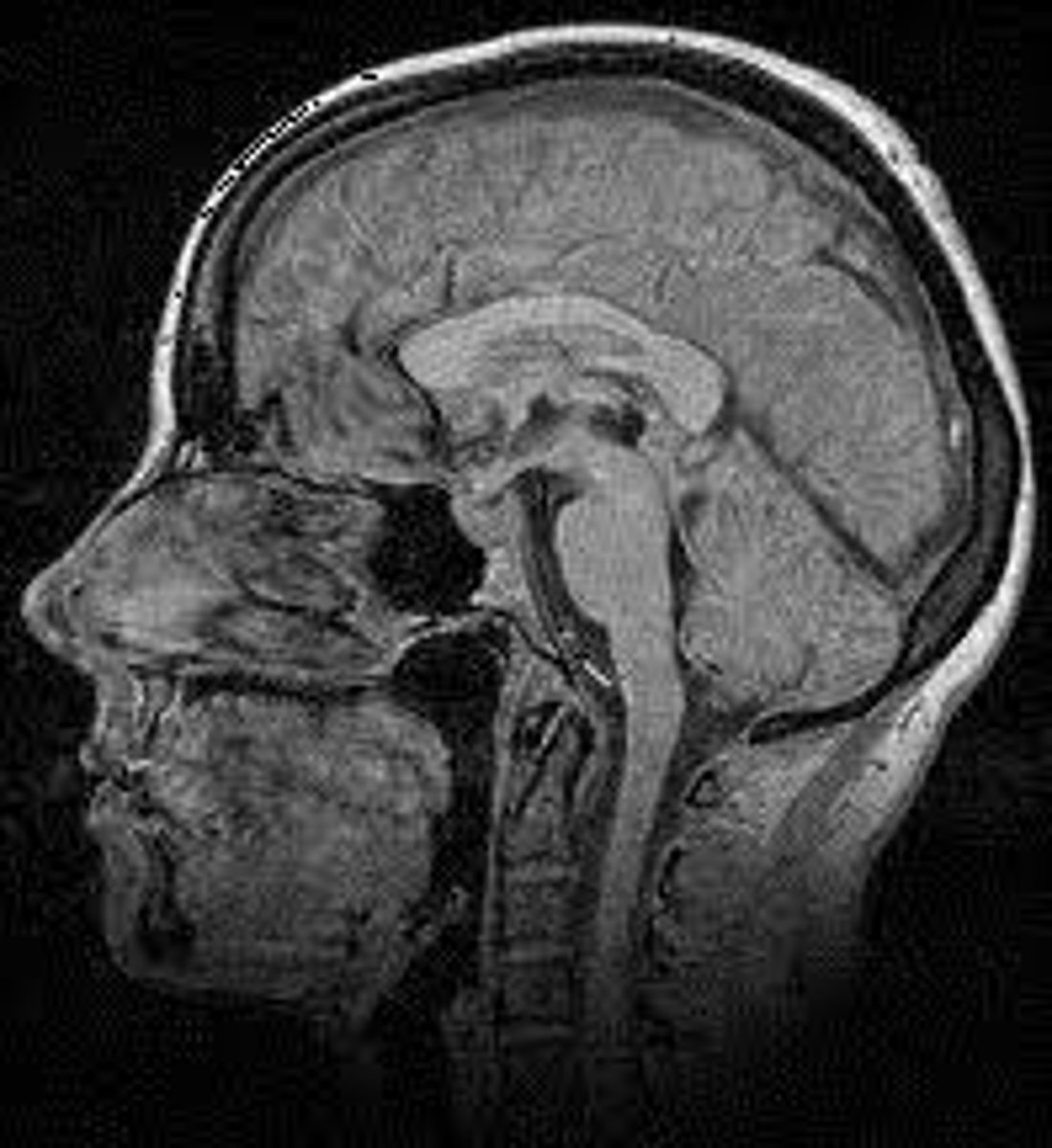
axial
ID the plane of view:
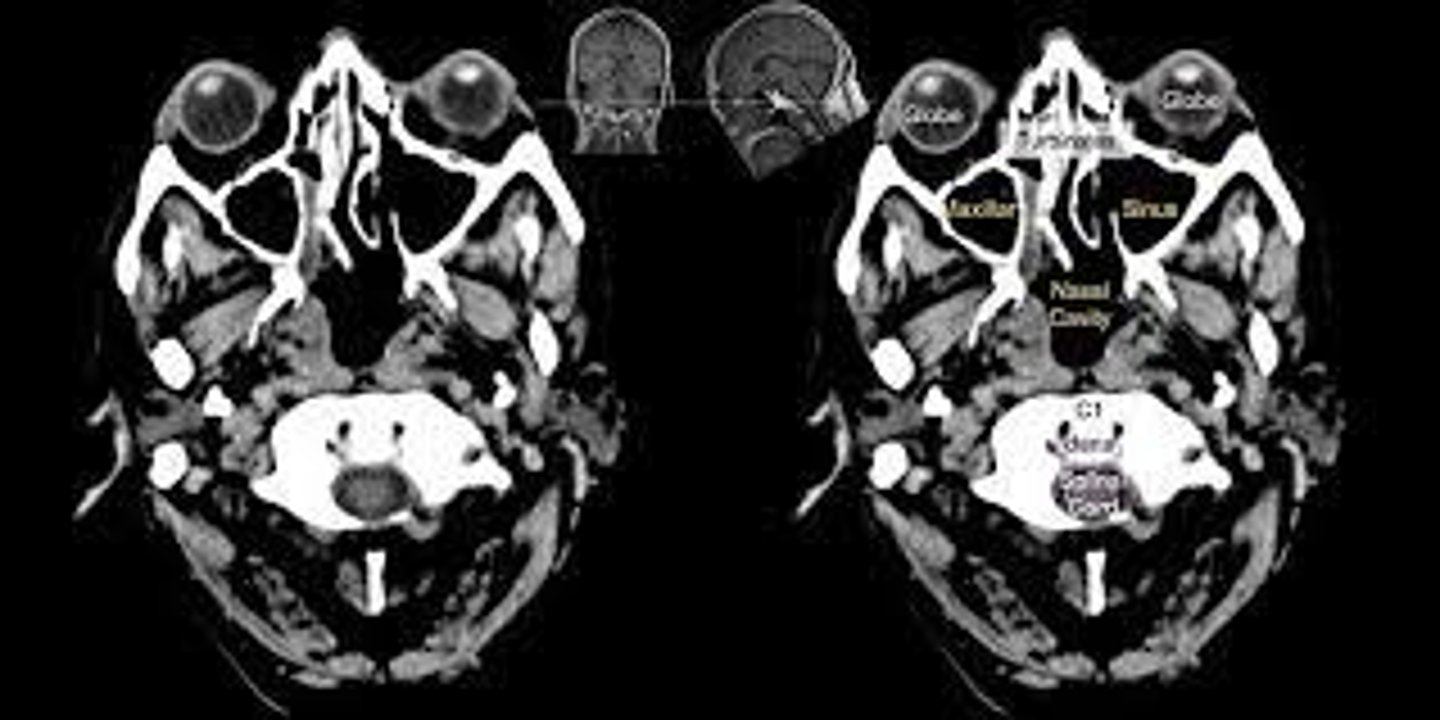
oblique reformats
ID the plane of view:
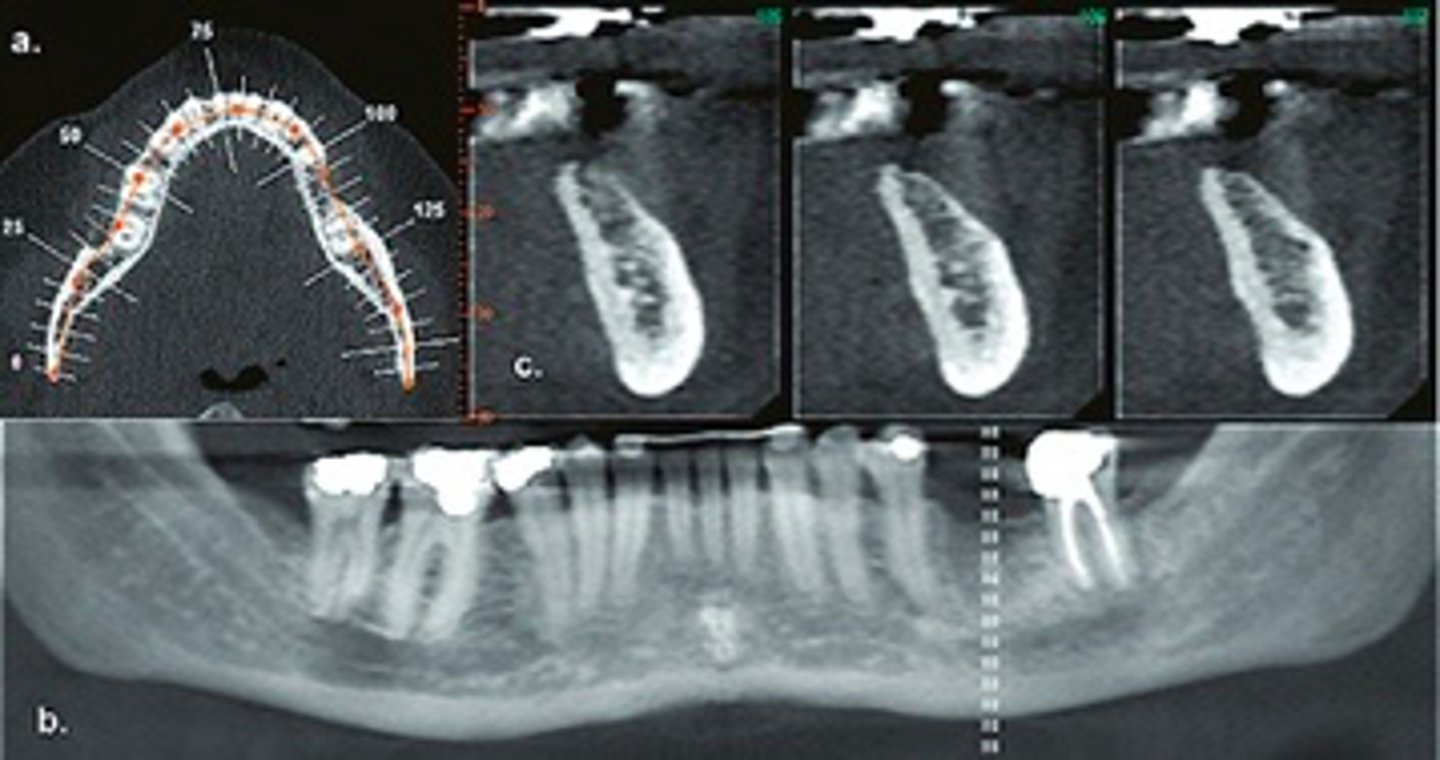
iodine
Soft tissue CTs can be enhanced with contrast that is usually ______-based contrast media
intravenously
In OMFS, if you need a tissue contrast, most of the time it is applied:
- intra-arterially
- intrathecally
- intra-abdominally
- intravenously
vessels around infection will engorge/inflame and form a visible rim around the infection = rim enhancement
What is the logic behind using intravenous CT contrast?
-Fast
-Good soft tissue and bone imaging
What are the pros of using a CT:
-High radiation
-Cost
-Requires iodine based contrast for soft tissue (can not be done for iodine allergic or pts with poor kidney function)
What are the cons of using a CT:
- pts allergic to iodine
- pts with poor kidney function
What type of patients should NOT undergo an iodine contrast enhanced CT?
Cone Beam Computed Tomography
What does CBCT stand for?
cone
A CBCT captures images in a ________ - shaped geometry
- Lower radiation compared to standard CTs
- Less artifact scatter
What are the pros of using a CBCT:
-For evaluation of osseous structure and NOT soft tissue structures
-Not covered by medical insurance
What are the cons of using a CBCT:
MRI
This imaging modality applies a magnetic field to tissue, picks up signals produced by magnetized protons, signals are processed using Fourier transform to generate an image:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
magnetic resonance imaging
What does MRI stand for?
