Chemistry Terms & Definitions: Exam 1 Study Set
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
ester hydrolysis results in what
break ester into carboxylic acid and alcohol
primary function of methylation
attenuation of activity
very weak forces that occur between all atoms and molecules
van der waals
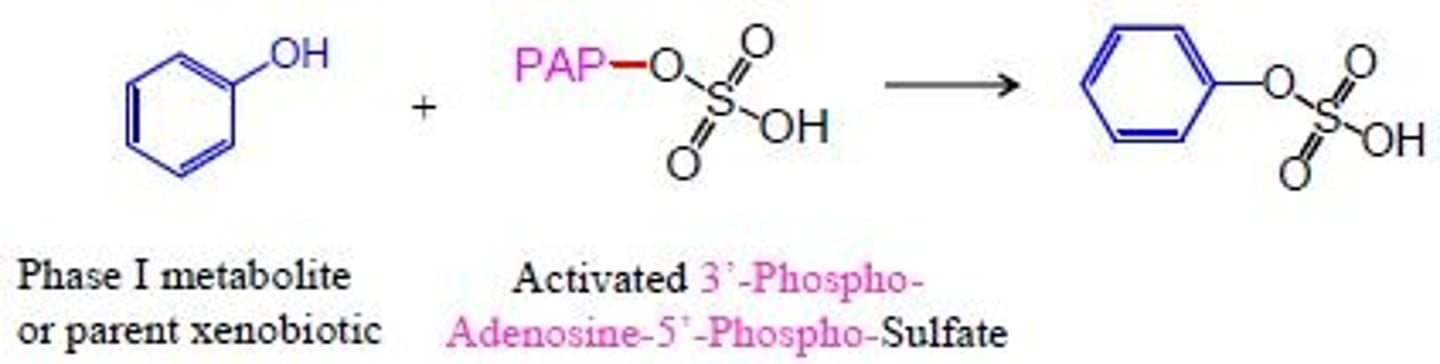
coenzyme involved in sulfate conjugation
PAPS
which compounds undergo methylation reactions?
phenol, catechol, tertiary amine, thiol and aromatic amine
sharing electroms
covalent
formed between ions of opposite charges
ionic bonding
with who is acetylation rapid?
eskimos and orientals
with who is acetylation slow?
egyptian and west european
what enzyme activates glucuronic acid?
UDP: Uridine-5-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase
B-glucuronidases
break down glucuronide in the intestine during enteroheptic circling
oxidation of alkene leads to what?
vicinal diol(epoxide in the middle)
on what functional groups does sulfate conjugation occur on?
phenols, aromatic amines, alcohols, n-hydroxy compounds
addition of acetyl group to a nitrogen: carbonyl
n-acetylation
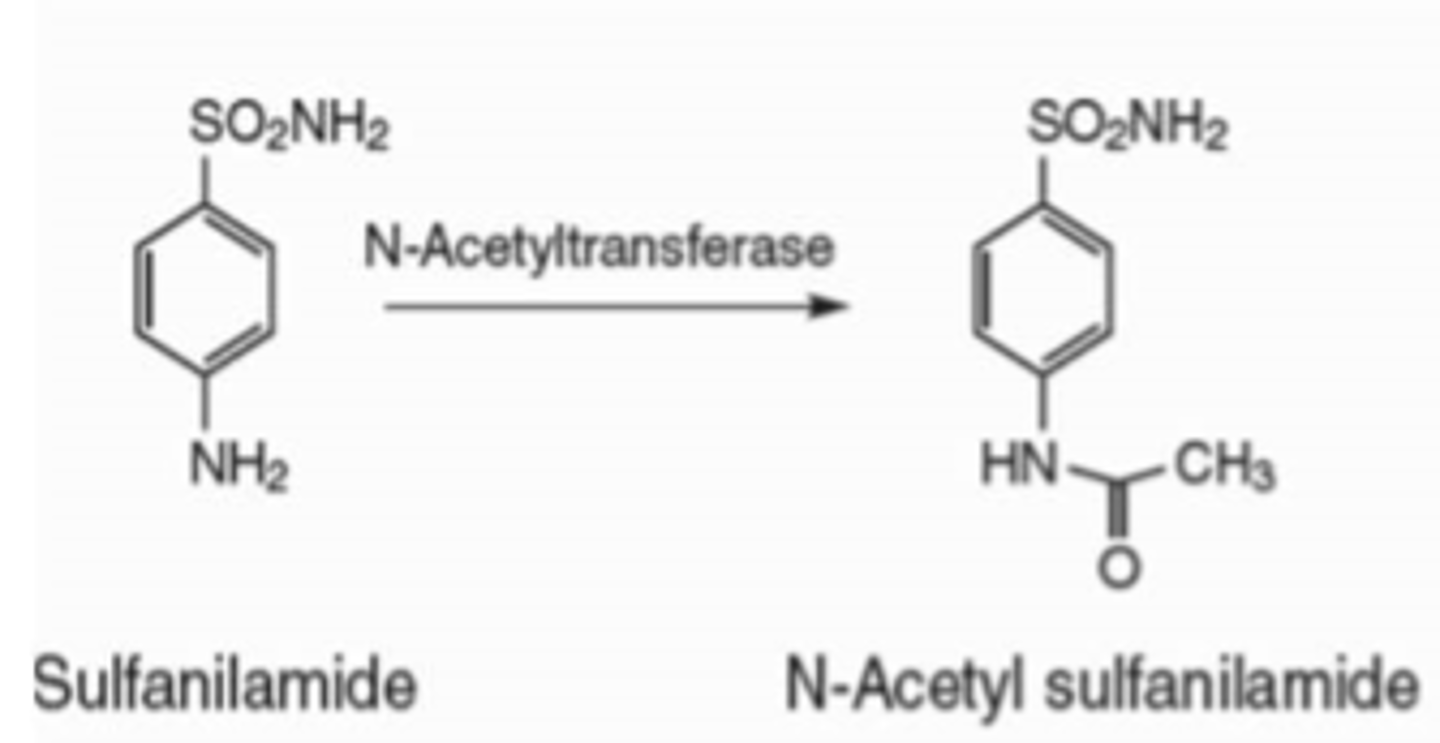
enzyme for conjugation with glycine and glutamine
n-acyltransferase
helps to detoxify reactive electrophilic species that may covalent bond with nucleophilic groups
conjugation with glutathione
turning an amine into an amide
acetylation
conjugation of glutathione enzyme
glutathione s-transferases
enzyme used for deamination
MAO
primary alcohol oxidation results in
alcohol to aldehyde to carboxylic acid
secondary alcohol oxidation results in
alcohol to ketone
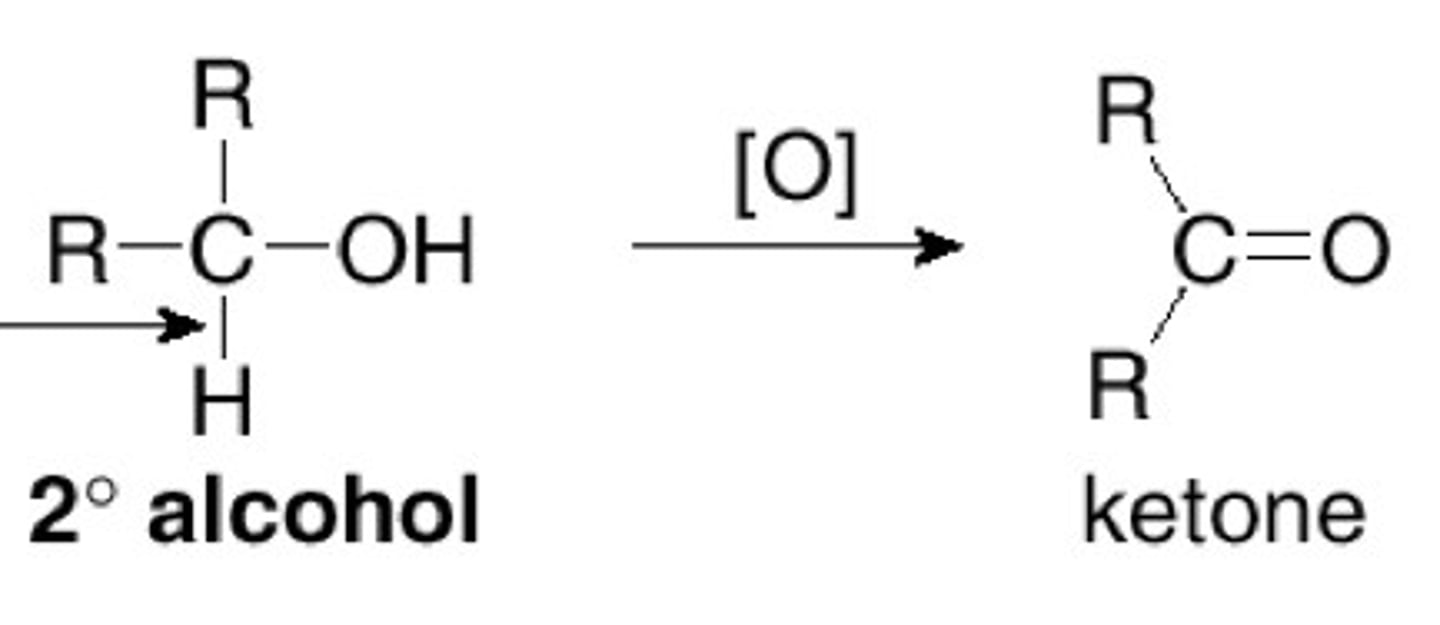
tertiary alcohol oxidation results in
no reaction
amide hydrolysis results in what
breaking of amide bond to make carboxylic acid and amine
esterases does what?
hydrolyzies ester links: uses water to break ester bonds into alcohol and carboxylic acid
amidases do what?
hydrolyze amide bond: uses water to break amide bonds
makes amine and carboxylic acid
what enzyme does sulfate conjugation?
sulfotransferases
aromatic hydroxylation
add alcohol to benzene ring to make a phenol
must be para to the substituent on the ring
activating groups
OH, OCH, NH2, NHR, and alkyl groups
deactivating groups
F, Cl, Br, NO2, SO2NHR, COR
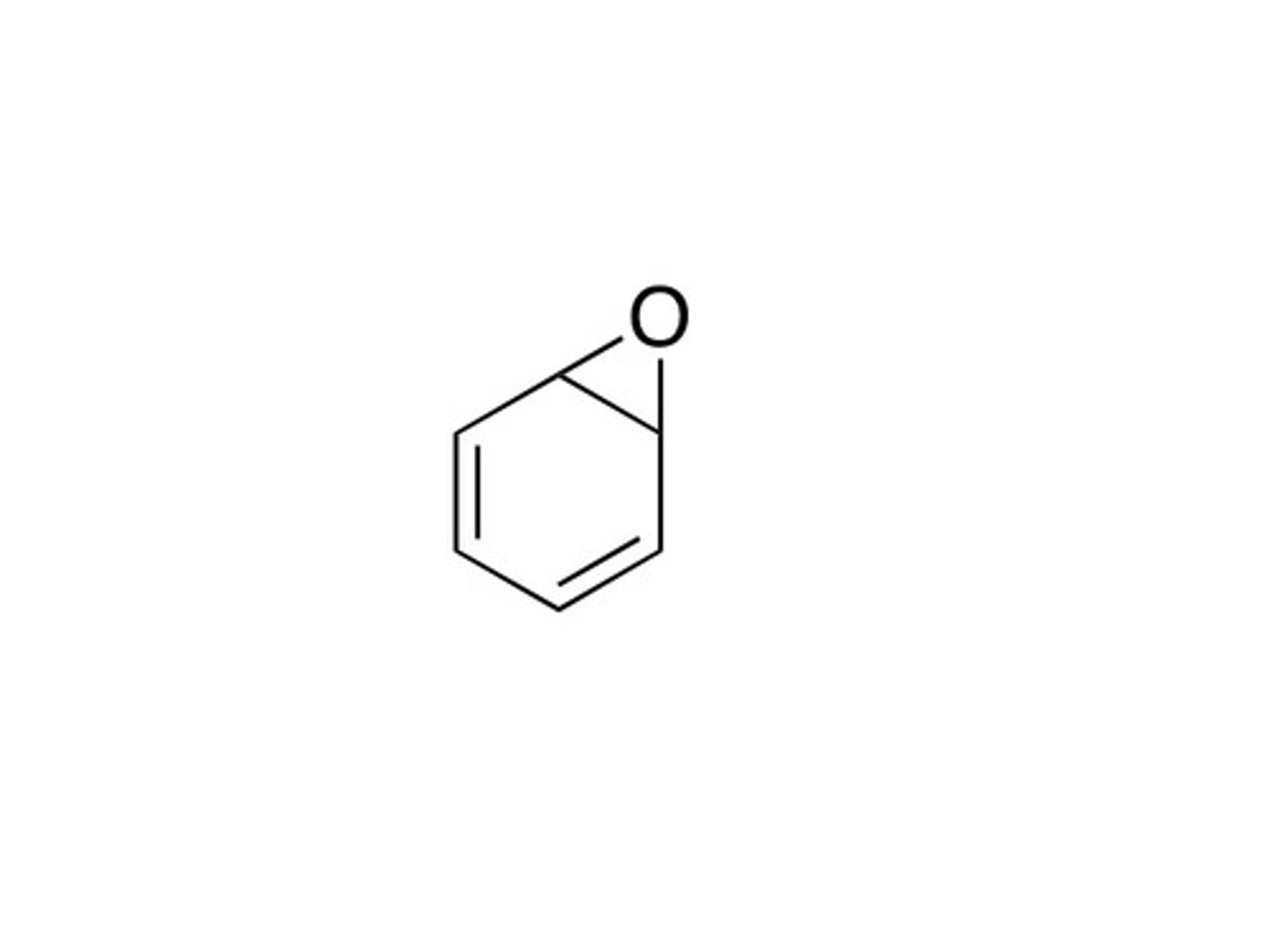
what is the intermediate in aromatic hydroxylation?
