Cell specialization & differentiation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is a specialised cell?
A cell that has a structure that aids its specific function - this could relate to cell shape, or the combination of cellular structures present within the cell.
What is cell differentiation?
The process by which a cell changes to become specialised for its function.
When does cell differentiaton occur in animals?
Cell differentiation occurs as the organism develops. In most animal cells, the ability to differentiate is lost at an early stage after becoming specialised.
When does cell differentiation occur in plants
Lots of plants don’t ever lose the ability to differentiate, so can differentiate at any point in their life span.
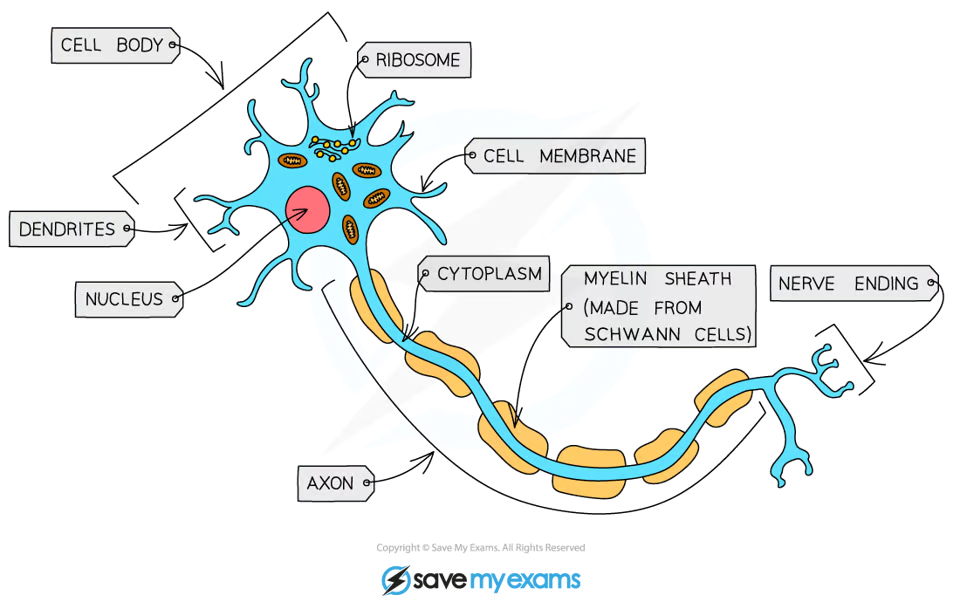
What is the function of nerve cells?
Carry electrical signals/impulses from one part of the body to another.
How are nerve cells specialised for their function?
Are long so can cover more distance - can conduct nerve impulses between different areas of the body
Have extensions of the cytoplasm called dendrites - allow nerve cells to form branched connections with other nerve cells and receive/send impulses to muscles & glands
Have a myelin sheath that insulates the axon & speeds up the transmission of impulses along the nerve cell
Nerve endings have many mitochondria - supply the energy to make special transmitter chemicals (neurotransmitters) which allow the impulse to be passed from one cell to another
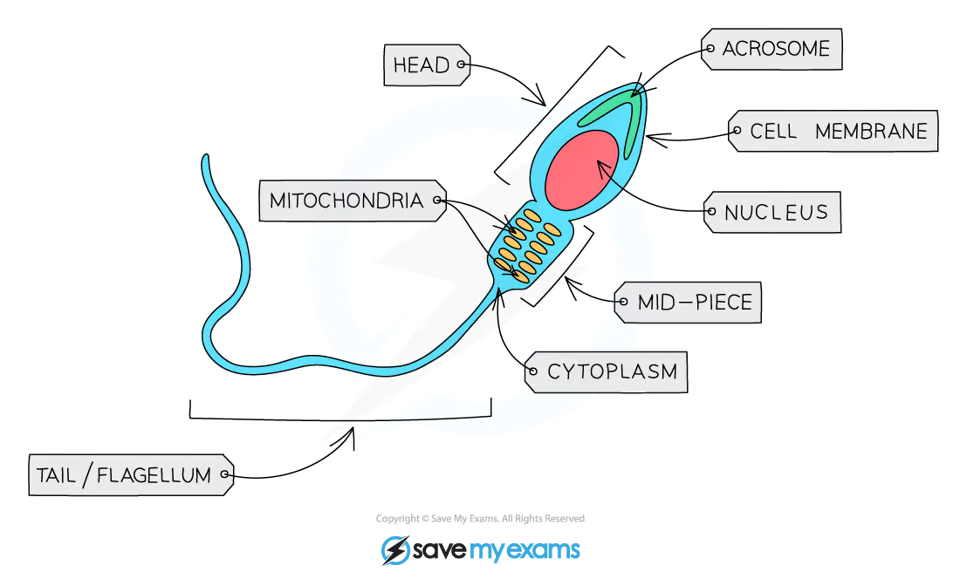
What is the function of sperm cells?
