L22 The Chemical Senses (Imported from Quizlet)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Oldest, common
The chemical senses are the ________ and most _________ form of sense
Identify food sources, avoid noxious substances, find a mate or mark territories
What are the functions of the chemical senses?
Cravings
What can deficits in nutrients lead to?
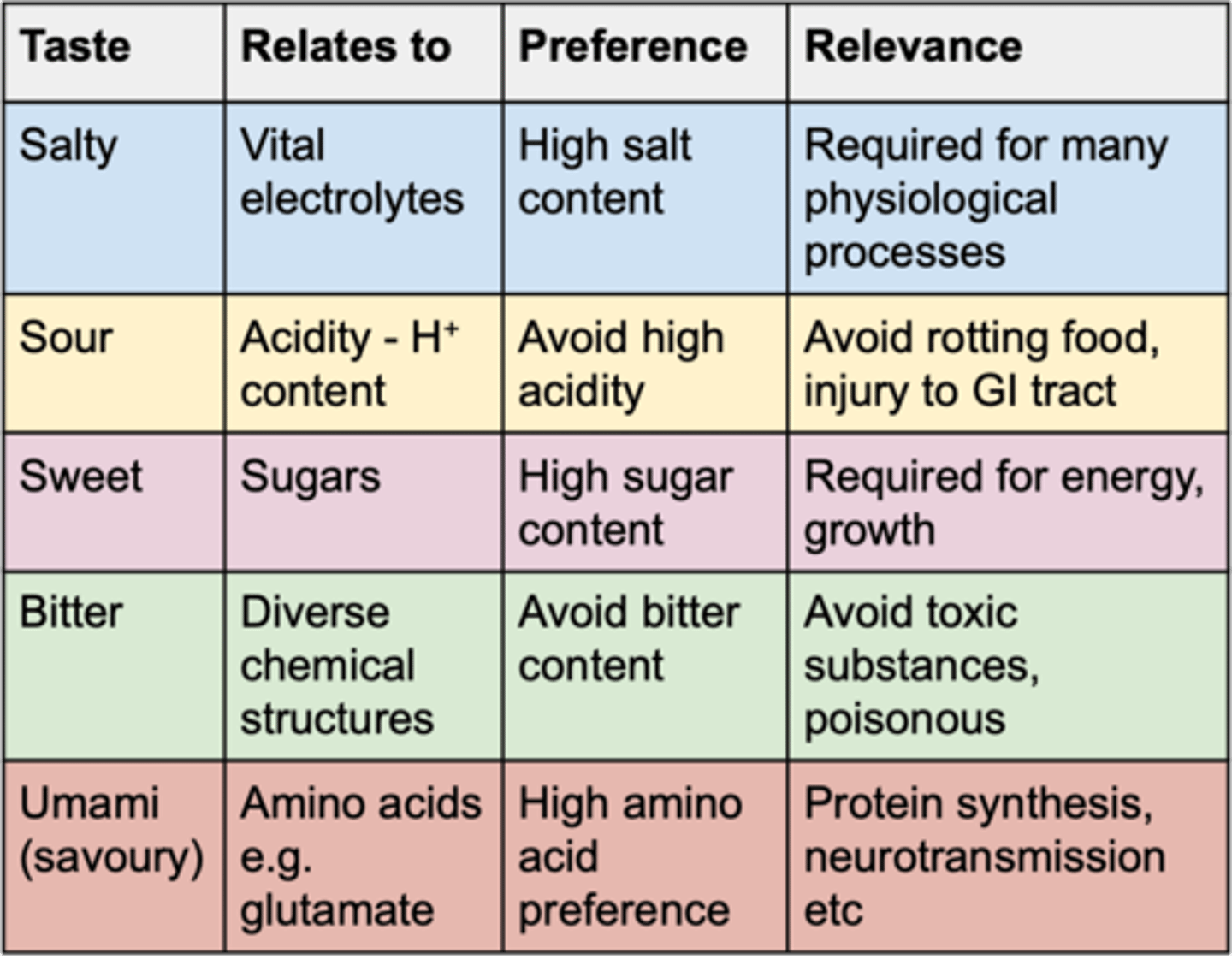
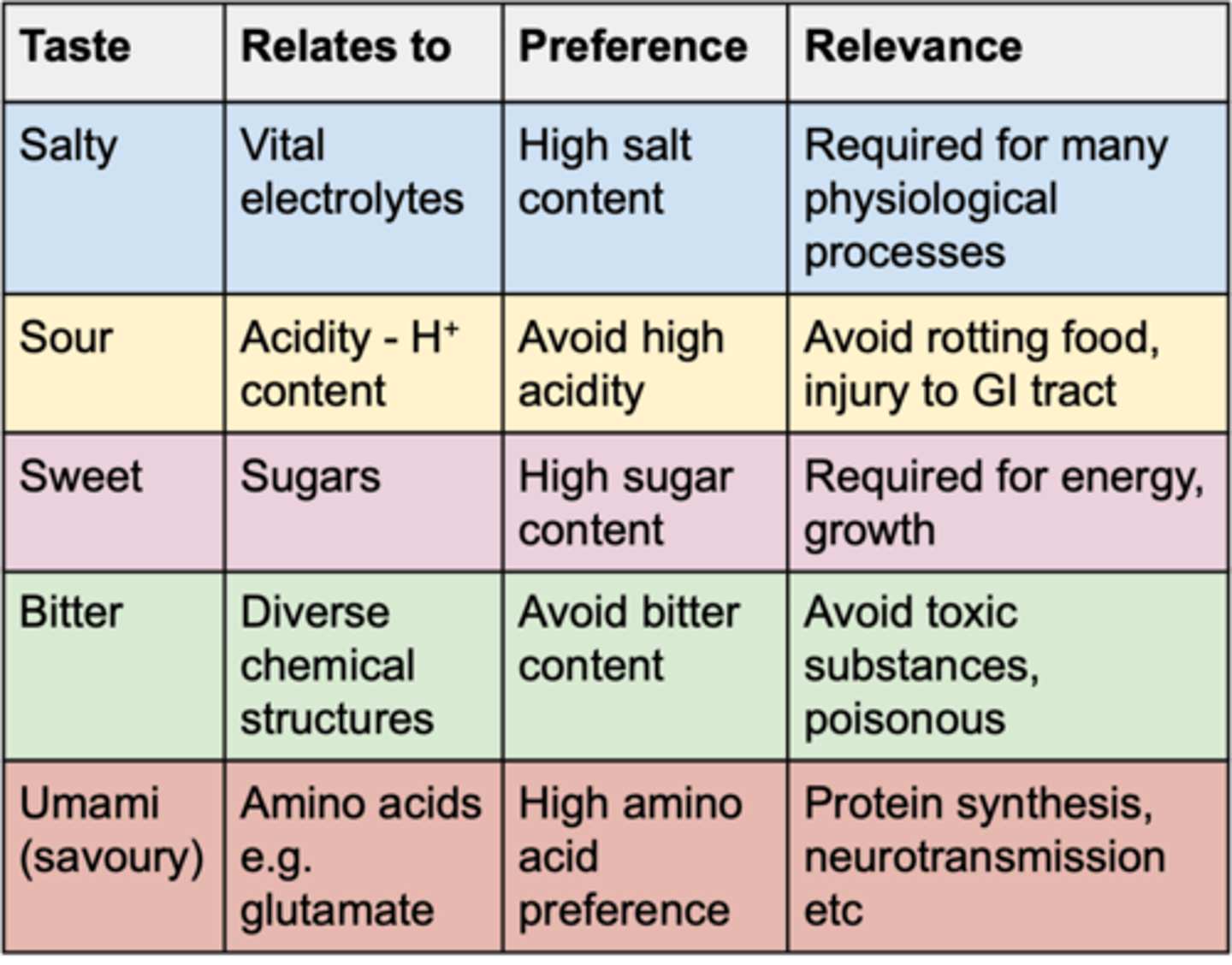
The 5 basic tastes
