Summary of eukaryotic cell structures and organelles
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
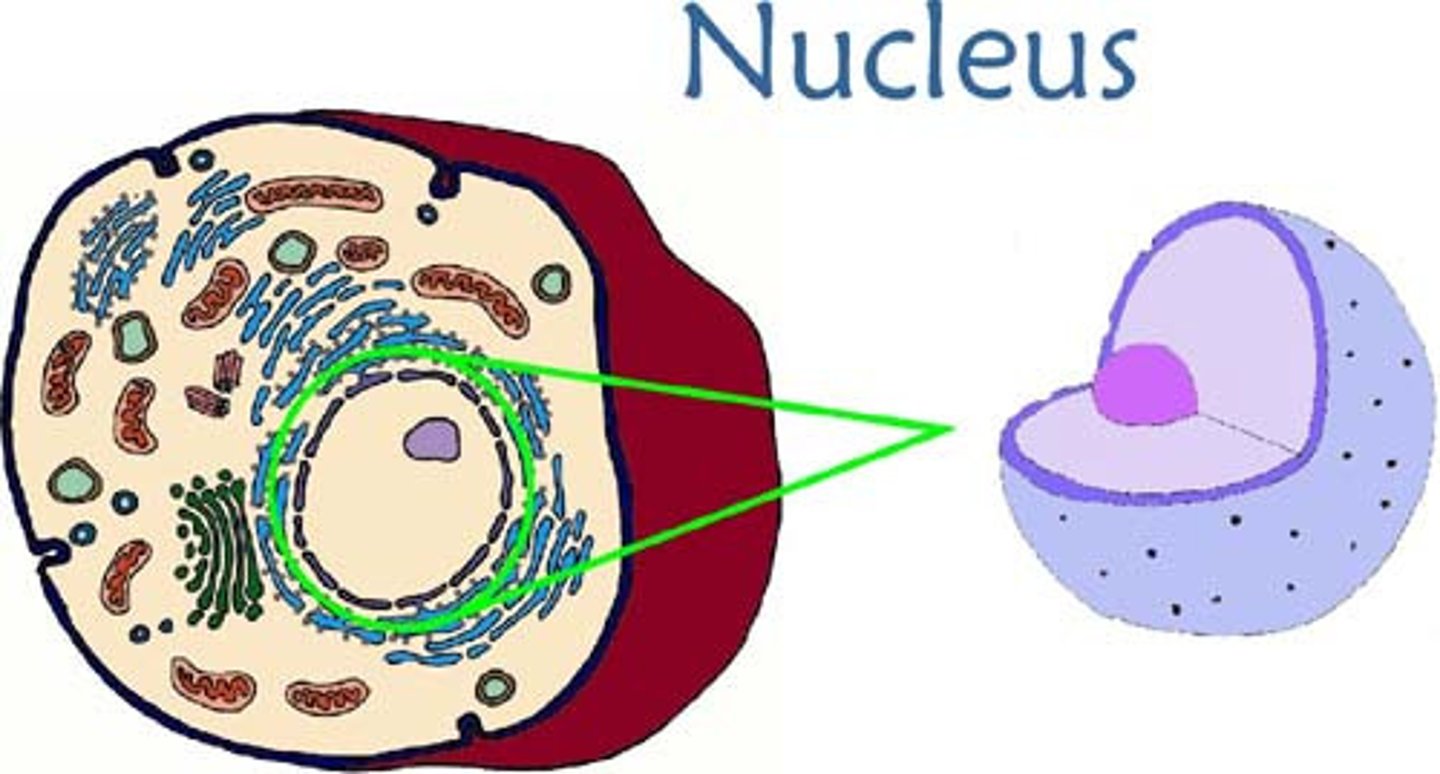
Nucleus
Largest and most prominent organelle. Separated from plasma membrane by the nuclear envelope and contains DNA information to make cellular proteins.
Cytosol