arene oxide
aliphatic hydroxylation
add a alcohol to aliphatic
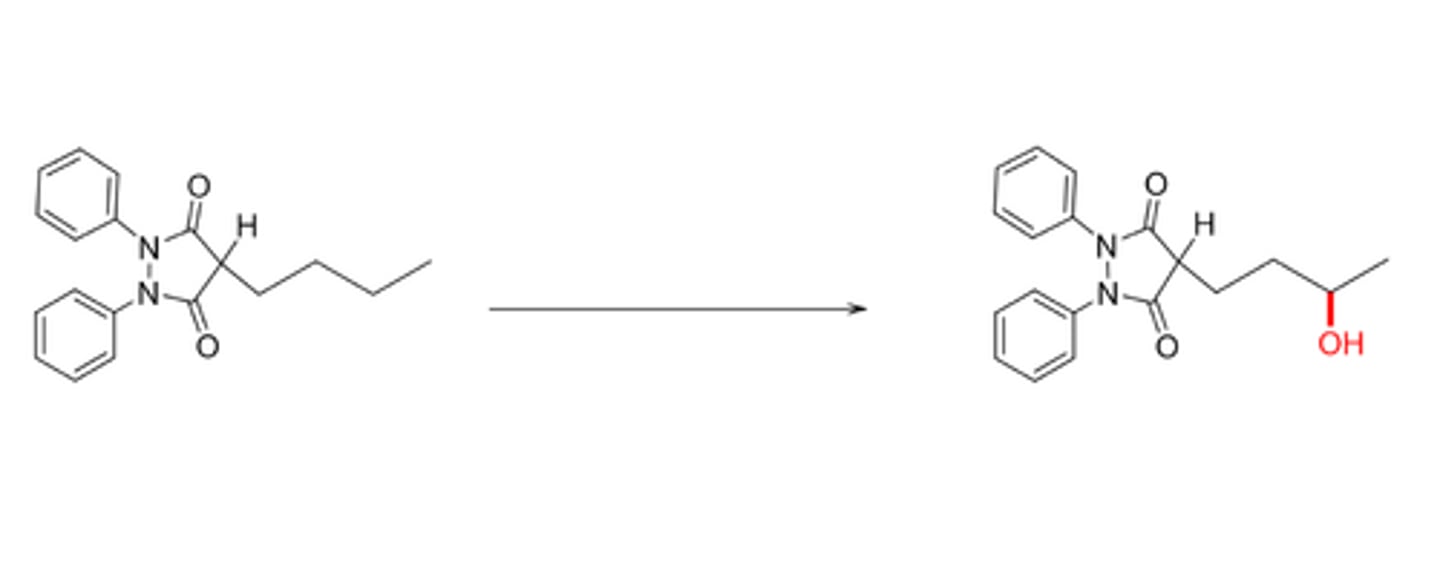
O-demethylation
oxidation of ether to an alcohol and formaldehyde(aldehyde)
n-deethylation
remove ethyl group from secondary nitrogen to make amide and ethanal(aldehyde)

ketone reduction
secondary alcohol
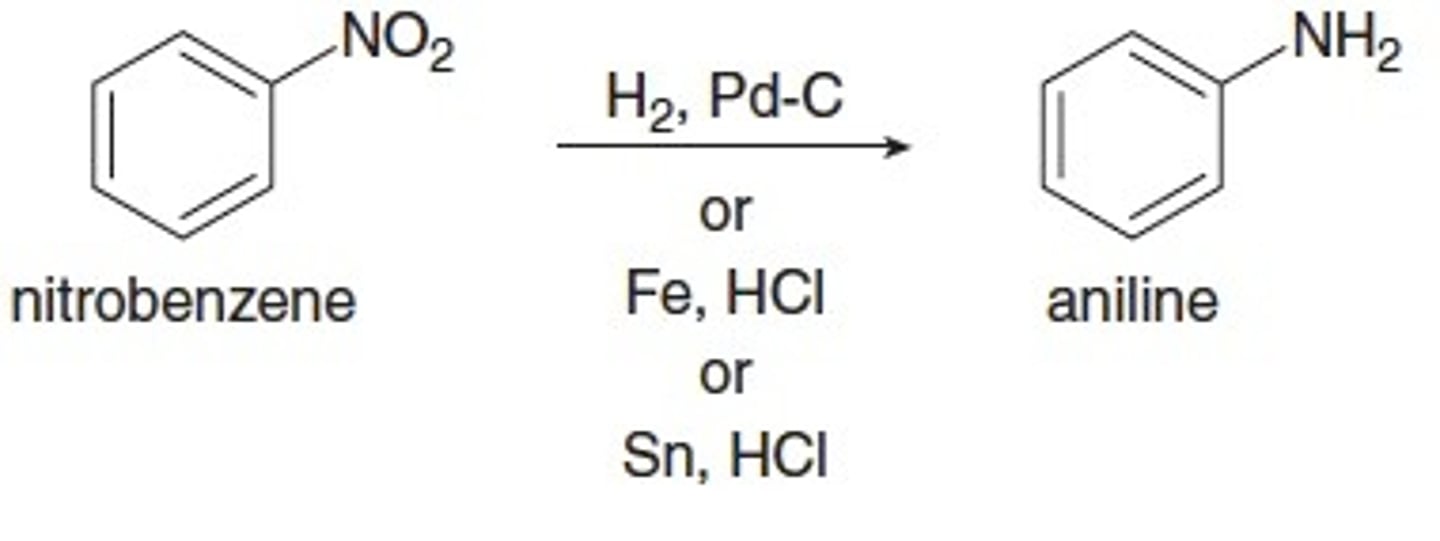
nitro group reduction
primary amine
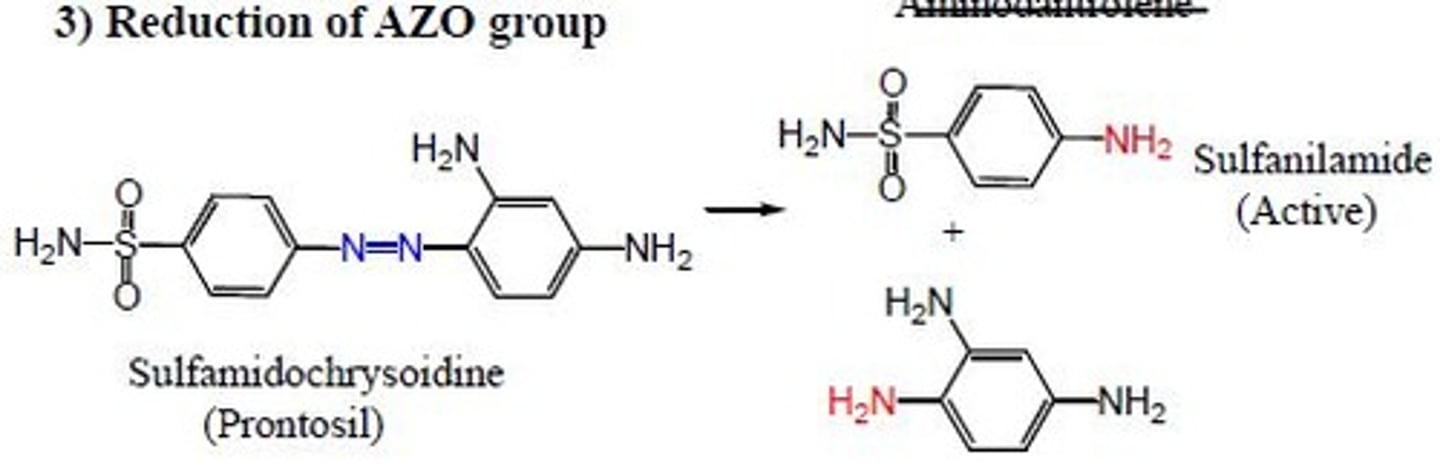
azo group reduction
two primary amines
ester hydrolysis
carboxylic acid + alcohol
Hydrolases
enzymes that use water to break something
amide hydrolysis
carboxylic acid + amine
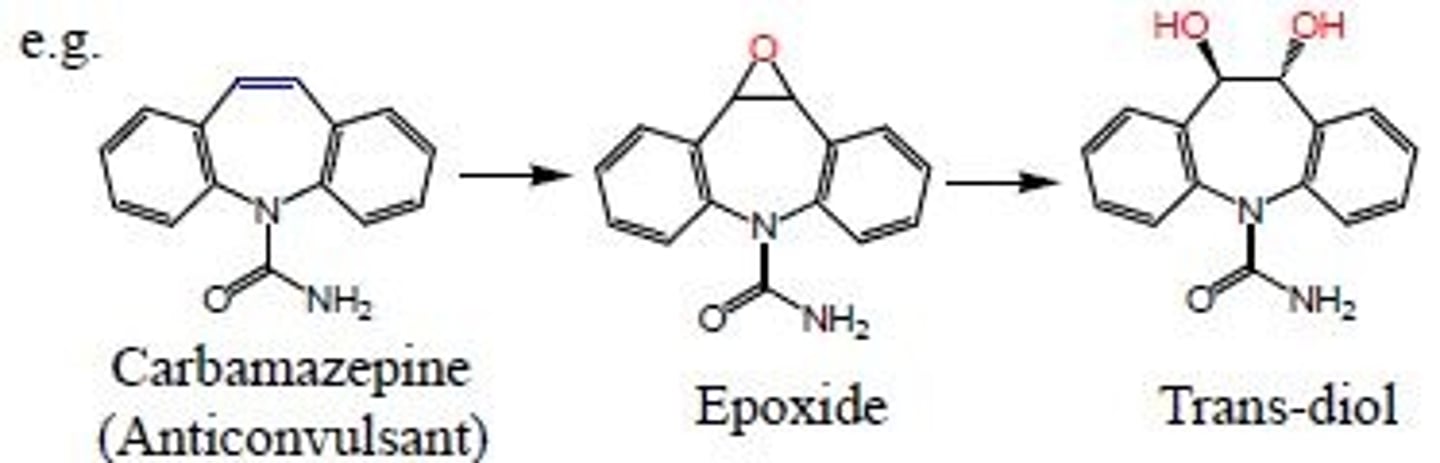
