Joints: Anatomy and Physiology (chp 9)
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A series of flashcards covering key terms and definitions related to the anatomy and physiology of joints.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Joint
-A point of contact between two or more bones, cartilage and bone, or teeth and bone
-aka articulation/arthrosis
Fibrous Joints
-lack articular cavity, held together by dense irregular connective tissue, little/no movement
-sutures; synotosis
-Syndesmoses; interosseous ligament, interosseous membrane, gomphosis
Cartilaginous Joints
-lack articular cavity, held tgt with cartilage connective tissue, little/no movement
-eg; synchondroses, symphyses
Synovial Joints
-has articular cavity, connecting bones covered with articular cartilage held tgt by ligaments, surrounded/sealed off by articular capsule
-contains bursae (sac’s, cushion movements of body parts) n tendon sheaths (tube like bursae, helps with friction around tendons)
-large rom
Functional Joint Classifications
-synarthoses: immovable, suture
-ampiarthroses: slightly moveable, pubic symphysis
-diarthoses: freely moveable, elbow
Sutures
Fibrous joints found between skull bones; they are immovable.
Flexion
Decrease in angle between articulating bones, usually in a forward direction.
Extension
Increase in angle between articulating bones, usually backwards.
Abduction
Movement of bone away from the midline of the body.
Adduction
Movement of bone toward the midline of the body.
Gliding
-flat bones moving back n forth or side to side, little change in angle between bones
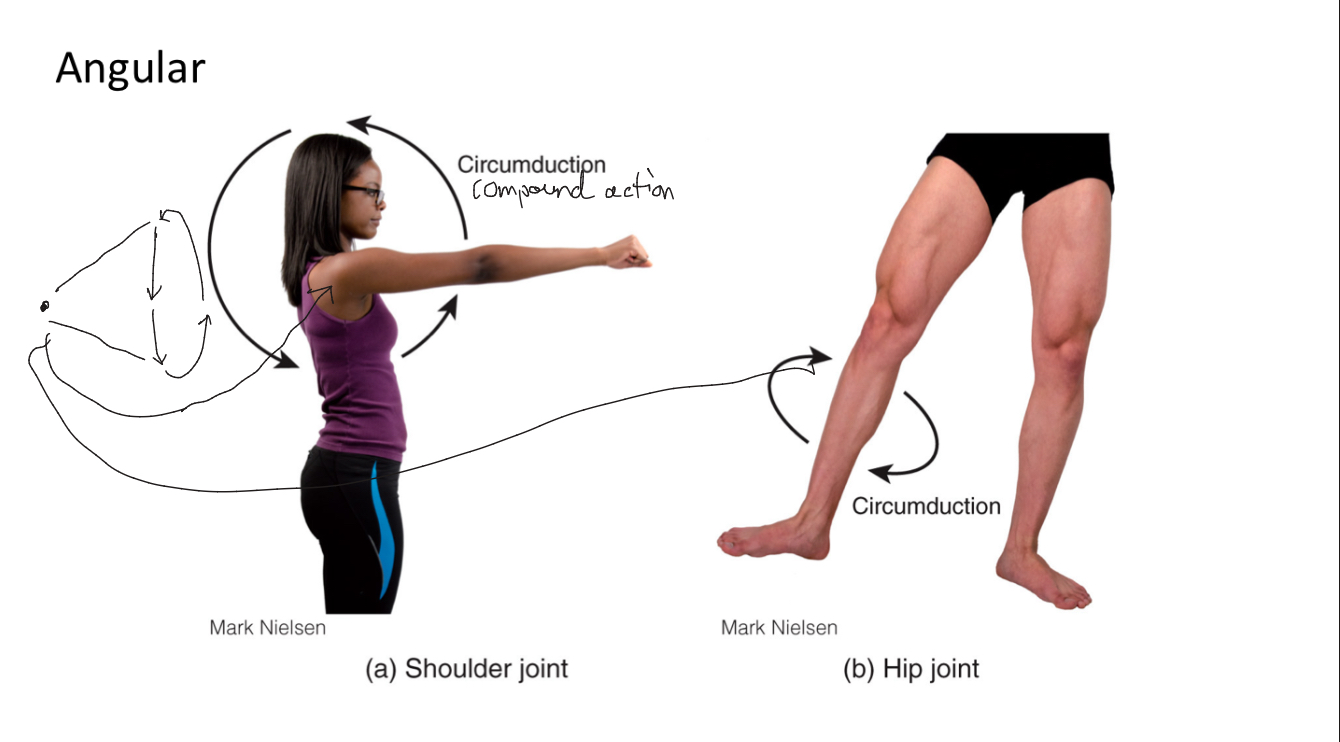
Circumduction
