Exercise 1: Histopath review
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Cell swelling
identify
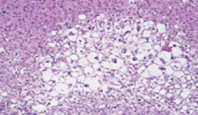
Hydrophobic degeneration
identify
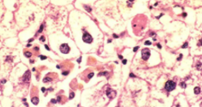
Hyaline degeneration
identify
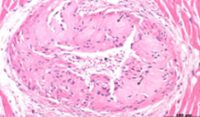
Amyloidosis
identify
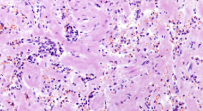
Fatty degeneration
identify
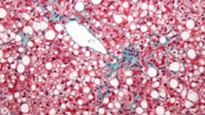
Fatty infiltration
identify
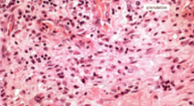
Fibrinoid degeneration
identify
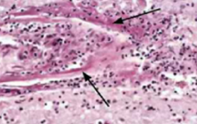
Mucoid degeneration
identify
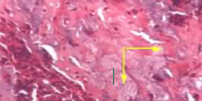
Coagulative necrosis
identify
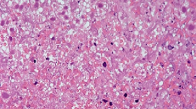
Caseation necrosis
identify
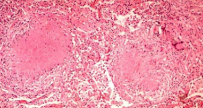
Liquefactive necrosis
identify
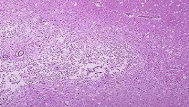
Fat necrosis
identify
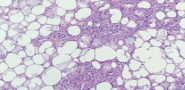
Gangrene
identify
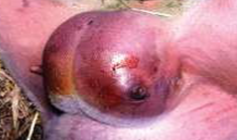
Zenker’s necrosis
identify
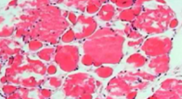
Atrophy
qualitative decrease
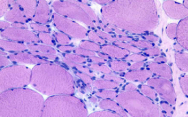
Hypertrophy
qualitative increase
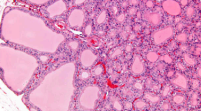
Hyperplasia
quantitative increase
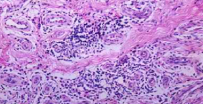
Metaplasia
Transformation of one tissue type to another
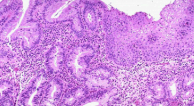
Hypoplasia
failure of organ development
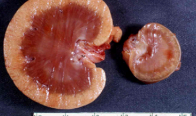
Anaplasia
Cell reversion to a more primitive & undifferentiated type
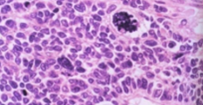
Dysplasia
cell development and maturation are disturbed → size abnormality
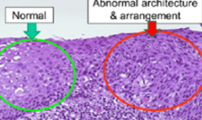
Hyperemia
increase blood flow
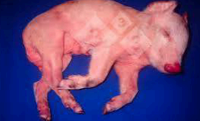
Congestion
Impaired venous outflow
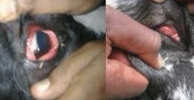
Ischemia
inadequate blood supply to organ or tissue
Hemorrhage
escape of blood from blood vessels
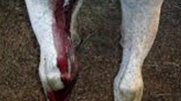
Petechiae
pinpoint hemorrhages

Ecchymoses
Larger areas of hemorrhage
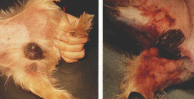
Agonal
Small hemorrhages occurring during dying process
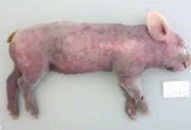
Suffusion
Blood diffuses into tissues without a defined border
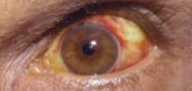
Hematocyst
Cystic rupture filled with blood
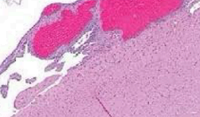
Purpura
larger than petechiae, smaller than ecchymoses
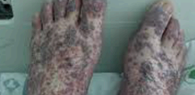
Sludge blood
thickened, slow-moving blood due to dehydration or circulatory stasis
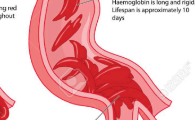
Thrombosis
Formation of solid blood clot within blood vessel
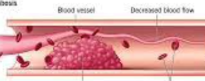
Embolism
blood vessel obstruction by transported material

infarction
necrosis due to thrombosis or embolim
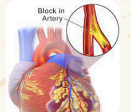
Edema
Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the interstitial space
Shock
critical condition caused by inadequate tissue perfusion → cell and organ dysfunction