Olefinic oxidation
oxidation of olefinic double bond leads to epoxide then leads to trans-diol
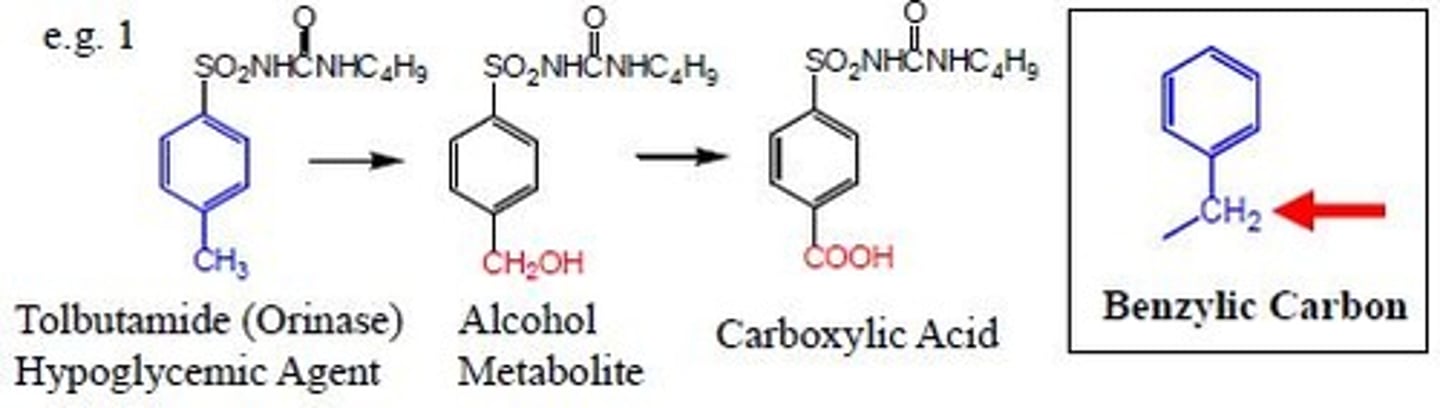
benzylic carbon oxidation
benzene carbon to primary alcohol then carboxylic acid
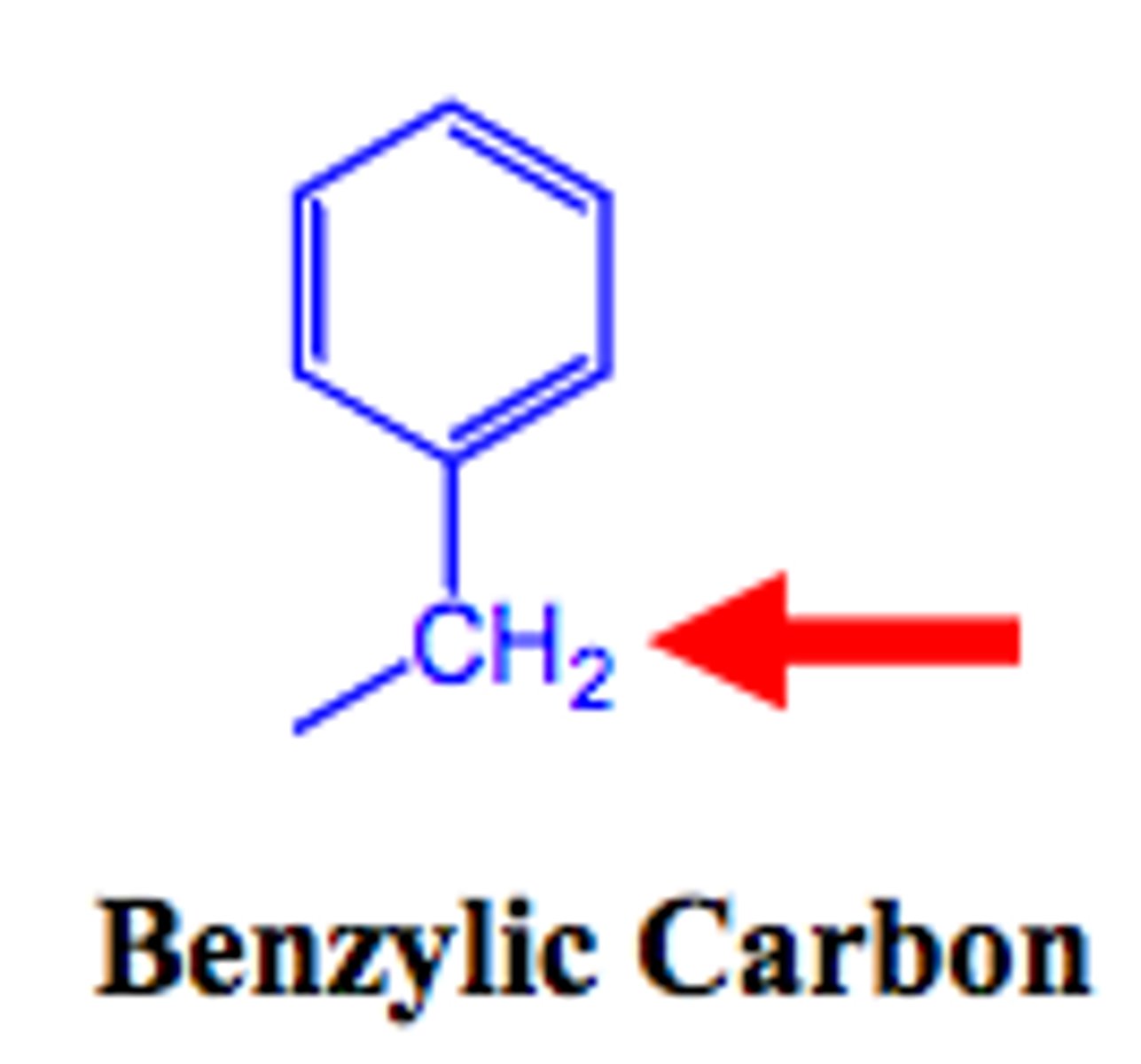
benzylic carbon
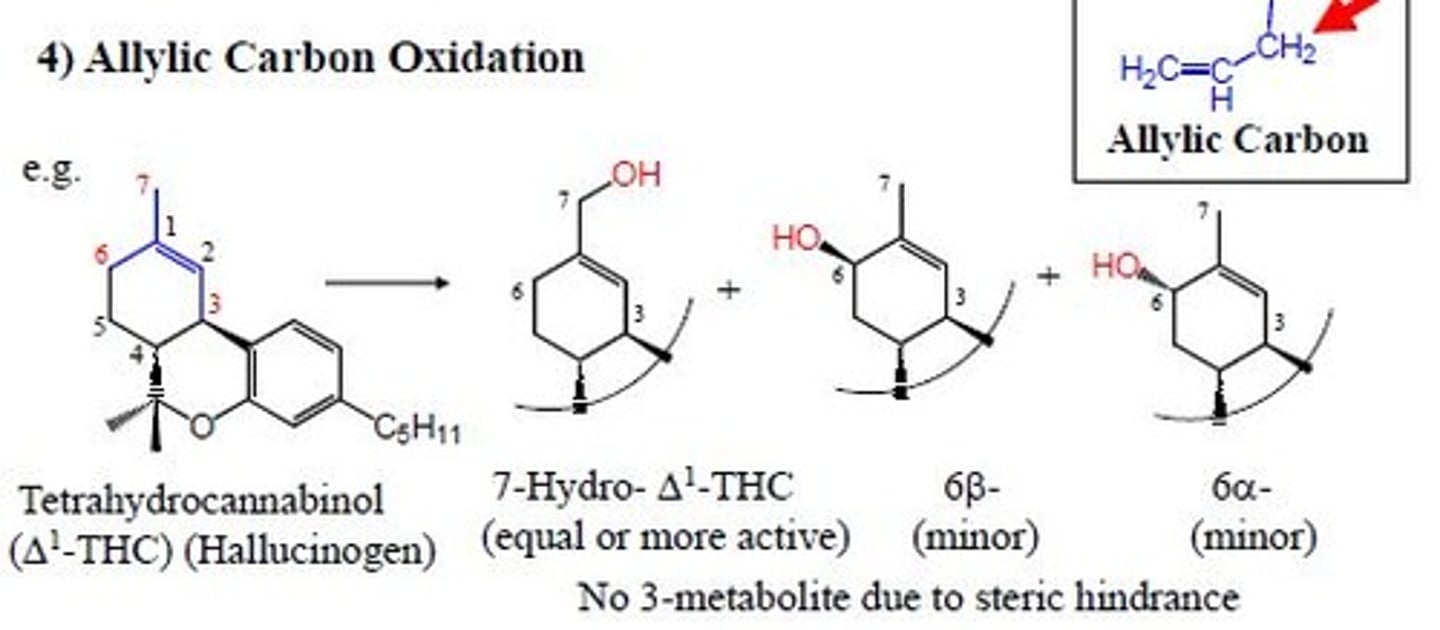
allylic carbon
carbon bonded to a carbon with a double bond
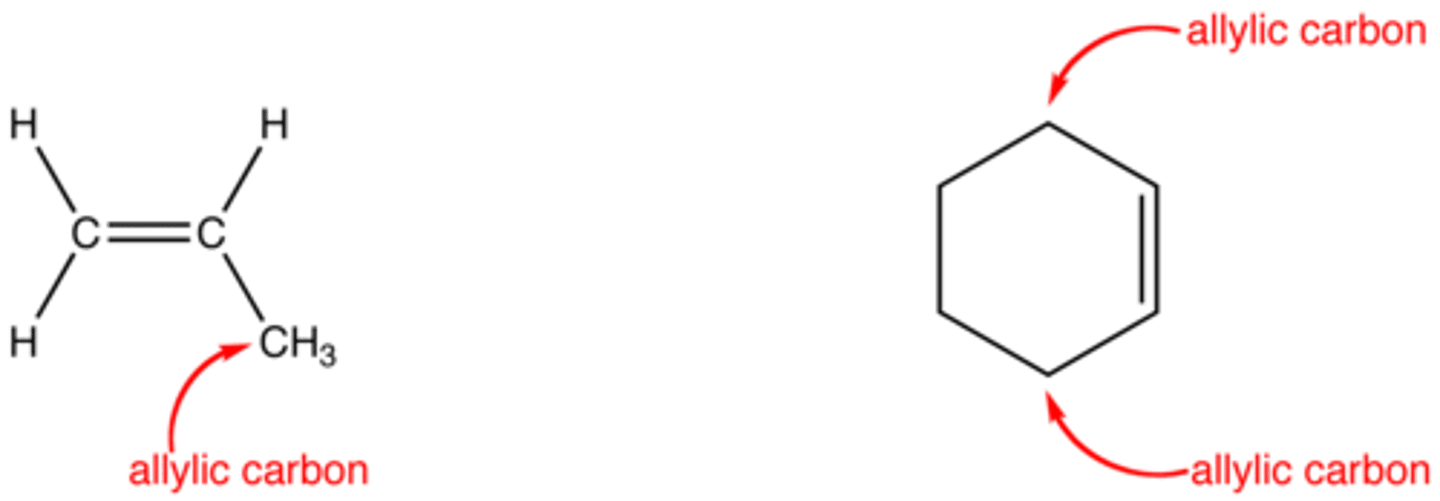
allylic carbon oxidation
add OH group to carbon attached to carbon carbon double bond
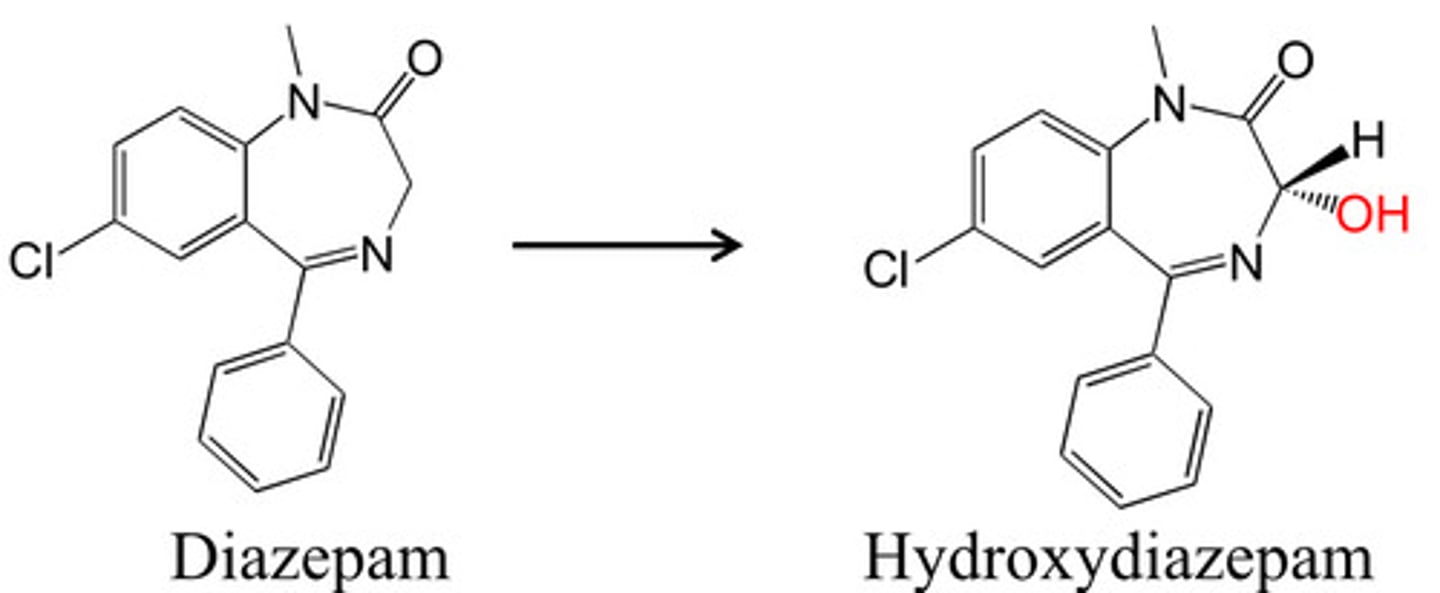
oxidation of carbon atom a to C=N
find carbon attached to a c=N and add OH to it
