MCB 244 Skeletal System
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
269 Terms
Types of bone
compact and spongy
Compact bone
dense or cortical bone
80% of bone mass
Spongy bone
cancellous or trabecular bone
located internal to compact bone
appears porous
20% of bone mass
Cartilage
semirigid CT, more flexible than bone
types: hyaline cartilage and fibrocartilage
structures composed of dense regular CT
____ connect bone to bone, ____ connects muscle to bone
ligaments; tendons
Hyaline Cartilage
attaches ribs to sternum, covers ends of some bones, within growth plates, model for bone formation
Fibrocartilage
weight-bearing cartilage that withstands compression (intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, menisci of knee)
Coastal cartilage
located in the ribs
Where is fibrocartilage found
thorax, cartilage of inverterbral disc, and pubic symphysis
Where is hyaline cartilage found
in bone sockets of shoulder, arm, wrist, fingers, femur, knees, and toes
Where is articular cartilage found
Kids: at the neck followed by epiphyseal plate at each end
Adults: joints of ankles and shoulders
Function of bones
support, protection, levers for movement, storage of mineral and energy reserves, and hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis
blood cell production; occurs in red bone marrow CT
What are the classifications of bones based on shape
long bones
short bones
flat bones
irregular bones
Long bones
greater in length than width
ex: femur, humerus
Short bones
length nearly equal to width
ex: carpal and tarsals
Flat bones
flat, thins surfaces, may be slightly curved
ex: cranial
Irregular Bone
elaborate sometimes complex shapes
ex: vertebrae
Regions of a long bone
Diaphysis
Medullary (marrow) cavity
Epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
Metaphysis
Epiphyseal plate
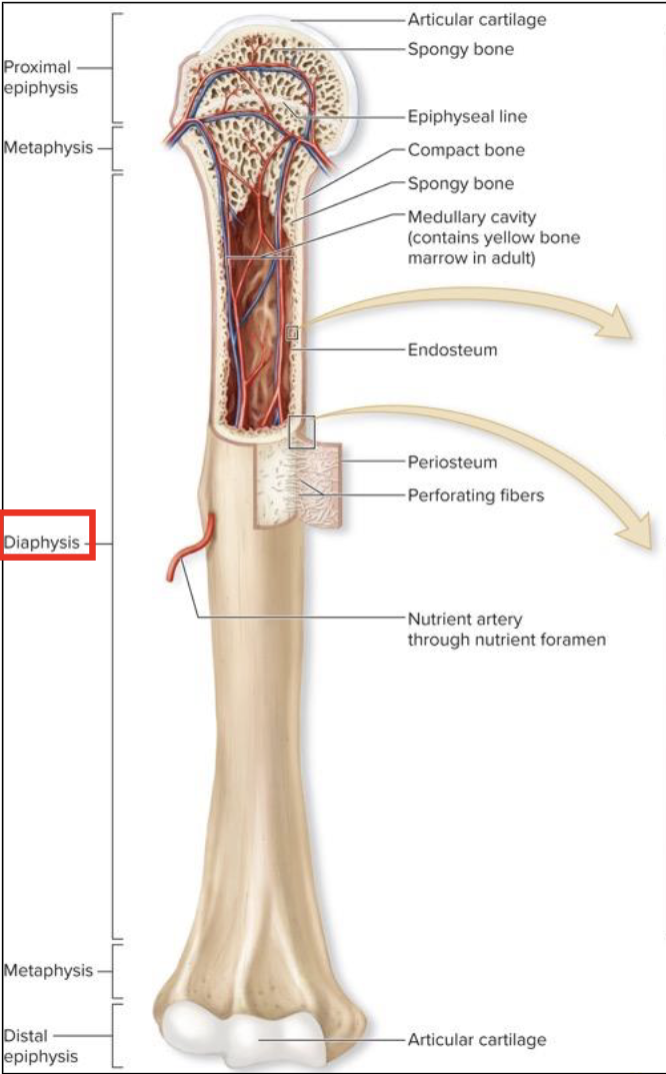
Diaphysis
elongated, usually cylindrical shaft
provides leverage and weight support
compact bone with thin spicules of spongy bone extending inward
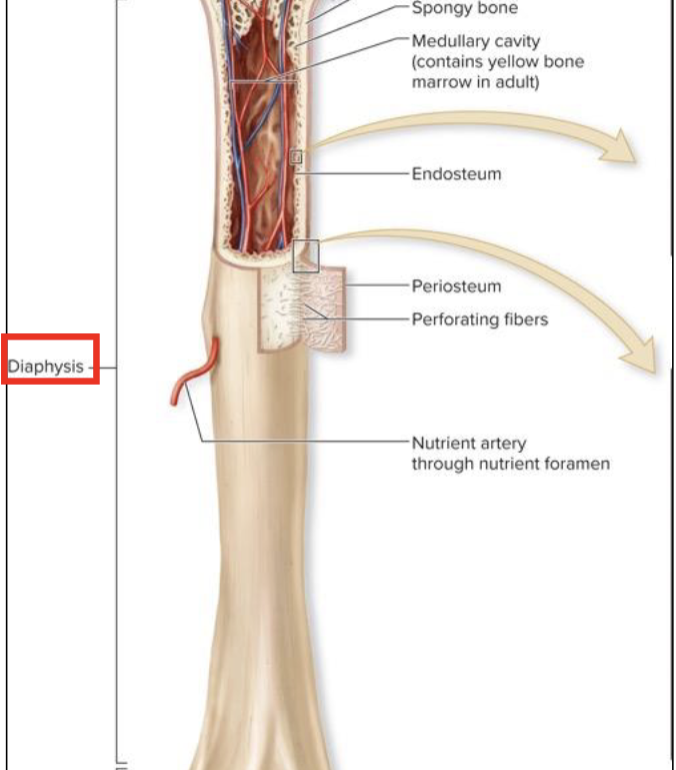
Medullary (marrow) cavity
hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis
contains red bone marrow in children
contains yellow bone marrow in adults
Epiphysis
knobby region at each end of long bone (2 long bones can meet end-to-end at their epiphyses)
proximal epiphysis
distal epiphysis
Proximal epiphysis
end of the bone closest to the body trunk
Distal epiphysis
end farthest from trunk; outer thing layer composed of compact bone; inner region composed of spongy bone
Articular cartilage
covers the joint surface
thin layer of hyaline cartilage
reduces friction
absorbs shock in moveable joints
Metaphysis
region where bone widens and transfers weight between the diaphysis and epiphysis
Epiphyseal plate
located in metaphysis
growth plate
thin layer of hyaline cartilage
provides lengthwise bone growth
in adults, the epiphyseal line, is the remnant of the epiphyseal plate
Periosteum
tough sheath covering outer surface of bone
outer fibrous layer
inner cellular layer
perforating fibers
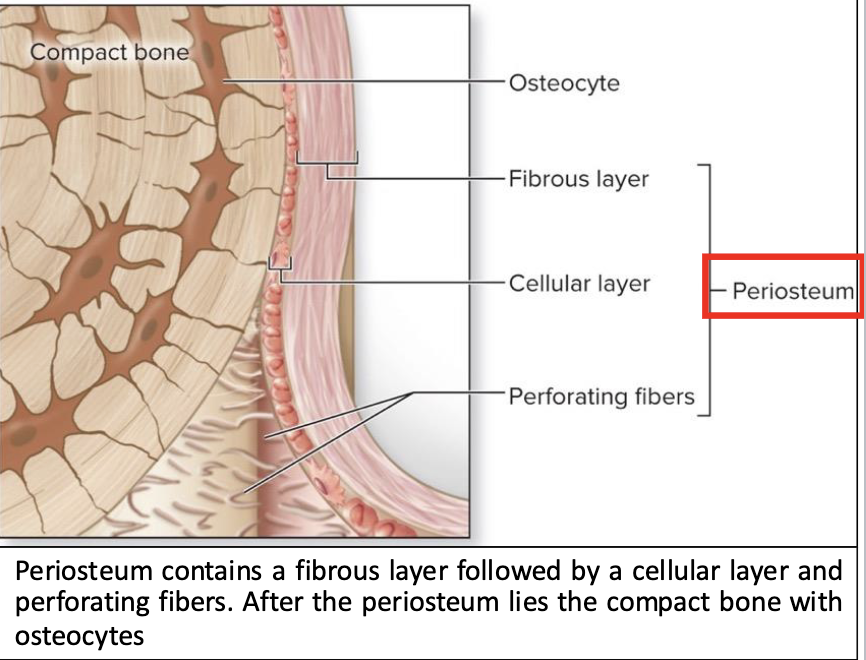
Outer fibrous layer of Periosteum
dense irregular CT
protects bone from surrounding structures
anchors blood vessels and nerves to bone surface
attachment site for ligaments and tendons
Inner cellular layer
includes osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts
attached to bone by numerous collagen fibers
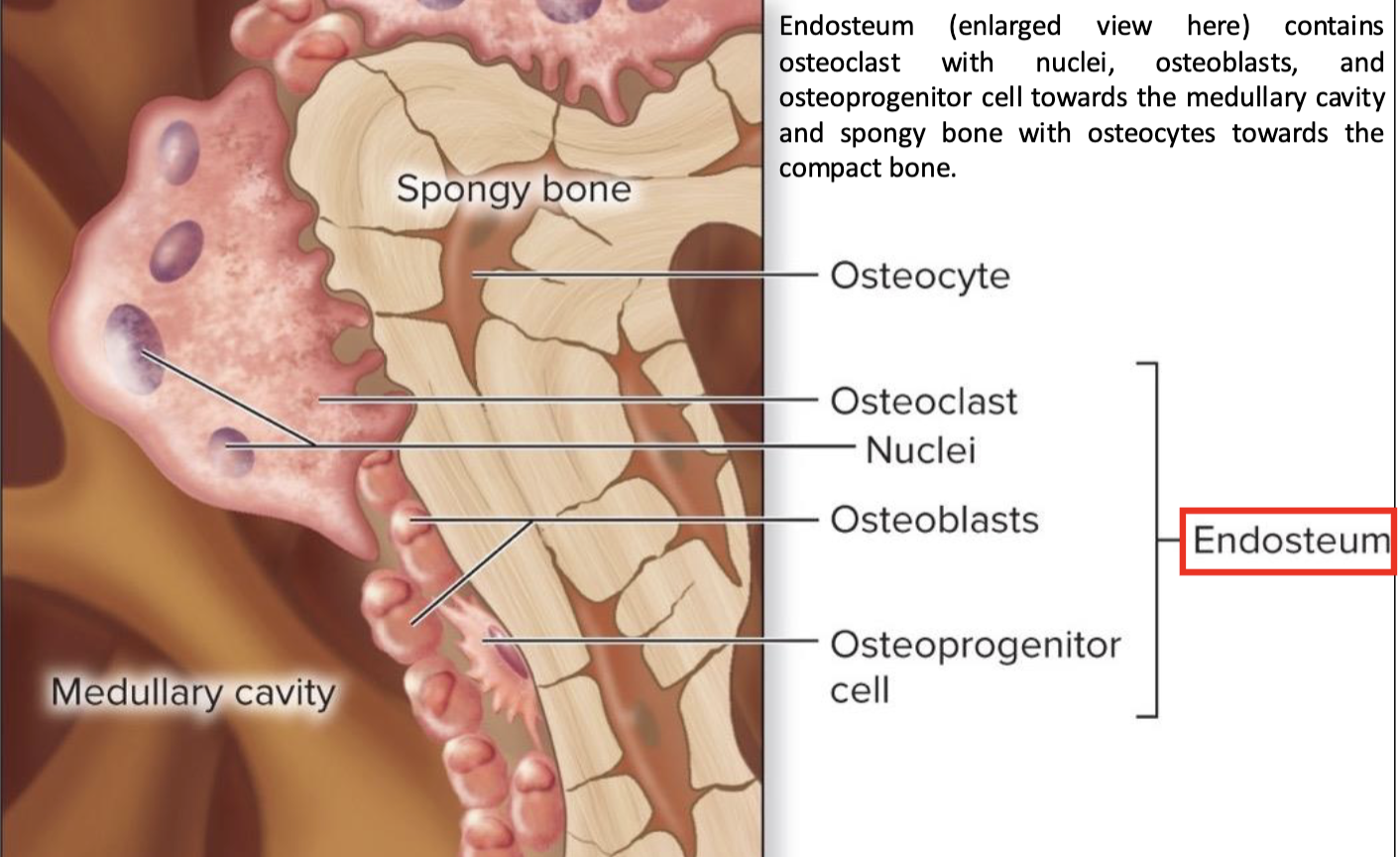
Endosteum
covers all internal surfaces of bone within medullary cavity
thin layer of CT containing osteoprogenitor cells, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
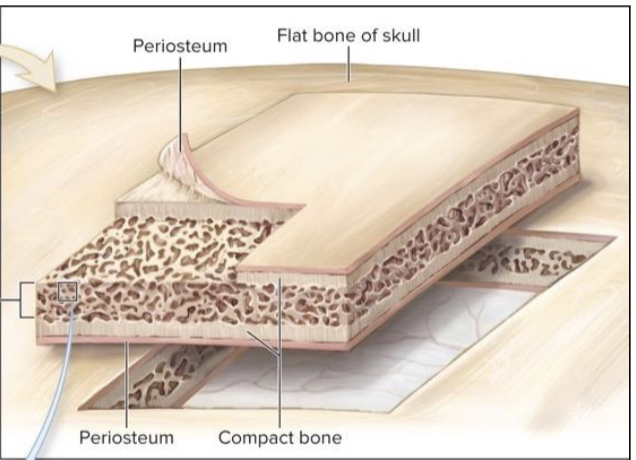
What anatomical similarities do short, flat, and irregular bones have that differ from long bones
external surface composed of compact bone covered by periosteum
interior composed of spongy bone
Diploe: spongy bone in flat or skull bone
no medullary cavity
Blood supply of bone
bone is hihgly vascularized
vessels enter from periosteum
nutrient foremen
small opening or hole in bone
artery entrance and vein exit here
Nerves that supply bones
accompany blood vessels through foramen
