Chapter 5, Lesson 2: Epithelial Tissue
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 5, Lesson 2 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Epithelia
Sheets of closely adhering cells that cover body surfaces and life body cavities; they have a high rate of mitosis
Avascularity
Lacking blood vessels; epithelia have this quality and are nourished by underlying connective tissue
Functions of epithelia
Protect deeper tissues from injury and infection
Produce and release chemical secretions
Excrete wastes
Absorb and filter substances
Sense stimuli
Basement membrane
The layer between epithelium and the underlying connective tissues; comprised of collagen and glycorproteins to anchor it down
Basal surface
Cell surface facing the basement membrane; the bottom
Apical surface
Cell surface that faces away from the basement membrane; the top
Lateral surface
Cell surface between the basal and apical surface; the sidewall
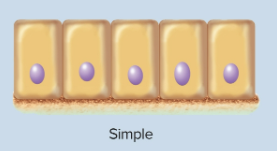
Simple epithelia
Contains one layer of cells and are named by their shape; all touching the basement membrane
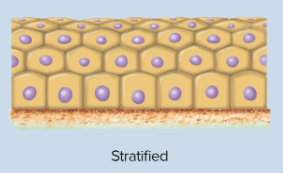
Stratified epithelia
Contains many layers of cells are named by their topmost (apical) shape; some may not touch the basement membrane and can rest on others
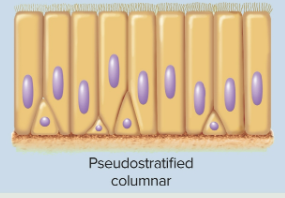
Pseudostratified columnar epithelia
Epithelia that may appear to be stratified but only differentiated by height of cells—located in the respiratory tract, sex cells, and male urethra, as it secretes and propels mucus
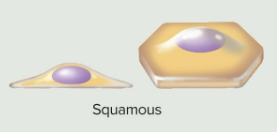
Squamous epithelia
Cells that are thin and scaly, flattened
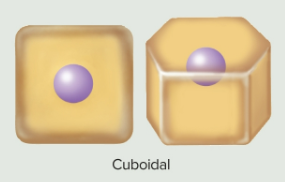
Cuboidal epithelia
Epithelia that are cube-shaped, square, or round
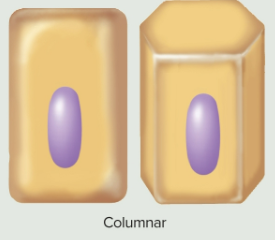
Columnar epithelia
Epithelia that are tall or narrow, shaped like columns
Goblet cells
Wineglass-shaped mucus-secreting cells in simple columnar and pseudostratified epithelia