Cortex
Combination of taste, smell and touch (texture) are combined in the _________
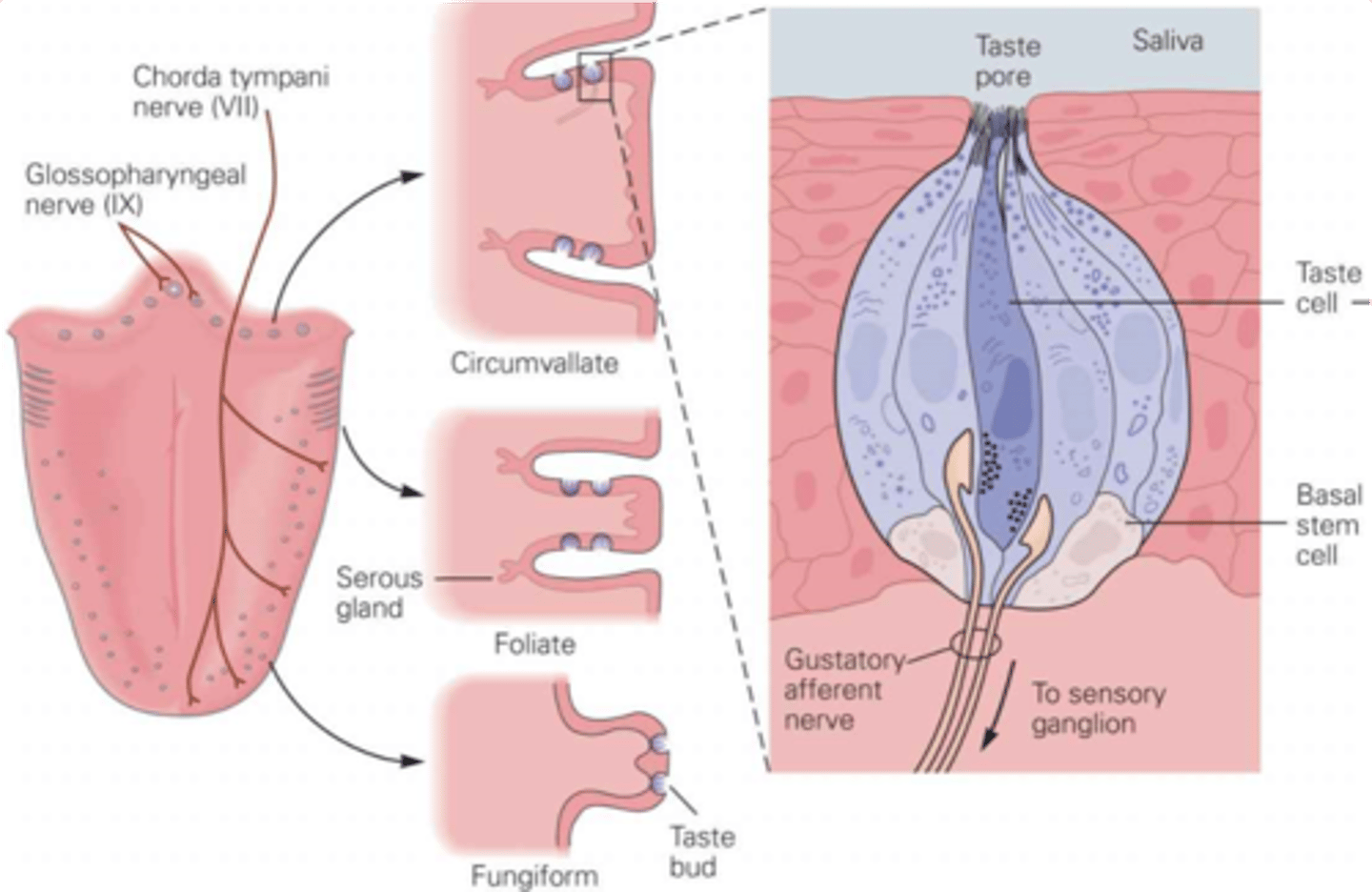
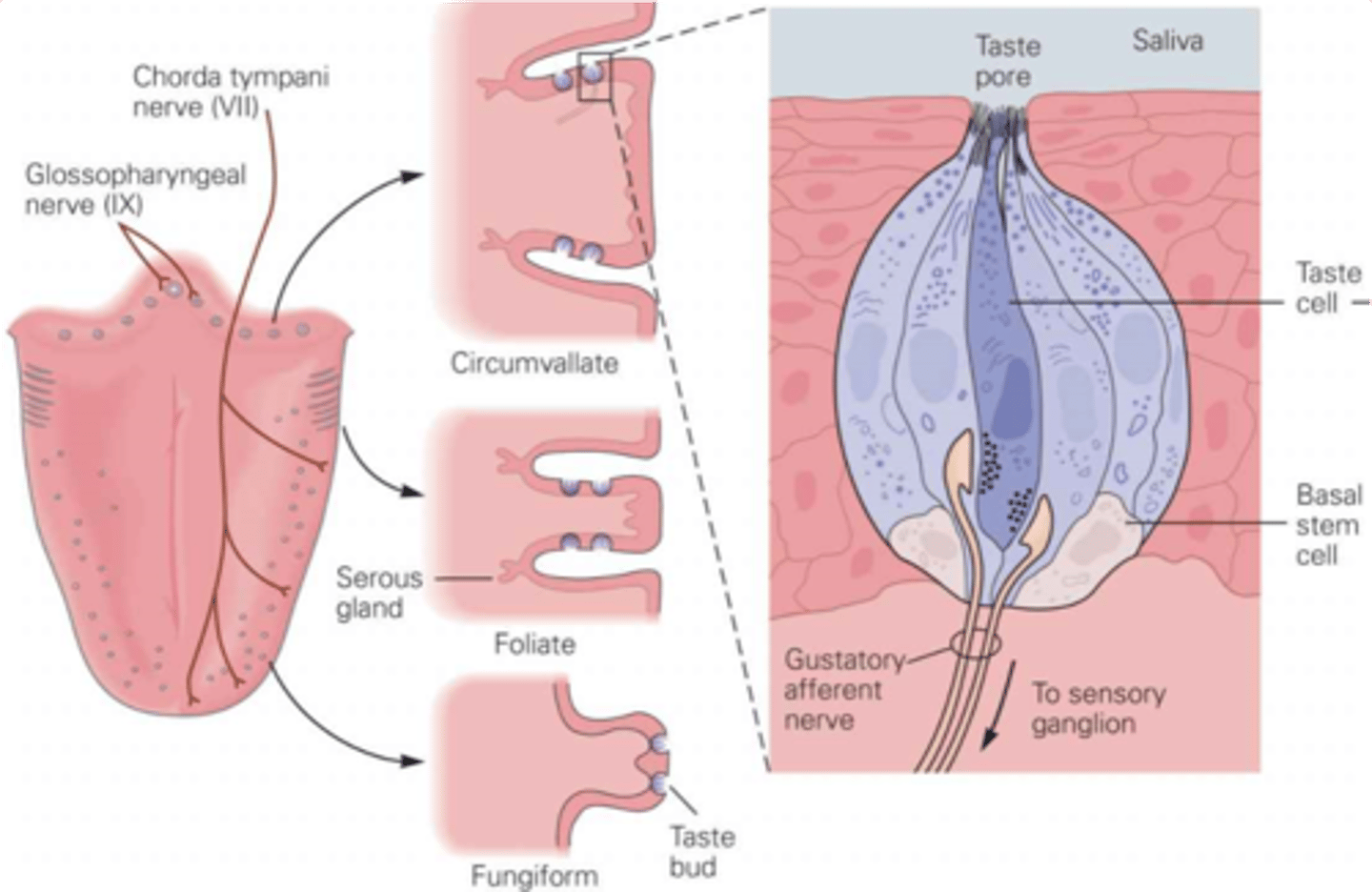
Taste buds
What does the lingual papillae contain?