innervate bone, periosteum, endosteum, and marrow cavity
mainly sensory nerves
Bone marrow
soft CT of bone
red and yellow bone marrow
Red bone marrow (myeloid tissue)
hematopoietic
reticular CT, developing blood cells, and adipocytes
in children: located in spongy bone and medullary cavity of long bones
in adults: located only in selected areas of axial skeleton (skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ossa coxae, proximal epiphyses of humerus and femur)
Yellow bone marrow
produce of red bone marrow degeneration as children mature
fatty substance
may convert back to red bone marrow
during severe anemia: condition with reduced erythrocytes (RBC)
facilitates production of additional erthrocytes
Bone CT (osseous CT)
primary component of bone; composed of cells and extracellular matrix
4 types of cells found in bone CT
osteoprogenitor cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
Osteoprogenitor Cells
stem cells derived from mesenchyme
cellular division yields another stem cell and a “committed cell” that matures to become an osteoblast
located in periosteum and endosteum
Osteoblasts
form from osteprogenitor stem cells
synthesize and secrete osteoid
initial semisolid organic form of bone matrix
osteoid later calcifies
becomes entrapped within the matrix
differentiate into osteocytes
Osteocytes
mature bone cells derived from osteoblasts
detect stress on bone; trigger new bone formation
Osteoclasts
large, multinuclear, phagocytic cells
derived from fused bone marrow cells
ruffled border increases surface area exposed to bone
located within/adjacent to depression/pit on bone surface
resorption lacuna-involved in bone resorption (bone breakdown)
Composition of bone matrix
made up of organic and inorganic components
Organic components of bone matrix
osteoid produced by osteoblasts contain:
collagen protein
semisolid ground substance of proteoglycans and glycoproteins
give bone tensile strength by resisting stretching, and contribute to bone flexibility
Inorganic components of bone matrix
salt crystals- primarily made of calcium phosphate, which interacts with calcium hydroxide to form hydroxyapatite crystals