Jelly-like fluid that fills space between organelles. Provides an aqueous environment for cellular chemical reactions
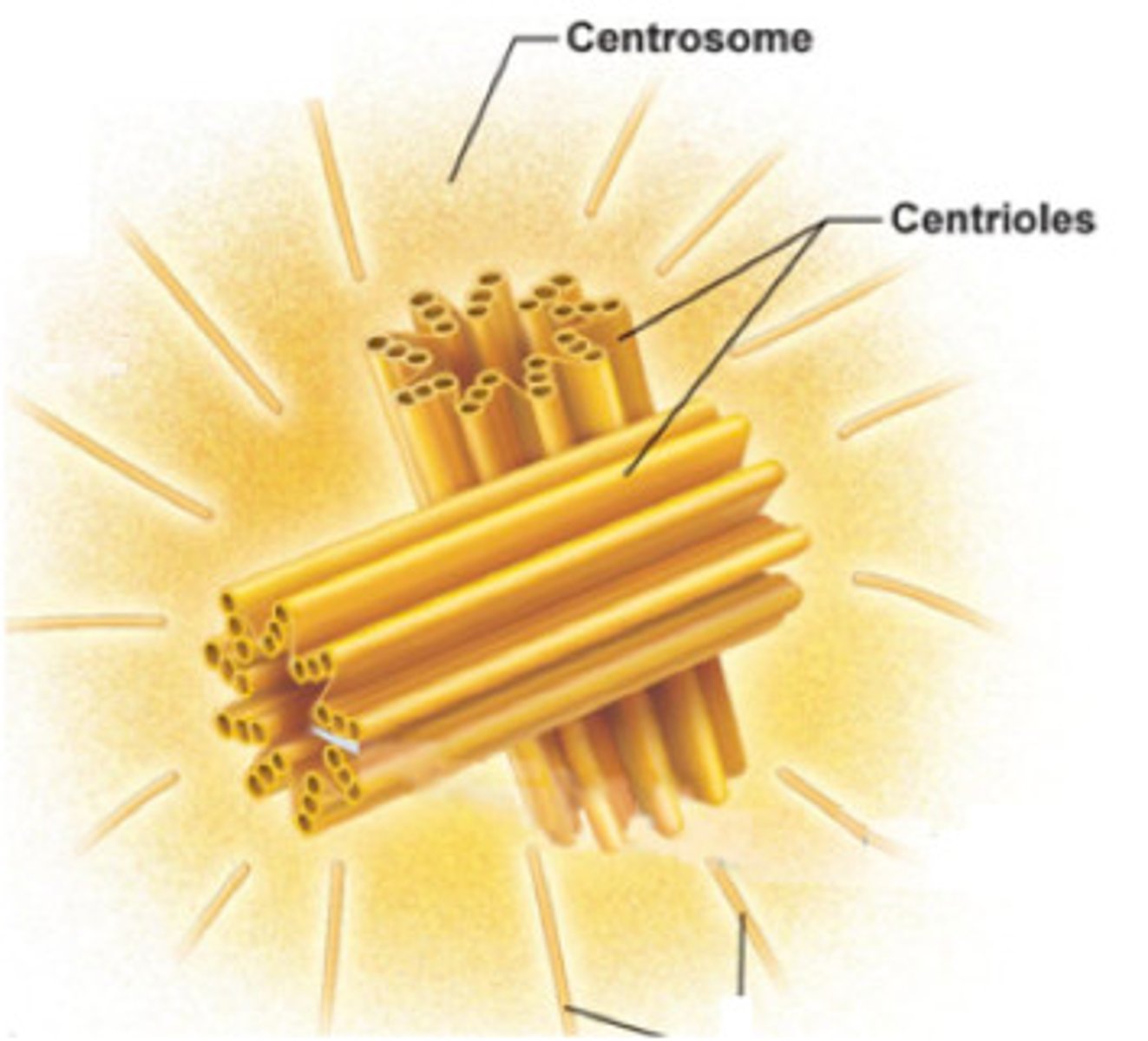
Centrosome
Grown from microtubules to create spindle-like shape. Organizes spindles for chromosome migration during cell division.
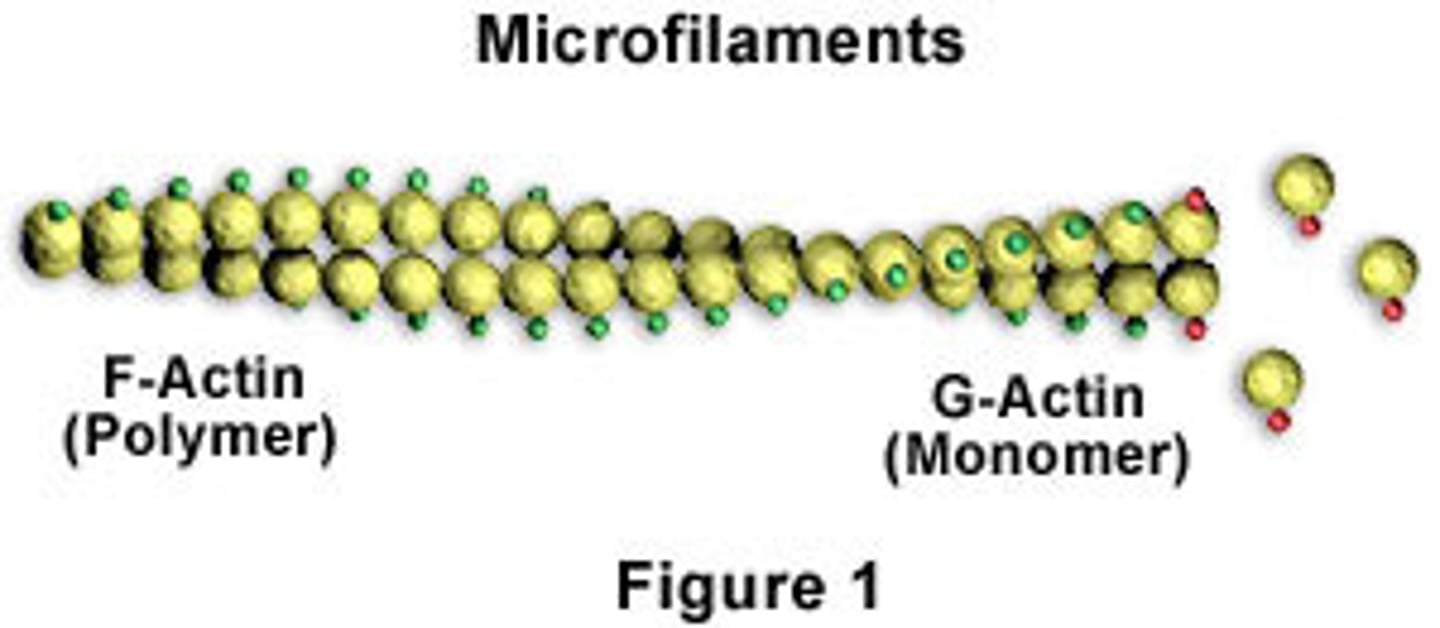
Microfilament
Thin
