Religion Unit 1 - Hinduism
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
186 Terms
Who was the German philologist, Sanskritist, and Orientalist who was one of the founders of western academic field of Indian studies and comparative theology at Oxford University, England (Victorian period)?
Friedrich Max Muller

What is the name of this?
Bronze Dancing Girl from Mohenjo-Dara circa 2500 B.C
does Hinduism have a single founder or founding dates?
no
Hinduism involves a _________ way of life
comprehensive (culture + religion)
What type of religion is Hinduism?
non-proselytizing
Hinduism is the ___ largest religion
3rd
approximately how many adherents does Hinduism have?
1 billion
what are the two root sources for “tree of Hinduism” and the Indian Religion?
Indus Valley Civilization and Aryan Culture
Where are the four ancient urban civilizations located within?
Egypt, Mesopotamia, South Asia, and China
what time period was the Indus Valley civilization and its peak?
c. 2500 - 1500 BCE, peak at 1900 BCE
where were the main centers of the Indus Valley Civilization?
Harappa and Mohenjo Daro fluorished along the Indus River
what type of economy was it during the Indus Valley Civilization?
agricultural based, complex city planning, written script
what wa the religion based on during the Indus Valley Civilization?
archeological remains
example of archaelogical remains during the Indus Valley Civilization:
Goddess figurines
Great bath
Depictions animals/nature
Yogic seal
Burial items

Which script is shown?
Indus/Harappan
what does the indo-european family of languages include?
indo-iranian and indi-european groups
indo-european languages
Greek and Latin
into-iranian languages
Avestan (sacred language of the Zoroastrians), Sanskrit and north Indian vernaculars
Mohenjo Daro and Harappa
Sophisticated water technologies
Grid pattern thoroughfares
Multi-roomed houses
Bathing room connected to a street drain.
An estimated 700 wells
Mature Phase - Parts of city rebuilt several times
what type of well was there at the Mohenjo Daro site?
private
what type of well was there at the Harappa site?
public
what type of streets were in Mohenjo Daro?
narrow side
what was the public building at Mohenjo Daro called?
The Great Bath
what type of halls and buildings do Mohenjo Daro and Harappa have?
granaries, large buildings and halls (assembly halls and colleges)
do Mohenjo Daro and Harappa have palaces and funerary structures?
no

which artifact is this?
Unicorn Seal

which artifact is this?
Zebu Bull

which artifact is this?
burial pottery

which artifact is this?
ornament/jewelry

which artifact is this?
terracotta images

which artifact is this?
‘priest-king’