the crystals incorporate other substances like calcium carbonate, sodium, magnesium, fluoride during bone calcification
crystals deposit around long axis of collagen fibers in ECM
harden matrix and account for rigidity in bones
What happens if organic and inorganic proportions of bones aren’t correct
inadequate organic: brittle bones
inadequate inorganic: soft bones
Bone formation
begins with secretion of osteoid
Calcification occurs, deposition of hydroxyapatite crystals: Ca and PO3 ions precipate out, form crystals
Requires:
vitamin D
vitamin C
calcium and phosphate for calcification
Bone resorption
bone matrix is destroyed by substance released from osteoclasts
lysosomes within osteoclasts release proteolytic enzymes, which digest organic matrix components
calcium and phosphate dissolved by hydrochloric acid
Freed Ca and PO3 ions enter blood
occurs when blood calcium levels are low
Osteitis Deformans
results from disruption between osteoclast and osteoblast function
characterized by excessive bone resorption followed by excessive bone deposition
large osteoclasts resorb bone at higher rate
newly deposited bone poorly formed
most commonly affected bones: pelvis, skull, vertebrae, femur, tibia
Osteons
make up compact bone
small cylindrical structures
basic functional and structural unit of a mature compact bone
oriented parallel to bone diaphysis
appears like a bull’s eye target
Components of Osteon
central (haversian) canal
concentric lamellae
osteocytes
canaliculi
Central (Haversian) canal
cylindrical channel at center of osteon and paralel to it
blood vessels and nerves extend through channel
Concentric Lamellae
rings of bone CT
surround central canal
collagen fibers
90 degree from previous and next lamellae
give bone strength and resilience
Canaliculi
tiny, interconnecting channels within bone CT
extend from each lacuna, travel through lamellae and connect to lacunae and central canal
house osteocytes projections that allow intercellular contact