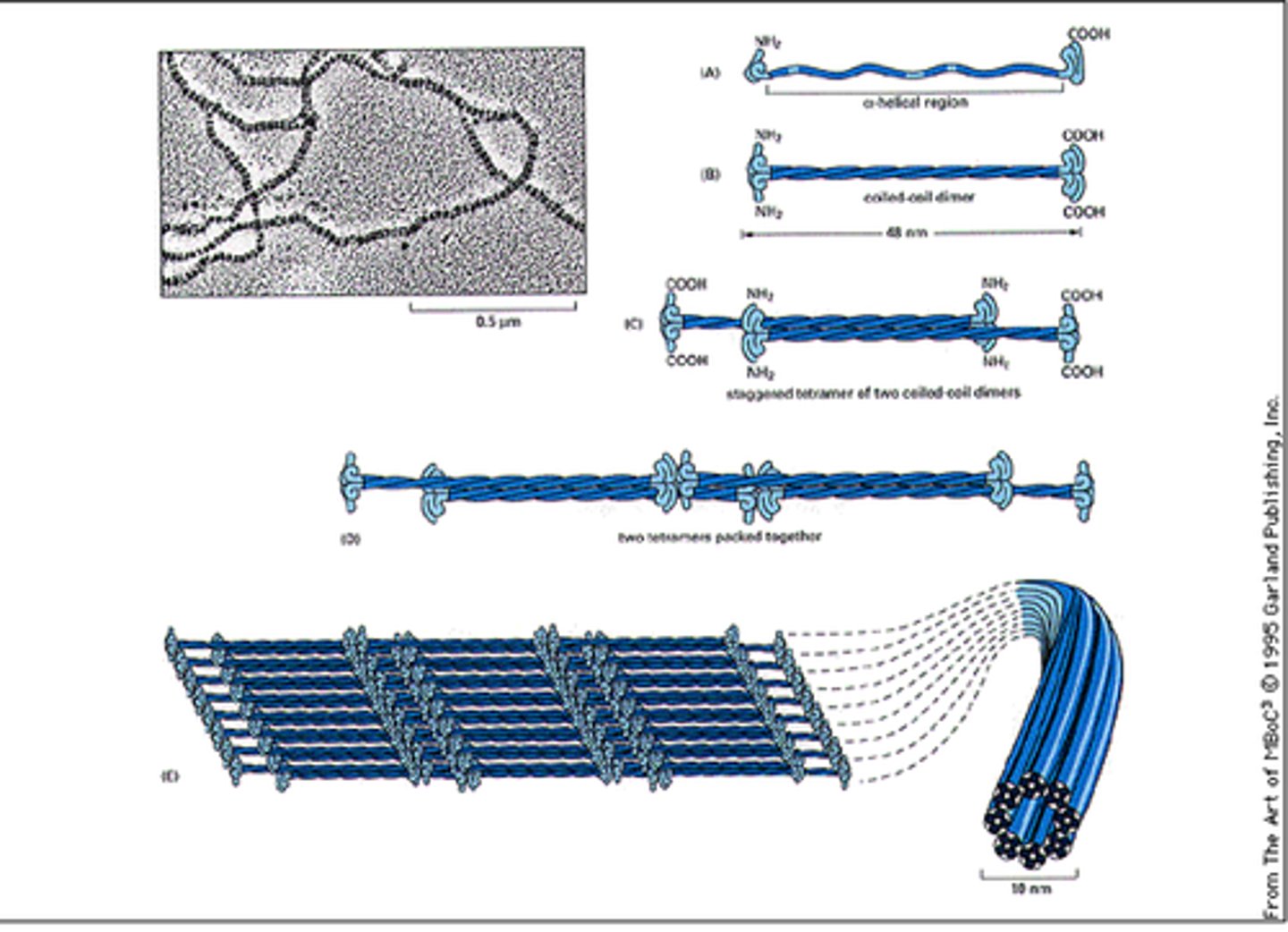
Intermediate filament
Composed of different fibrous proteins such as keratin. Provides great tensile strength and anchors organelles such as the nucleus.
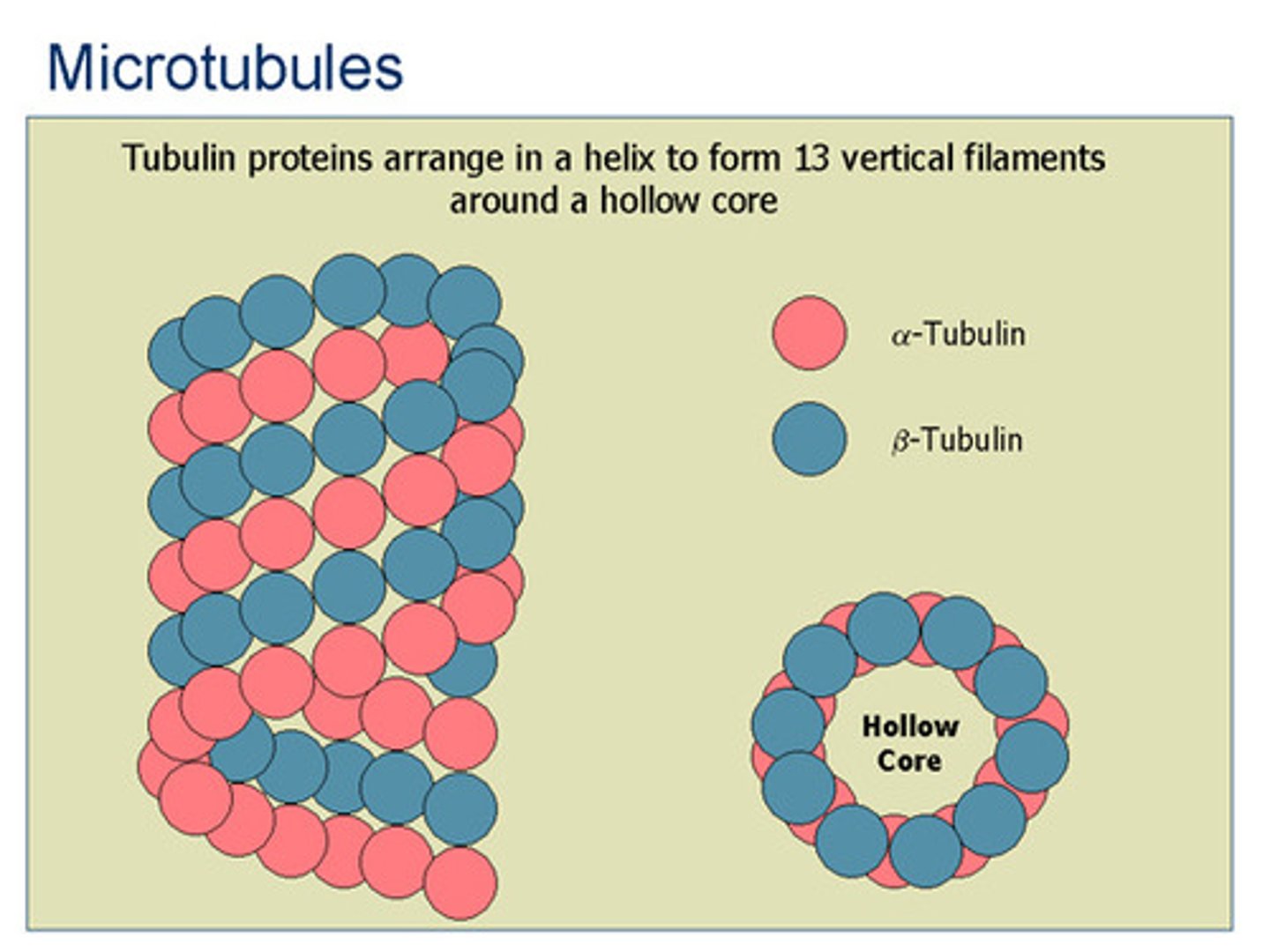
Microtubule
Large cytoskeleton made of tubulin that can rapidly assemble and disassemble. Acts as "tracks" for organelle