Transfer the male DNA to to an egg cell for fertilisation.
How are sperm cells specialised for their function?
Mid piece is full of mitochondria to release energy (through respiration) for the tail
Long tail (flagellum)& streamlined head help it swim to egg
Carries digestive enzymes located in the acrosome that can break down the outer layers of membrane of the egg cell
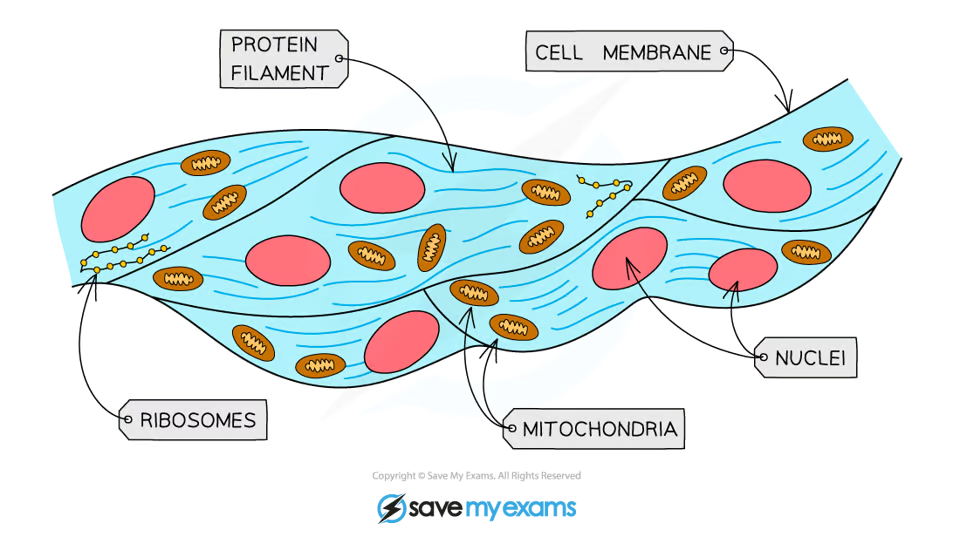
What is the function of muscle cells?
To contract quickly for movement.
How are muscle cells specialised for their function?
Long so they have space to contract
Have many mitochondria to release energy (through respiration) for contraction
Contain protein filaments that can slide over each other to allow muscle contraction
What is the function of red blood cells?
To carry oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues.
What protein do red blood cells contain? What does it do?
Haemoglobin. It binds to oxygen so it can be carried in the red blood cells and releases it in tissues.
How are red blood cells specialised for their function?
Biconcave shape - increases surface area for faster oxygen diffusion and makes it easier to move through narrow capillaries
No nucleas - leaves more room for haemoglobin, which carries oxygen
Contain haemoglobin pigment - binds to oxygen in the lungs & releases it in the tissues
Small & flexible - can squeeze through tiny capillaries to reach every cell
What 2 sub-cellular structures do RBCs have?