allow exchange of nutrients, minerals, gases, and wastes between blood vessels and osteocytes
Osteocytes
mature bone cells
found in small spaces between concentric lamellae
maintain bone matrix
non-osteon structures in long bone
perforating (volkmann) canals
circumferential lamellae
interstitial lamellae
Perforating canals
perpendicular to central canal
connect central canals within different osteons
Circumferential lamellae
external: rings of bone run immediately internal to periosteum
Internal: rings of bone run internal to the endosteum
both run the entire circumference of the bone
Interstitial lamellae
components of compact bone between osteons or partially resorbed osteons
Sponge bone components
trabeculae
parallel lamellae
Trabeculae
open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bones
bone marrow fills spaces
meshwork of crisscrossing bars
resistance of stresses
Parallel lamellae
bone matrix
osteocytes between lamellae
canaliculi radiate from lacunae
Structure of hyaline cartilage
cells scattered through matrix of protein fibers
embedded in gel-like ground substance
include proteoglycans but not calcium
resilient and flexible
high percentage of water
highly compressile and good shock absorber
avascular and contains no nerves
Components of hyaline cartilage
chondroblasts
chrondrocytes
perichondrium
Chondroblasts
cells that produce cartilage matrix
Chondrocytes
chondroblasts encases within the matrix
occupy small spaces, lacunae
maintain the matrix
Perichondrium
dense irregular CT
covers cartilage and helps maintain its shape
Interstitial growth in cartilage
chondrocyte within lacuna begins to exhibit mitoic activity
2 chondroblasts grow
each cell produces new matrix and beings to separate
cartilage continues to grow internally
Appositional Growth in cartilage
mitotic activity occurs within the perichondrium
new undifferentiated stem cells and committed cells that differentiate into chondroblasts are formed. Chondroblasts create new matrix at periphery
as result of matrix formation, the chondroblasts push apart and become chondrocytes. Chondrocytes continue to produce more matrix.
