Anatomy Unit 1
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomical Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
anatomy
the study and science of the structure of the human body
body cavities
the organization of the internal body into spaces
anatomical sections
body’s cavities and organs with specific cuts
organ systems
functional groups that the body’s organs are combined into
anatomical position
how most specimens are presented in a standard position - body is facing forward with toes pointing forward, and palms facing forward
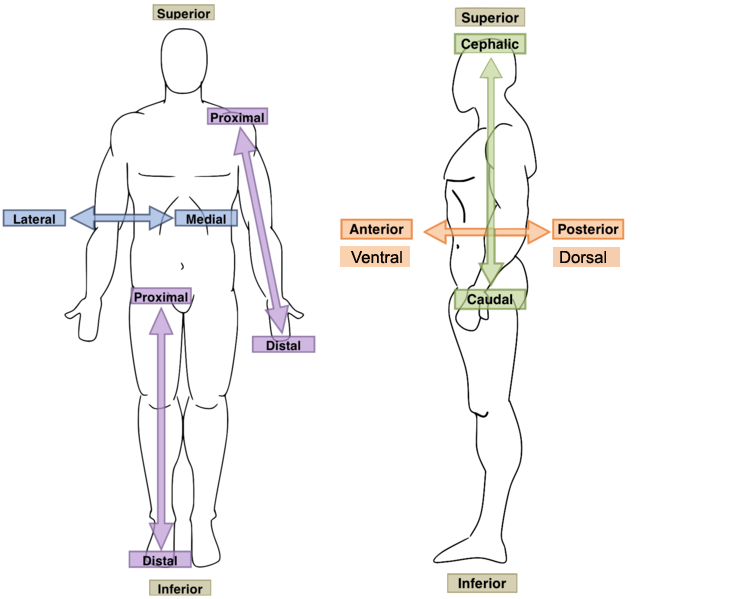
directional terms
makes communication easier and less prone to errors - to which they define the location of body parts and markings
anterior position (ventral)
refers to the front of the body or of a body part
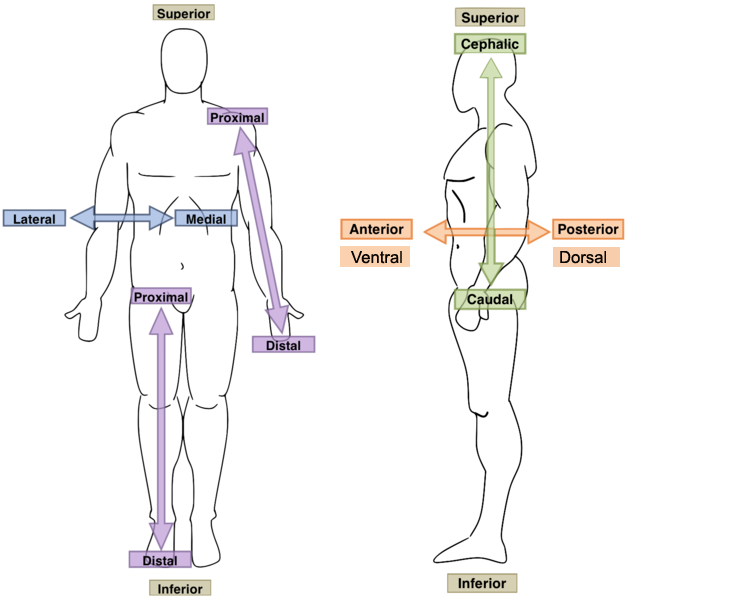
posterior position (dorsal)
the opposite of anterior - it can refer to the back side of the body, or the back of a body part, or to a structure that travels toward the back side of the body
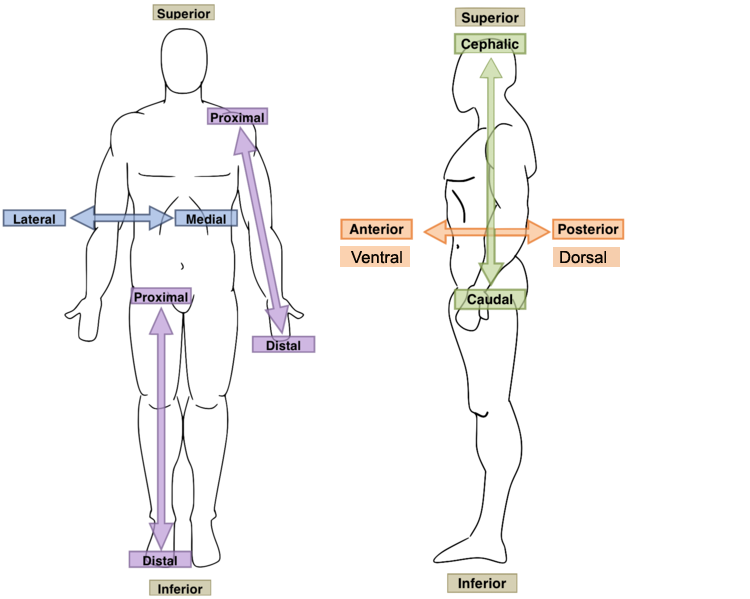
superior position
describe structures that are toward or closer to the head
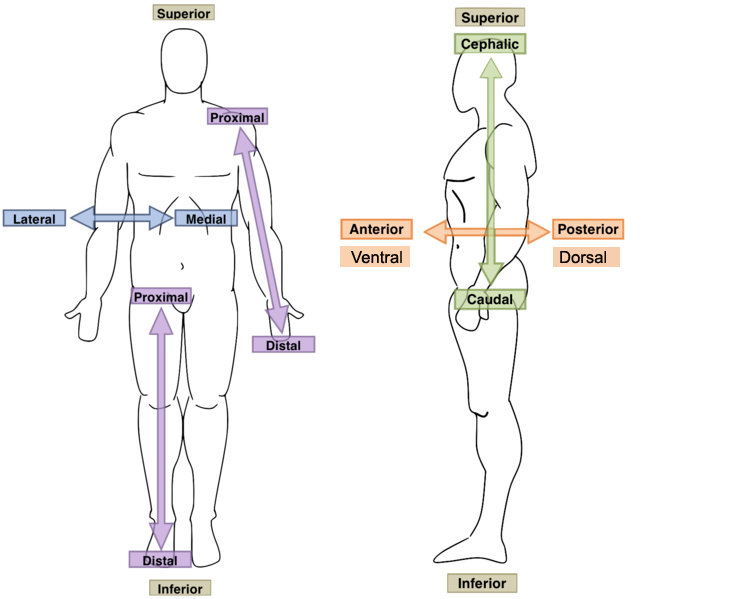
inferior position
means away from the head or toward the tail
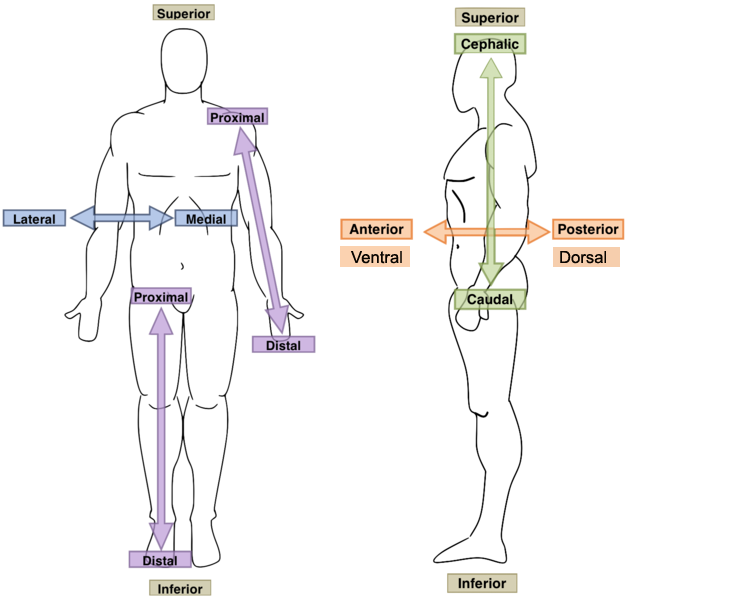