which artifact is this?
harappan burial site: male
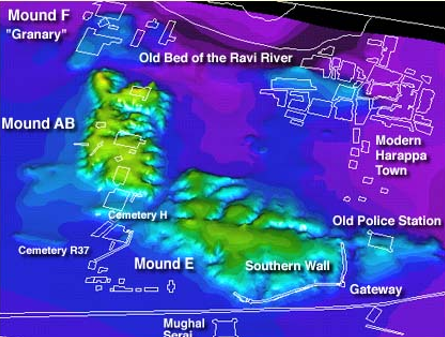
which artifact is this?
topography: harappa
where and when did Aryans come from?
central Asia via Afghanistan around 1500 BCE
where did Aryans migrate to?
some groups to region thats now Iran, other groups also went west into Europe
who developed Vedic Sanskrit?
Aryans
What is Vedic Sanskrit primaril worshipped through?
yajna
Vedic pantheon of elemental deities
Indra and Agni ‘messenger of the gods’
Aryan Migration Thesis
reasons for linguistic/cultural change
Cultural Diffusion hypothesis
Aryan Migration thesis re-examined
Asko Parpola involved
relations to Brahui language
what is the basis of Vedic religion?
Veda, meaining “knowledge”
classification of sruti
from Sanskrit root, sru - “to hear”
how as the vedic religion passed down?
orally by brahmins and vedic rituals
smrti
“smr” - to remember
smrti literature
regarded as a product of human composition
contrast between “revealed” and “traditional” religious literature
shruti is revealed/heard literature and smrti is remembered literature
what do Vedas contain?
a well developed set of rituals and myths
what are many deities called and related to?
called devas or ‘shining ones’ and related to natural forces
who is regarded as a creator deity in the Vedas?
Prajapati (Lord of Creatures)
is there a single “high god” in vedas?
no
vedic texts
vedas/veda samhita (collection)
four vedas
Rg, Sama, Yajir, Atharva
Brahmanas
vedic texts of ritual exegesis
Aranyakas
vedic text that bridge the concerns of the Brahmanas with the Upanishads
Upanishads
vedic text whose primary concern is with the nature of Absolute Reality (Brahman) and the true nature of the individual self (atman)
Rta
often translated as ‘right way’ and rendered as ‘cosmic order’
what does Rta show?
the Aryan civilization was aware of an overarching order in the cosmos (movement of planets, seasonal cycles)
vedic fire sacrifice
increase power of devas
humans and devas work together to maintain rta in the world
granted benefits for the sponsor are worldly concerns
what are vedic rituals called?
yajna
what does vedic literature begin to emphasize?
yajna even more than gods to show that yajna is a source of power even for the gods
what was necessary for anyone desiring to enter the heavenly realms?
performance of yajnas
what were most yajnas performed for?
the cosmic good or for the social well-being of society
srauta rites
use of three rites
maintain alignment with cosmos natural order
sponsor obtained beneficial fruits-prosperity, fertility, power
according to Hindu cosmology, what does the universe undergo?
vasty cycles of creation, dissolution, and recreation
according to Hindu cosmology, what is the devine intelligence behind all the cycles the universe goes through?
Brahman (the impersonal Absolute) or Ishvara/Bhagvan (personal God or “Lord”)
according to Hindu cosmology, what is the purpose of creation?
the manifestation of order in the universe
what are the four main Yugas (ages) that are each progressively shorter in duration?
Satya or Kata yuga
Treta yuga
Dvapara yuga
Kali yuga
what happens to yugas through time?
degeneration, life-spans diminish by ¼ and dharma decays
Upanishads
referred to as Vedanta the last or culmination of the vedas, consists of jnana that is salvific and leads to liberation
when were the Upanishads composed?
c. 800 to 400 BCE
what the Upanishads introduce?
several central concepts and practices
search for the one behind the many
‘the one in the many, the many in one’
Atman
Brahman
Atman
self (soul; inner spiritual reality)
what was Brahman later characterized by?
3 attributes: sat-cit-ananda [being, consciousness, bliss]
what are the four main caste groups (varna)
Brahmin
Kshatriya
Vaishya
Shudra
Avarna
without caste, outside the varna system, outcaste
terms from avarna groups:
Dalits, Harijan, scheduled castes, scheduled tribes
Dalits
oppressed ones
Harijan
children of god
who termed “Harijan” and what was it named before"?
Ghandhi, named “untouchables” before
who uses the terms “scheduled castes” and “scheduled castes” to describe avarna groups?
the government
caste system ranking from top of pyramid to bottom
Brahmin
Kshatriya
Vaishya
Sudra
Untouchable
which are the twice born groups in the caste system?
Brahmin, Kshatriya, and Vaishya
which part of the body do Brahmins represent?
mouth
which part of the body do Kshatriya represent?
arms
which part of the body do Vaishyas represent?
thighs
which part of the body do feet represent?
shudras
can one’s caste change within the current lifetime?
no, its hereditary
what are the dviisons within caste groups called?
Jatis
what is a complexity of the caste system?
caste does not correspond to wealth
Dharma Shastras
texts that provide a detailed description for the appropriate behavior of each varna; social codes of conduct
why are texts important to Brahmins?
they hold Brahmins to a very high standard of ethical and moral behavior, they are the caste associated with religious/spiritual status, knowledgem ritual skill, preservation of traditions
what are ritual purity and pollution?
religious categories that are not necessarily related to secular or scientific conceptions of clean/unclean or hygienic/unhygienic
what does Hinduism regard as worthy goals?
dharma and moksha
what does Hindu orthodoxy prescribe?
living life in an orderly manner, passing through sequential rites in accordance with one’s varna and gender
life transitions are marked by rites of passage: life-cycle rituals or samskaras
four major rites
upanayana
marriage (vivaha)
householder’s rites (also childrens rites)
final sacrifice (antyesti) funerary rites
four stages of life - Ashrama
student or brahmacarya (to about age 22)
householder or ghrhasta (married, with children)
retiree or vanaprasta (when ones child has a child, one can begin to withdraw from work and family responsibilities, to focus more on spiritual goals)
renouncer or samnyasa (ascetic), if one chooses
what are the four discrete stages that most people will pass through in life called?
Ashrama
what are the 4 aims or goals that are recognized as attractive to human life and deemed worthy of pursuit within the sphere of dharma?
Purushartha
4 aims or goals of life - Purushartha
Dharma istelf
Artha - material wealth and well-being
Kama - aesthetic/physical enjoyment or pleasure
Moksha - liberation; awakening; freedom from the cycle of rebirth
what is the initiation ceremony into the study of the Vedas (for the upper 3 caste males) or “twice born” or dvija called?
upanayana