Cell membrane - controls what enters/leaves the cell
Cytoplasm - where haemoglobin is dissolved
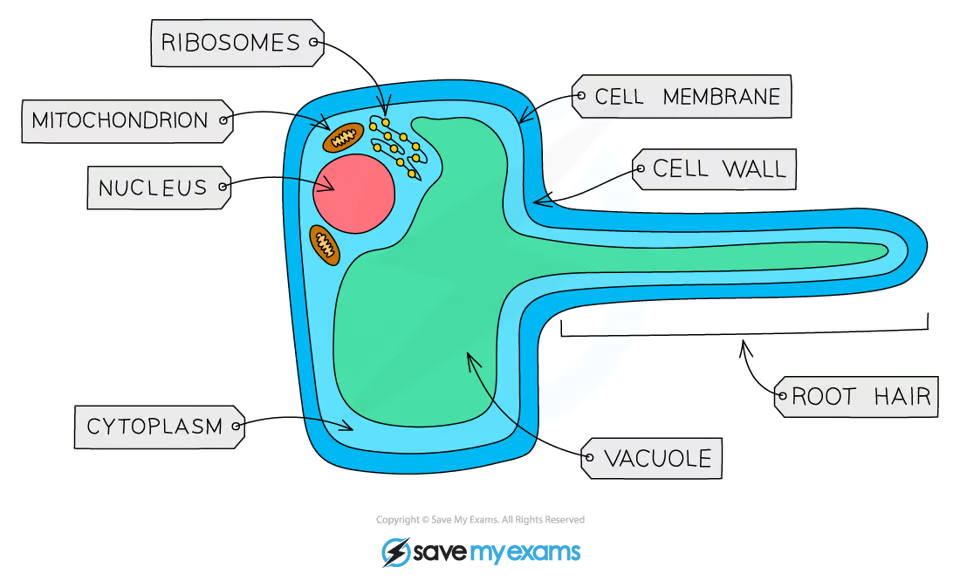
What is the function of root hair cells?
To absorb water & mineral ions from soil.
How are root hair cells specialised for their function?
Root hair cells increase SA so the rate of water uptake by osmosis is greater
Thinner walls than other plant cells so water can move through easily due to shorter diffusion distance
Mitochondria release energy for active transport of mineral ions into root hair cell
What is the function of xylem cells?
To transport water & dissolved ions up the plant from roots to shoots.
How are xylem cells specialised for their function?
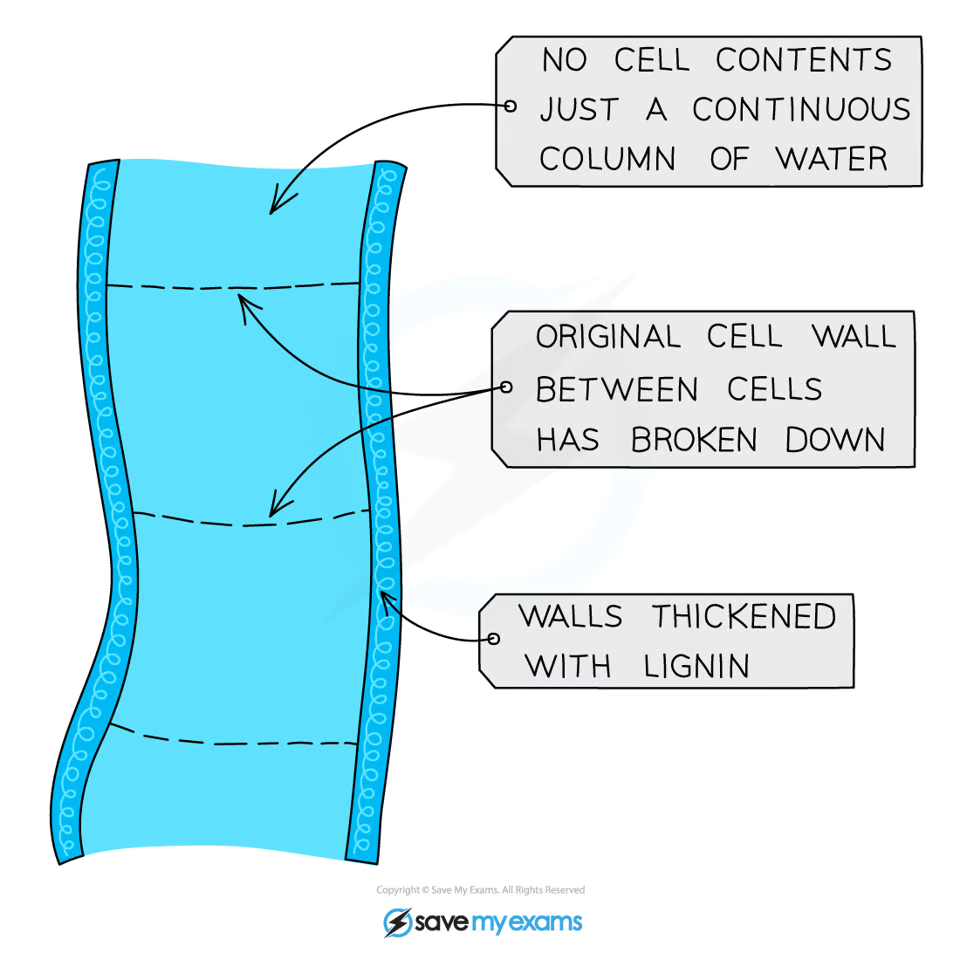
No walls between cells to form continous hollow tubes where water is drawn upwards towards the leaves
Cells contain no organelles or cytoplasm allowing free passage of water
Outer walls are thickened with lignin, strengthening the tubes & providing support for the plant
What is the function of phloem cells?