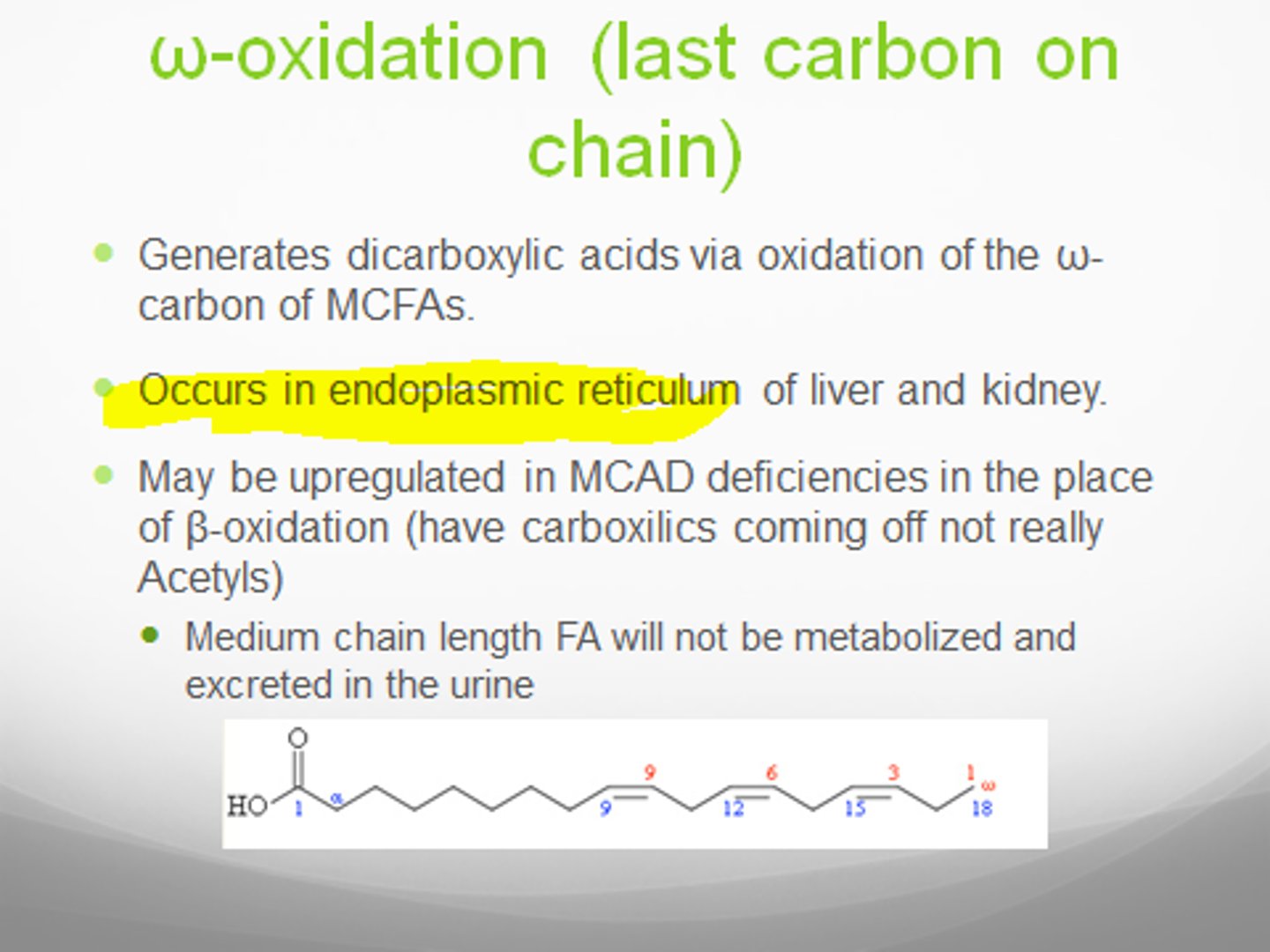
w(omega)-oxidation
oxidation at terminal carbon: add OH group to last carbon on none COOH end
w(omega)-1 oxidation
oxidation at penultimate carbon: add OH group to second to last carbon on non COOH end
Alicyclic Hydroxylation
Addition of hydroxyl group to a chair conformation
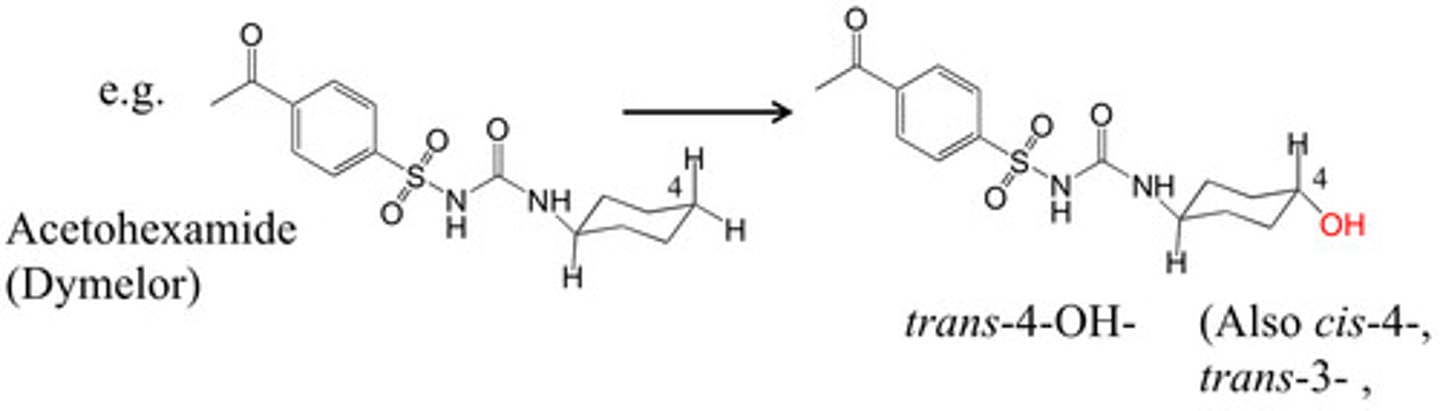
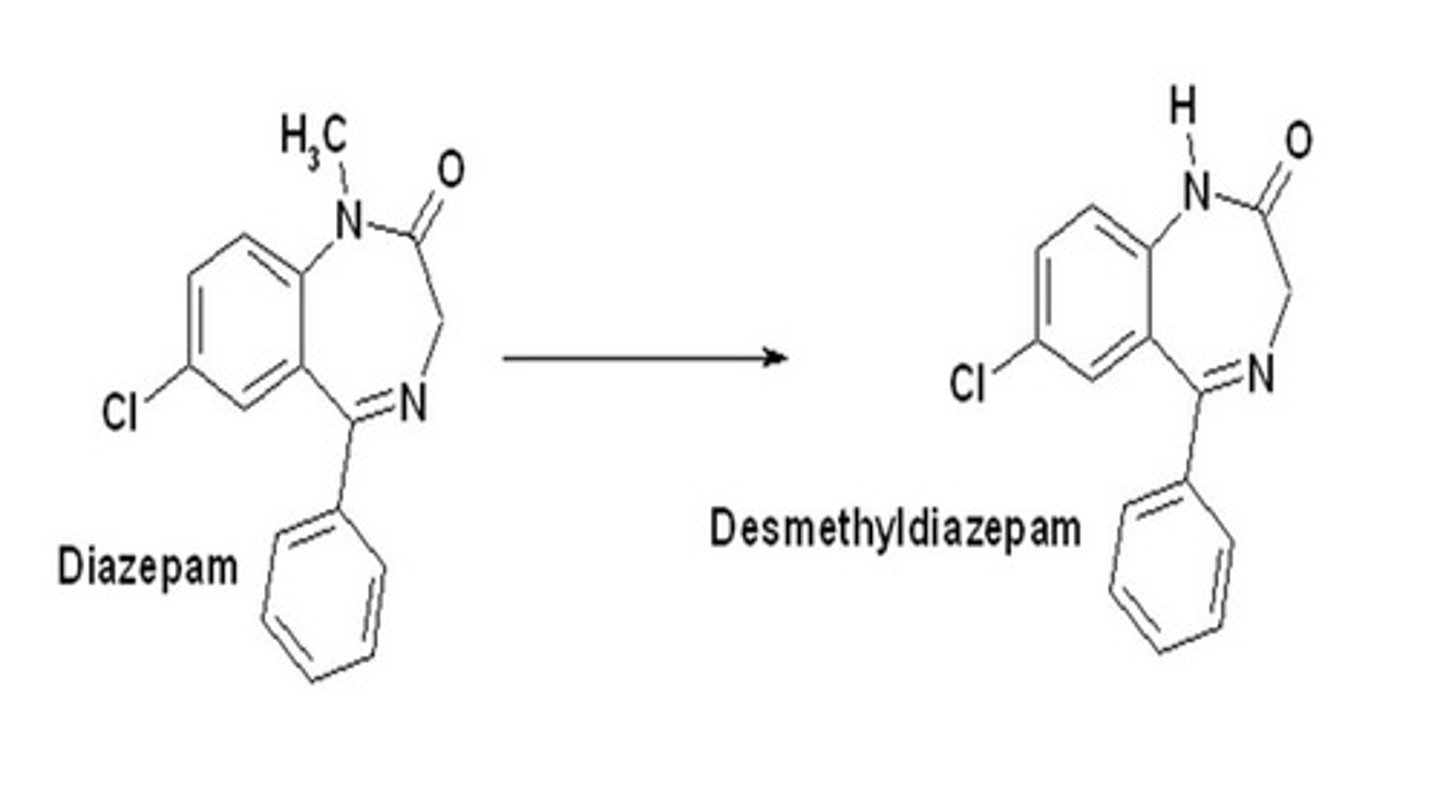
Oxidative N-dealkylation
removing alkyl group from nitrogen
-small group is preferentially removed
-first alkyl group is removed at faster rate than the second one
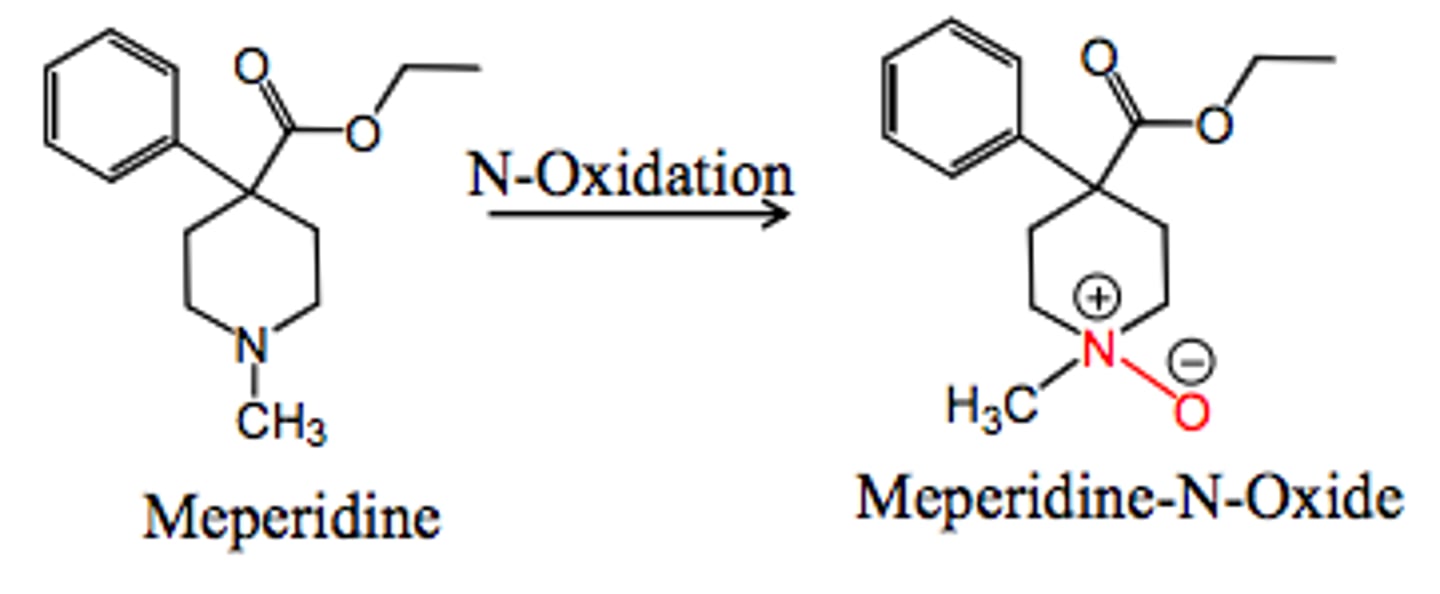
direct oxidation on N atoms
Addition of O to N