movement and chromosome migration during cell division. Also forms cilia and flagella
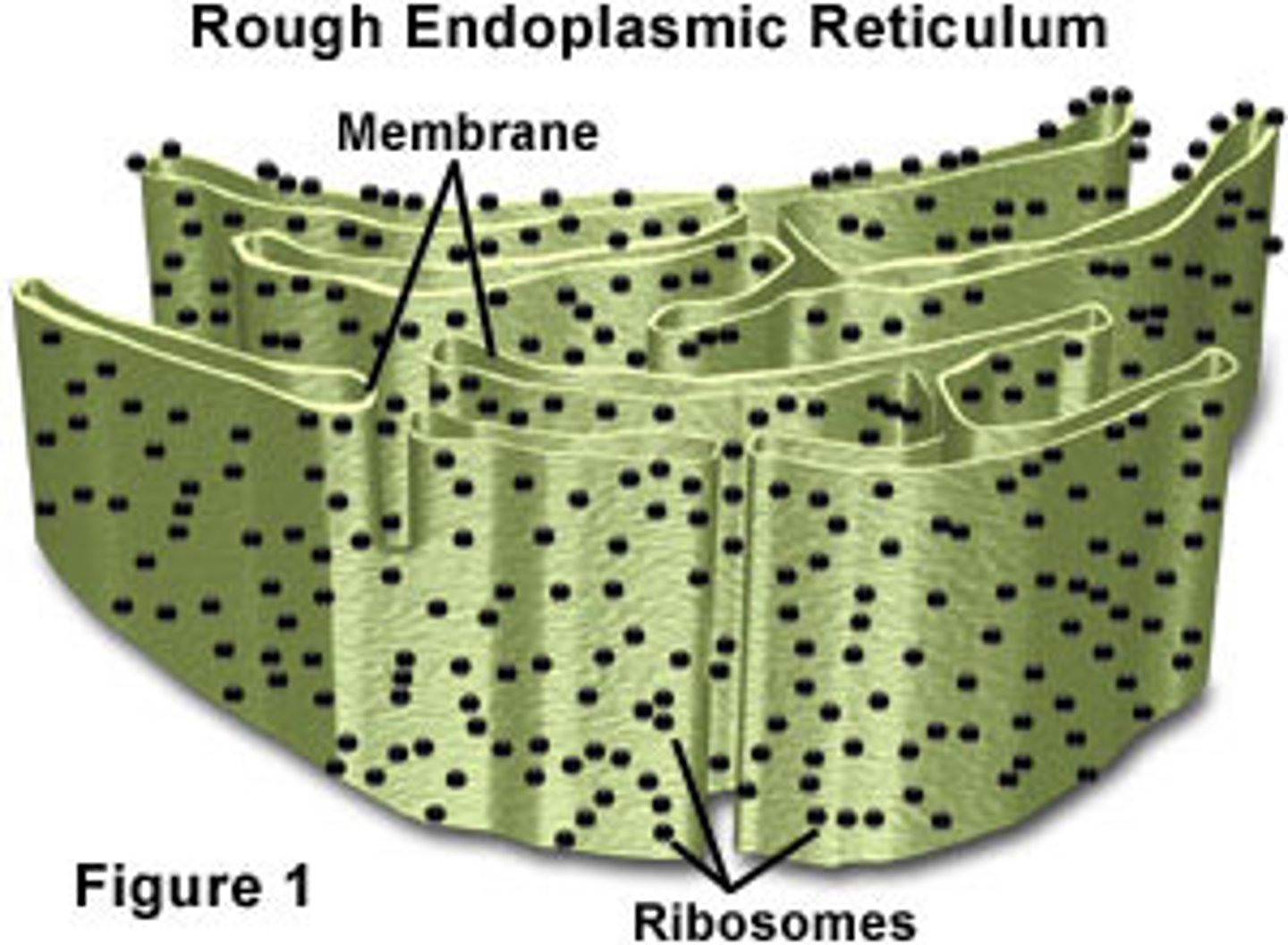
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in synthesis of secretory proteins, membrane proteins, and organelle proteins.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down. Stores calcium ions.