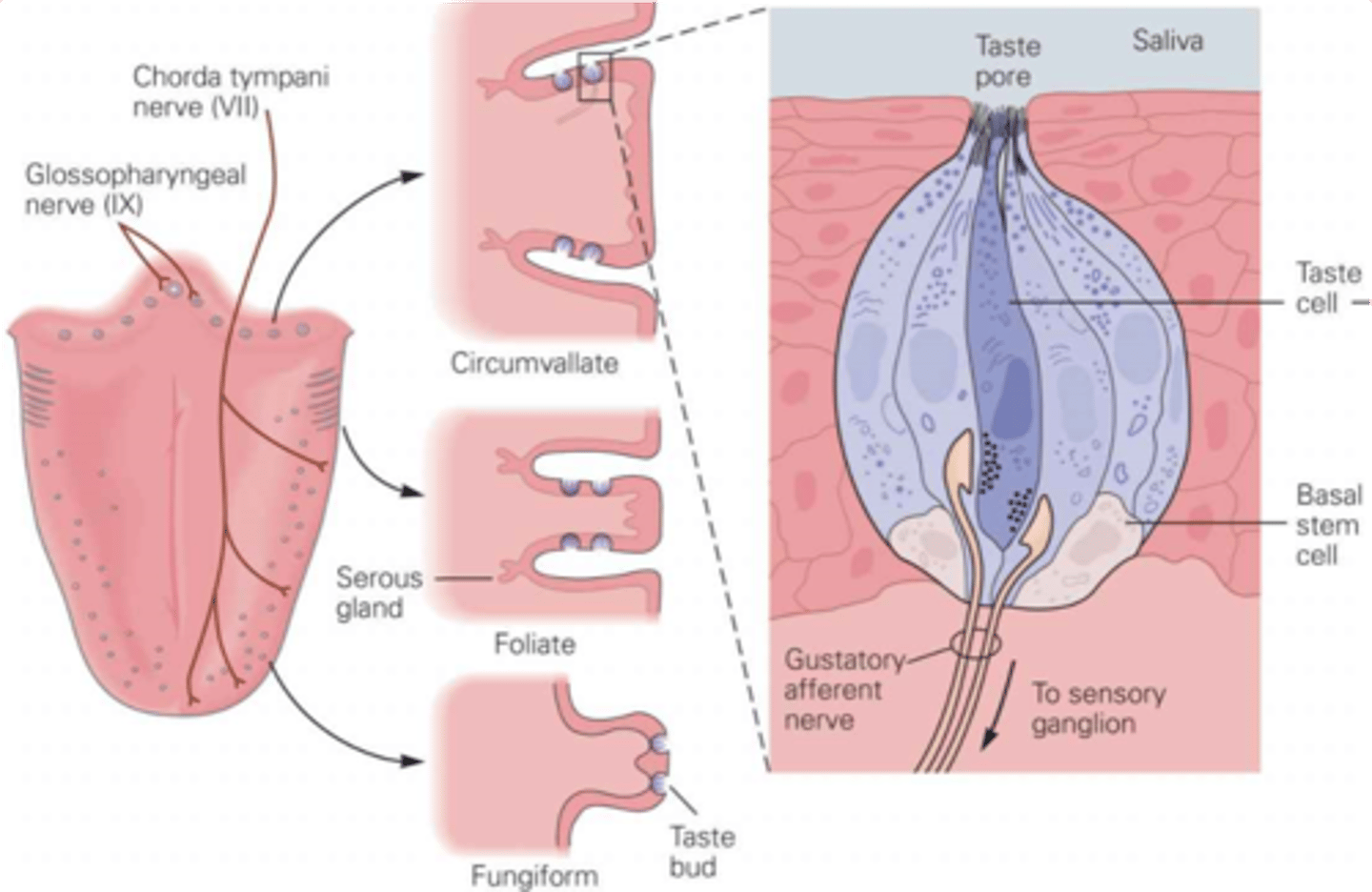
Groups of taste cells
What are taste buds?
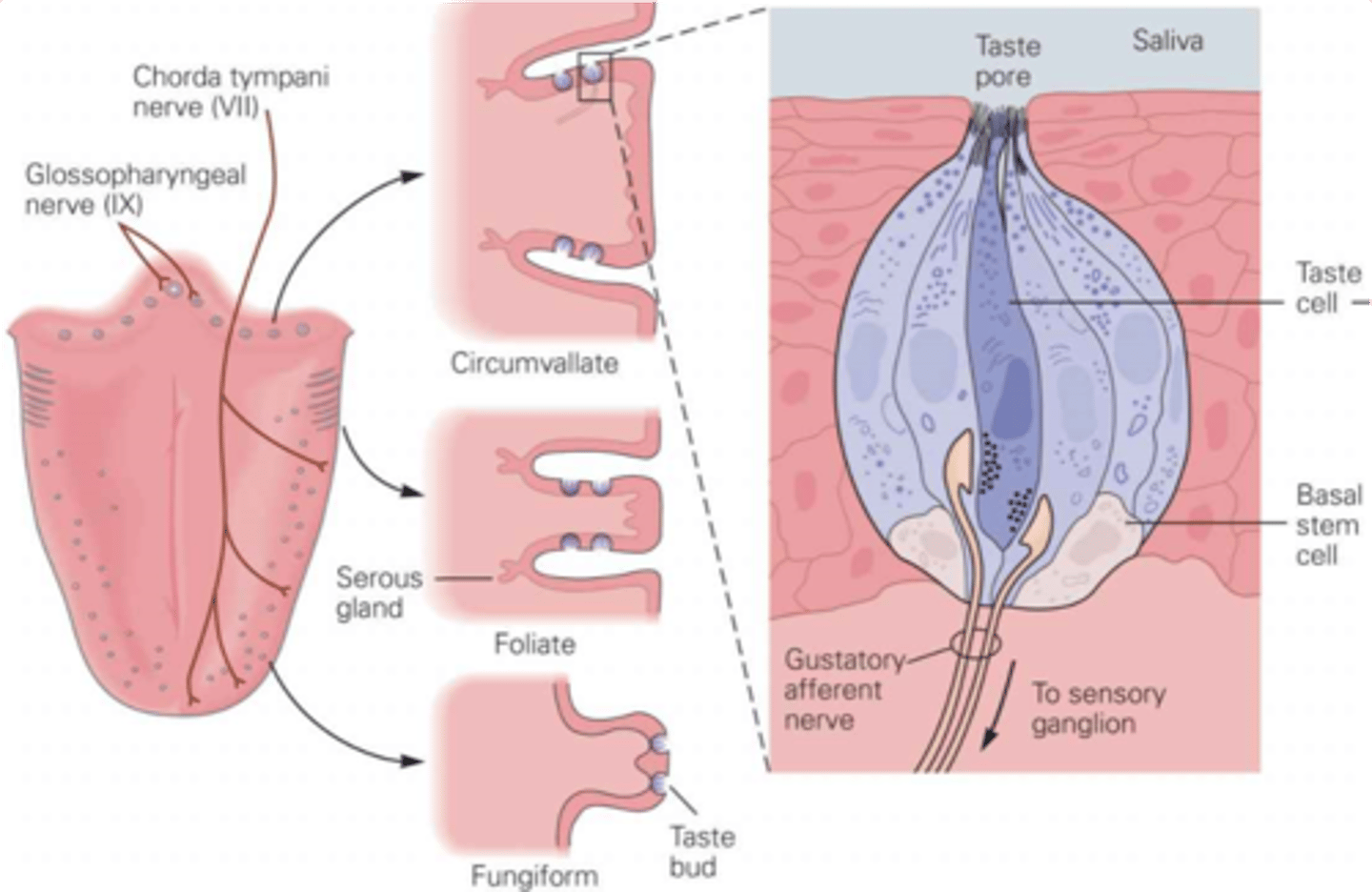
Primarily tongue, also cheeks, soft palate, pharynx, epiglottis
What are the taste organs?