oxidative deamination
remove amine and add a carbonyl group to it, ammonia is released as by product
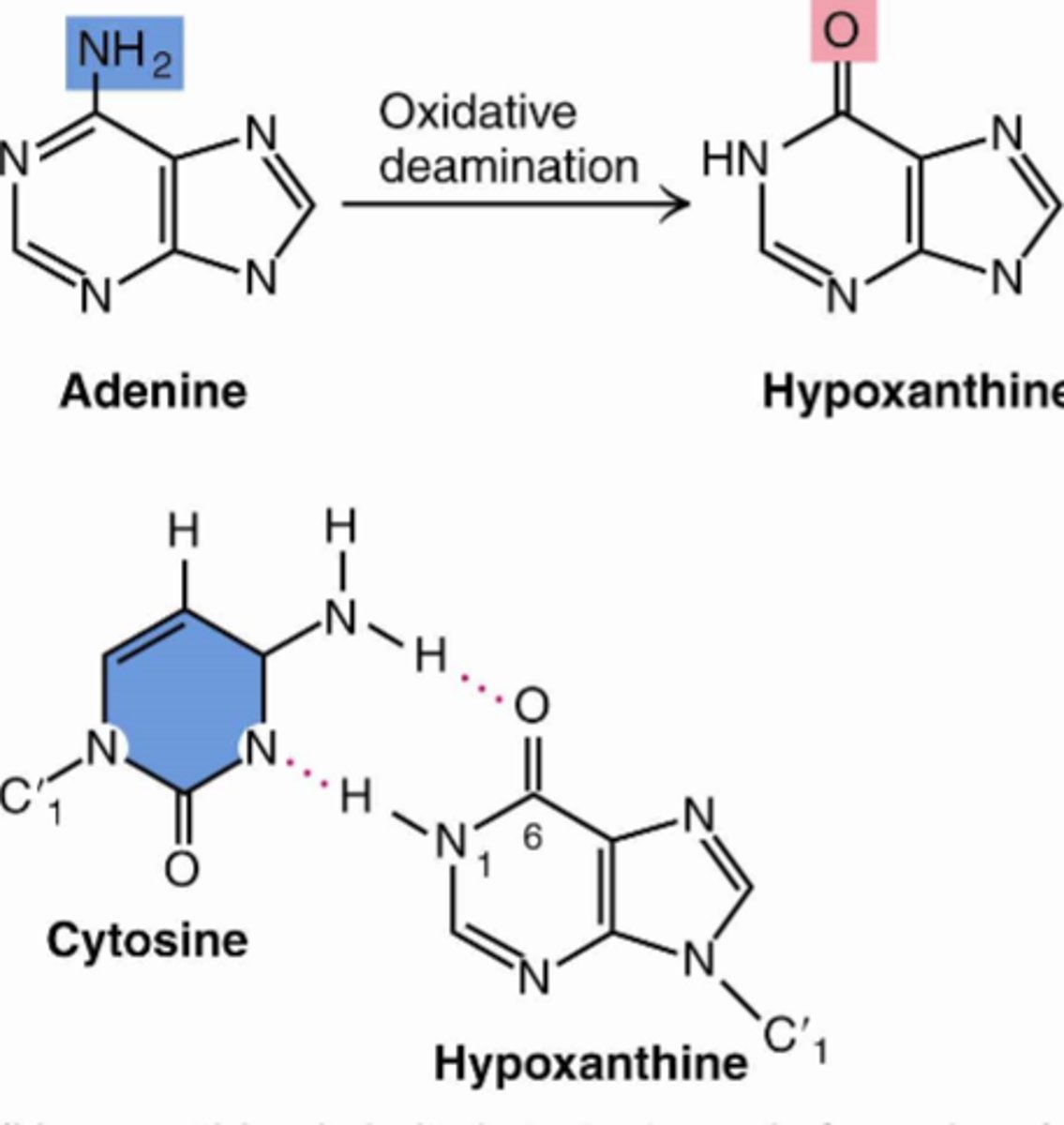
monoamine oxidases(MAO)
group of enzymes responsible for deamination
What does monoamine oxidase do?
breaks down catecholamines(dopamine, norepi, seratonine etc) through deamination
O-dealkylation
removing an alkyl group from oxygen in ether: makes an aldehyde and OH group where the O was in the ether
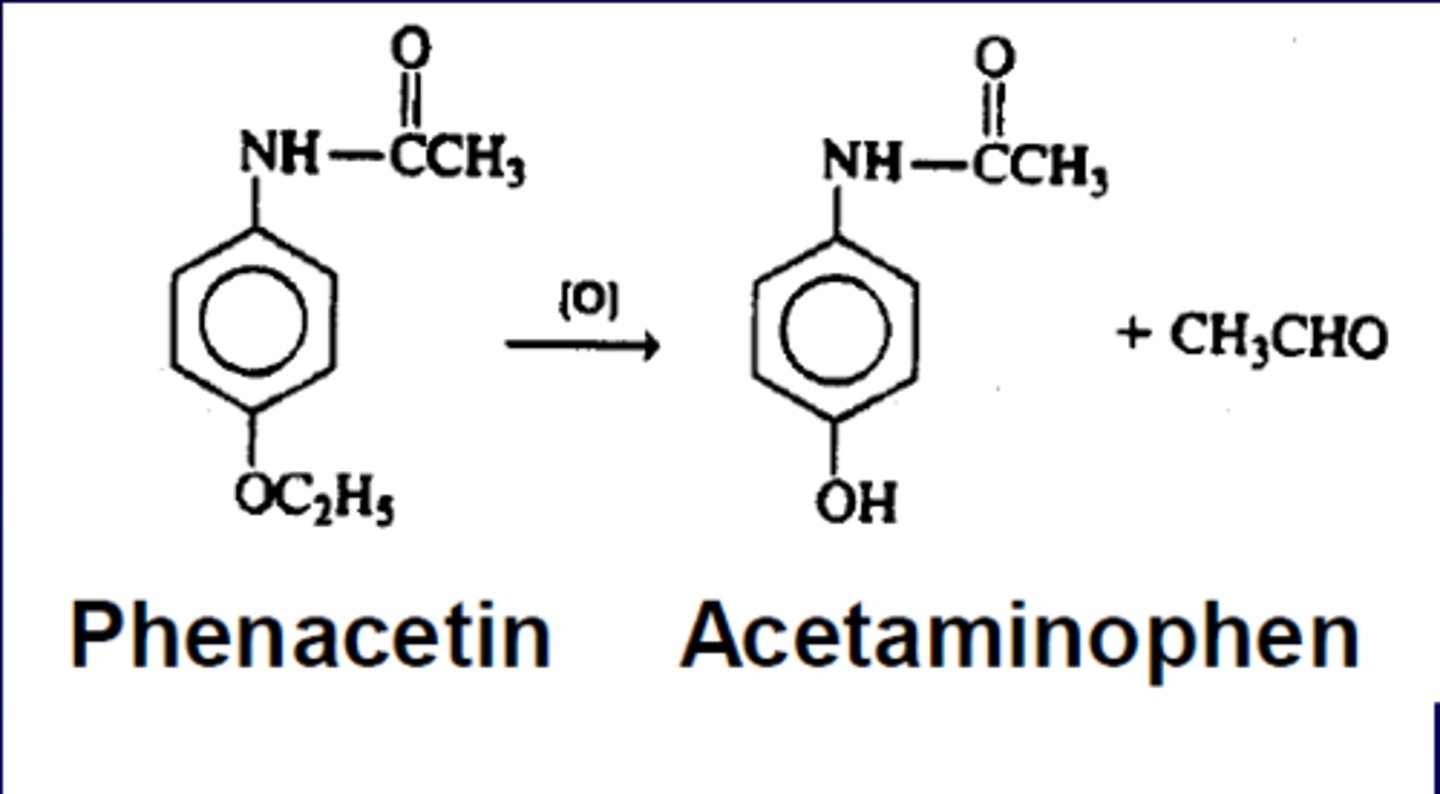
what groups go through glucuronic acid conjugation?
phenols, and alcohols, amines, sulfonamides, and thiols
who goes through sulfate conjugation?