proximal position
refers to the closeness (proximity) of a structure to its point of origin
appendicular region
limbs in the upper and lower part of the body
distal position
the farness (distance) of a structure from the shoulder or the hip
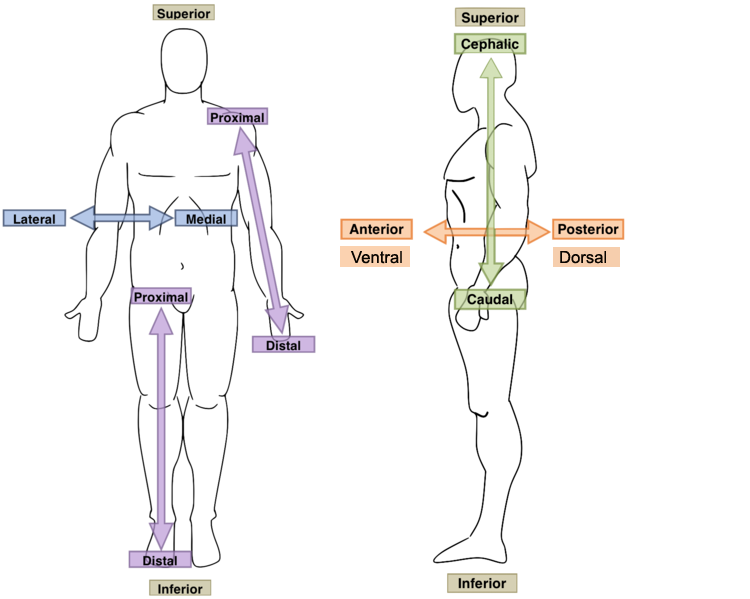
medial position
when a structure’s position is closer to the midline
lateral position
when a structure’s position moves further away from the midline
superficial position
a position that is closer to the surface of the body or closer to the skin
deep position
structure’s that are further away from the skin’s surface
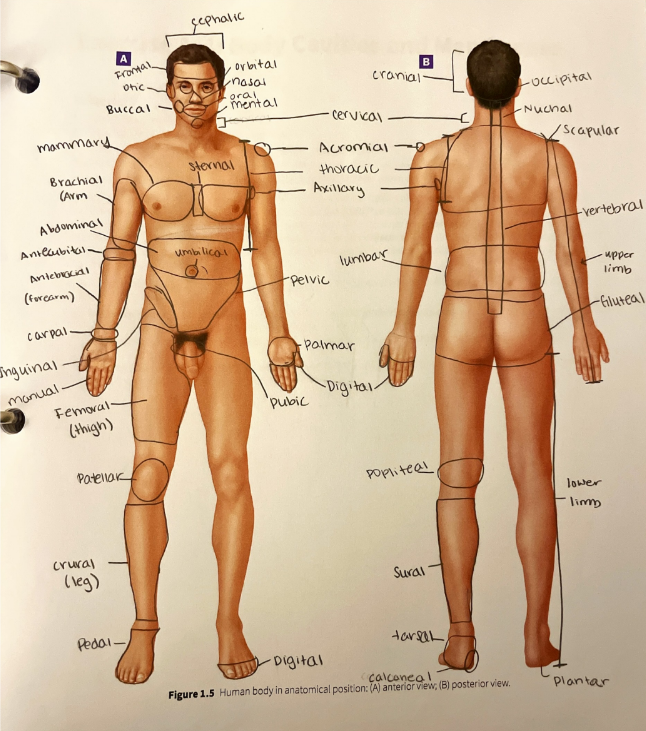
regional terms
more specific words used to another standard practice used to make descriptions as specific as possible and to reduce the potential for errors in communication
abdominal region
the area over the abdomen that is inferior to the diaphragm and superior to the bony pelvis
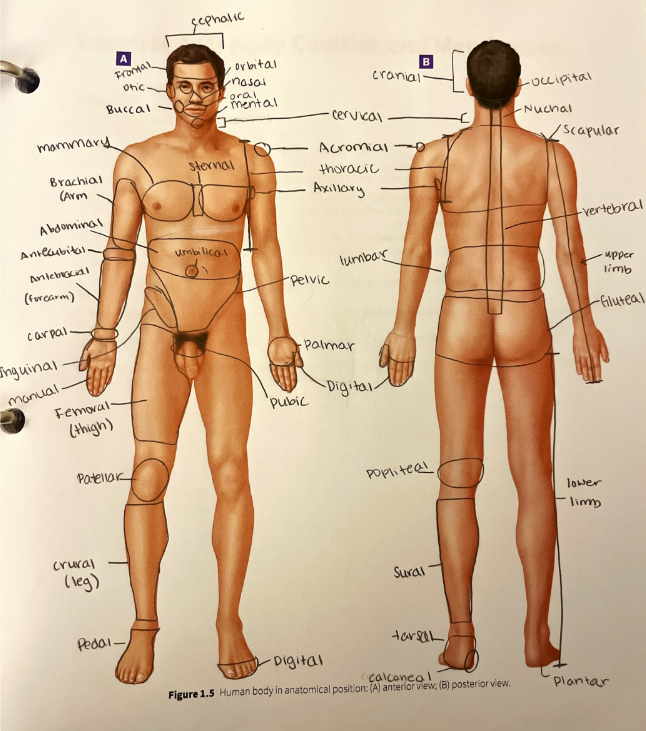
acromial region
the area over the lateral part of the shoulder that contains the acromion of the scapula
antebrachial region
the anterior forearm
antecubital region
the anterior upper limb between the forearm and arm over the elbow joint
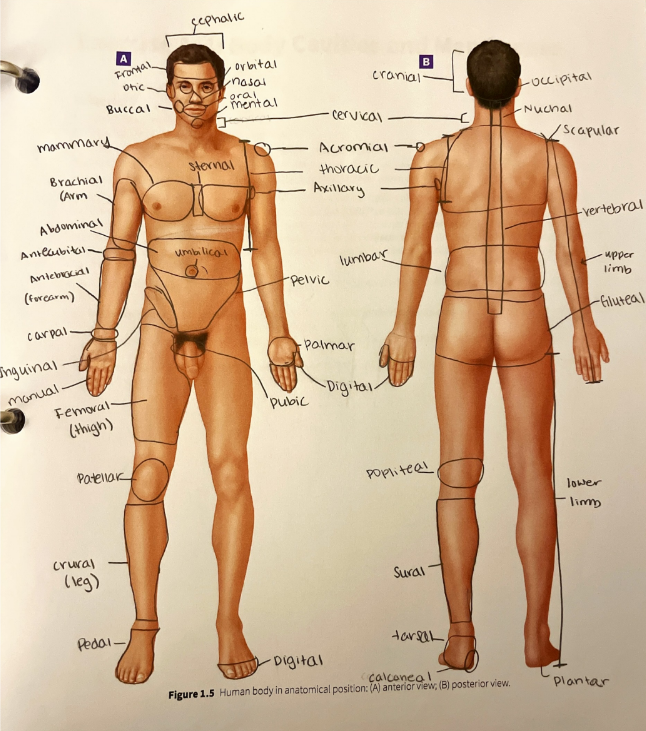
axillary region