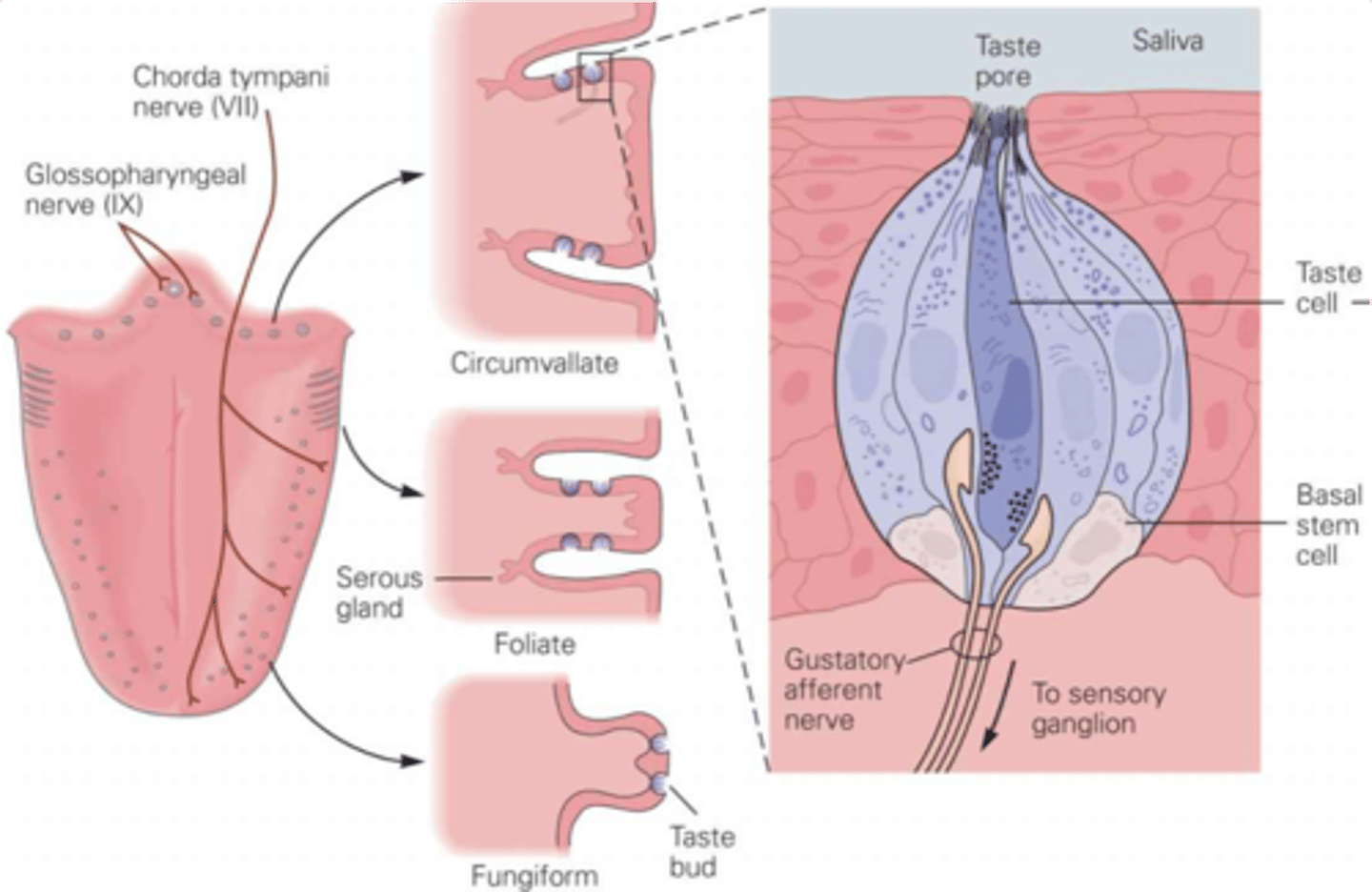
Filiform - spiked, no taste buds, sense texture, most abundant
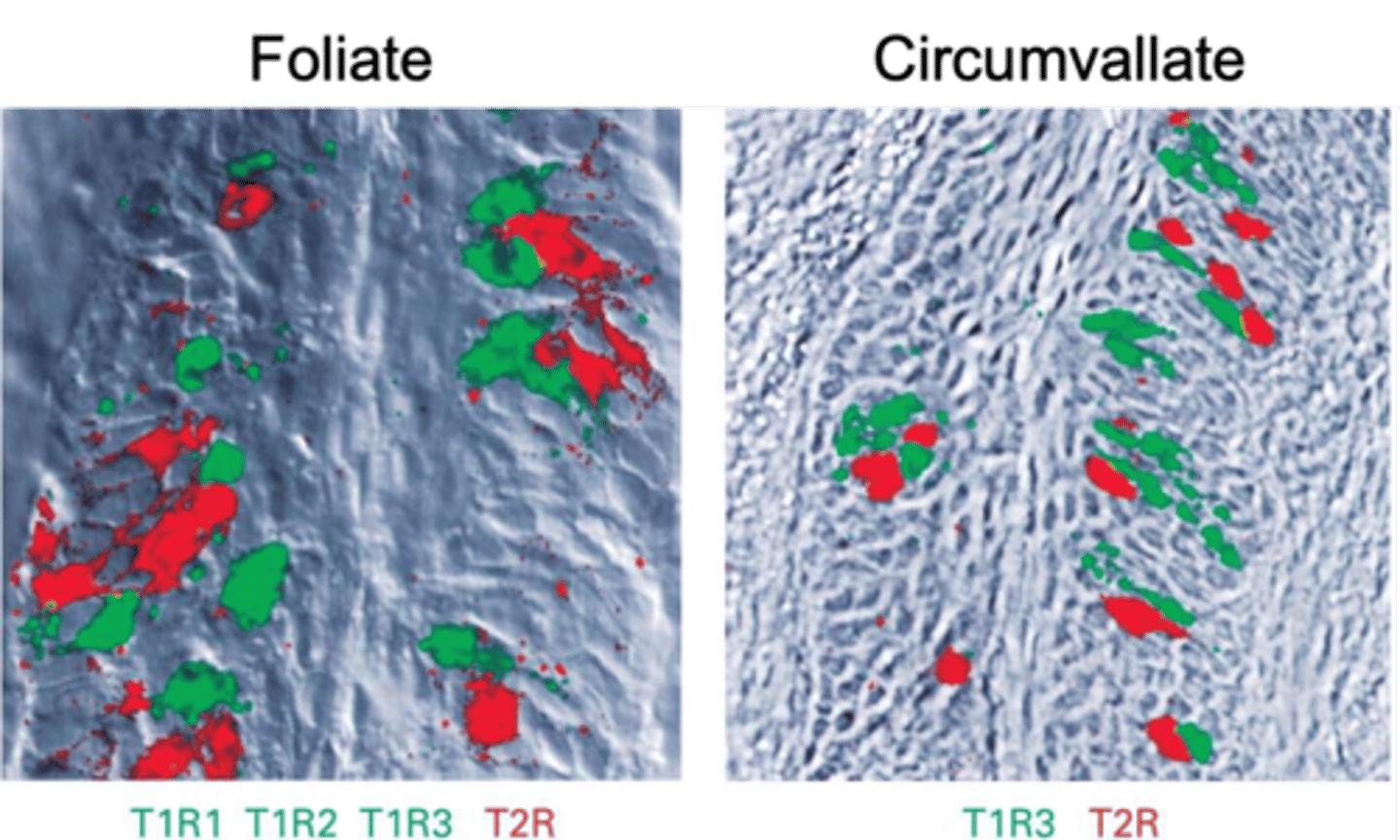
Foliate - ridges
Fungiform - mushrooms, mainly at sides and front
Circumvallate - pimples, large, contain about half of all taste buds
