Chemistry Exam November
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
How many protons & neutrons in Helium-3
2 Protons, 1 Neutron
Two reagents to test for phosphate ions in aqueous solution
Ammonium Molybdate, Nitric Acid
Explain energy levels
Fixed energy / Quantised energy / Energy in an orbit / Energy in a shall of an electron
Distinguish between ground and excited states in hydrogen’s electron
Ground = Lowest energy / n = 1 / Stable
Excited = Greater Energy / n > 1 / Unstable
What happens when an electron goes from excited to ground
Energy is released: (only 1 necessary)
as a photon
as light
as em radiation
at a specific frequency
Em - En = hf
Name the instrument used to examine the line spectrum of an element
Spectrometer / Spectroscope
Explain: Uncertainty Principle
Impossible to measure position & velocity at the same time
S, P, D electron config of Neon (10)
1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz2
Distinguish between an energy sublevel and an atomic orbital
Sublevel: 2p
Orbital: 2px
Sublevels are regions of space such as S, P, D whilst orbitals are specific regions like 2px
Neon is unreactive, explain this through its electron config
full outer shell / full p sublevel / satisfies octet rule
Explain how successive ionisation energy values of Ne provide evidence of energy levels
Ninth (ionisation energy) significantly greater than the eighth
Draw the shape of a p orbital
dumb-bell shape
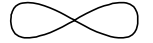
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show valence electrons in BF3 Boron (5) Fluorine (9)
Image
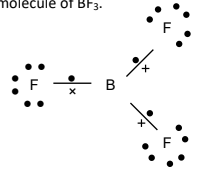
Would you expect a B-F bond to be polar or non-polar? Justify your answer
Polar because of a large electronegativity difference
Would you expect a BF3 molecule to be polar or non-polar
non-polar
Phosphane (PH3) is colourless, flammable, highly toxic and gaseous. Predict the shape of a molecule.
Pyramidal: three bond pairs and one lone pair (on P)
Neither BF3 nor PH3 is very soluble in water, explain
non-polar / little hydrogen bonding / little intermolecular forces
Define: Atomic Number
number of protons in nucleus of an atom
Define: Mass Number
number of protons and neutrons in nucleus of an atom
Taking the valency of gallium (Ga) as 3, write the formula formed from Gallium and Nitrogen
GaN
Taking the valency of gallium (Ga) as 3, write the formula formed from Gallium and Oxygen
Ga2O3
Predict the two possible shapes of a molecule ABn where n = 2
V - Shaped & Linear
What is diffusion?
Spreading (movement) of a substance (compound, molecules) from high to low concentration to fill a container (volume)
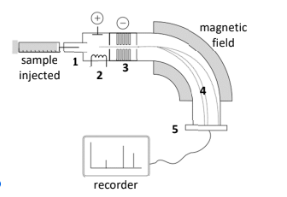
Identify stages 2 & 4 of this mass spectrometer
2: Ionisation
4: Separation

How did Thomson account for the fact that atoms are electrically neutral
Plum pudding model of atom where electrons (negatives) were embedded in a sphere of positive matter balancing the charges

State one piece of evidence for the existence of energy levels in atoms
Atomic Spectra
Flame Tests
Periodic Table Layout

State Two limitations of Bohr’s atomic theory that led to its modification
Only works for hydrogen
Wave-like motion not included
Uncertainty Principle not included
Did not explain sublevels
Define: an atomic orbital
a region in space where there is a relatively high probability of finding an electron
Write the S P D config for bromine (35) in its ground state
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4px² 4py² 4pz¹