the area in and around the axilla (armpit)
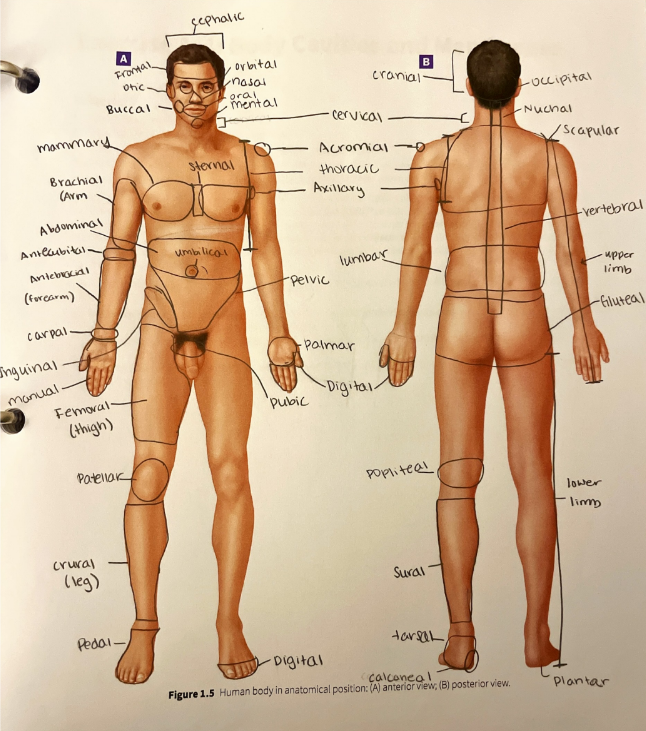
brachial region
the anterior and posterior arm (between the elbow and the shoulder)
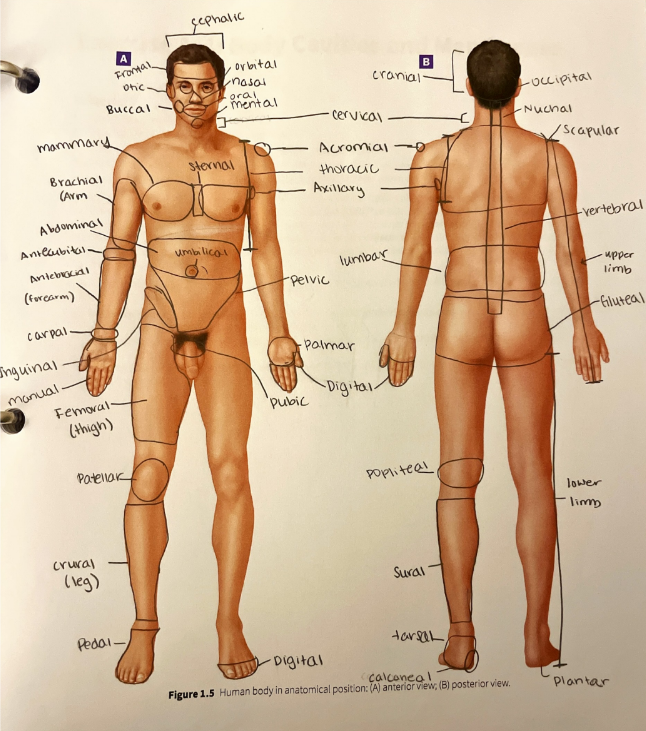
buccal region
the lateral portions of the face corresponding to the cheeks
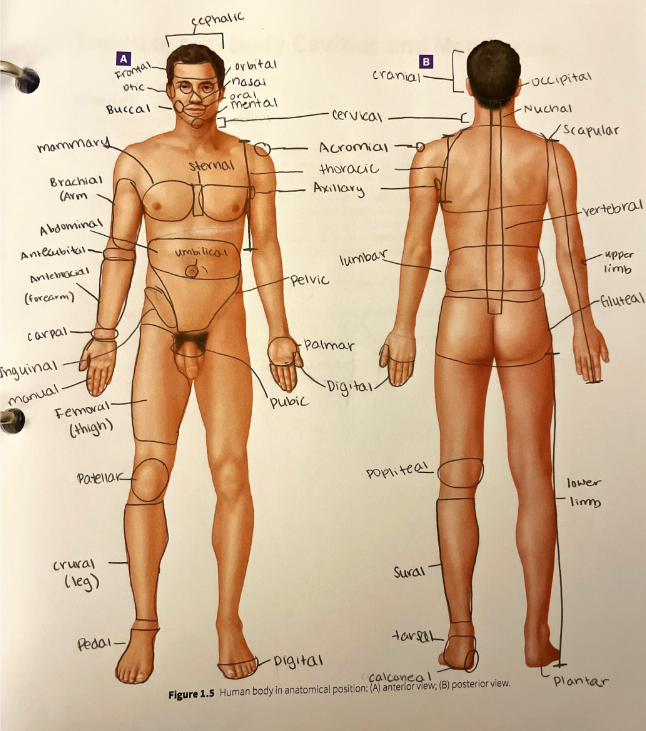
calcaneal region
the heel of the foot
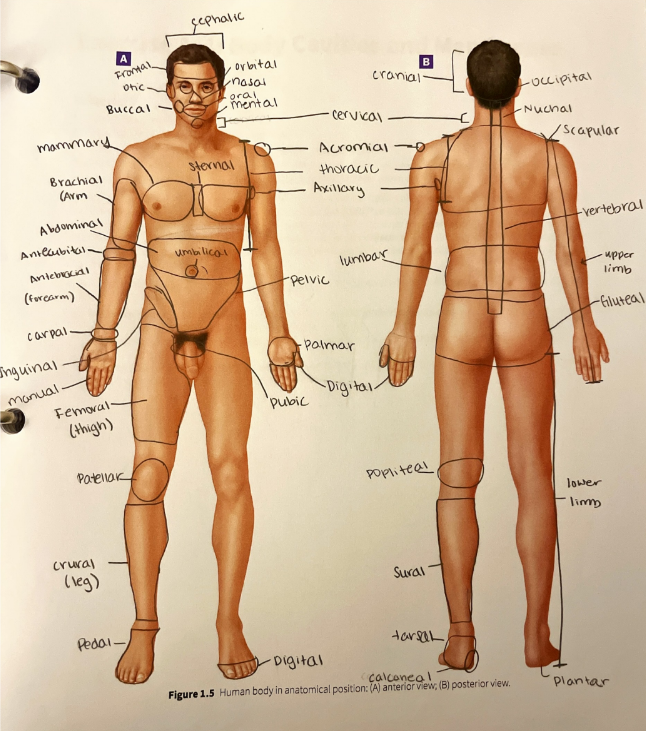
carpal region
the wrist
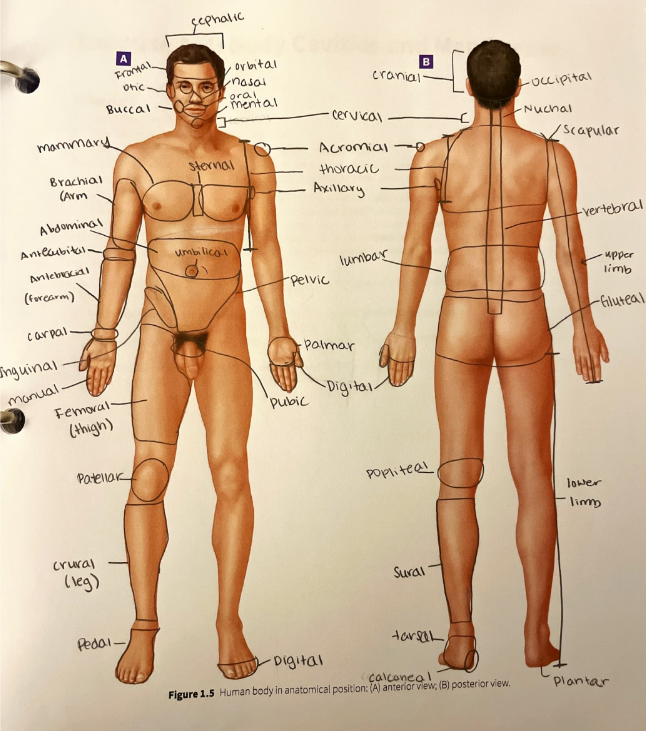
cephalic region
the entire head from the chin to the top of the head
cervical region
the neck
cranial region
the top of the head, or the portion of the skull that encases the brain
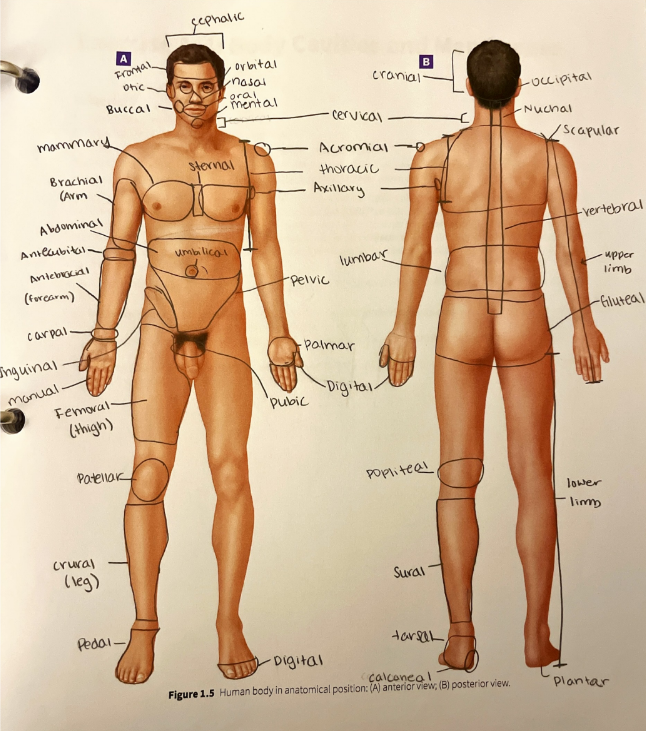
crural region
the anterior leg (or the shin)
digital region
the fingers or the toes
femoral region
the thigh
frontal region
the forehead
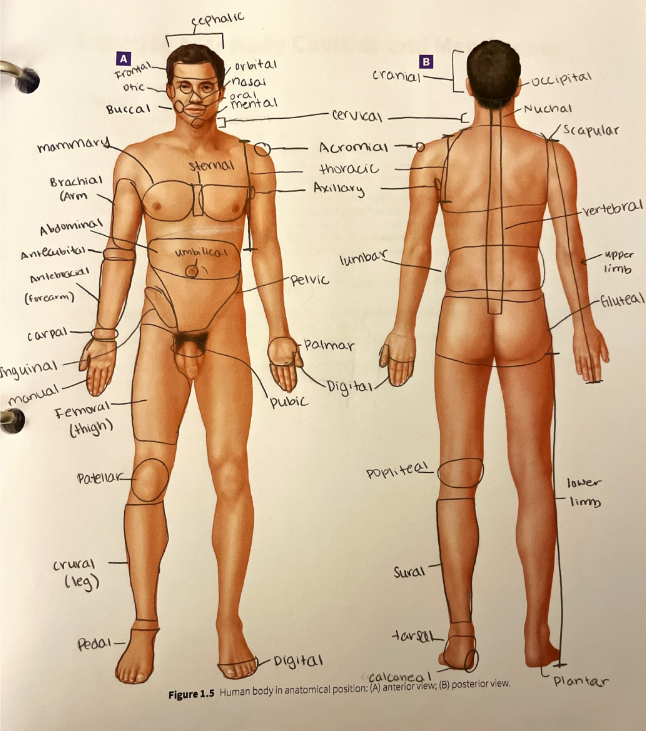
gluteal region
the buttock
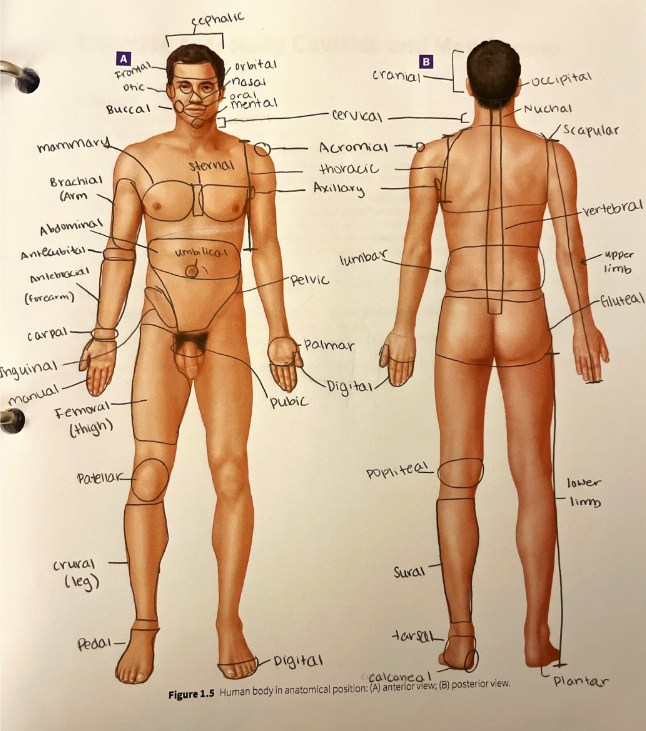
inguinal region
the area along the inguinal ligament that divides the pelvis from the thigh
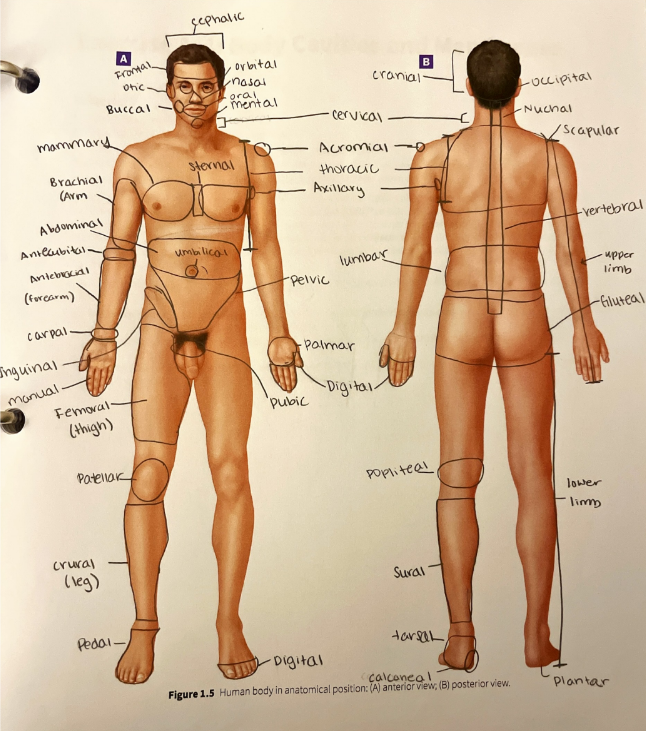
lumbar region
the lower back
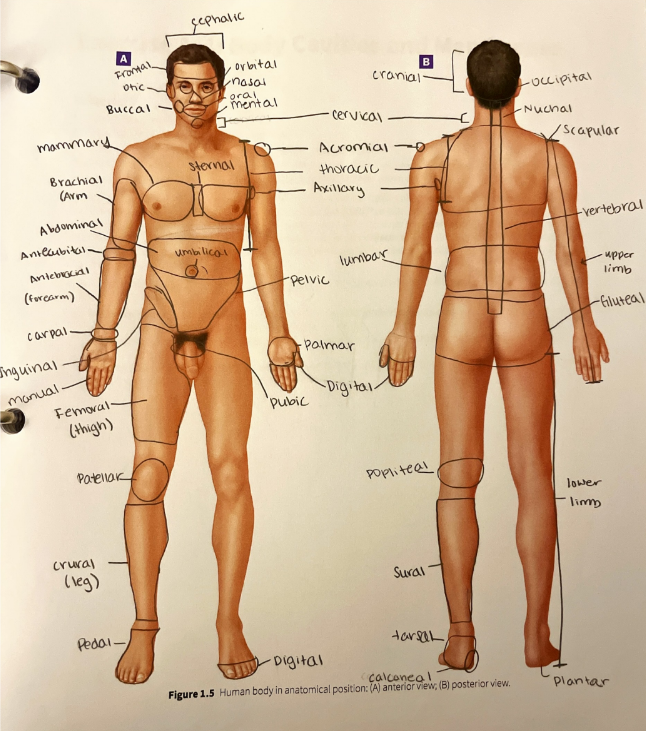
mammary region
the area around the breast
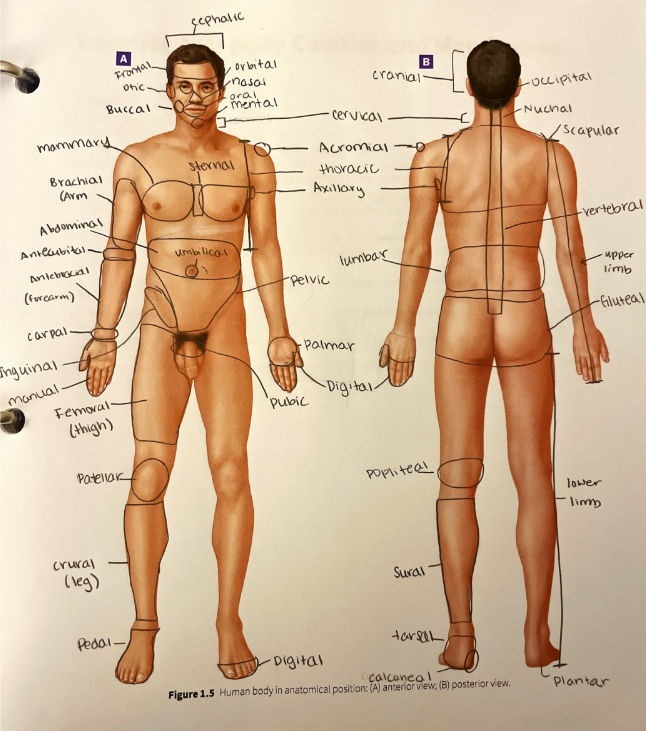
manual region
the general area of the hand