Ossification (osteogenesis)
formation and development of bone CT
begins in the embryo
continues through childhood and adolescence
by 8th-12th week of embryonic development, skeleton beings to form
intramembraneous ossification
endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
bone growth within a membrane; called dermal ossification
produces flat bones of skull, some facial bones, mandible, central part of clavicle
Steps of intramembranous ossification
ossification centers form within thickened regions of mesenchyme beginning at 8th week of development
osteioid undergoes calcification
woven bone and surrounding periosteum form
lamellar bone replaces woven bone, as compact bone and spongy bone form
Endochondral ossification
begins with hyaline cartilage model
produces most bones of skeleton, including bones of upper and lower limbsm pelvis, vertebrae, ends of calvicle
Steps in long bone development in a limb
fetal hyaline cartilage model develops
cartilage calcifies, a periosteal bone collar forms
primary ossification center forms in diaphysis
secondary ossification centers form in epiphyses
bone replaces cartilage, except articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
lengthwise growth continues until epiphyseal plates ossify and form epiphyseal lines
Epiphyseal plate intersistial growth
dependent upon cartilage growth in epiphyseal plate
plate is divided into 5 phases beginnings with zone 1, zone 2, zone 3, zone 4, and zone 5
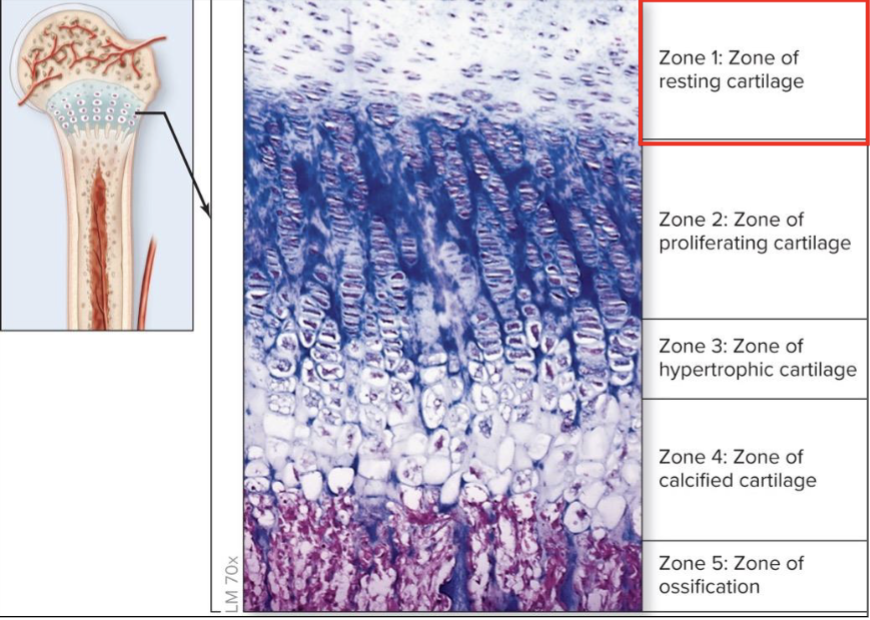
What are the zones of cartilage in the bone
zone 1: resting cartilage
zone 2: zone of proliferating cartilage
zone 3: hypertonic cartilage
zone 4: calcificed cartilage
zone 5: zone of ossification
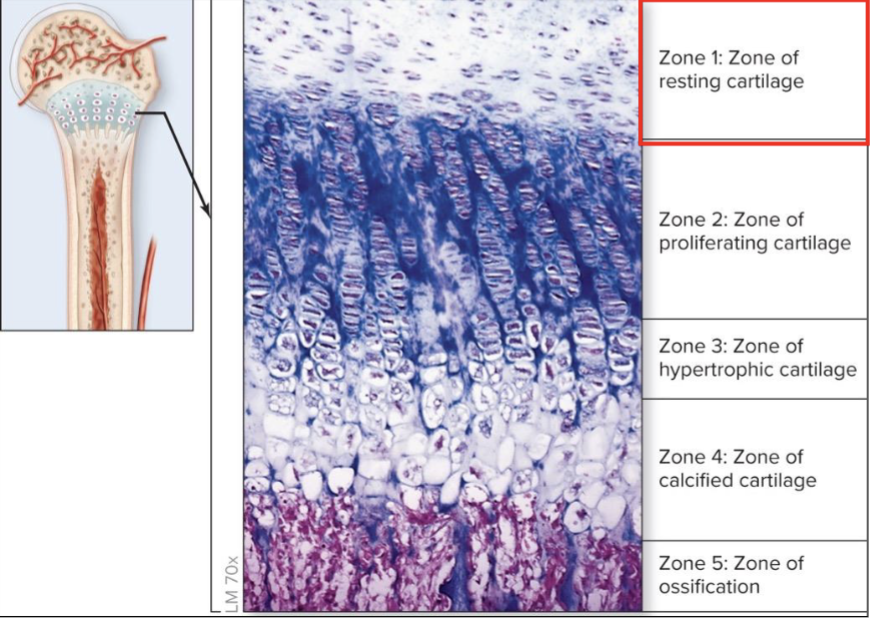
Zone 1 of resting cartilage
zone closest to epiphysis
small chondrocytes distributed throughout matrix
resembles mature hyaline cartilage
secures epiphysis to epiphyseal plate
Zone 2 of proliferating cartilage
chondrocytes undergo rapid mitotic division
align into longtiudinal columns of flattened lacunae