phenol or amine
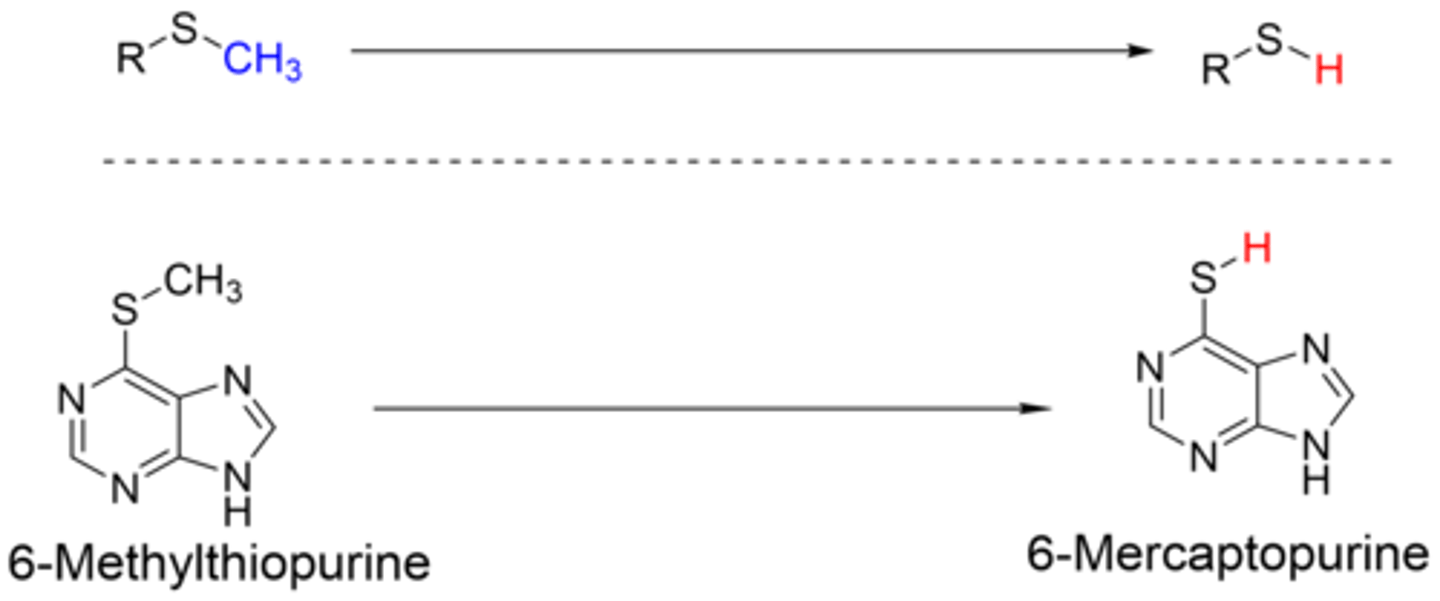
S-dealkylation
Removal of alkyl group from S and makes a mercapto
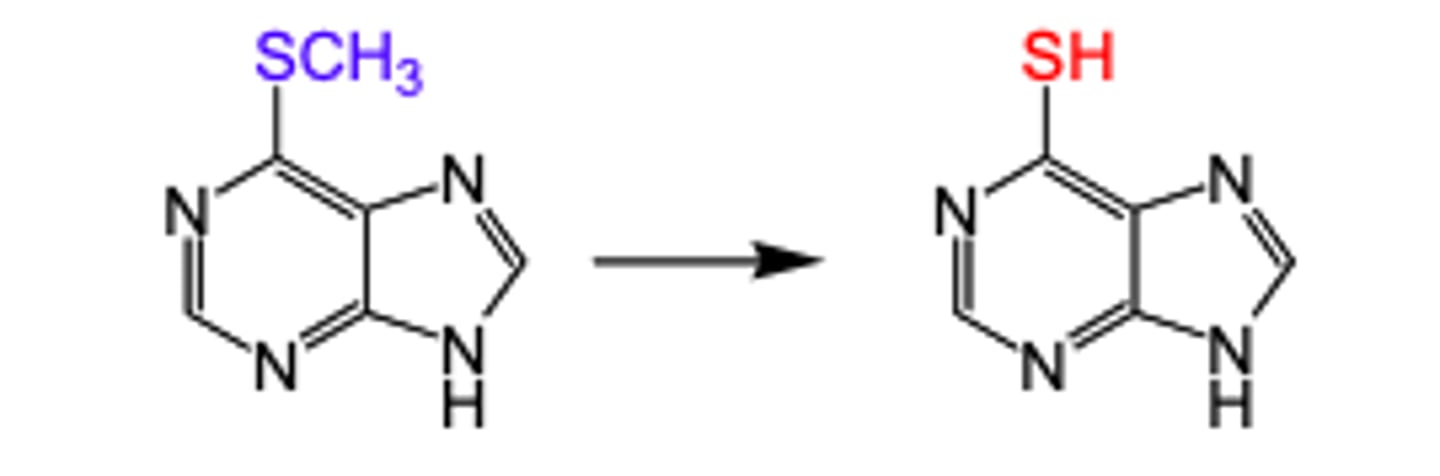
desulfuration
removal of S and replace with O
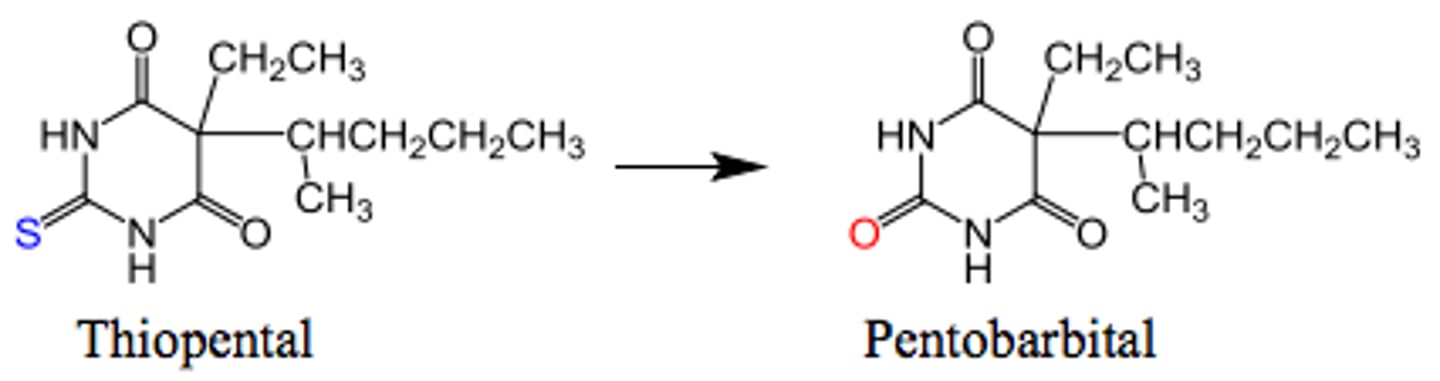
direct oxidation of sulfur
Addition of O to S to make a sulfoxide
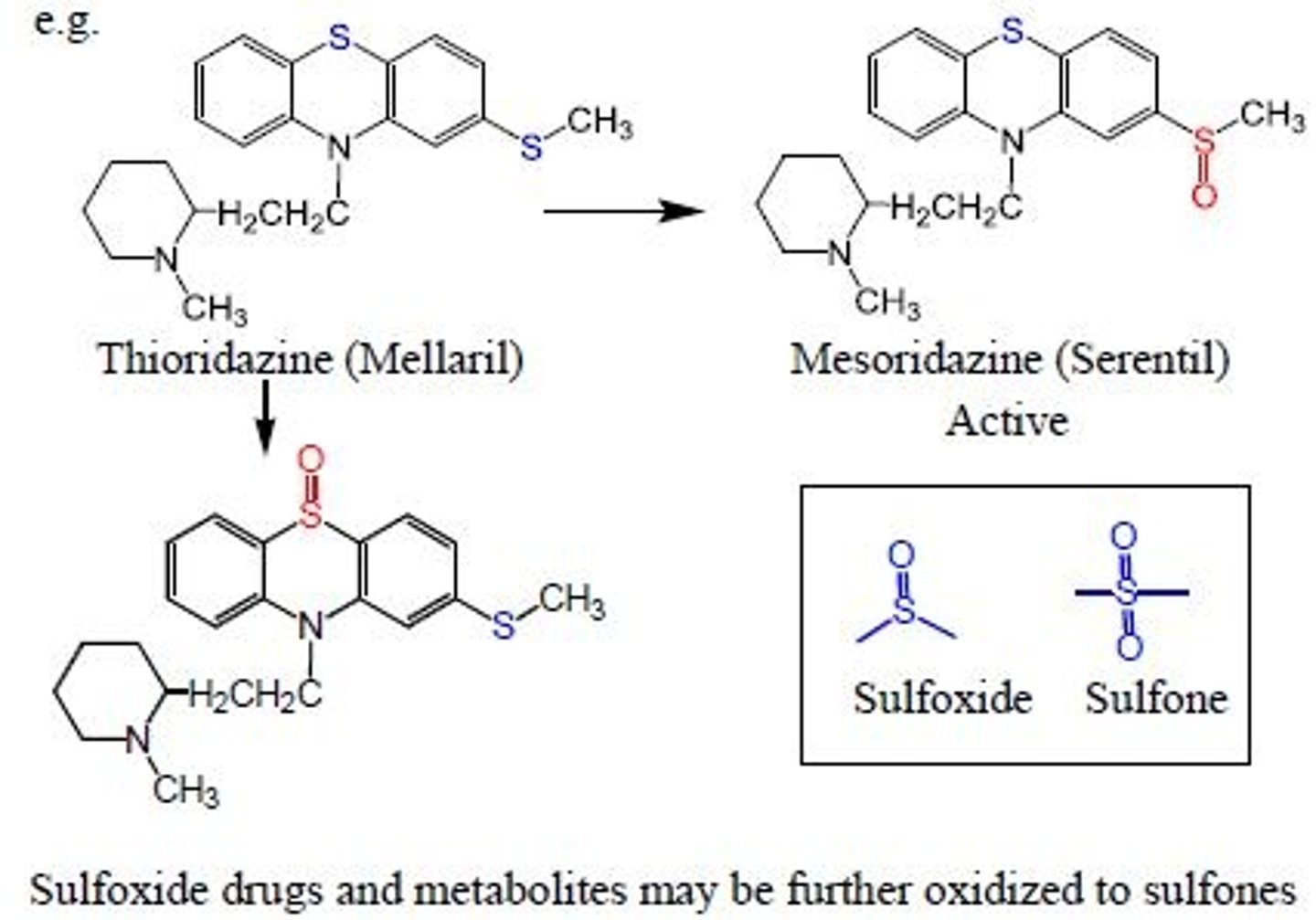
oxidation of alcohol
aldehyde and then to carboxylic acid
aromatization
turn a non-aromatic ring into an aromatic ring
-turn non aromatic carbonyl into hydroxyl and aromatic ring
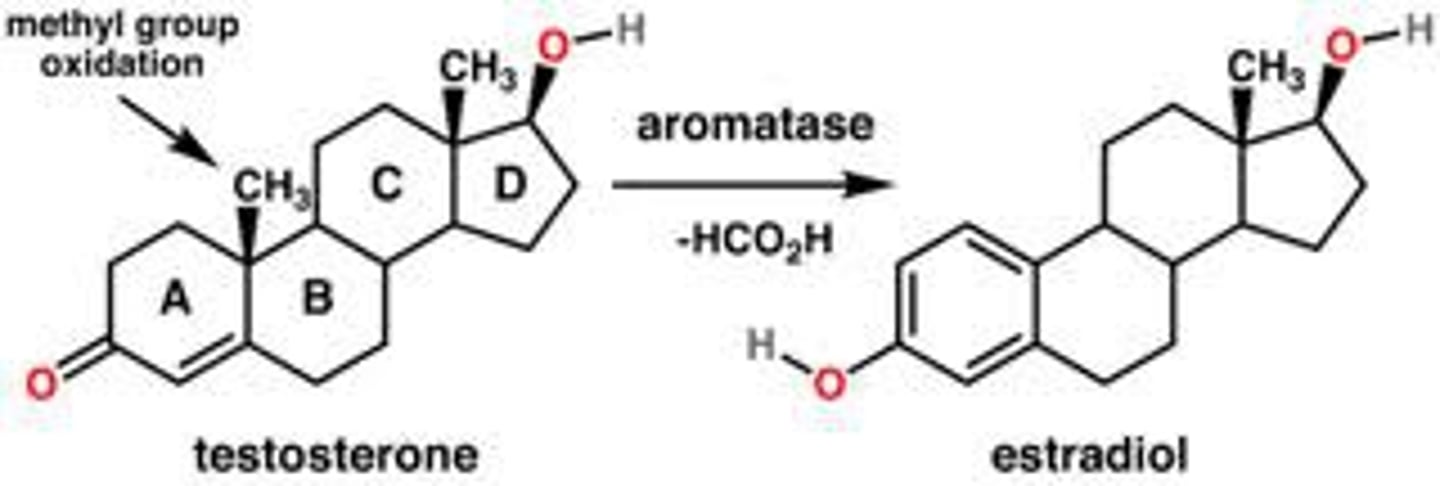
dehalogenation
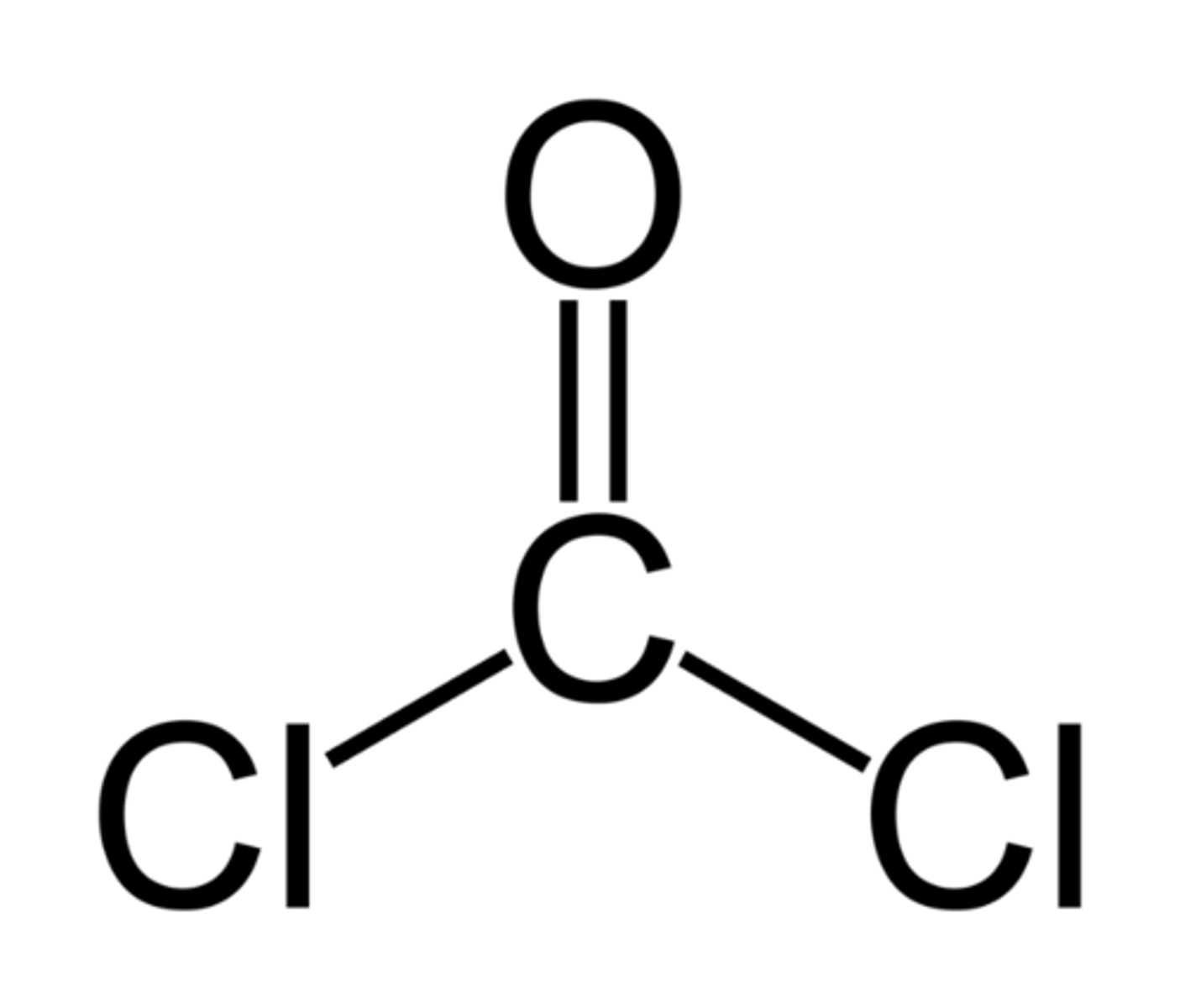
Removal of halogen to make a phosgene
phosgene
reduction of c=o
turn carbonyl group into alcohol group
what is palmitate ester made for?