mental region
the chin
nasal region
the nose
nuchal region
the ridge that runs along the back of the skull at the superior boundary of the occipital region
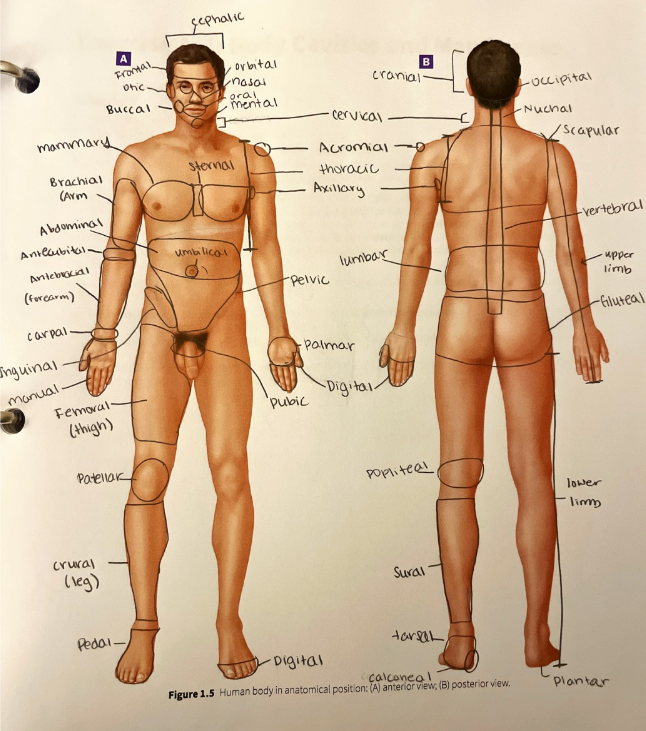
occipital region
the general area of the back of the skull
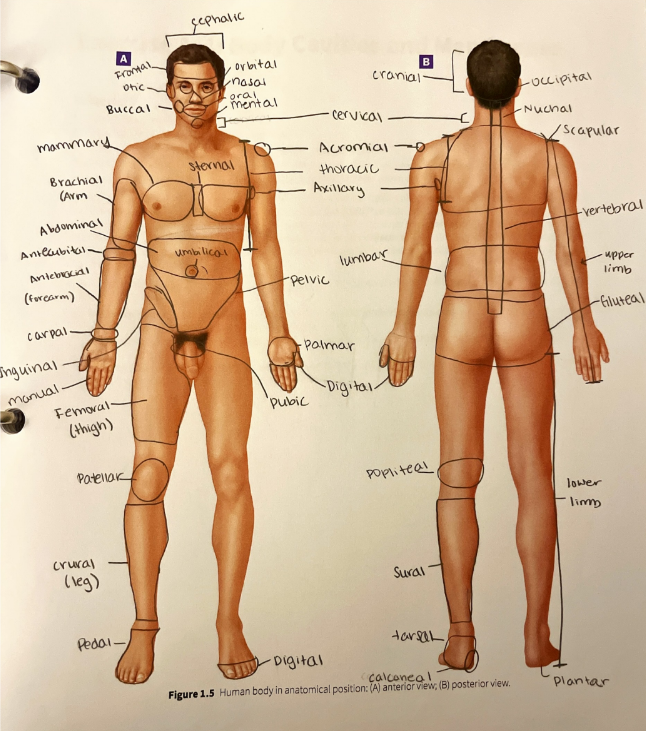
oral region
the mouth
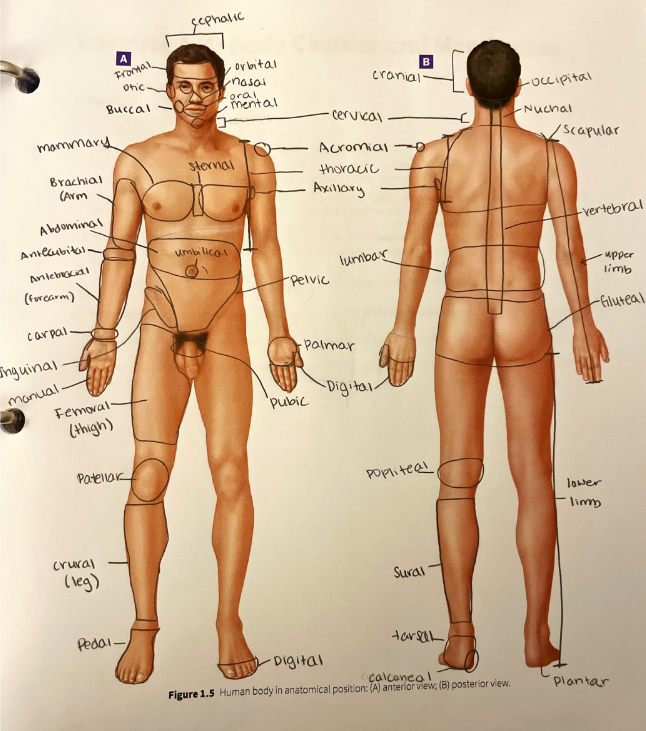
orbital region
the area around the eye
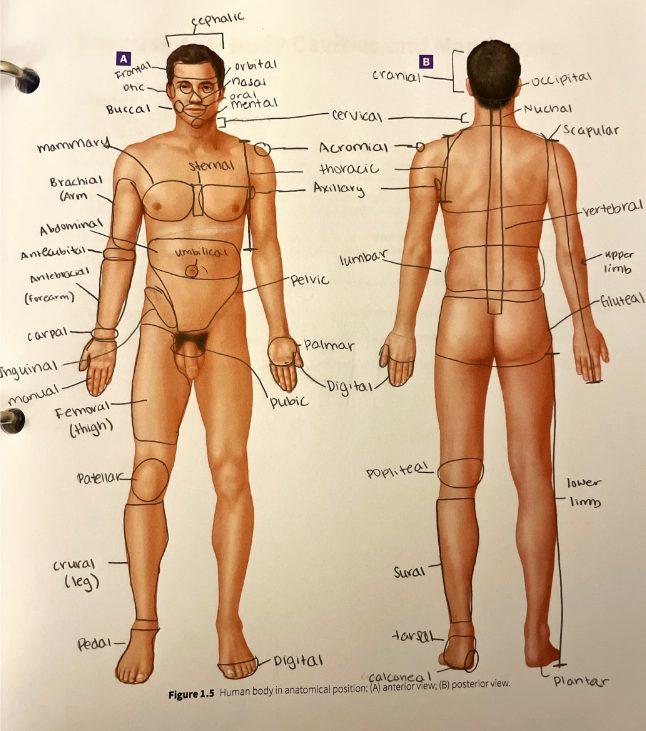
otic region
the area around the ear
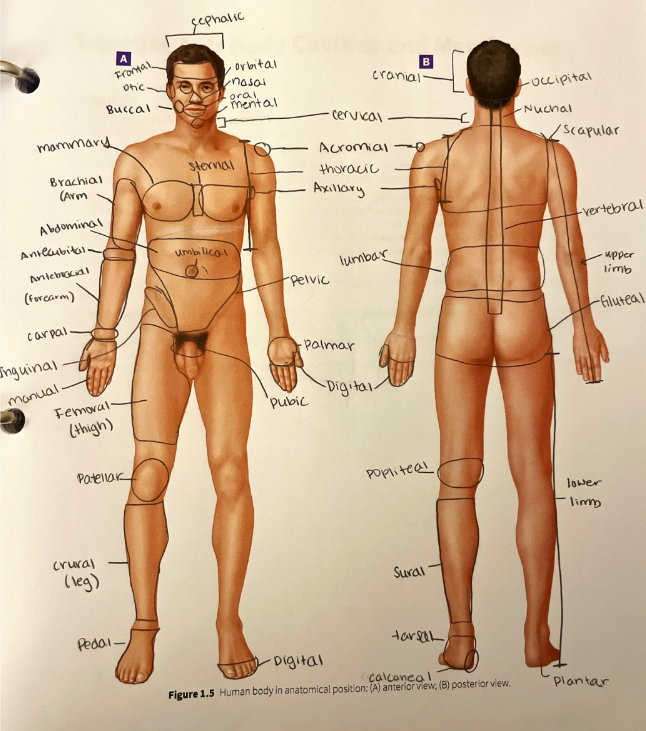
palmar region
the anterior hand (the palm of the hand)
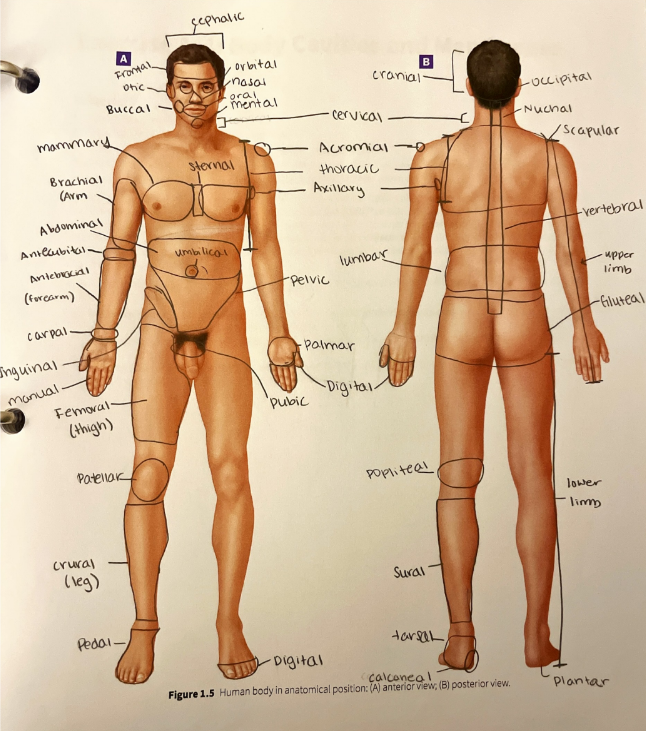
patellar region
the anterior part of the knee over the patella (kneecap)
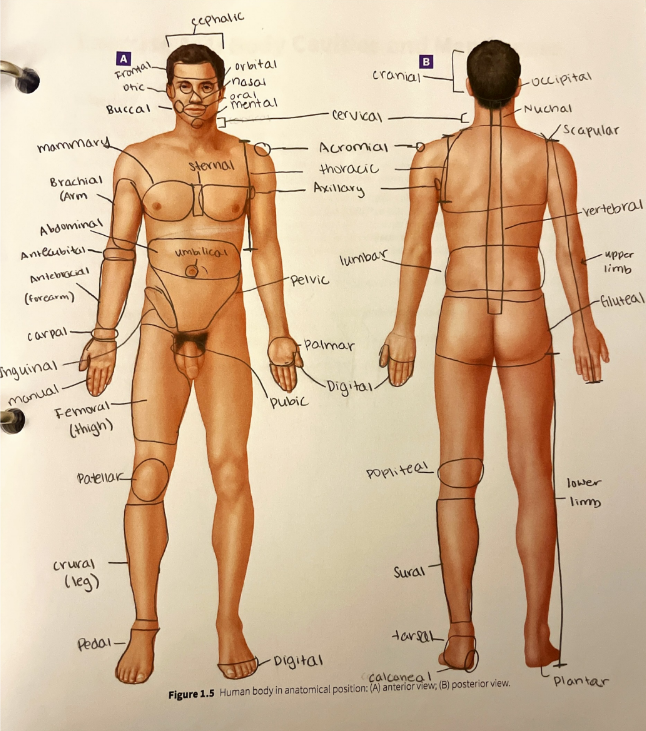
pedal region
the foot
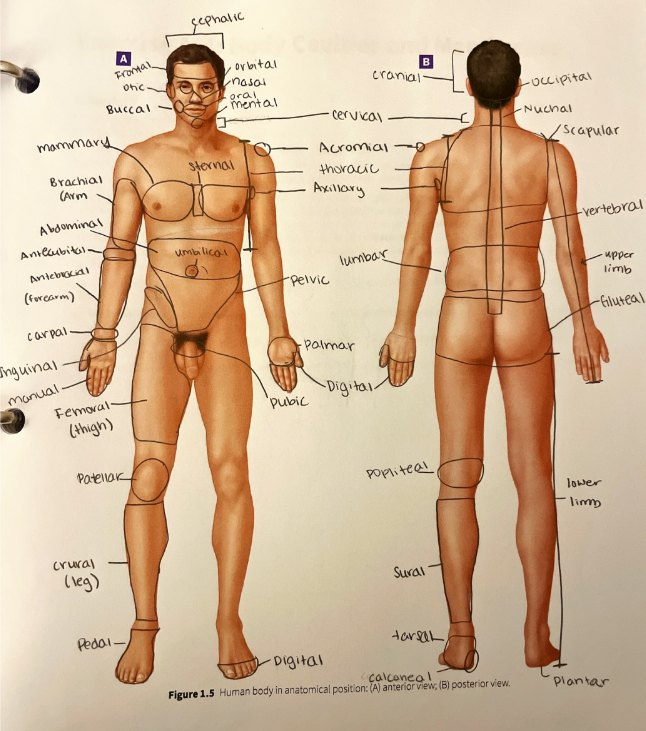
pelvic region
the anterior pelvis
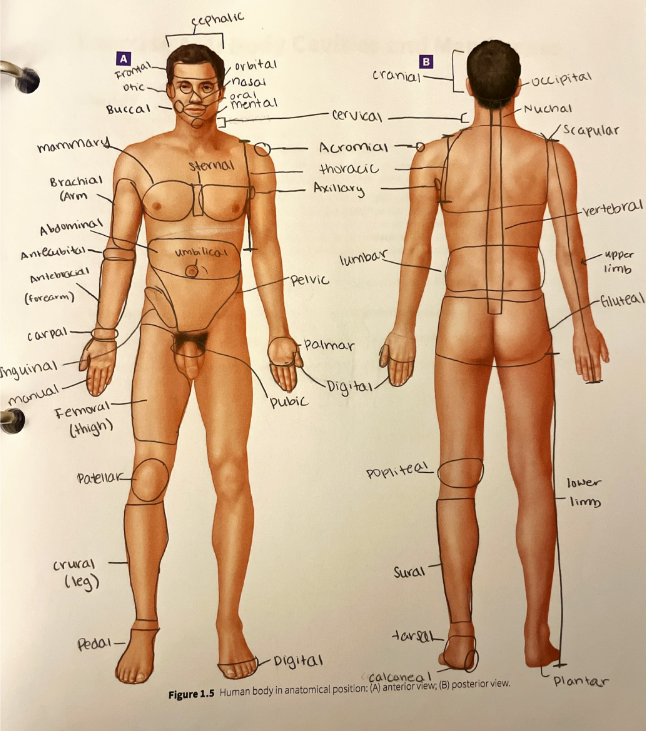
plantar region
the bottom of the foot
popliteal region
the posterior side of the knee joint
pubic region
the area over the pubic bone of the pelvis
scapular region
the area over the scapula in the superior back
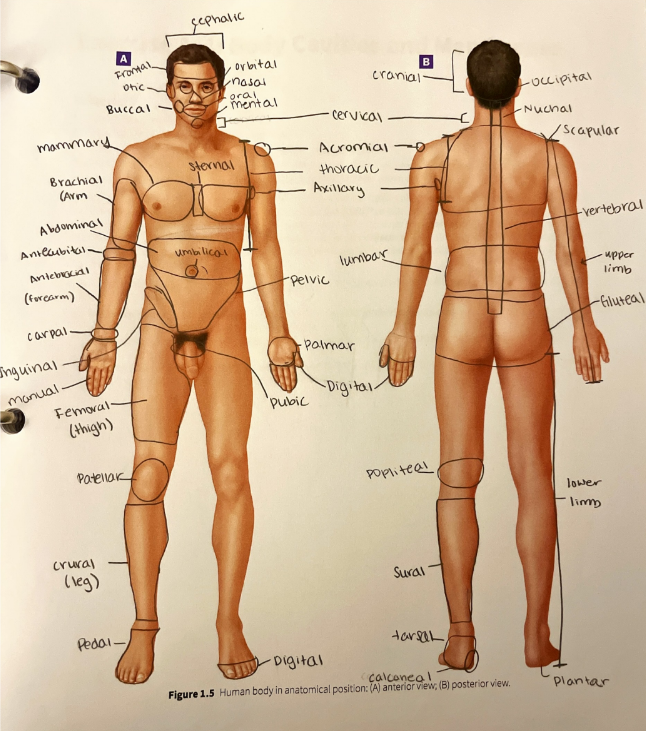
sternal region
the area in the middle of the chest over the sternum
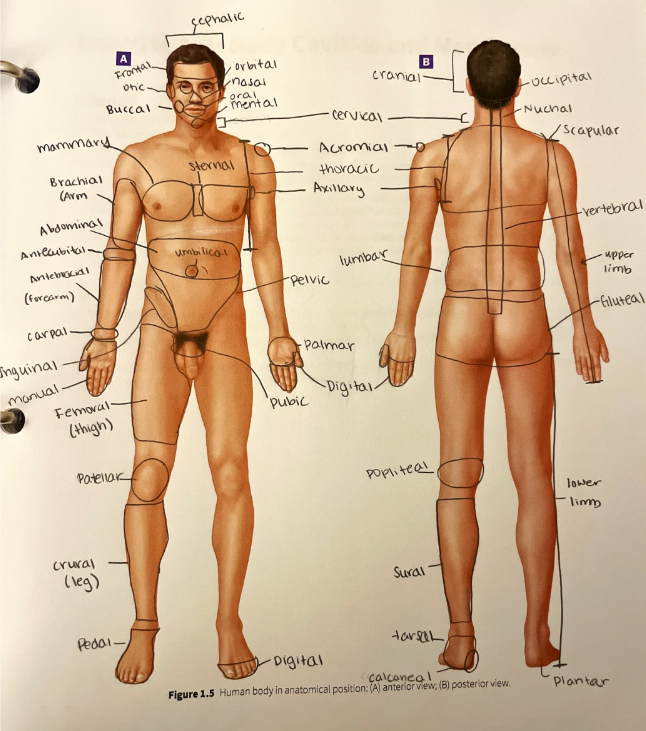
sural region
the posterior part of the leg (the calf)