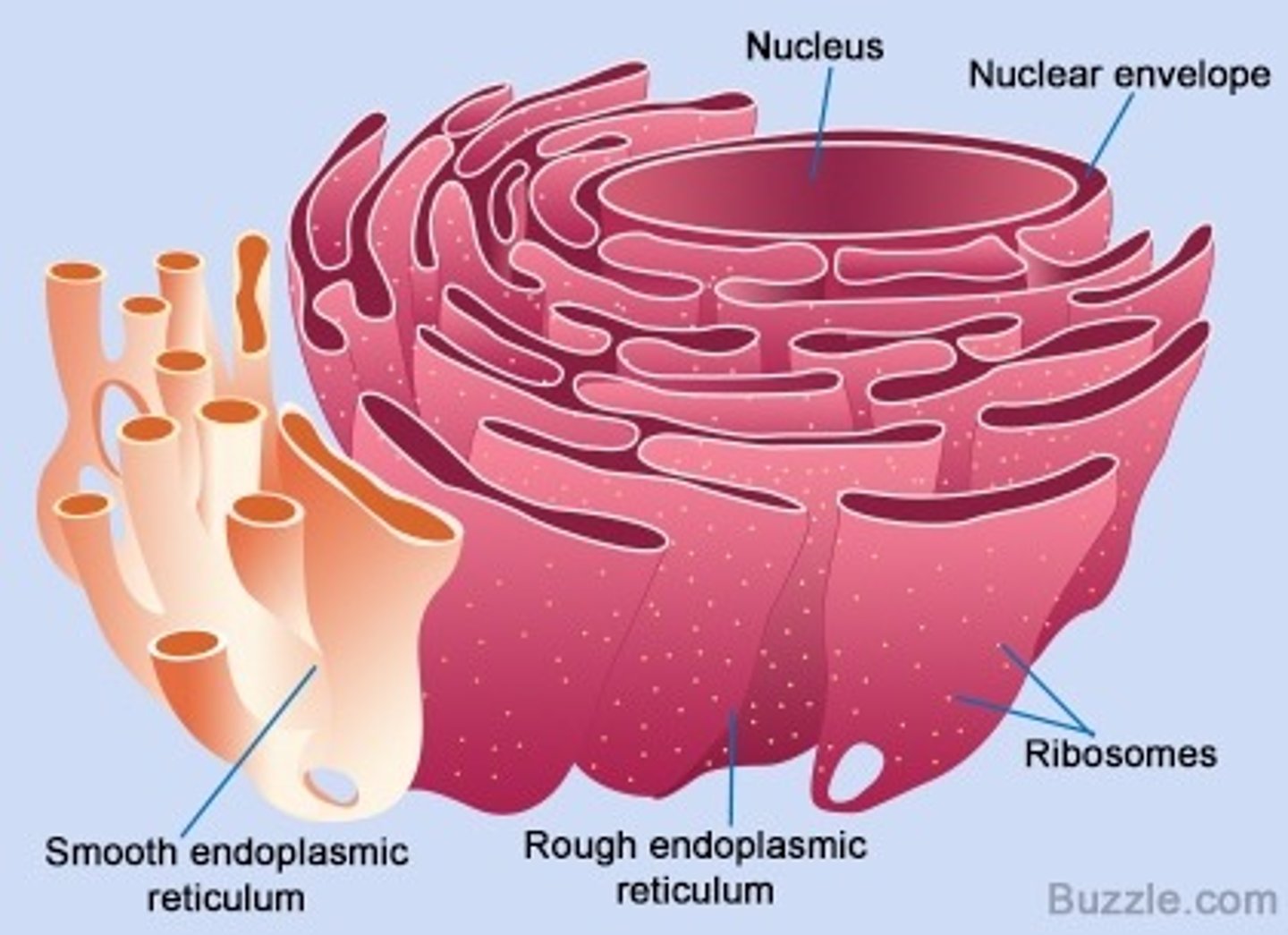
Ribosome
Translate one biological molecule into another. aka synthesis of proteins

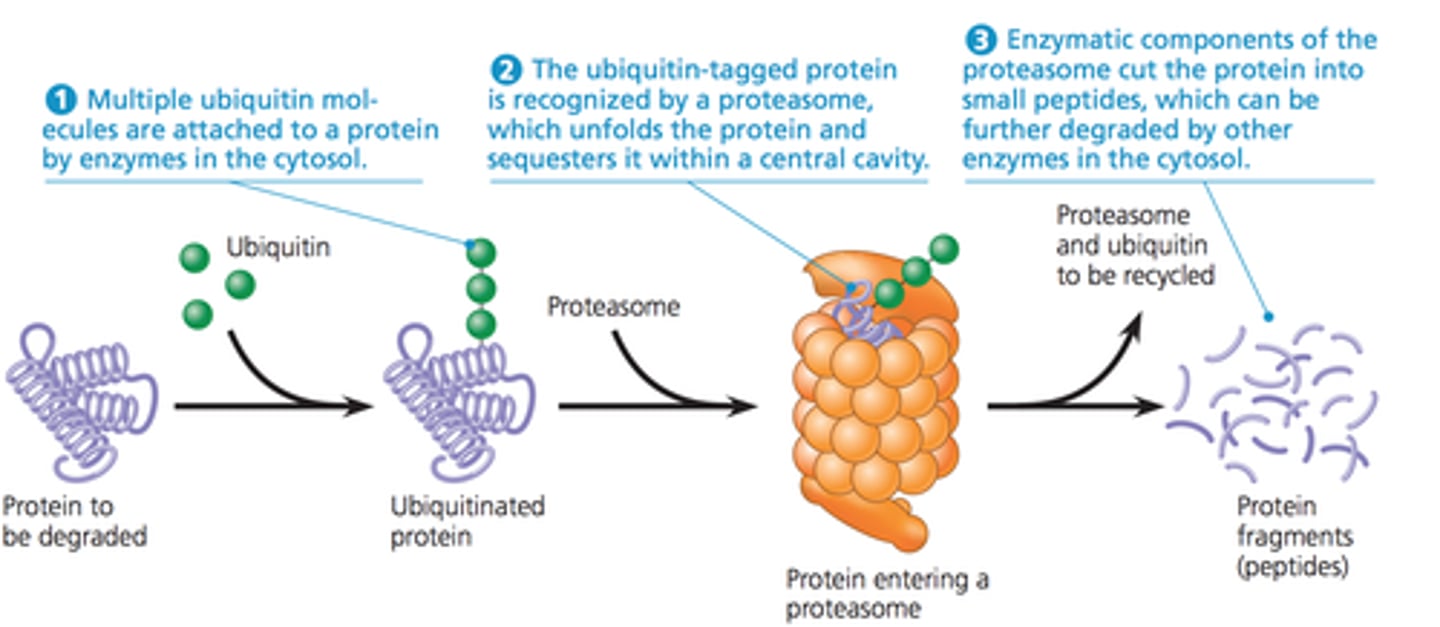
Proteasome
A giant protein complex that recognizes and destroys proteins tagged for elimination by the small protein ubiquitin. Breaks large polypeptides into smaller polypeptides. Defects of it result in diseases such as parkinson's and alzheimers