to mask bitter taste
indanyl ester
increase absorption
what phase 2 reactions do not make it more water soluble?
methylation and acetylation
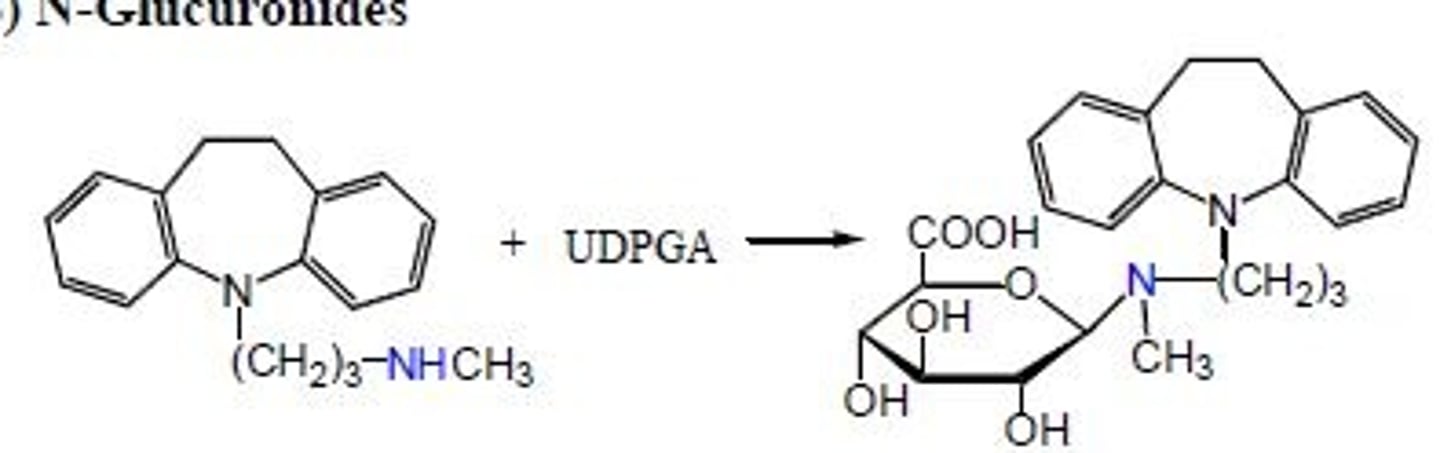
n-glucuronides
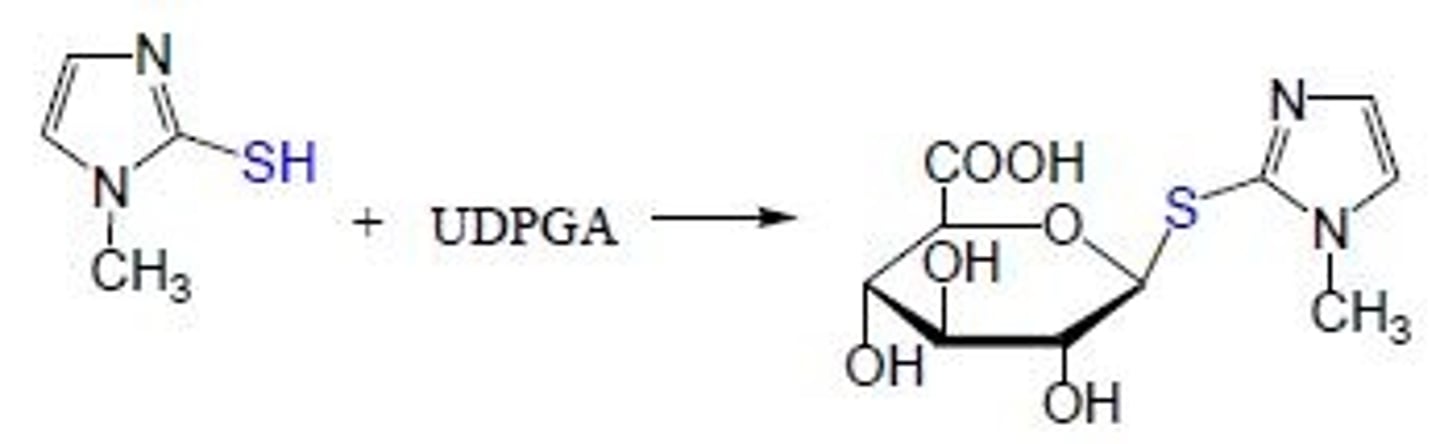
S-glucuronides
sulfate conjugation
n-methylation
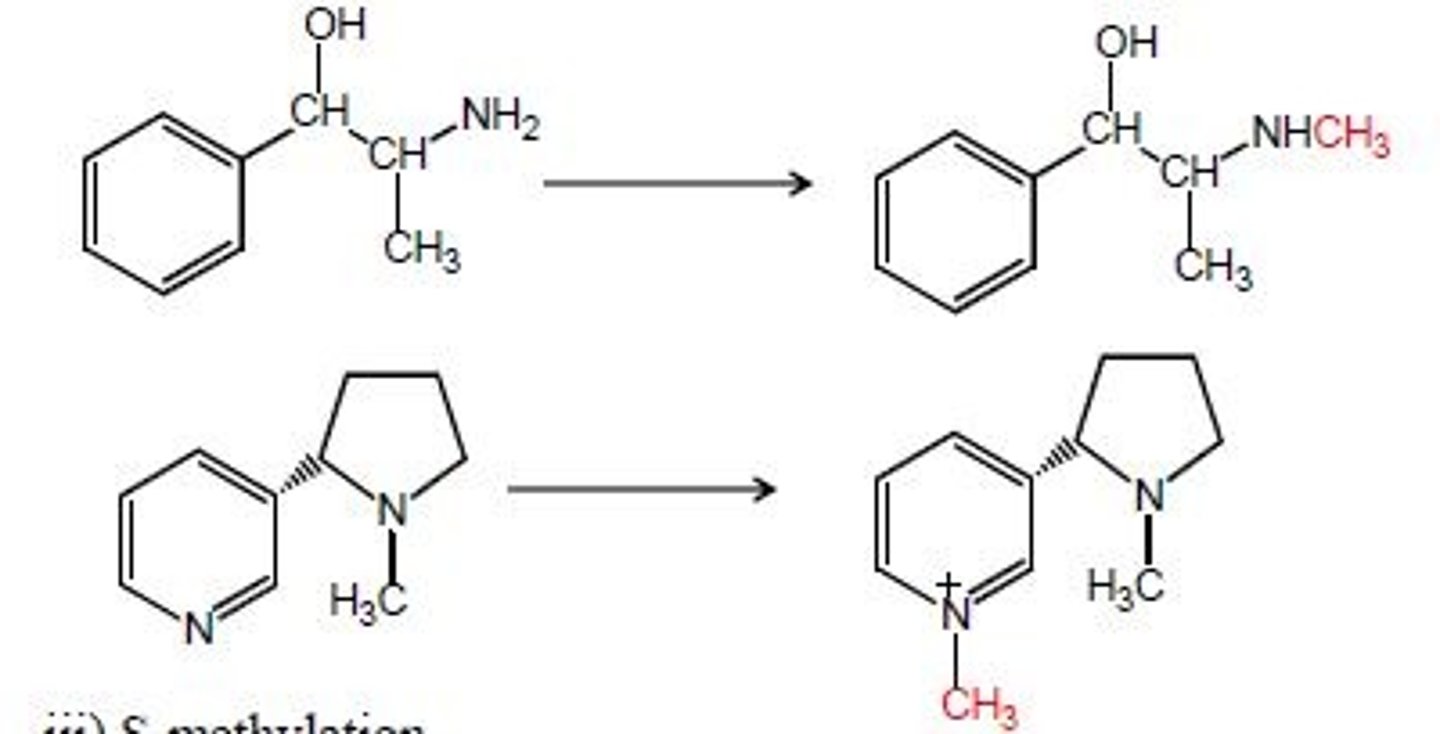
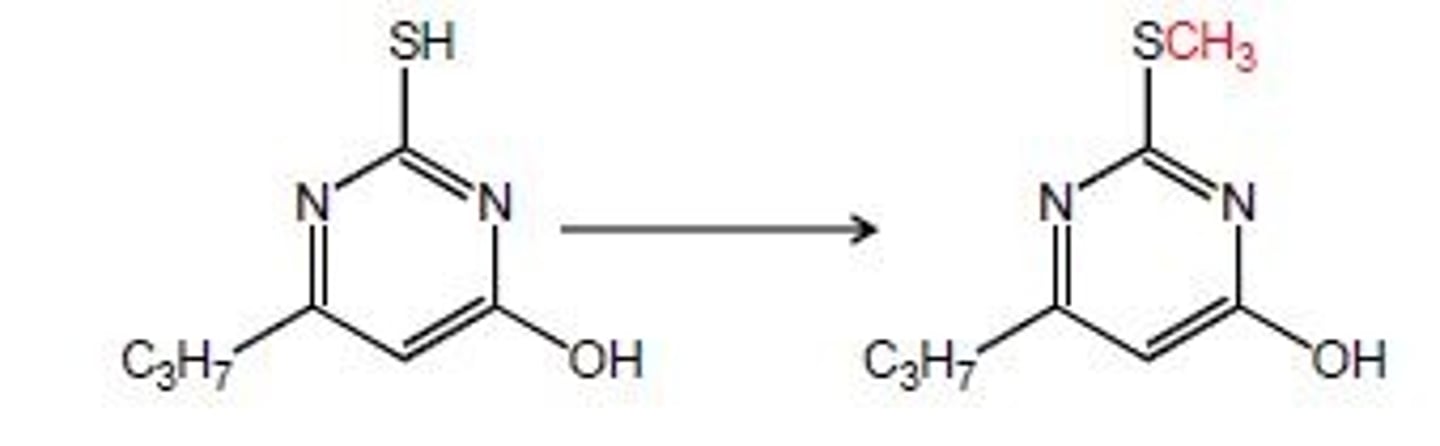
s-methylation
coenzyme to reduce reactions
NADPH
coenzyme
substance that works with an enzyme
coenzyme for methylation
Sam: s-adenosylmethionine
coenzyme for acetylation
Aceyl CoA
coenzyme for oxidation
NADP+
enzyme for NO2 reduction
nitro reductase
hydrolyze ester
carboxylic acid and alcohol
enzyme to hydrolyze ester
esterases
aldo keto reductases
reduces ketone into alcohol
coenzyme of aldo keto reductase
NADPH: helps to turn carbonyl to alcohol
pro drug
formation of active drugs from deliberately masked drugs
which enzyme methylates catechols?