There are 4 types of lingual papillae, what are they and describe their properties
2000-5000
____-____ taste buds
100
~___ chemoreceptive taste cells per taste bud
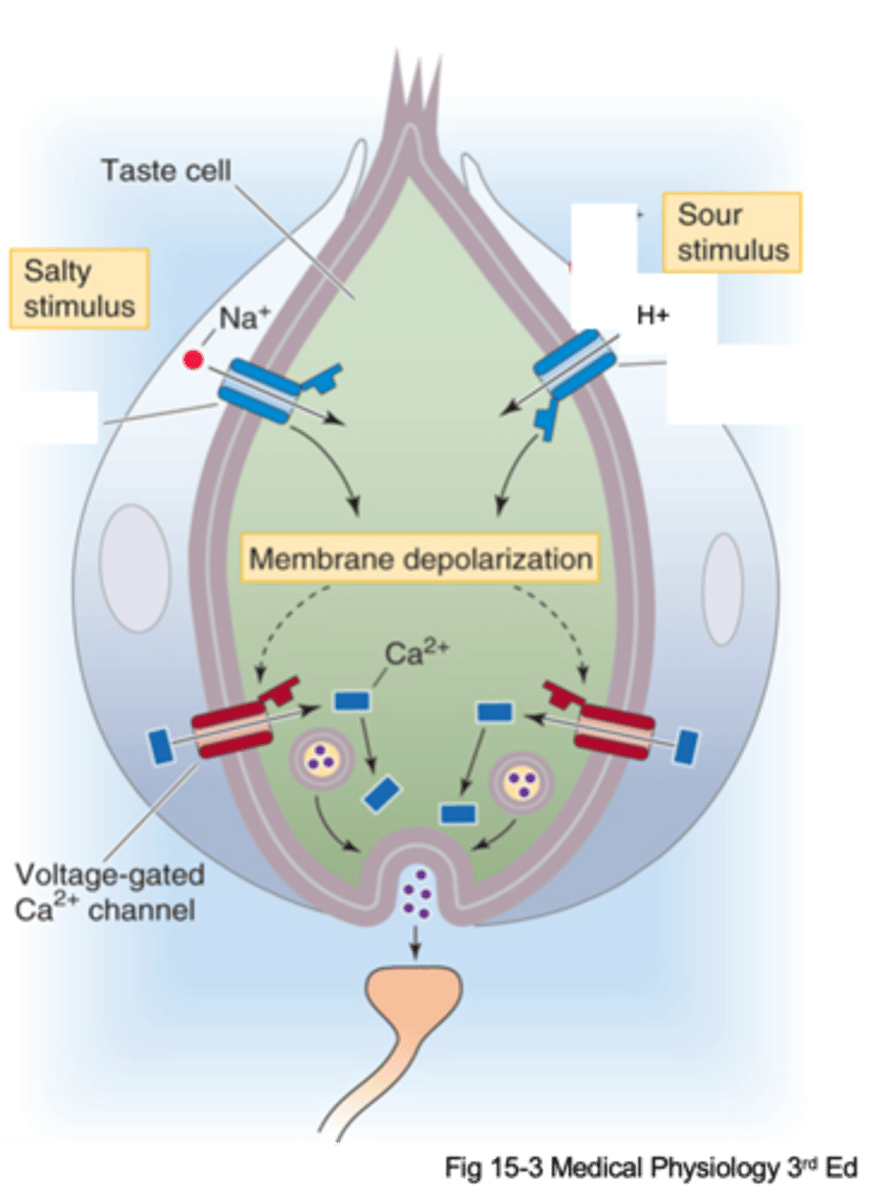
Sensory transduction by microvilli
What do taste pores allow?