Circular movement involving flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
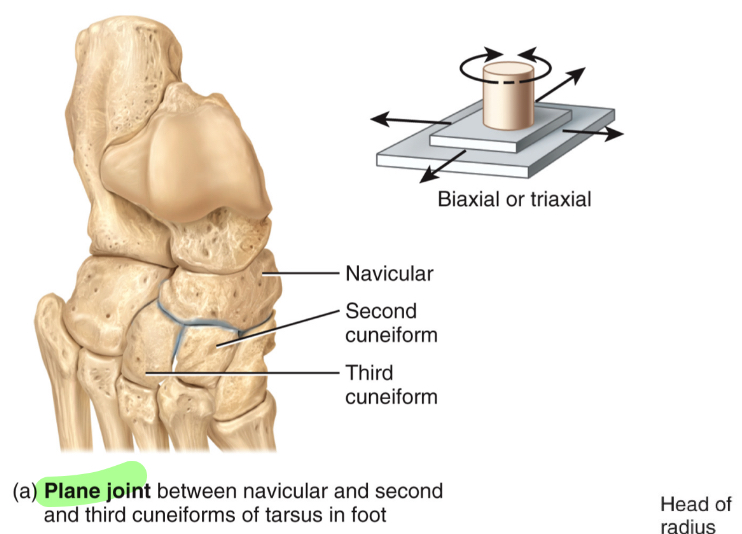
Plane Joint
Articulated surfaces flat or slightly curved
back/forth, side/side, rotate
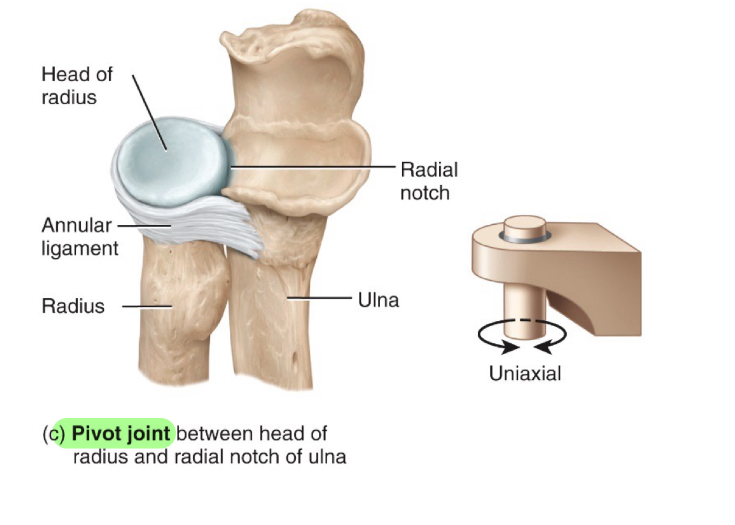
Pivot Joint
rounded or pointed surface fits into ring formed by bone n ligament
Rotation
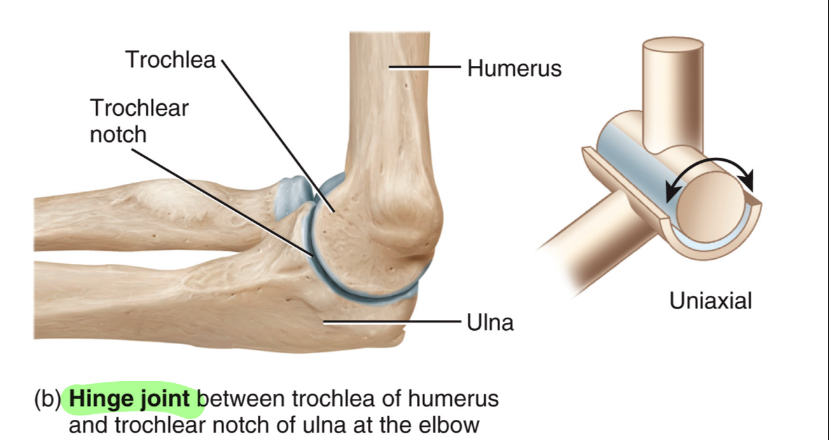
Hinge Joint
convex surface fits into concave surface
Flexion/extension
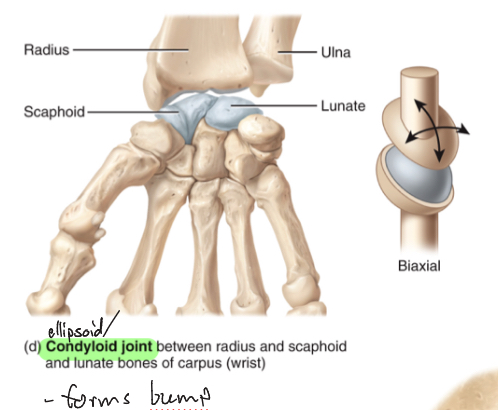
Condyloid Joint
oval shaped projection fits into oval shaped depression
Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction
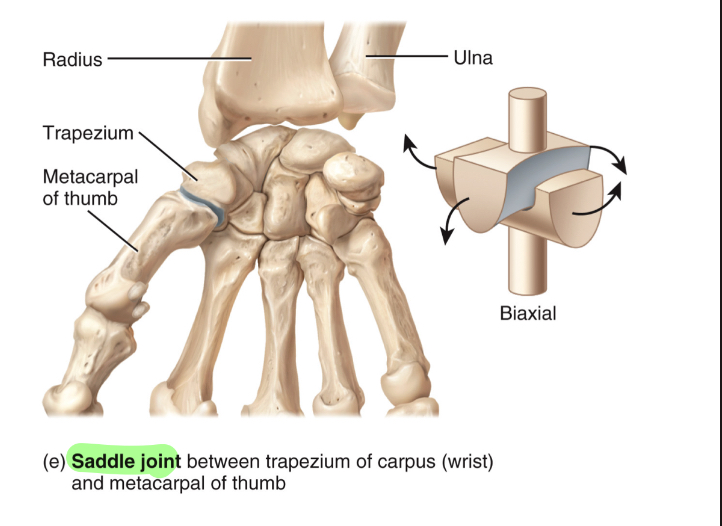
Saddle Joint
articular surface of one bone is saddle-shaped, articular surface of other bone “sits in saddle
Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction
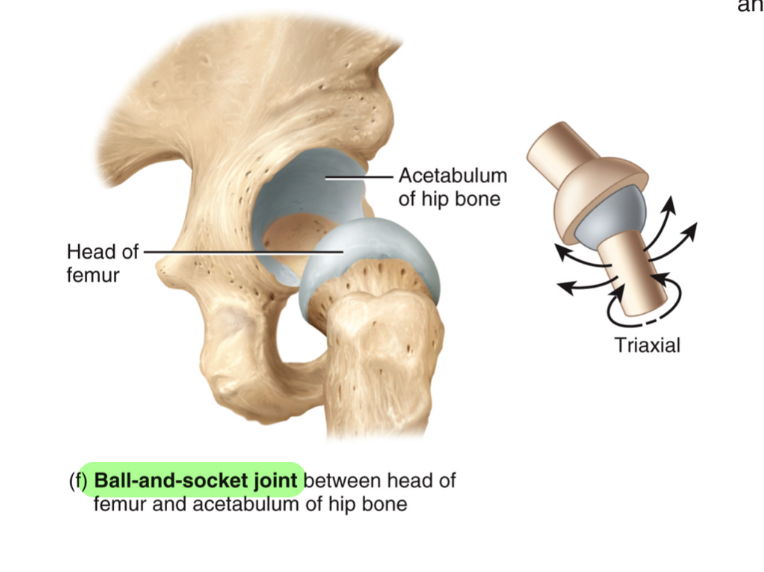