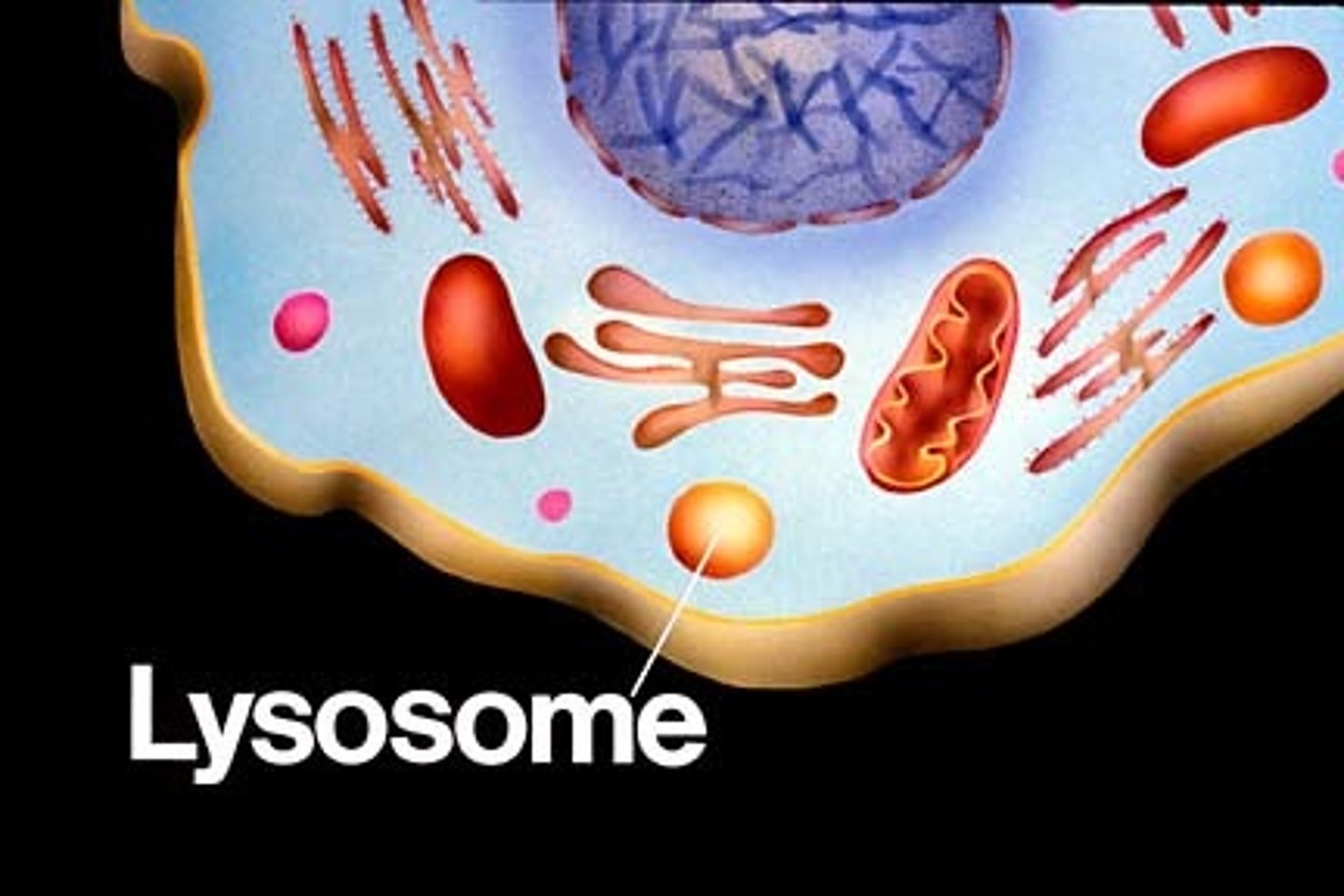
Lysosome
Membrane bound-sacs containing digestive enzymes. When fused with molecules or damaged cell components it breaks them down. Also actively pumps H+ into the interior of the cell to maintain pH 5.
Peroxisome
Membrane-bound compartments that contains oxidases to metabolize fatty acids and detoxify alcohols. Contains catalase to degrade toxic metabolic byproducts such as hydrogen peroxide.