COMT
what coenzyme helps methylate catechols?
SAM
enzyme for glucuronic acid conjugation
UDP-glucuronyl transferase(UGT)
what is the glucuronic acid conjugation?
synthesis of activated glucuronic acid and enzymatic transfer by UGT
Steps of enterohepatic circulation
1.Drug undergoes glucuronidation in the liver
2. Glucuronide excreted in the bile
3. Hydrolyzed by b-Glucuronidases in intestine
4. Hydrolyzed drug reabsorbed in intestine
why does the body use enterohepatic circling?
to excrete things that have a molecular weight more than 300 DA
what is the job of cytochrome P-450?
transferring an oxygen atom to the substrate
where is the site of drug biotransformations?
liver
attaches polar and ionizable endogeneous group to acheive a more complete solubility
phase 2 reactions
what are the phase 1 reactions?
Oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
formaladehyde
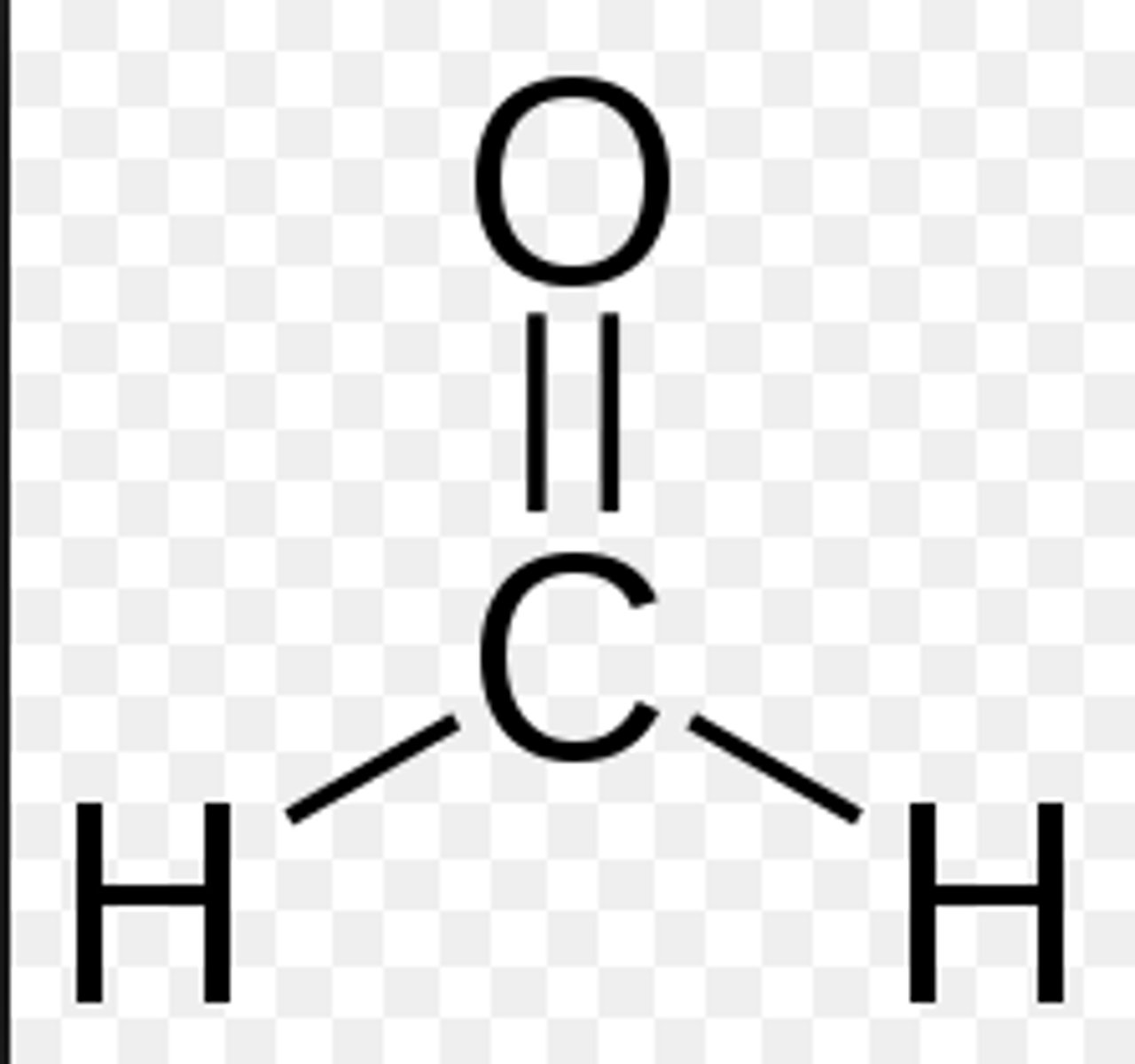
vicinal diol
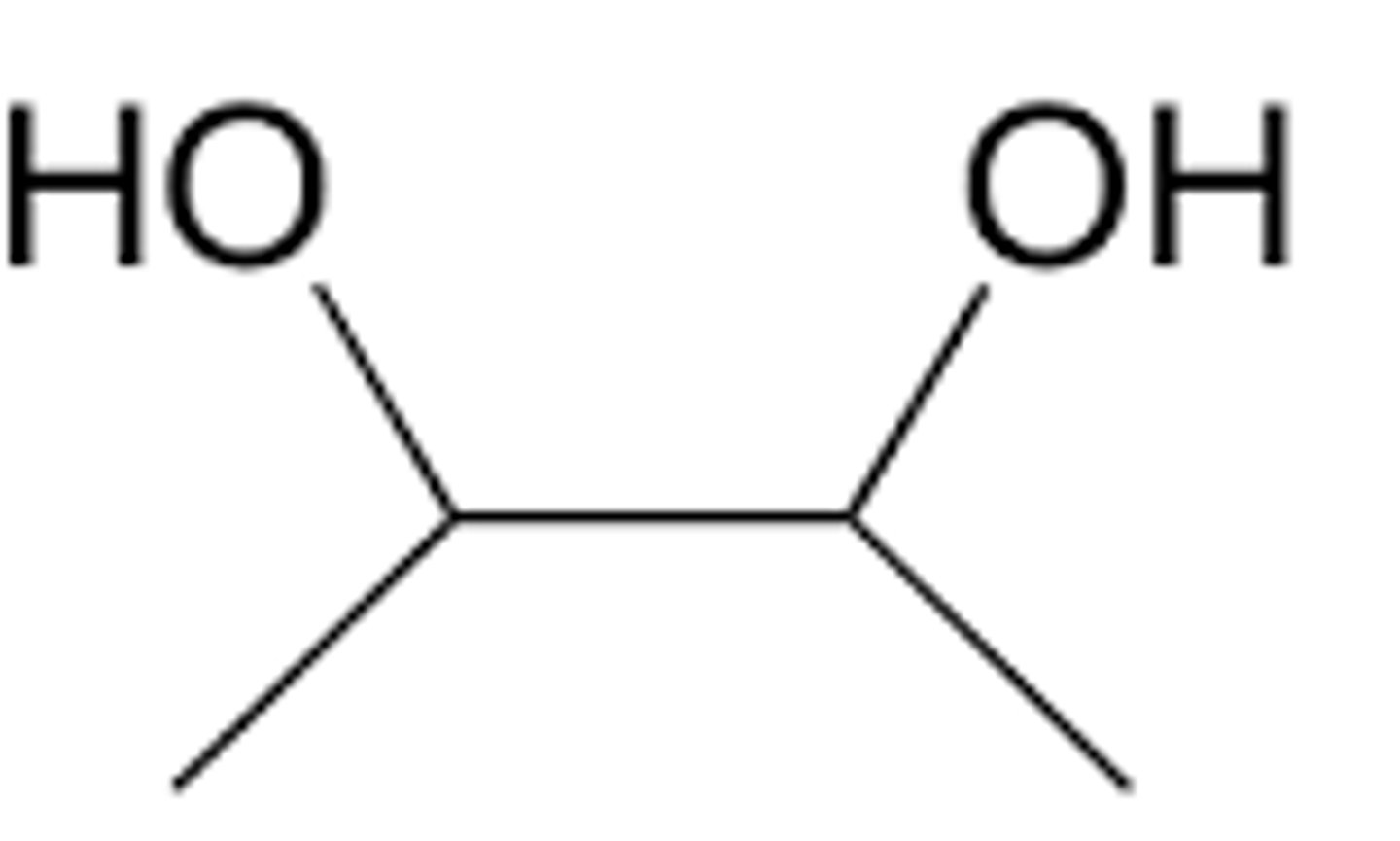
oxidation of secondary alcohol
ketone
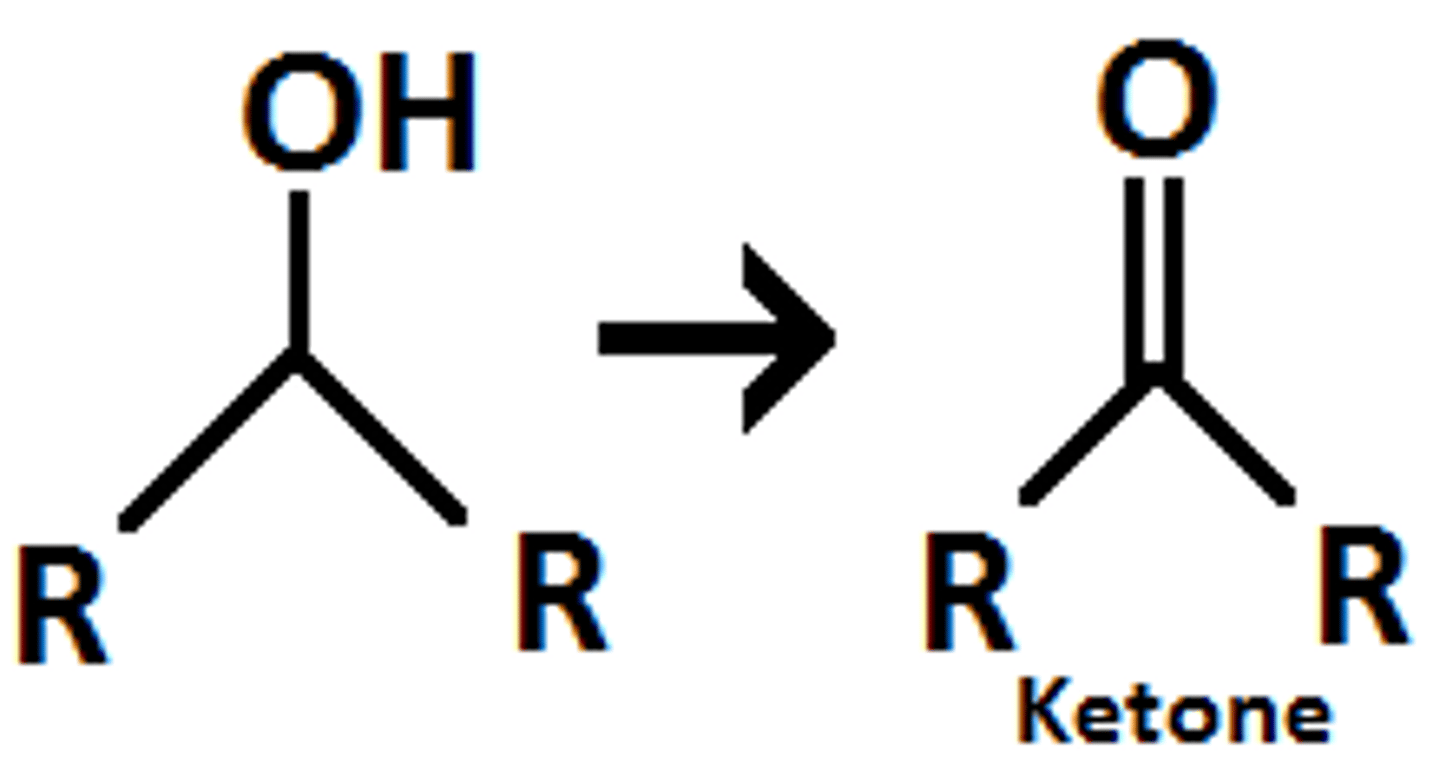
enzyme that oxidizes alcohol to aldehyde
dehydrogenase
enzyme that oxidizes aldehyde to carboxylic acid
oxidase