forensics 5
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
eyewitness testimony
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
eyewitness misidentification prologue
69% wrongful convictions involved eyewitness misidentification- biggest signle cause however % is decreasing as it was 75% 2 years ago
jennifer Thompson and Ronald Cotton
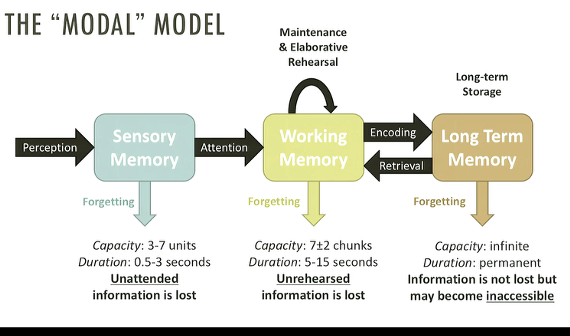
the “MODAL” model
to be an accurate eyewitness, people must complete 3 stages of memory processing: acquisition, storage, retrieval. errors and forgetting can happen at any of thes etsages but eyewitness memory is reasonably good under proper circumstances
estimator vs system variables- Wells
variables that affect eyewitness accuracy.
estimator variables- not under the control of the jsutice system but might eb used to estimate accuracy
system variables- under the control of the jsutice system
estimator variables (incident factors)
event characteristics
witnss characteristics
testimony characteristics
event characteristics- errors of acquisition
disguise, viewing conditions, greater stress, weapon focus (expectedness), own race bias
disguise
accurate idenitifcation is difficult if during thr witnessed event the person wears sunglasses (Hockley et al), knit caps (or anything covering their hairline) and especially if they wear both (Mansour)
viewing conditions: rule of 15
duration of exposure: longer the better. doistance of witness from target: 15m is reliable. amount of illumination at crime scene: reliable 15 lux, dropssharply with bad streetlights. people greatly overestimate time especially under stress and they overestimate distances
crimes in field and lab
24% of violent crimes committed between 8pm and midnight- peaking at 9pm. person descriptors best during day and start of twilight vs night- Yarmley. the longer one sees the perpetrator the better the idnetificaiton is
event characteristics: stress and anxiety
most crimes are events of high stress and p’s experience high level of negative emotions. most studies show that stress decreases both accuracy and detailedness of memories. under soem special conditions certaind etiasl become sharper- Deffenbacher
stress: london dungeon study- Valentine
stress: the US army survival camp studies- Loftus
•Real military personnel under POW-like training
•48-hr Isolation + Food- & Sleep deprivation
•Several 30 min interrogations, separated by 4 hr-s
•Well-illuminated room
•Low stress >>> High stress interrogation (within-subject design)
•Under high-stress: less accurate about interrogators & what happened
•More than 1/3 of high stress could not identify their interrogators
•“Generalizable to eyewitness-situations” (?)
•Experimental lab studies did not find identification differences (Clifford & Hollin, 1981)
•Meta-analysis: High stress impairs both recall & recognition (Deffenbacher, 2004)
event characteristics: weapon focus
more difficult to identify the criminal if a gun, sword or knife is present vs a check, money or pen is present: pepoples eye track the gun rather than the criminal- Loftus
explanation for weapon focus effect
attentional narrowing- Steblay. prescence of a harmless but novel object has the same effect- Erickson
expectedness- Fawcett
racket vs gun at tennis court, gun vs racket at shooting range. accuracy best in both conditions when weapon was expected
novelty- Ericson et al
presence of a harmless but novel object has the same effect
witness characteristics: alcohol
•Intoxicated witnesses are very common
•73% of officers report interviewing at least 1 within a month period
•13% of prosecuted cases have at least 1
•72% of sexually assaulted university student women intoxicated
•
•In lab alcohol vs placebo p-s on a staged conversation (Schreiber et al, 2011)
•No difference in person descriptions
•Same amount of detail, but focus on subjective vs physical details
•In real bar low vs high intoxicated p-s on a staged event (Altman, 2018)
•No difference in correct ID-s from a line-up
•Intoxicated worse on accuracy & details
witness charateristics: cannabis
18% witnesses under infleucne of cannabis. cannabis impairs memory to word lists
witness characteristics: race
people are better at recognising other people if they are the same race as they are- Brigham et al
witness characteristics: own age bias and other age effects
poeple have dififculty discriminating between poeple of different age groups
confidence, speed and accuracy
is very powerful however it is an estimator variable. confidence and speed is something thats easy to manipulate and greatly influenced by factors that can and shoulkd be changed
system variables: Wells
all system variables can be estimator variables but no estimator varibales can be system variables
system variables
line up construction/ fairness: similarity of foils
line up administration: simultaneous vs sequential
testimony administration: who doe sit? how is it done?
pre lineup factors- retention phase
retention interval= time between crime and identification- the sooner the better. 1 week later= 50% drop, 4hours later= 20% drop
need to minimise extraneous info and multiple viewings
suspect usually changes features. description accuracy and idneitifcaiton accuracy is weakly related. once sketched can contaminate memory of the witness
identification- the retrieval phase
designing lineups