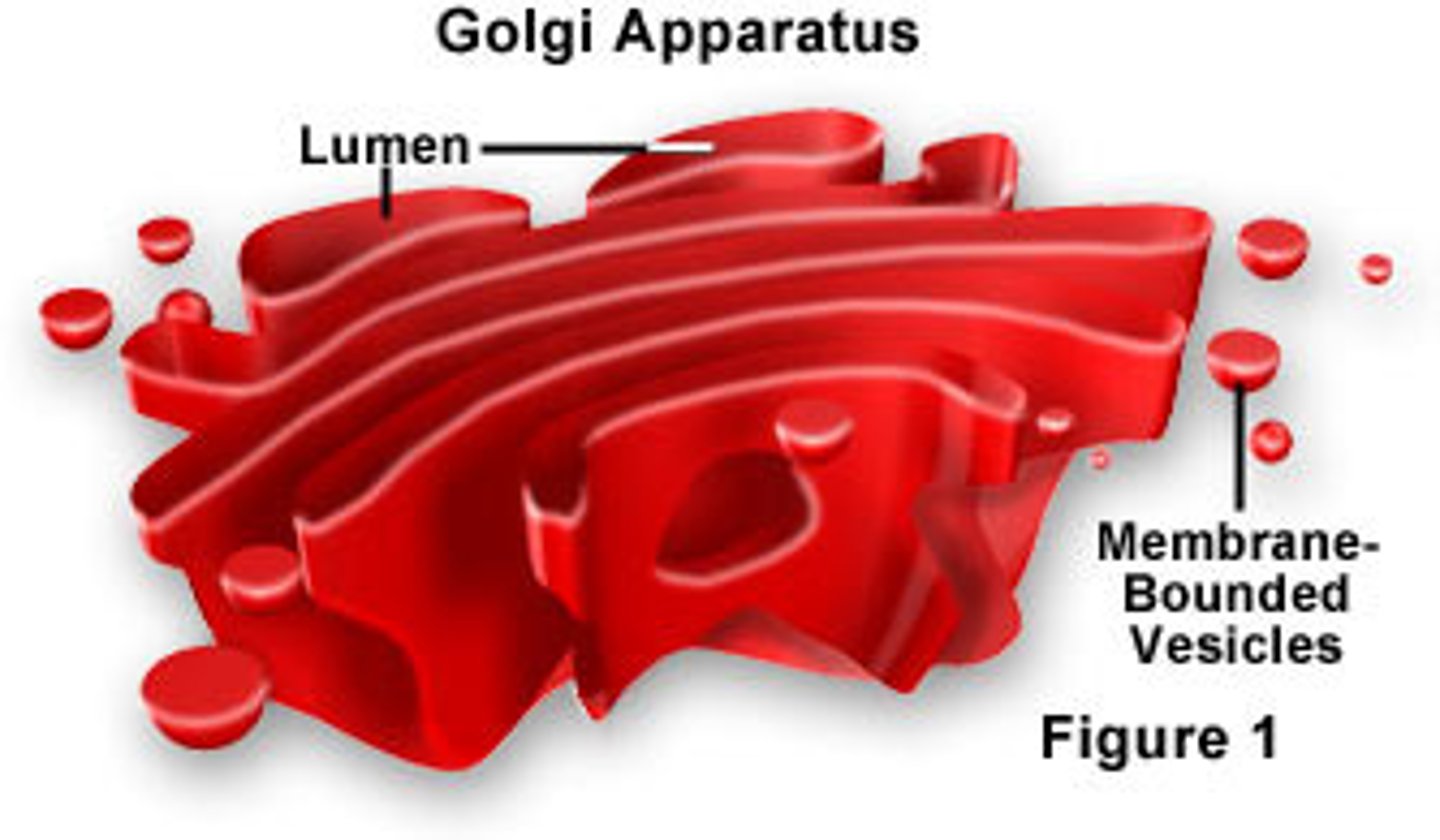
Golgi apparatus
Consists of stacks of membranous sacs that perform final protein modifications. Receives cellular proteins from RER and then are modified, stored, and packaged into vesicles for export to different destinations.
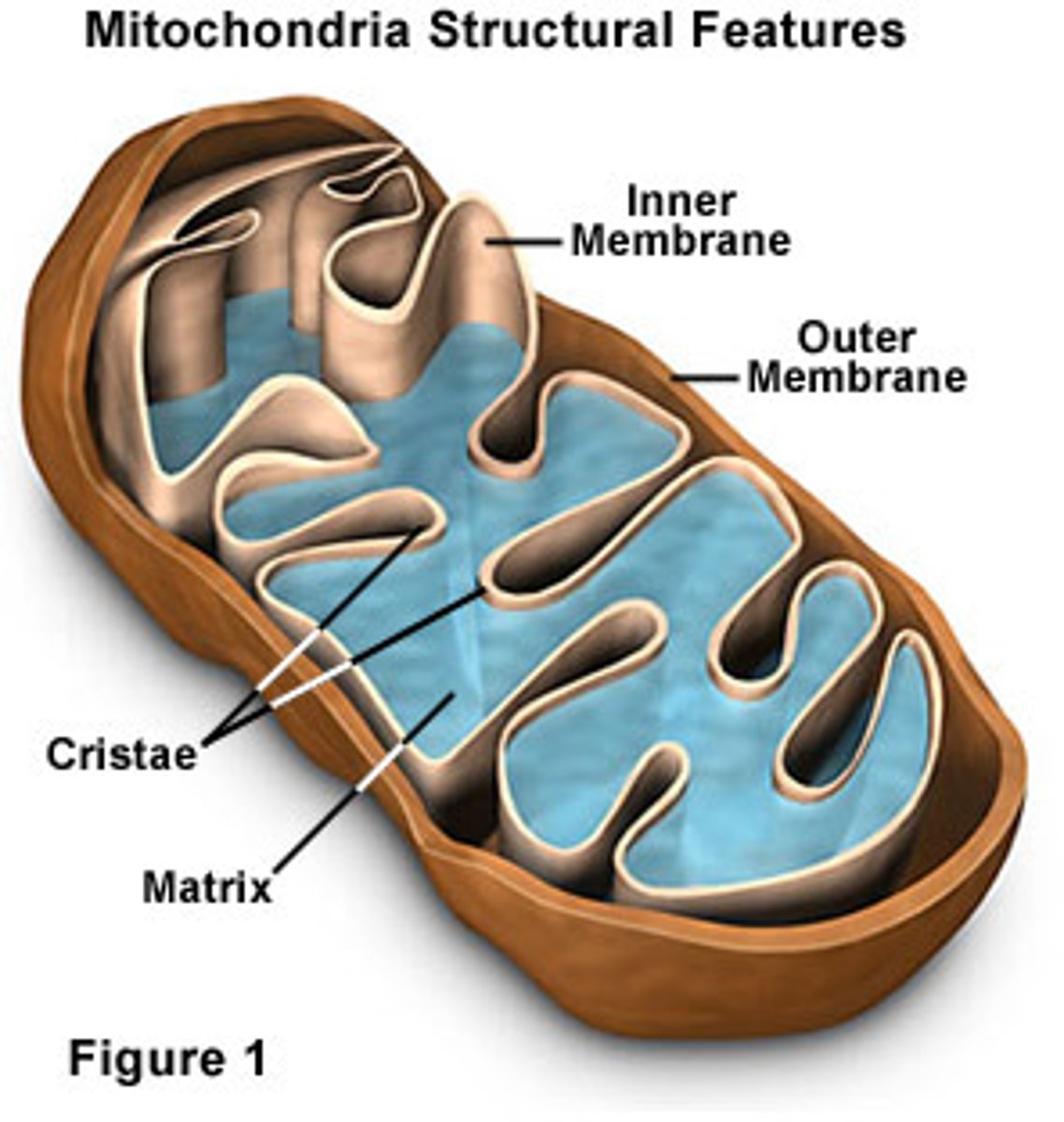
Mitochondrion
Bounded by inner and outer mitochondrial membranes. Site of aerobic cellular respiration where chemical reactions that extracts chemical potential energy from glucose and permits the cell to store it as ATP in the presence of oxygen