Ball n Socket Joint
ball like surface fits into cuplike depression
Flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, rotation
Factors Affecting ROM at Synovial Jointa
structure/shape of articulating bones
Strength n tension of joint ligaments
Muscle arrangement n tension
Soft part contact
Hormones
Disuse
Suture
-between skull bones
-fibrous
-no movement
Atlanto-Occipital Joint
-between atlas n condyles of occipital bone
-synovial (Ellipsoid)
-nods head up n down, lat flexion of head
Atlanto-Axial Joint
-between atlas n axis
-synovial (pivot)
-rotate head
Radioulnar Joint
-radius head n notch of ulna
-synovial (pivot)
-Forearm rotation
Wrist Joint
-Radius n metacarpals
-synovial (ellipsoid)
-lots of movement of wrist
Interphalangeal Joint
-heads of phalanges n bases of distal phalanges
-synovial (hinge)
-flexion/extension of phalanges
Pubic Symphysis Joint
-between anterior surfaces of hip bones
-cartilaginous (symphysis)
-slight movement, more during pregnancy
Ankle (talocrural) Joint
-between tibia n talus
-synovial (hinge)
-dorsiflexion/plantar flexion
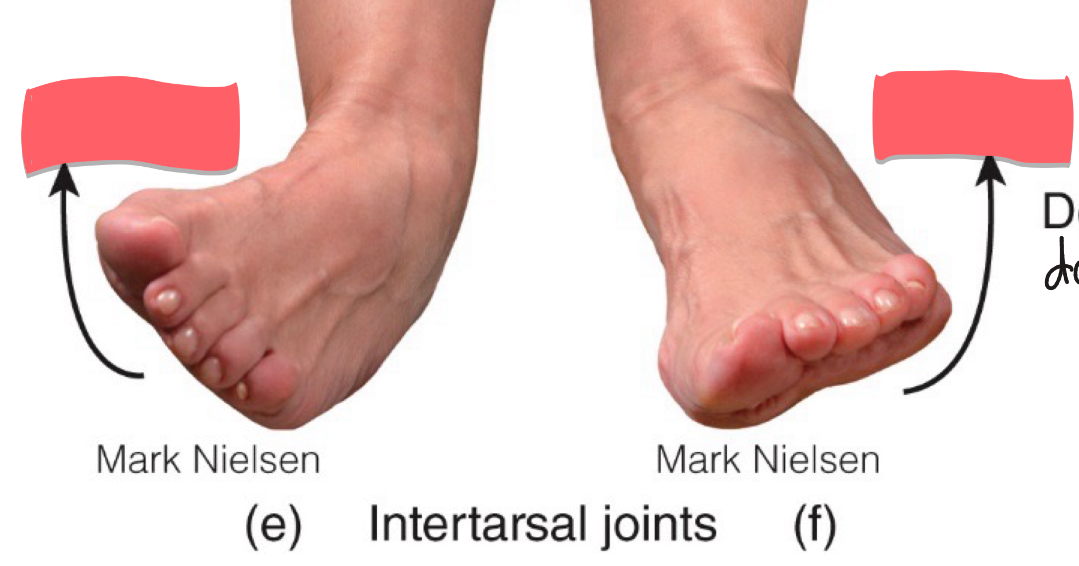
Intertarsal Joint
-talus n tarsus
-synovial (plane and saddle)
-inversion n eversion of foot
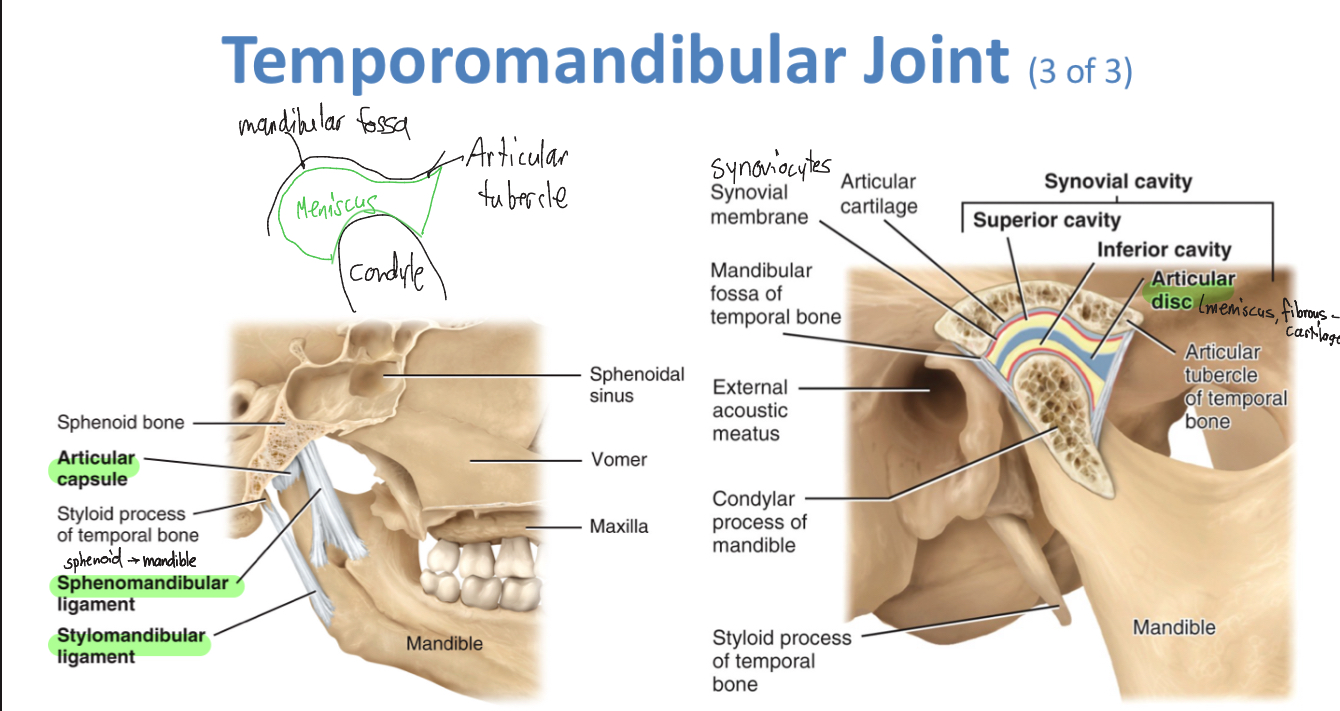
TMJ (synovial)
-meniscus, lateral ligament, sphenomandibular ligament, stylomandibular ligament
-
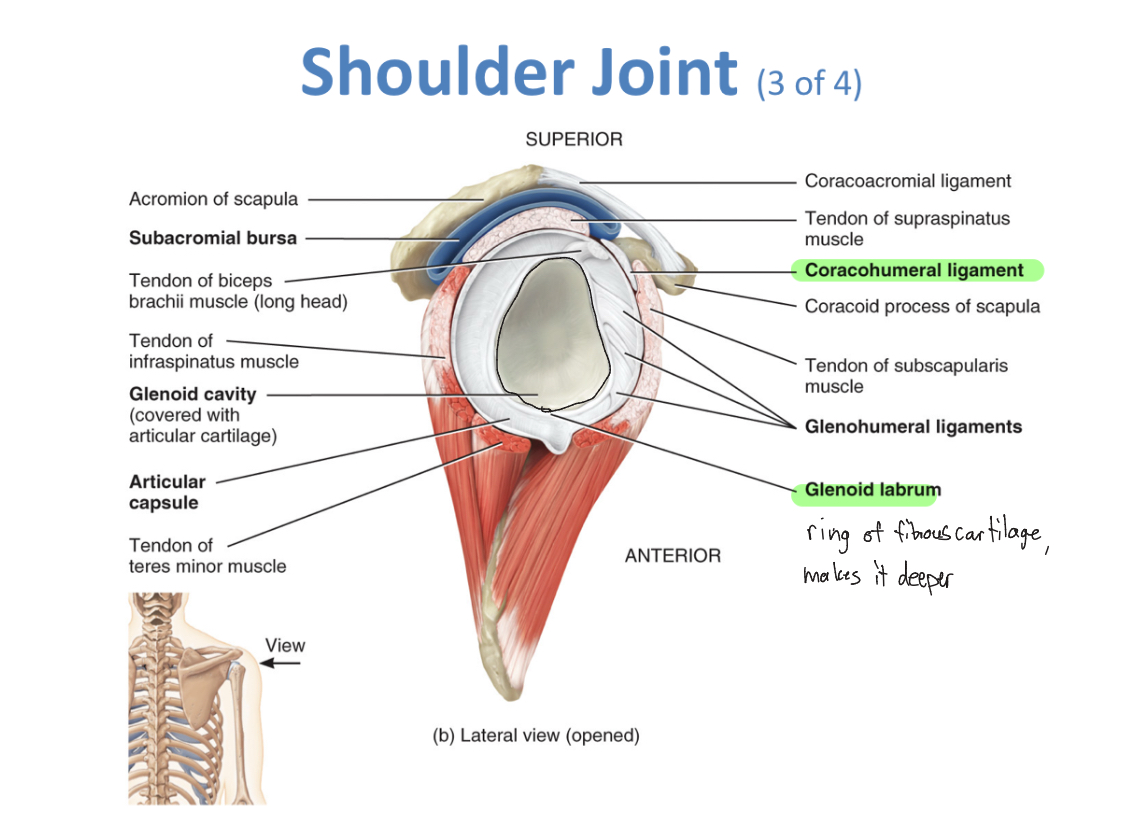
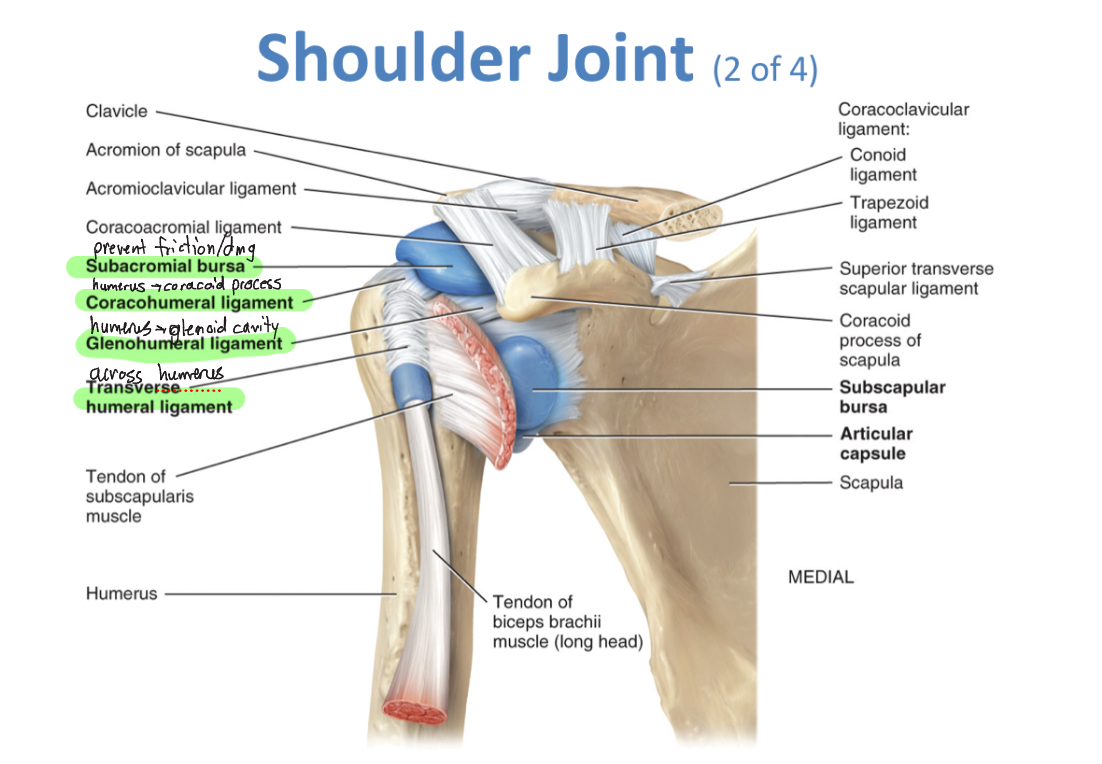
Shoulder Joint (ball n socket)
-coracohumeral ligament, glenohumeral ligaments, transverse humeral ligament, glenoid labrum, bursae
Rotator Cuff Injury
An injury caused by wear and tear, often associated with repetitive shoulder motion.