Which membranous receptors are expressed
What does transduction of different stimuli depend on?
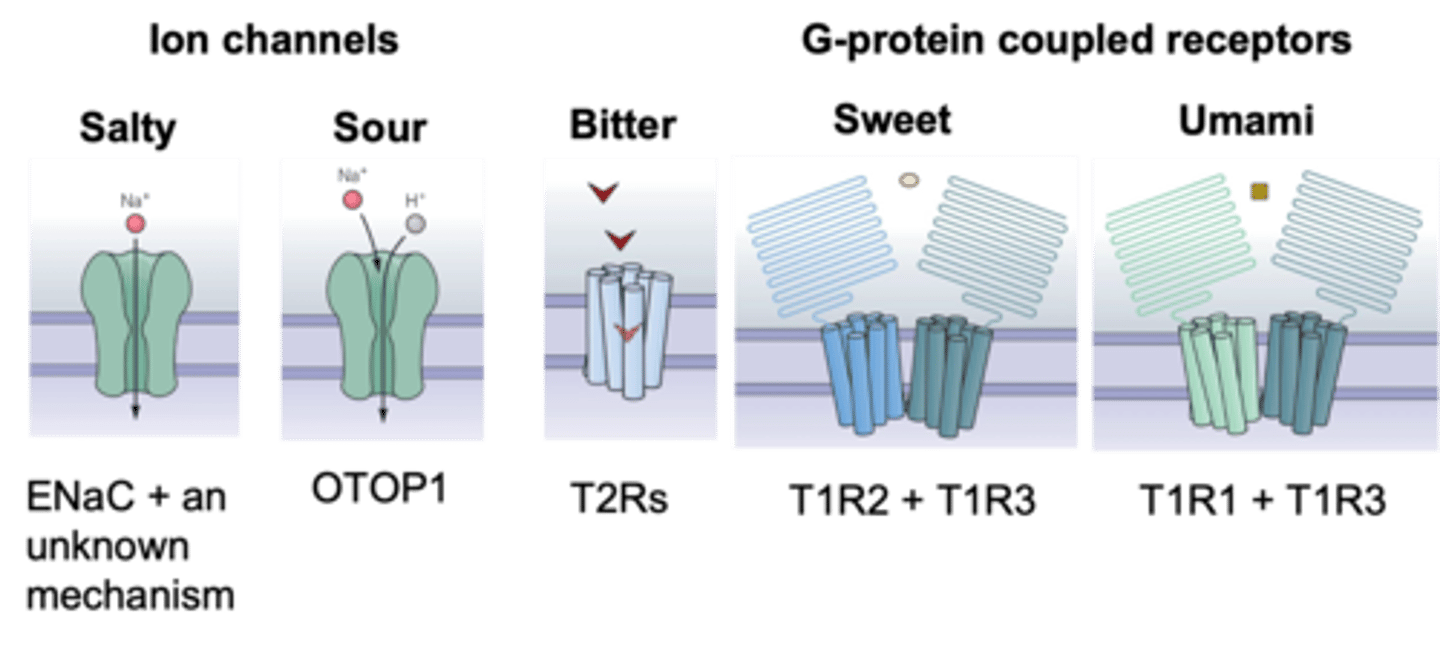
Taste cells appear to only respond to one type of stimuli but taste buds contain taste cells which respond to various stimuli
What is the difference between taste cells and taste buds?
Neurotransmitter release across the synaptic cleft
Gustatory afferents are separate cells to the taste cells, what do they require?