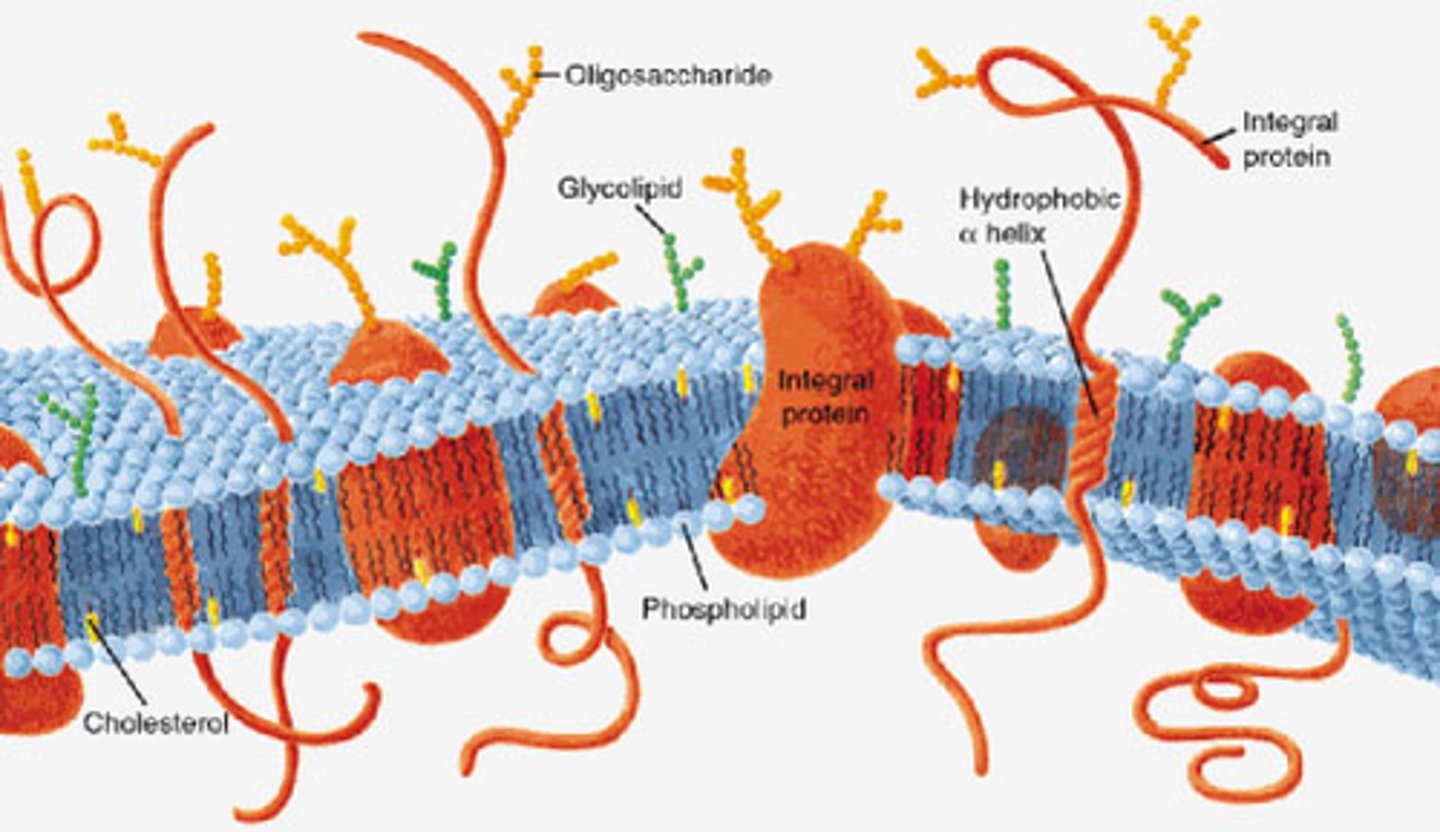
Plasma membrane
Flexible phospholipid bilayer that separates the external and internal environment. Regulates exchange of materials with the environment and facilitates communication between cells
Cilia
Short bundles of microtubules that paddles through surrounding fluid like oars and are found on cells in the upper respiratory tract and oviducts.
Flagellum
Long bundles of Microtubules that whip through surrounding fluid to propel cells. Found on sperm cells