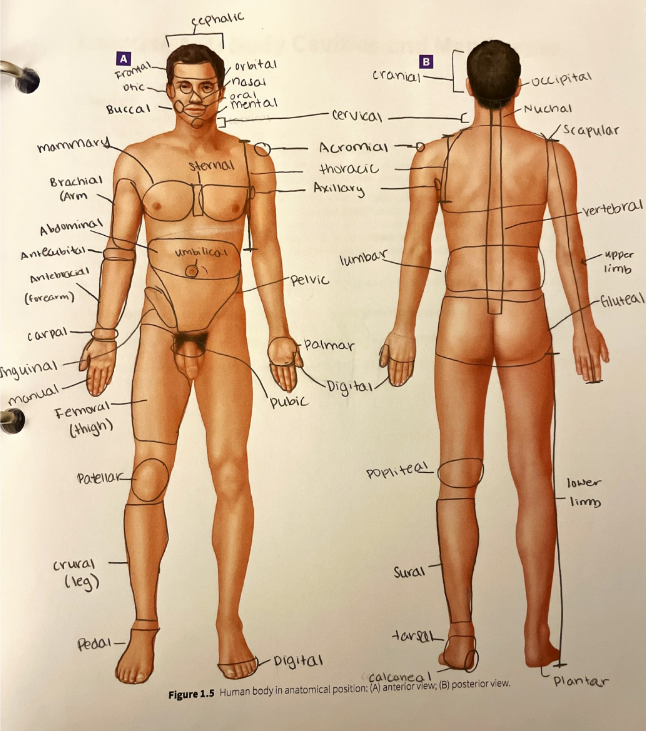
tarsal region
the proximal foot and ankle region
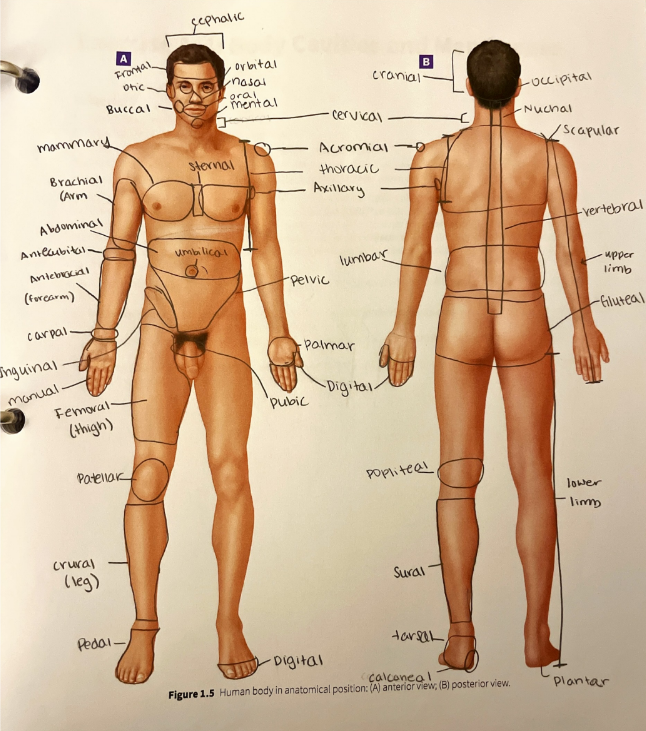
thoracic region
the general chest area
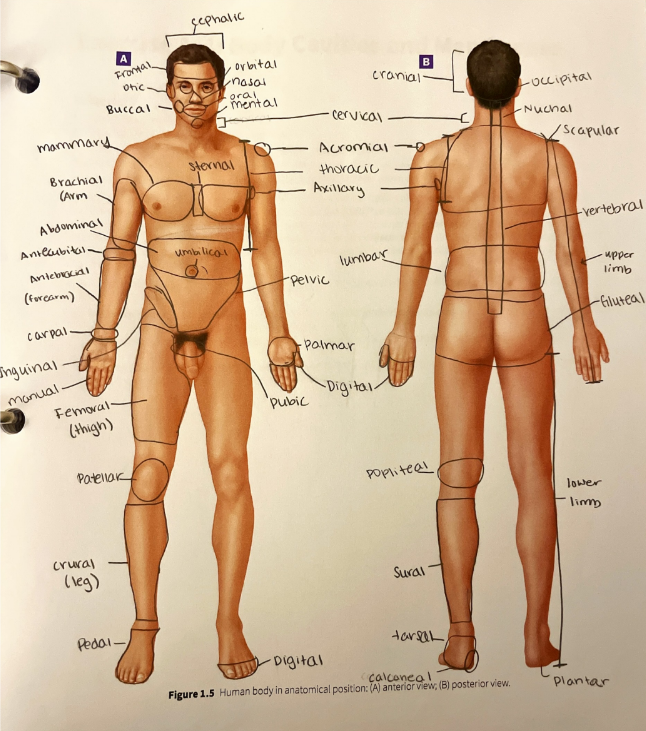
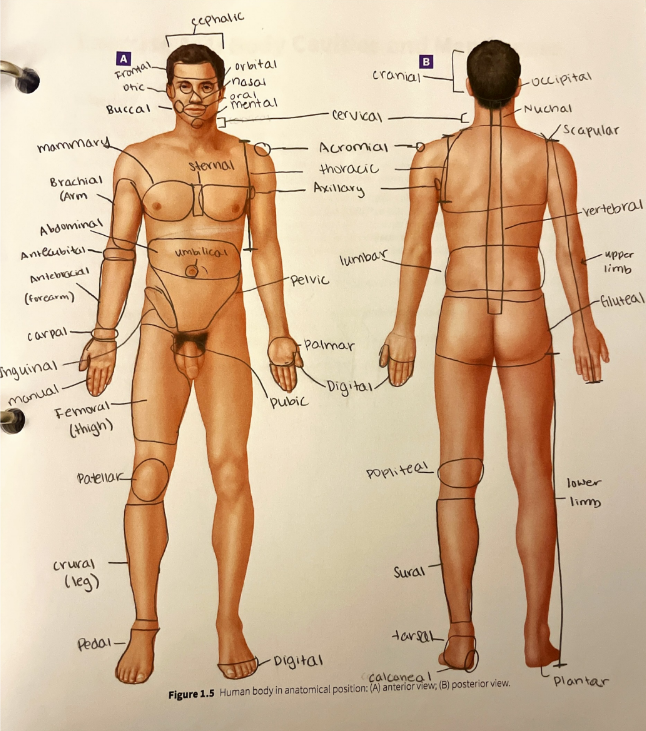
umbilical region
the area around the umbilicus (belly button)
vertebral region
the area over the vertebral column (spine)
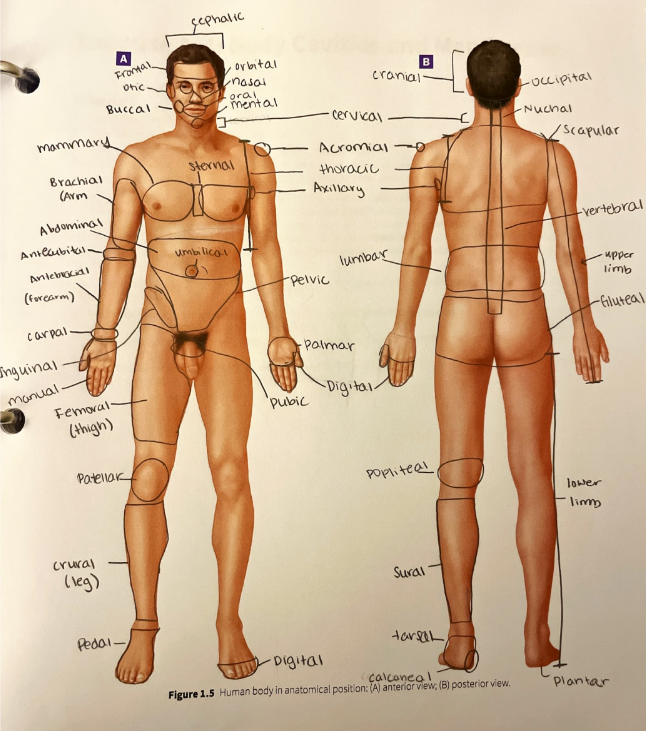
arm
the portion of the upper limb from the elbow to the shoulder
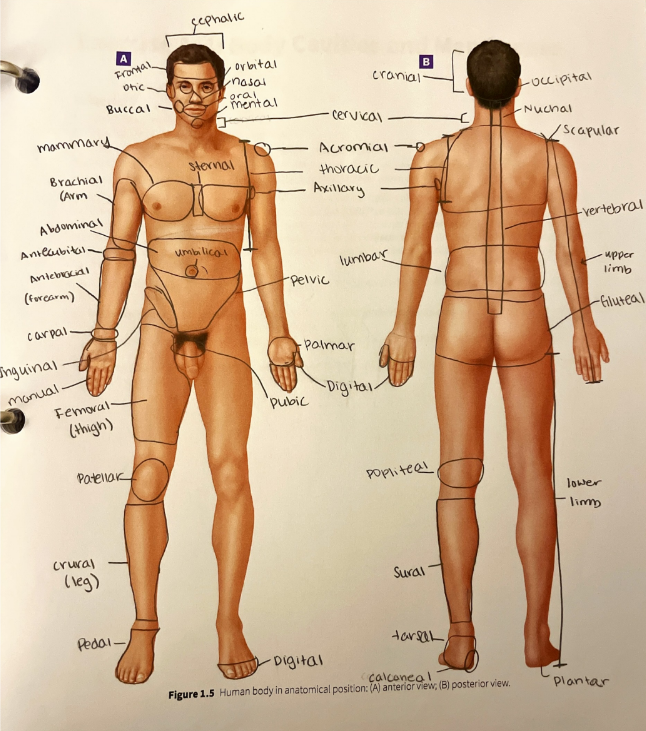
forearm
the portion of the upper limb from the elbow to the wrist
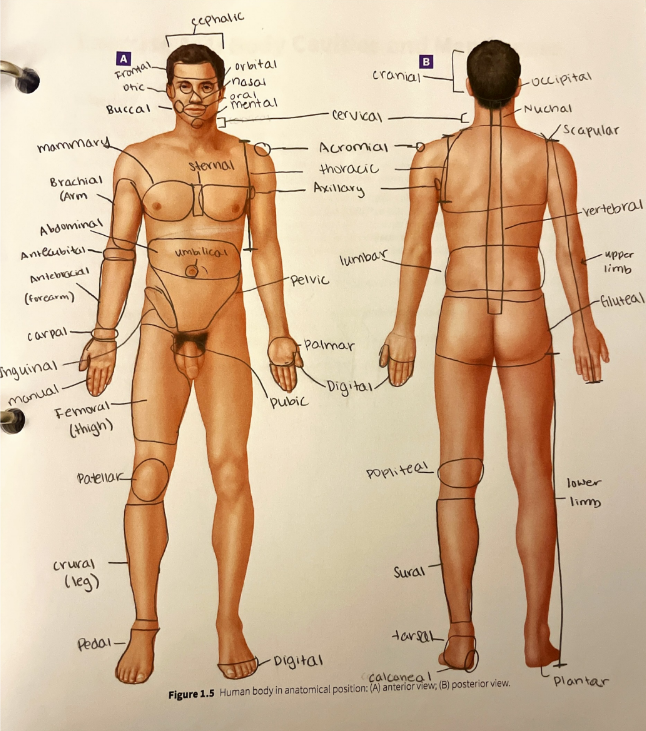
leg
the portion of the lower limb from the knee to the ankle
lower limb
the entire portion of the body from the hip to the digits of the foot
thigh
the portion of the lower limb from the hip to the knee
upper limb
the entire portion of the body from the shoulder to the digits of the hand
serous membranes
several of the fluid-filled body cavities are formed by thin sheets of tissue
composed of 2 layers
serous fluid
cells of the serous membranes produce a thin, and watery fluid
parietal layer
1 of the 2 layers of the serous membrane that is an outer layer that’s attached to the body wall and surrounding structures
visceral layer
