Therapeutics - Gastrointestinal
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Constipation
condition of unsatisfactory defecation through passing stools less frequently than normal, difficulty passing stools or the feeling of incomplete emptying when opening the bowel
what is normal varies
classified as - spontaneous bowel movement occurring fewer than 3 times per week
constipated info
affects all ages
2-3 times more common in women than men
more common over 60 years
question patients frequency and consistency
risk factors - sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, avoiding going to the toilet when needed
can be drug induced - opioid analgesics
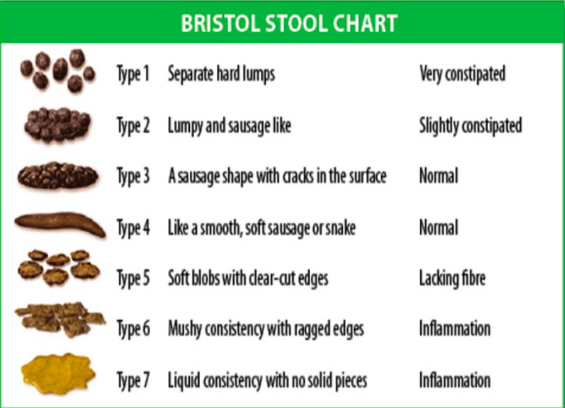
bristol stool chart
constipation management - pharmacological
managed with laxatives
bulk forming ispaghula
osmotic e.g. lactulose or macrogels
surface-wetting agents - docusate
stimulant - senna, sodium picosulphate
enemas and suppositories - phosphate enemas, glycerol suppositories
Prucalopride - available on prescription
constipation - management - non pharmy
increase physical activity
increase fluid intake
eat a balanced diet - regular eating pattern
regular toilet routine
Diarrhoea overview
WHO defines as passing or more loose or liquid stools per day
Classified as acute, persistent or chronic
acute < 14 days
persistent >24 days
chronic > 4 weeks
Chronic diarrhoea associated with IBS, IBD, coeliac disease, bowel cancer
diarrhoea causes
viral
bacterial
side effect of meds
anxiety
food intolerance
diarrhoea diagnosis
any triggers, duration, frequency, severity of symptoms
is it normal for Pts
any recent foreign travel
stool sample taken in more severe cases
need to rule out red flags-unexplained weight loss, blood in the stool, nocturnal symptoms
important to asses dehydration - pinch test
diarrhoea treament
Electrolyte imbalances and dehydration need to
be addressed – rehydration salts (e.g.
Dioralyte®) appropriate, particularly in children,
pregnant women and the elderlyLoperamide (e.g. Imodium®) can be given but
should be avoided where the cause is
infectiousOpioid analgesics cause constipation as a side-
effect and can be considered where
appropriate – codeine is licensed to treat acute
diarrhoea
Irritable bowel syndrome over view
chronic, relapsing condition triggered by biological, psychological and social factors
not IBD
affects 5-20% of the globe but more common in young adults
IBS symptoms
lower abdominal pain - spasmodic/sharp
bloating
bouts of constipation
bouts of diarrhoea
IBS diagnosis
presence of symptoms for 6 months
symptoms made worse by eating but relieved by defecation
Blood and stool tests used to rule out other causes IBD or cancer
IBS - management non pharmy
dietary changes - more or less fibre increased fluid
regular physical activity
stress management - brain-gut link
IBS - management pharmy
Loperamide for diarrhoea
Laxatives for constipation
Abdominal pain/spasms managed with
antispasmodics such as hyoscine butylbromide,
mebeverine, dicycloverineTricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) or Selective
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) can be
used where symptoms do not respond to
antispasmodics – note: these are POMs
Indigestion
Indigestion / heartburn occurs when the acidic
contents of the stomach move back up into the
oesophagus due to the sphincter at the base of the
oesophagus being less effective
main symptom of indigestion
The main symptom is a burning sensation in the
middle of the chest – it is important to distinguish
this from a heart attack!
• Patients may visually describe the feeling by
clenching their fist across the chest and moving it
downwardsOther symptoms include unpleasant taste in the
mouth, a non-productive cough, bloating and
nausea
Indigestion red flags
unexplained weight loss
blood in vomit/stool
difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
Signs of a heart attack (myocardial infarction)
sweating
pain radiating to left arm, jaw, neck or back
feeling faint or dizziness
indigestion management - non pharmy
avoid trigger foods
eat smaller more frequent meals
raise the head of the bed to bring chest above the level of waist
reduce stress
wear loose fitting clothing
reduce alcohol intake
indigestion management - pharmy
antacids - reduce pH of the stomach contents
alginates - form raft on top of stomach contents to help protect oesophagus
Proton-pump inhibitors - used to manage GORD, mostly POM but some P meds
Histamine H2 antagonists - limited due to adverse effects with ranitide