Ionization Chambers
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What type of detector is this?
ionization chamber
What is the practical quantity of interest for ion chambers
the total number of ion pairs created along the track of the radiation
Is the average energy lost per ion pair formed is always less than or greater than the ionization energy?
Greater
Explain how an ion chamber works
Incoming radiation passes through a fill gas and ionizes atoms directly or indirectly, creating electrons and positively charged atoms. The resulting charges are collected by applying an electric field between electrodes
Are ion chambers operated in pulsed or current mode?
Both
What is an ion pair?
the resulting positive ion and free electron after a neutral molecule is ionized
What are the basic constituents of the electrical signal developed by the ion chamber? What is the practical quantity of interest?
Ion pairs; total number of ion pairs created along the track of the radiation
In order to permit ionization, what is the a minimum energy a particle must transfer?
energy greater than the ionization energy of the gas molecule (between 10 - 25 eV)
What is W?
The average energy lost by the incident particle per ion pair formed
What is W for air with incoming fast electrons?
33.97 eV
What is W for air with incoming alpha particles?
32.2 eV
What is the most important aspect for a relative dosimeter?
Its precision
Why is exposure significant?
The energy fluence Ψ is proportional to the exposure X for any given photon energy.
The mixture of elements in air is similar to soft biological tissue (in atomic number).
The value of collision kerma Kc in muscle, per unit of exposure X, is nearly independent of photon energy.
How is charge, exposure, collisional karma, and air karma related?
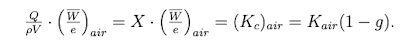
Whenever an external electric field is applied to the gas-filled region of an ion chamber, the electrons and ions will move…
away from their point of origin
For ions in a gas, at 1atm, and at a typical E field of 104 V/m, the drift velocity will be on the order of …
1 m/s
How much greater is the mobility of free electrons compared to ions?
1,000 times greater
Charge transfer collision
occurs when a positive ion encounters another neutral gas molecule. Electron is transferred, reversing the roles of each
Diffusion
the result of ions tending to diffuse away from regions of high charge density. More likely for electrons (than ions).
Most fill gases are …
electronegative
Why are electronegative gases good insulators?
Negative ions drift much slower than electrons so they will have a greater amount of time to “see” more positive ions (produced at a later time) and thus have a higher chance of recombining with them.
Recombination
When a positive and negative ion or positive ion and an electron interact, causing the electron to either be transferred from the negative ion to the positive ion or for the free electron to be captured by the positive ion
Why is recombination undesirable?
It results in less charge being collected than what was produced.
Initial recombination
same particle track
General recombination
different particle tracks
Initial recombination is mostly independent on the number of particle tracks. What is it more dependent on?
the density of the ionization along the track or Linear Energy Transfer (LET)
Is general recombination or initial recombination dose-rate dependent?
general recombination
If the production of ion pairs is uniform throughout the volume of the ion chamber, then the drift of charges will create some gradients and imbalances in the stead-state concentrations of the charge carriers. The concentrations will be highest where?
At either electrode
What is the direction of diffusion and its effect?
opposite of the normal direction due to the electric field, and the effect is a reduction in measured current
What bias is used to reduce recombination?
a higher bias but there is a point where electrical breakdown occurs
What is the one component common to all modern electrometers and critical to their operation?
Operational amplifiers
What is the function of the wall of a dosimeter?
provide a source of secondary charged particles to establish charged-particle equilibrium (CPE) or transient charged-particle equilibrium (TCPE)
shield the cavity from particles that originate outside of the wall.
How thick does a thick-walled dosimeter need to be?
the wall must be at least as thick as the range of secondary charged particles present in order to provide CPE
What is the rule of thumb for wall thickness of a thin-walled dosimeter?
neither the wall thickness nor that of the sensitive volume should exceed 1% of the range of the incident charged particles
Thick-walled dosimeters determine quantities based on the characteristics…
of the local photon field
Thin-walled dosimeters determine quantities based on the characteristics…
of the local secondary charged-particle field
When calculating effective Z, what is the exponent of 3.5 related to?
3.5 relates to an empirical formula for the photoelectric process
What detectors are temperature and pressure relationships most important?
air-communicating chambers
Why are temperature and pressure relations not necessary for sealed chambers?
Sealed chambers do not change with ambient conditions and are useful in certain situations where the temperature and pressure are difficult to monitor.
What is the formula for temperature and pressure corrections?
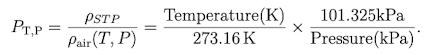
What purposes does a guard serve?
The guard shapes the electric field in the chamber volume in such a way that it defines the collection volume more consistently and smaller, if desirable.
The guard reduces unwanted ionization events from being collected outside the collection volume, sometimes referred to as stem effects.
What are the downsides of an unguarded chamber?
Small changes in the bias applied will change the effective collection volume.
Unwanted stray magnetic or electric fields (such as a person walking by) will affect the volume of the chamber, causing the chamber to be noisy.
What is the most common bias used in radiation dosimetry?
300 V
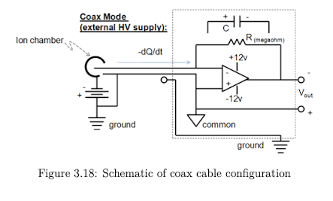
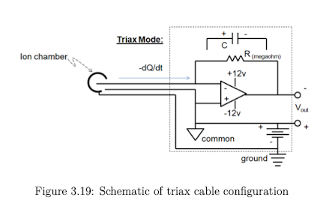
When is a coax cable typically used?
used for chambers with an external power supply or chambers without guarding
Triax Cable Schematic
Coax Cable Schematic