Dislocated Shoulder
Condition where the head of the humerus becomes displaced from the glenoid cavity.
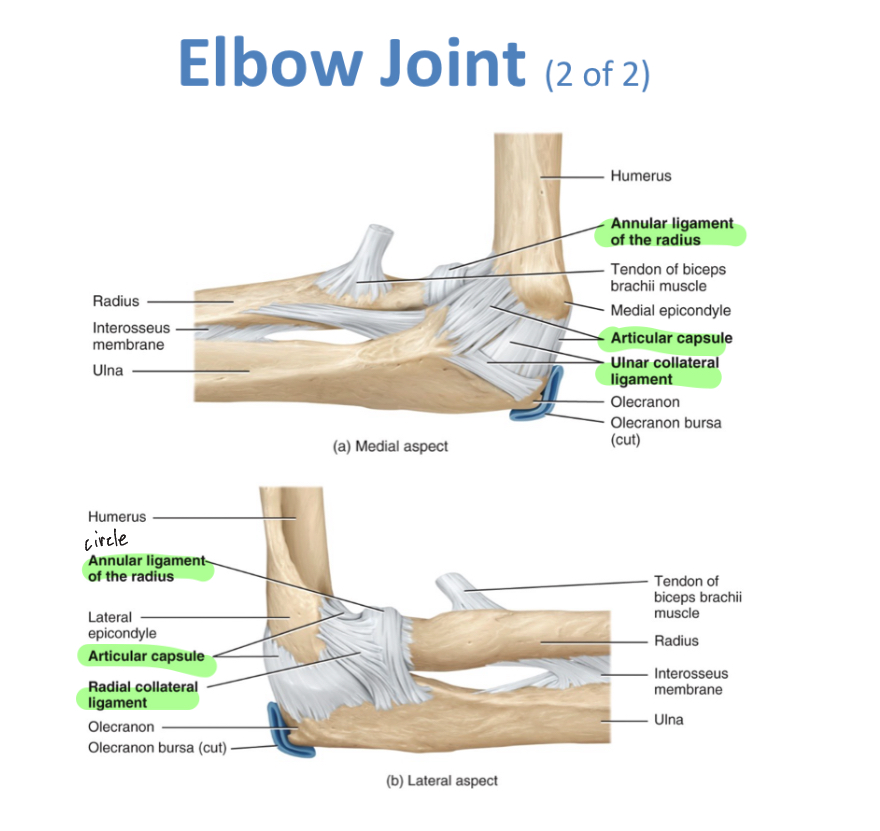
Elbow Joint (hinge)
Ulnar collateral ligament, radial collateral ligament, annular ligament of radius
-tennis elbow: pain at lateral epicondyle of humerus
-littlle league elbow: medial epicondyle inflammation
-radial head dislocation:radius head slides past radial annular ligament
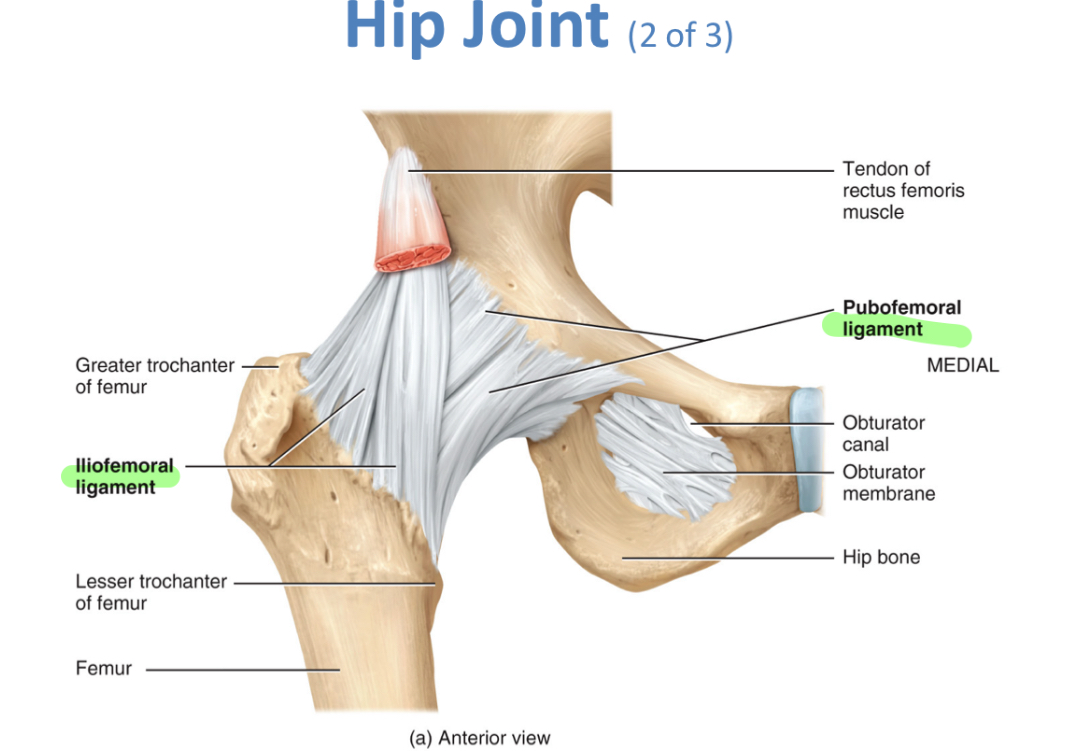