2 of the 2 layers of the serous membrane that is an inner layer that is attached to specific organs
posterior body cavity
largely on the posterior side of the body and is divided into 2 smaller cavities
cranial cavity (posterior body cavity)
the area encased by the skull. contains the brain and a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid
vertebral (spinal) cavity (posterior body cavity)
the area encased by the vertebrae. contains the spinal cord and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid
anterior body cavity
largely on the anterior side of the body and has 2 main divisions
thoracic cavity (anterior body cavity)
located superior to a muscle called the diaphragm and encompasses the area encased by the ribs
there are smaller cavities within the thoracic cavity
pleural cavity
surrounds one of the lungs - located between 2 layers of a serous membrane called the pleural membrane
parietal pleurae
attached to the body wall and the surface of the diaphragm
visceral pleurae
attached to the surface of the lungs - between the 2 layers is a thin layer of serous fluid
abdominopelvic cavity (anterior body cavity)
is located inferior to the diaphragm and extends into the bony pelvis
there are 3 subcavities within this cavity
abdominal cavity
the 1st subcavity of the abdominopelvic cavity
the area superior to the bony pelvis
houses many organs including the liver, gallbladder, small intestine, stomach, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands, spleen, and much of the colon (large intestine)
pelvic cavity
the 2nd cavity of the abdominopelvic cavity
the cavity housed within the bony pelvis
contains certain sex organs, the urinary bladder, the rectum, and part of the colon
peritoneal cavity
the 3rd subcavity of the abdominopelvic cavity
is formed by a serous membrane called the peritoneal membrane
peritoneal membrane
forms the peritoneal cavity by this serous membrane
parietal peritoneum
the outer parietal peritoneum is attached to the body wall and surrounding structures
visceral peritoneum
the inner visceral peritoneum is attached to the surface of many of the abdominal and pelvic organs
peritoneal cavity
between the parietal and visceral peritoneum and is filled with serous fluid
retroperitoneal
organs that are posterior to the peritoneal cavity and includes the kidneys, adrenal glands, the sex organs, the urinary bladder, part of the colon, and part of the pancreas
parietal pleurae (cavity and structure)
cavity: thoracic
structure: lung
visceral pleurae (cavity and structure)