columns parallel to diaphysis
Zone 3 of hypertonic cartilage
chondrocytes cease dividing
cells greatly enlarge (hypertrophy)
walls of lacunae become thin
Zone 4 of calcified cartilage
composed of 2-3 layers of chondrocyte
minerals are deposited between columns of lacunae
destroys chondrocytes
Zone 5 of ossification
walls breaks down between lacunae in columns
spaces invaded by capillaries and osteoprogenitor cells
new bone matrix deposited on the calcified cartilage matrix
Where does bone growth take place
zone 2 and 3
pushes zone of resting cartilage towards epiphysis
Appositional bone growth
occurs within periosteum
bone matrix deposited within layers parallel to surface
osteoclasts resorb bone matrix along medullary cavity
Axial skeleton
composed of bones along central body axis
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
Appendicular skeleton
bones of upper and lower limbs
girdles of bones attach limbs to axial skeleton
pectoral girdle holds upper limbs in place
pelvic girdle holds lower limbs in place
What are the cranial bones
frontal bone
parietal bone (2)
temporal bone (2)
occipital bone
sphenoid bone
ethmoid bone
Facial bones
zygomatic bone (2)
lacrimal bone (2)
nasal bone (2)
vomer
inferior nasal concha (2)
palatine bones (2)
maximillae (2)
mandible
Auditory ossicles
malleus (2)
incus (2)
stapes (2)
hypoid bone
Vertebral column bones
cervical vertebrae (7)
thoracic vertebrae (12)
lumbar vertebrae (5)
sacrum
coccyx
Thoracic Cage
sternum
ribs (24)
Pectoral girdle
clavicle (2)
scapula (2)
Upper limb bones
humerus (2)
radius (2)
Carpals (16)
Metacarpais (10)
Phalanges (28)
Ulna (2)
Pelvis girdle
os coxae (2)
Lower limb bones
femur (2)
patella (2)
tibia (2)
fibula (2)
tarsals (14)
metatarsais (10)
phalanges (28)
Articulating surfaces of bone markings
condyle, facet, head, trochlea
Openings and spaces of bone markings
canal, fissure, foramen, meatus, sinus
Condyle
large, smooth, rounded, oval structure
facet
small, flat, shallow surface
head
prominent, round epiphysis