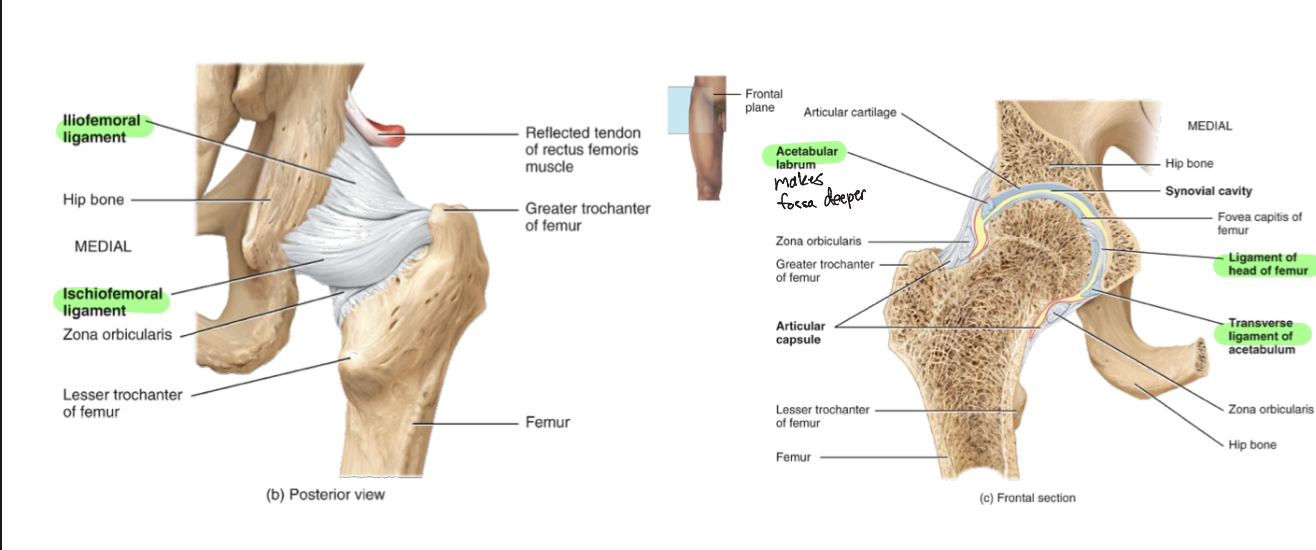
Hip Joint (Ball n socket)
-Iliofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, ischiofemoral ligament, ligament of the head of the femur, acetabular labrum, transverse acetabular ligament
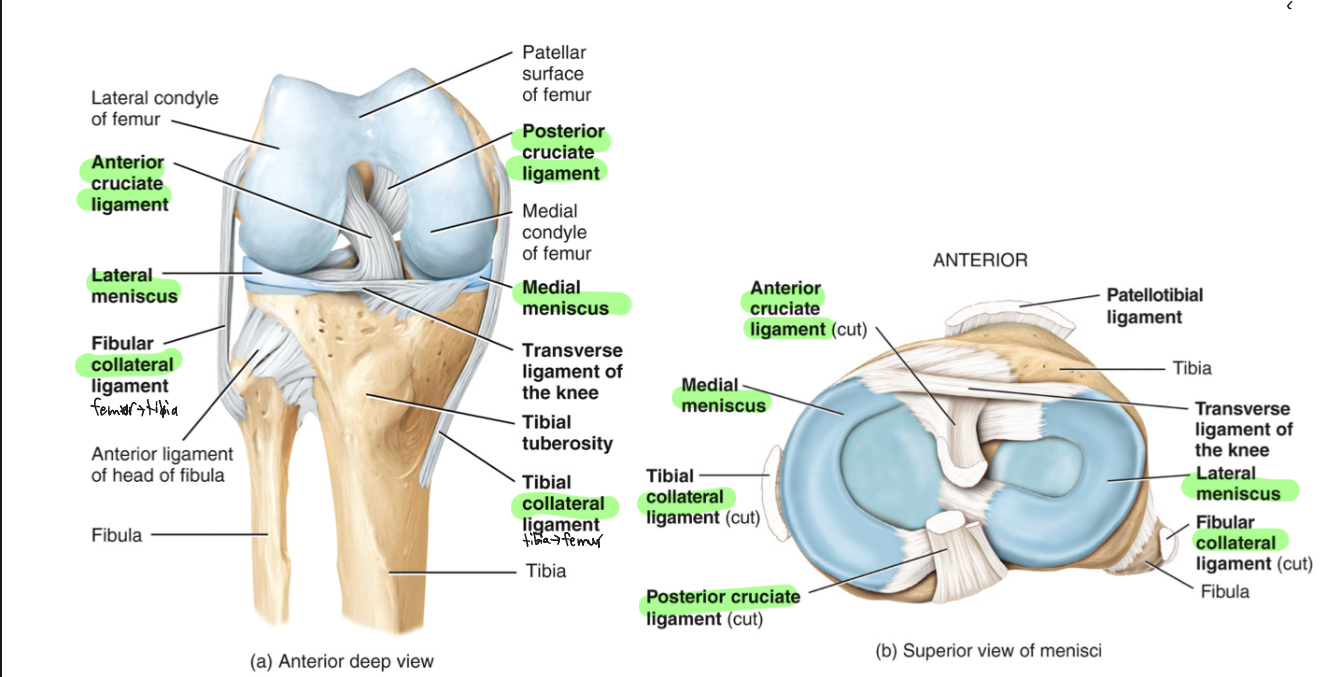
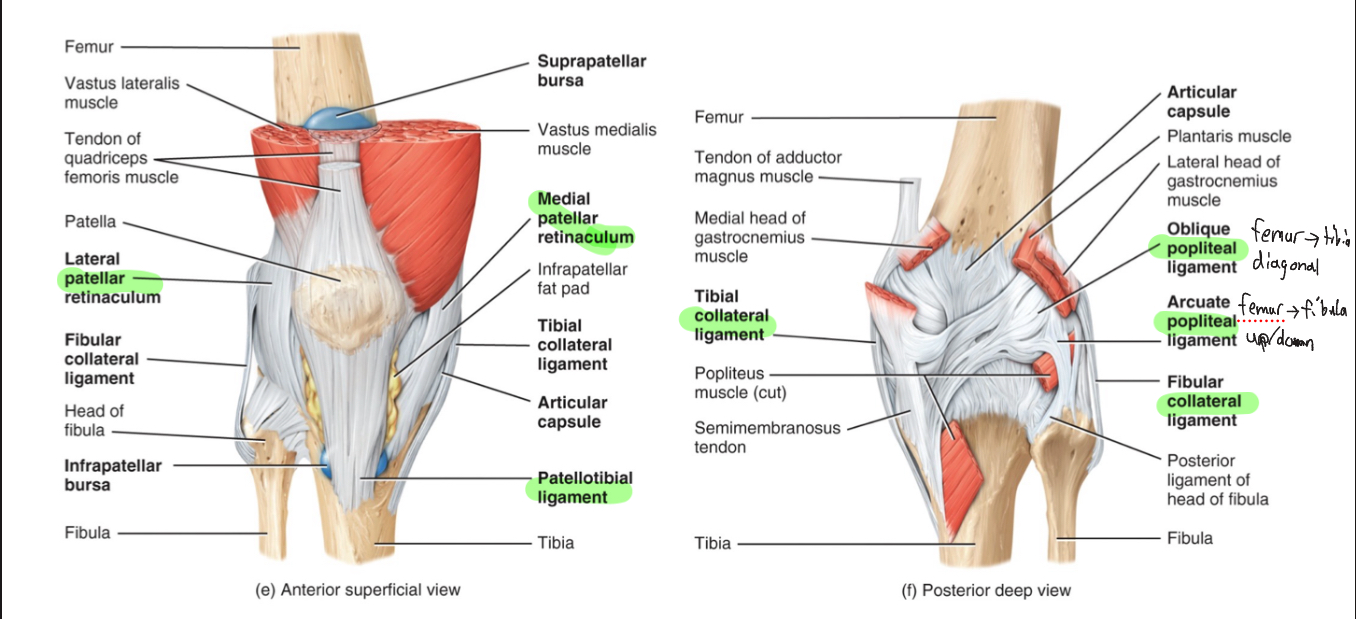
Knee Joint (modified, hinge)
-Medial and lateral patellar retinacula, patellotibial
ligament, oblique popliteal ligament, arcuate popliteal
ligament, tibial collateral ligament, fibular collateral
ligament, intracapsular ligaments (ACL and PCL), articular discs, bursae
Arthroplasty
Surgical procedure for joint replacement.
Aging n Joints
-decreased synovial fluid production
-thinning of articular cartilage
-loss of ligament length n flexibility
Disorders
-lyme disease: disease affects joint
-tenosynovitis: inflammed bursa
-spain/strain: overstrecthed/tore ligaments, tendons, ligaments