cavity: thoracic
structure: lung
parietal pericardium (cavity and structure)
cavity: thoracic
structure: heart
visceral pericardium (cavity and structure)
cavity: thoracic
structure: heart
parietal peritoneum (cavity and structure)
cavity: abdominopelvic
structure: small intestine, and others
visceral peritoneum (cavity and structure)
cavity: abdominopelvic
structure: small intestine, and others
anatomical section
different views of the internal structure of an organ or a body cavity. these views are obtained by making this along a specific plane
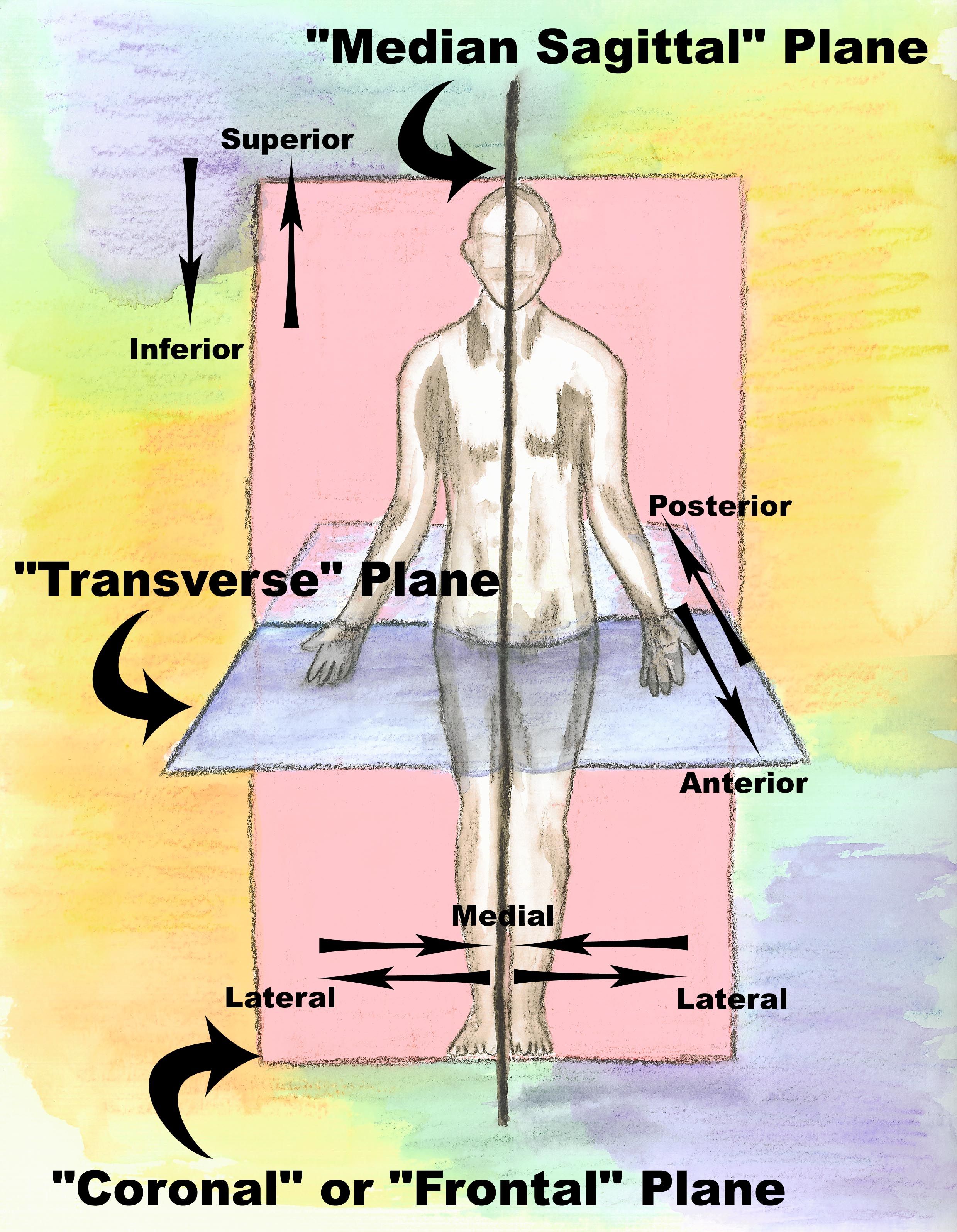
sagittal plane
a section along here divides the specimen into right and left parts
has 2 different variations
midsagittal sections (sagittal plane)
divides the specimen into equal right and left halves
parasagittal sections (sagittal plane)
divides the specimen into unequal right and left parts
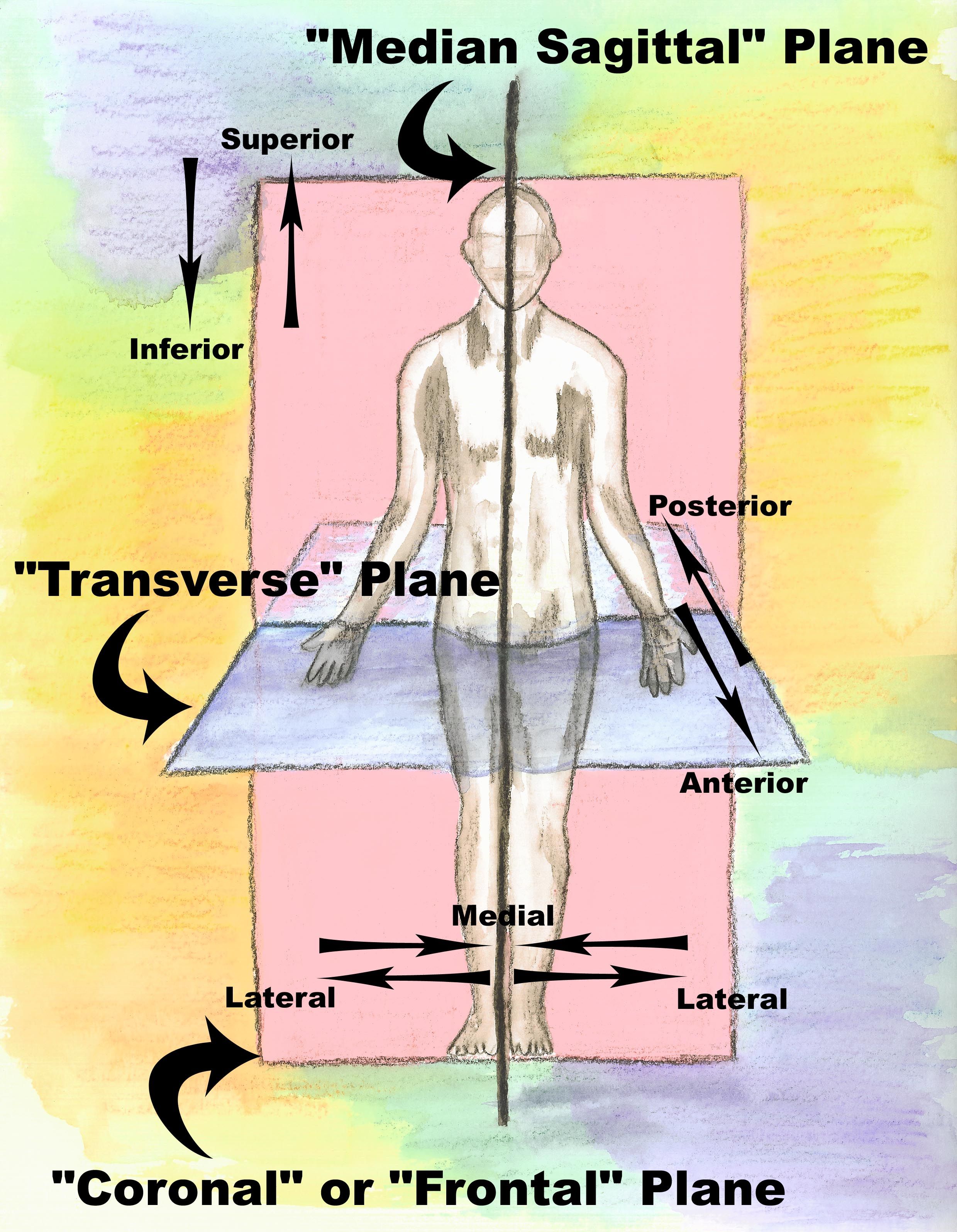
frontal plane (coronal plane)
divides the specimen into an anterior (front) part and a posterior (back) part
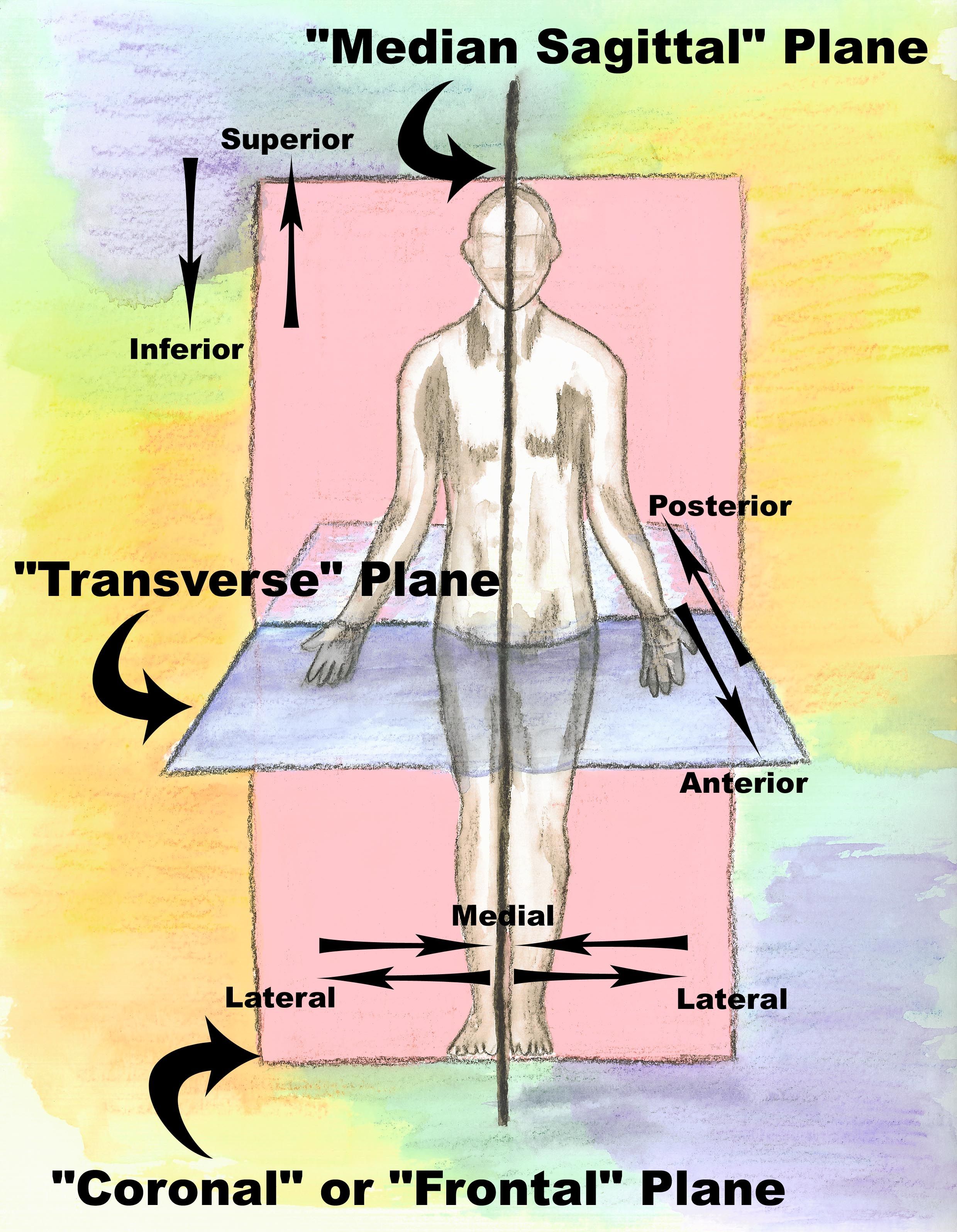
transverse plane (cross section) (horizontal plane)
divides the specimen into a superior (or proximal) part and an interior (or distal) part
organ systems
organs that are put into functional groups