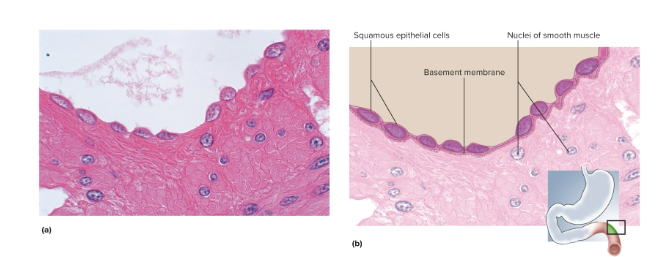
Simple squamous epithelium
A single row of thin cells with nuclei near the basement membrane; they permit rapid diffusion or transport of substances and secrete serous fluid—located in the alveoli (air sacs), capillaries, and endothelium
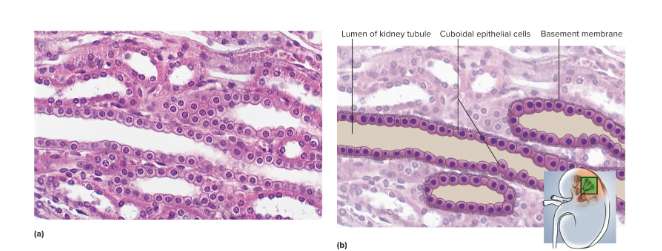
Simple cuboidal epithelium
A single layer of square or round cells; they absorb and secrete substances and aid mucus production and movement—located in the liver, thyroid, salivary glands, and kidney tubules
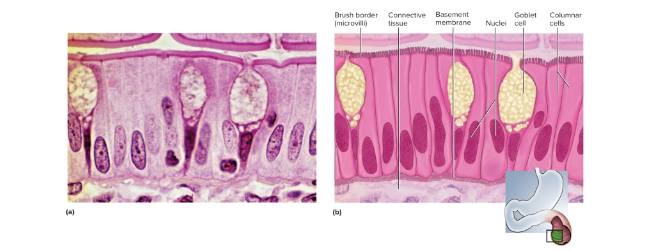
Simple columnar epithelium
A single row of tall, narrow cells; they are in the border of microvilli and aid in absorption and secretion of mucus—located in the GI tract as part of cilia and lining for absorption
Stratified squamous epithelium
The most widespread epithelium in the body; the deepest layers undergo continuous mitosis as cells are pushed up and die or flake off—lines oral cavity and anal canal
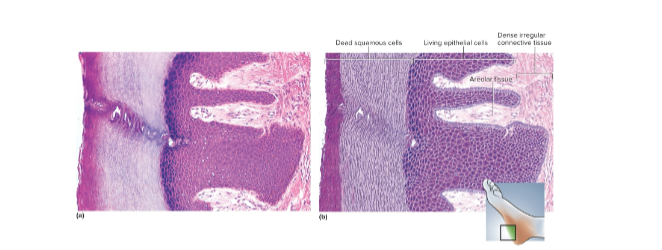
Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple cell layers, the cells become flat and scaly toward the surface; protects from outside by resisting abrasion, preventing water loss, and penetration by organisms—located in epidermis, palms, and soles
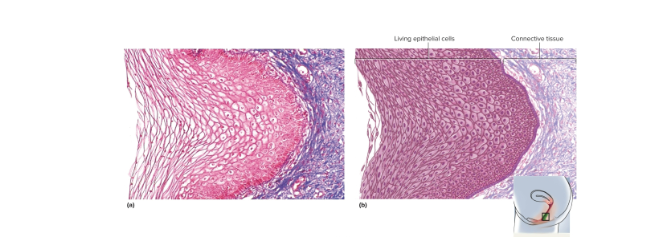
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Same as keratinzed epithelium without surface layer of dead cells, also resists abrasion and penetration—located on tongue, esophagus
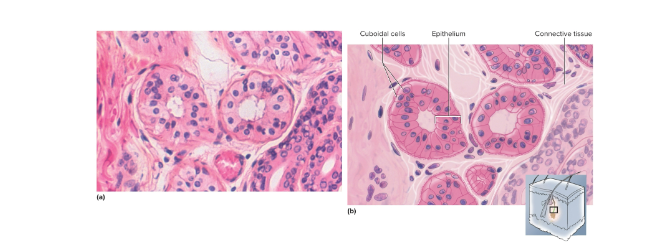
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
Two or more layers of square or round surface cells; secretes sweat, produces sperm, and hormones in sweat glands and reproductive organs
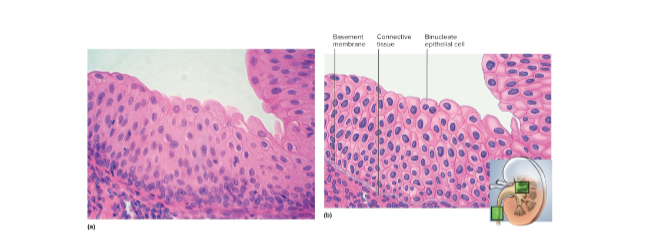
Urothelium (transitional epithelium)
Multilayered epithelium that can stretch between round and flat; located in ureter and bladder for filling of urinary tract