To transport dissolved sugar & amino acids to all parts of the plant.
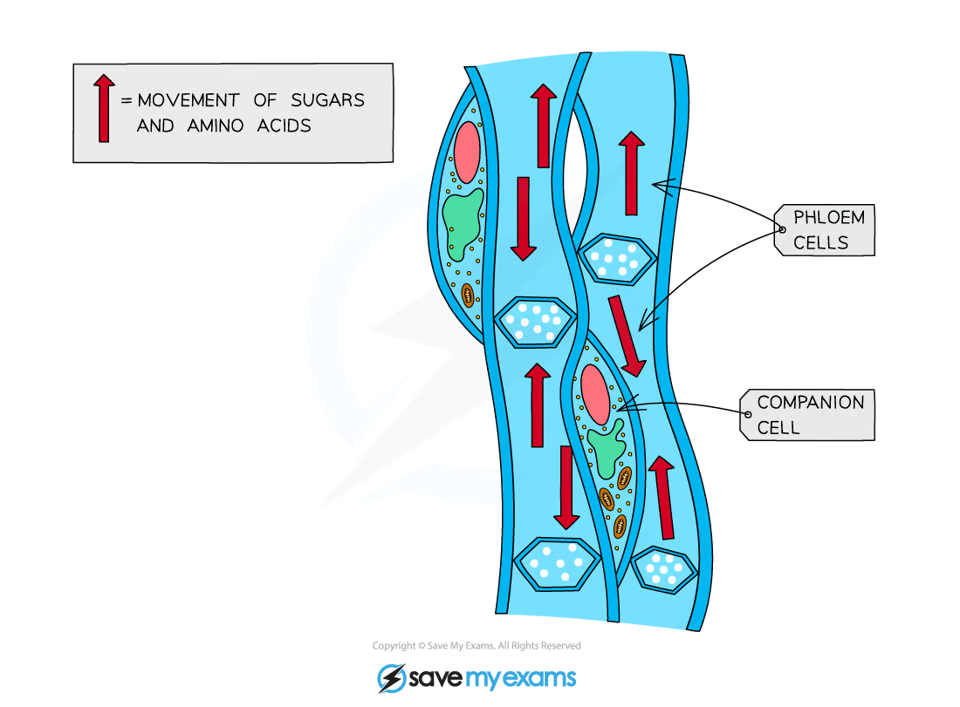
How are phloem cells specialised for their function?
Cells are joined end to end & contain holes in the end cell walls called sieve plates, which allow the movement of substances from cell to cell
Have very few subcellular structures to aid the flow of materials
Describe one way in which the nucleus of a sperm cell is different to that of a muscle cell:
A sperm cell nucleus has half the number of chromosomes (23) that a muscle cell nucleus does (46).
Compare the process of cell differentiation in animals vs plants:
In animals cell differentiation occurs only in early development, ability to differentiate is lost when cells become specialized. Cells in plants retain the ability to differentiate, so can differentiate at any point in their lifespan.