MRI
This imaging modality is good for delineating:
- soft tissue pathology (ie parotid gland pathologies)
- Evaluation of suspected osteomyelitis
- Perineural spread of malignancy
- Head and neck infections and neoplasms (requires gadolinium based IV contrast
- TMJ pathology
CBCT
This imaging modality is best for evaluation of osseous structures:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
MRI
This imaging modality is best for evaluation of TMJ pathologies:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
CT
This imaging modality is good for soft tissue and bone imaging:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
MRI
ID the type of Imaging modality:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
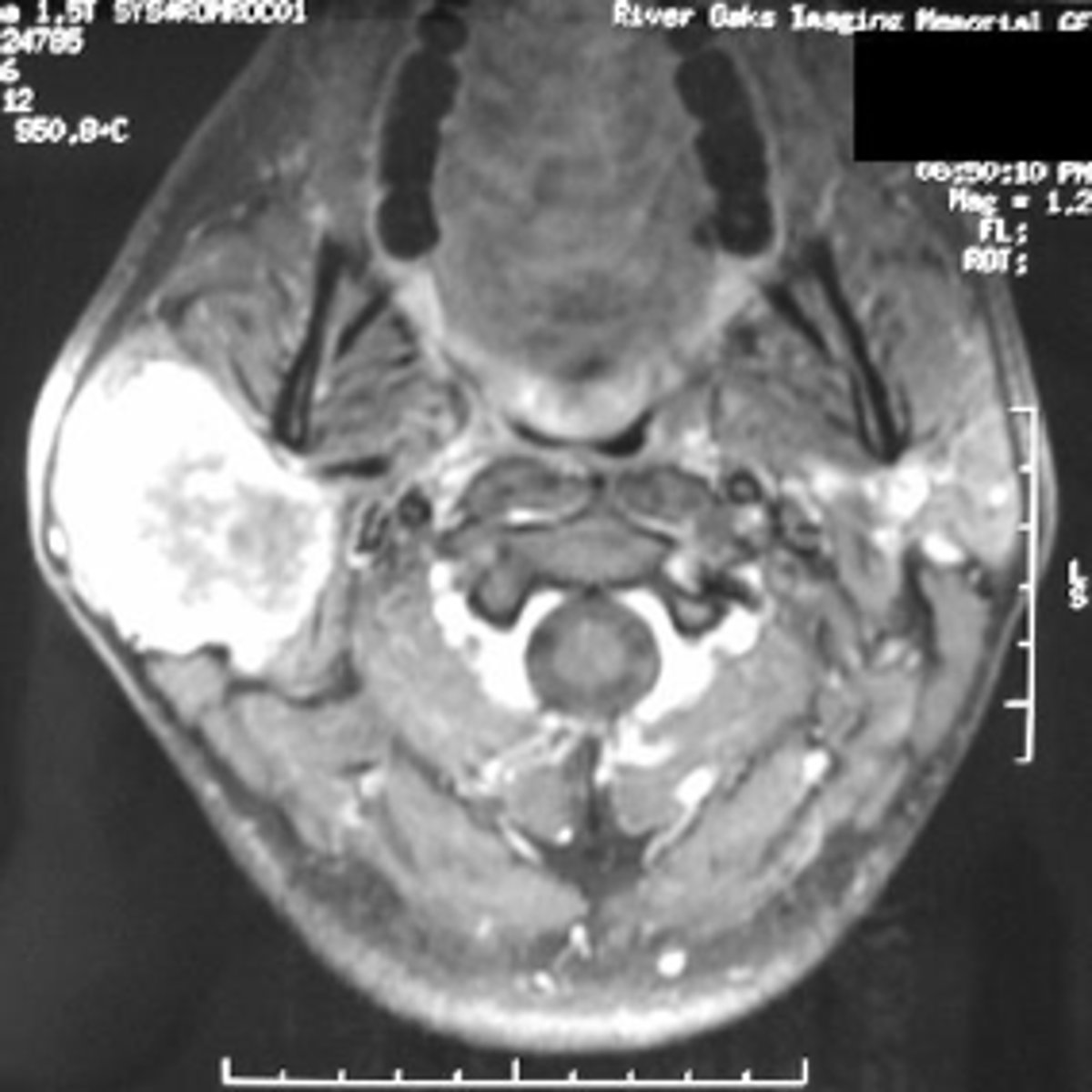
CT
ID the type of Imaging modality:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
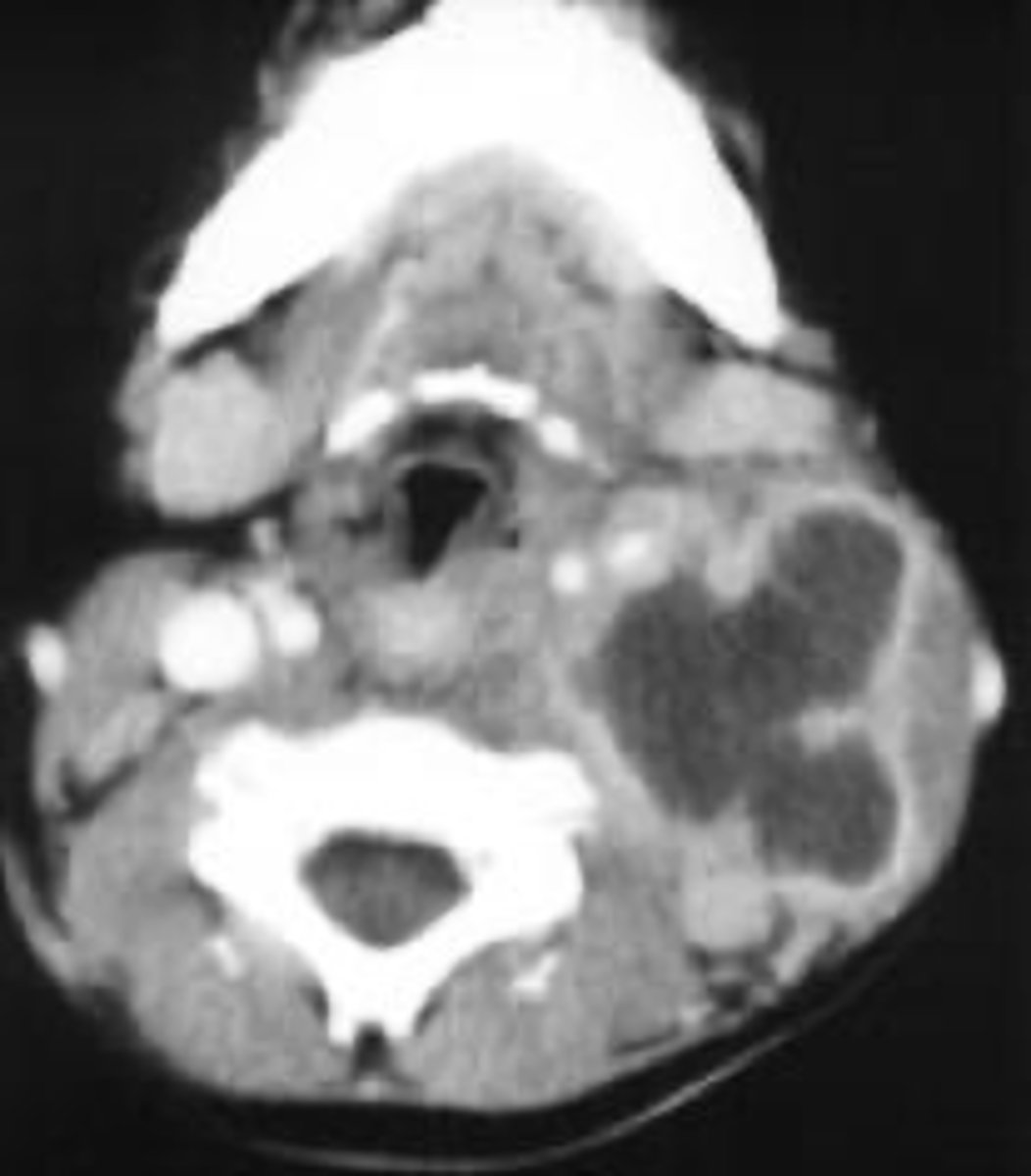
CBCT
ID the type of Imaging modality:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
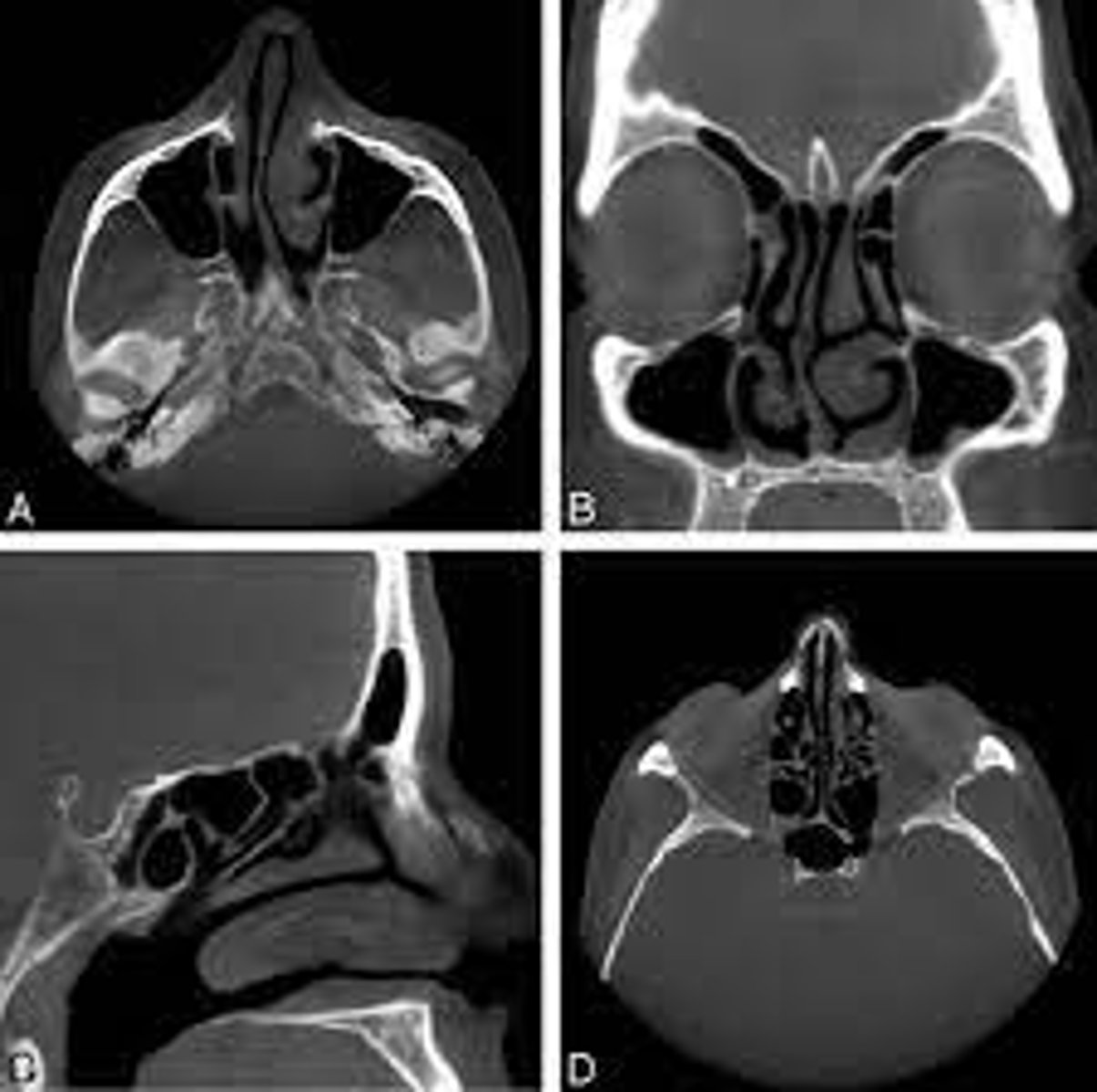
Technetium 99 bone scans
ID the type of Imaging modality:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
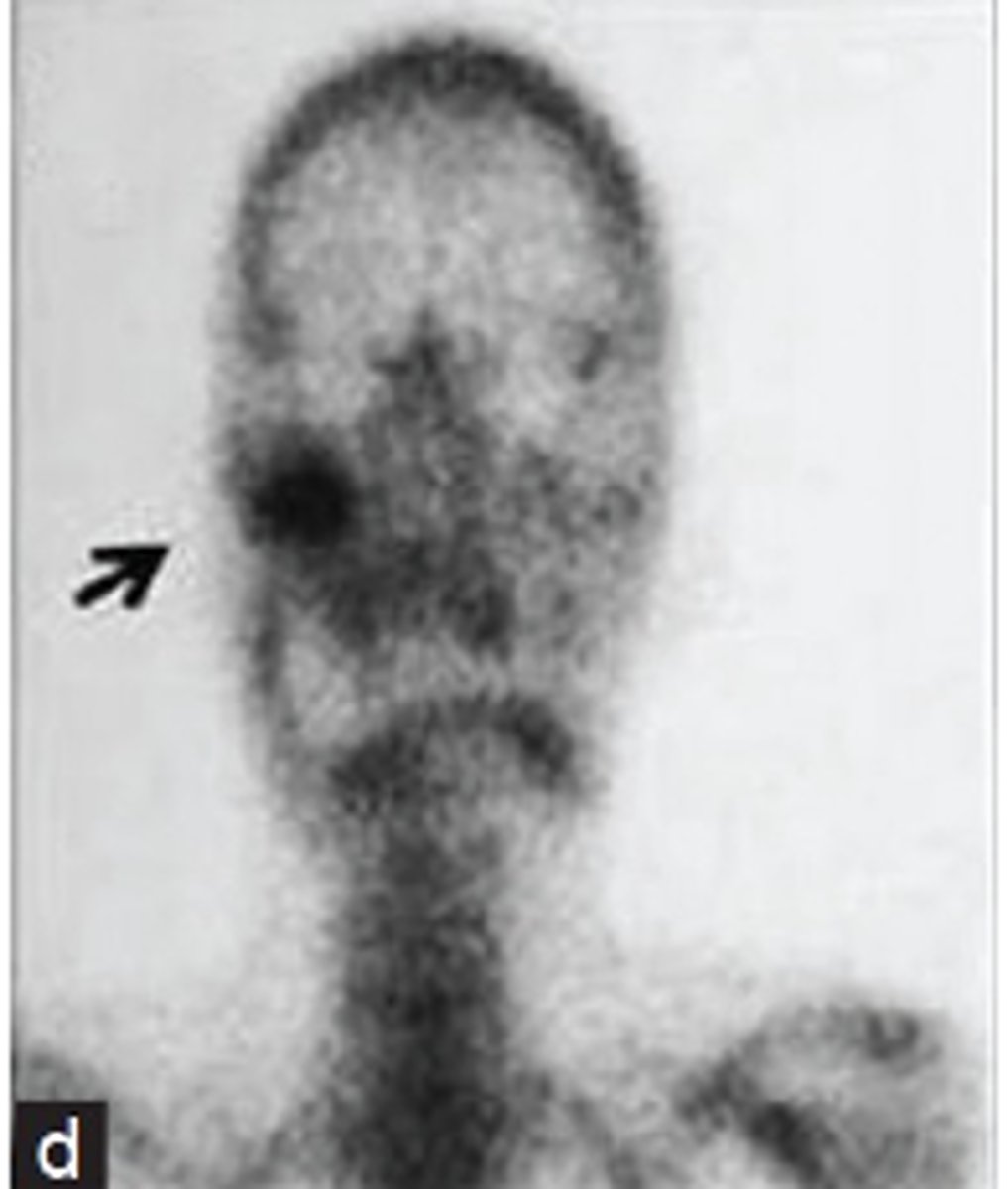
PET
ID the type of Imaging modality:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
MRI
This imaging modality does NOT use radiation:
-More time consuming
-More expensive
-Less accessible
-Gadolinium may cause nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with renal insufficiency
-Can not obtain MRIs in patients with pacemakers, neurostimulators, any feromagnetic implants/fragments near vital structures
What are the cons of using an MRI:
gadolinium
MRIs can be enhanced with contrast that is ______-based contrast media
MRI
The contrast used in this type of imaging modality may cause nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with renal insufficiency:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
MRI
This imaging modality is contraindicated in patients with pacemakers, neurostimulators, any feromagnetic implants/fragments near vital structures:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
Technetium 99 bone scans
This imaging modality determines bone metabolic activity:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
PET
This imaging modality uses 18-fluorodeoxyglucose (18FDG)
and is used to ID neoplasms ( because they have increased glucose metabolism than normal tissue)
Used for staging and surveillance of head and neck cancers:
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans
- PET
Positron emissions tomography
What does PET stand for?
CT
because PET scans are usually blurry, what other imaging modality is it superimposed with for identification and diagnostic purposes?
- Pano
- CT
- CBCT
- MRI
- Technetium 99 bone scans