Trillion
Odorants as low as a few parts per _________ can be detected
10, 170, 100
Human olfactory epithelium = __cm2
Dog olfactory epithelium = ___cm2
Dogs have ___x more receptors/cm2
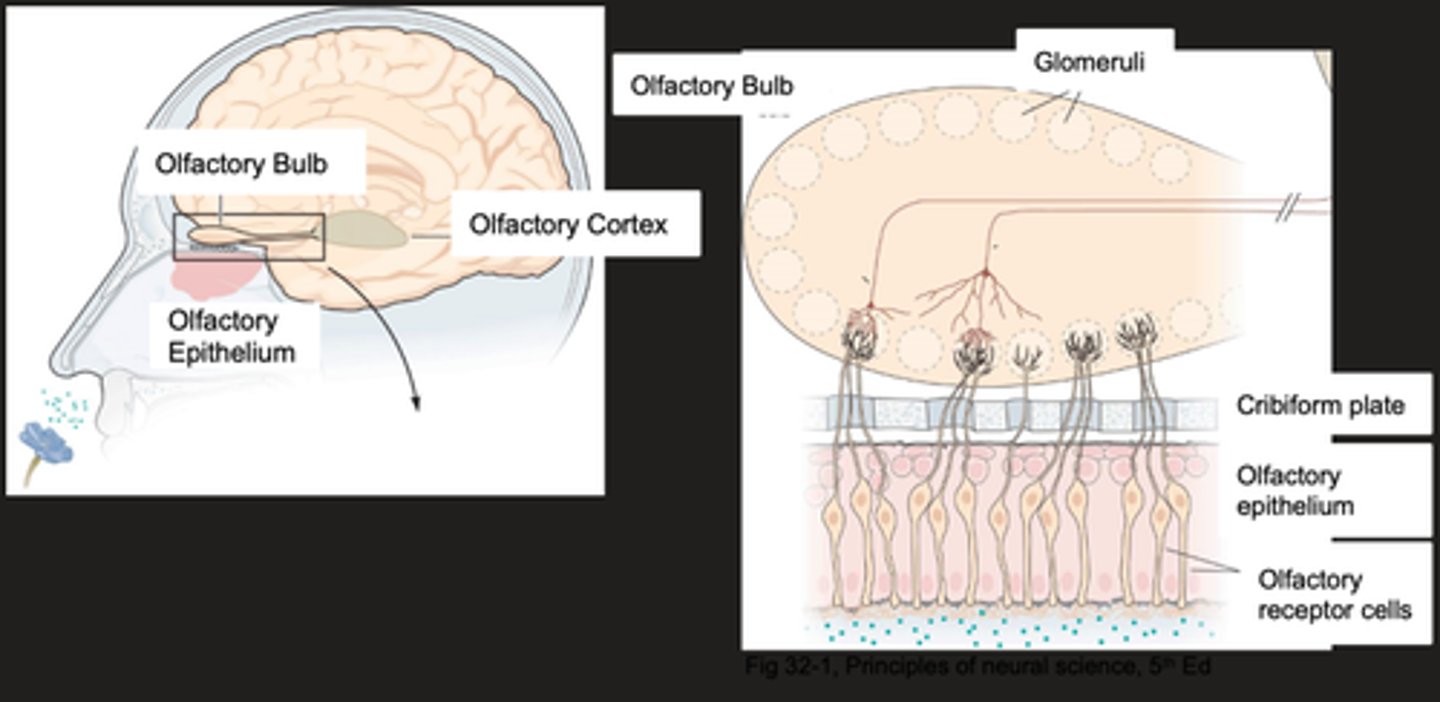
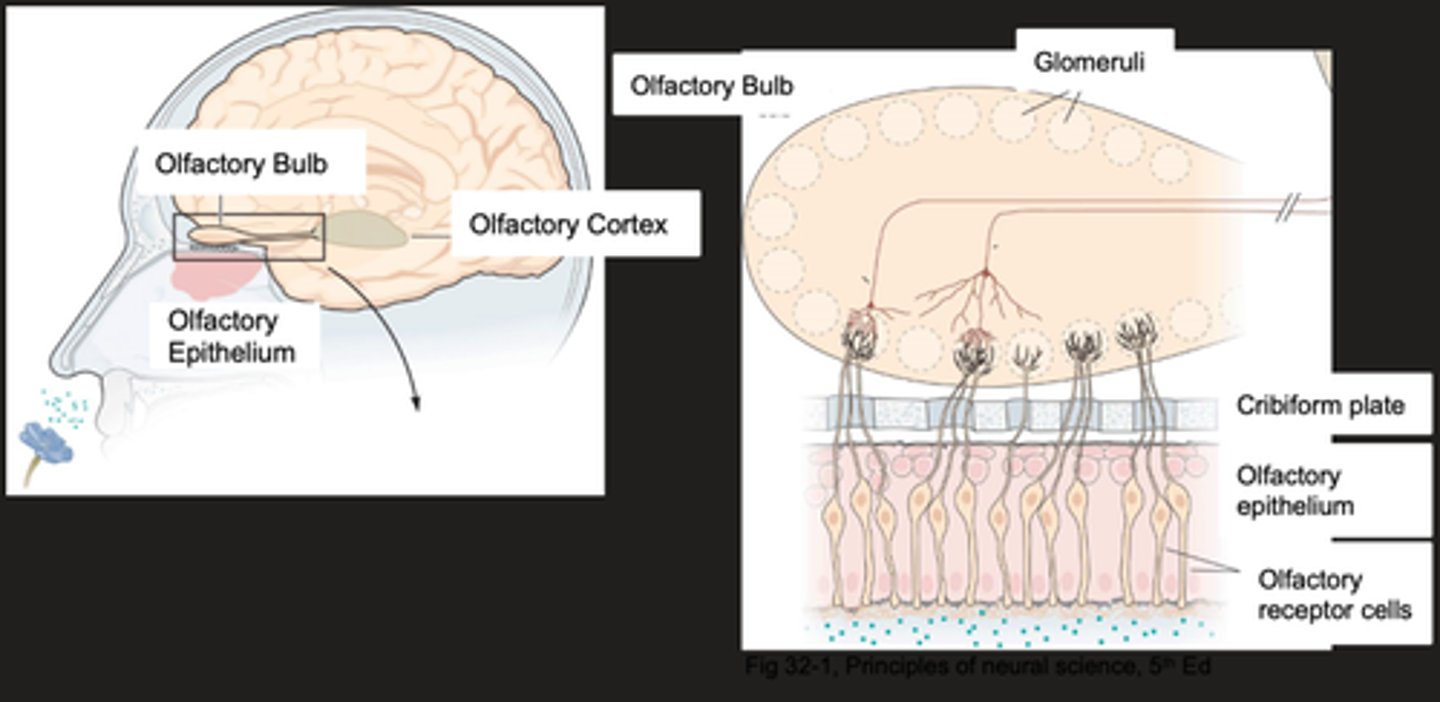
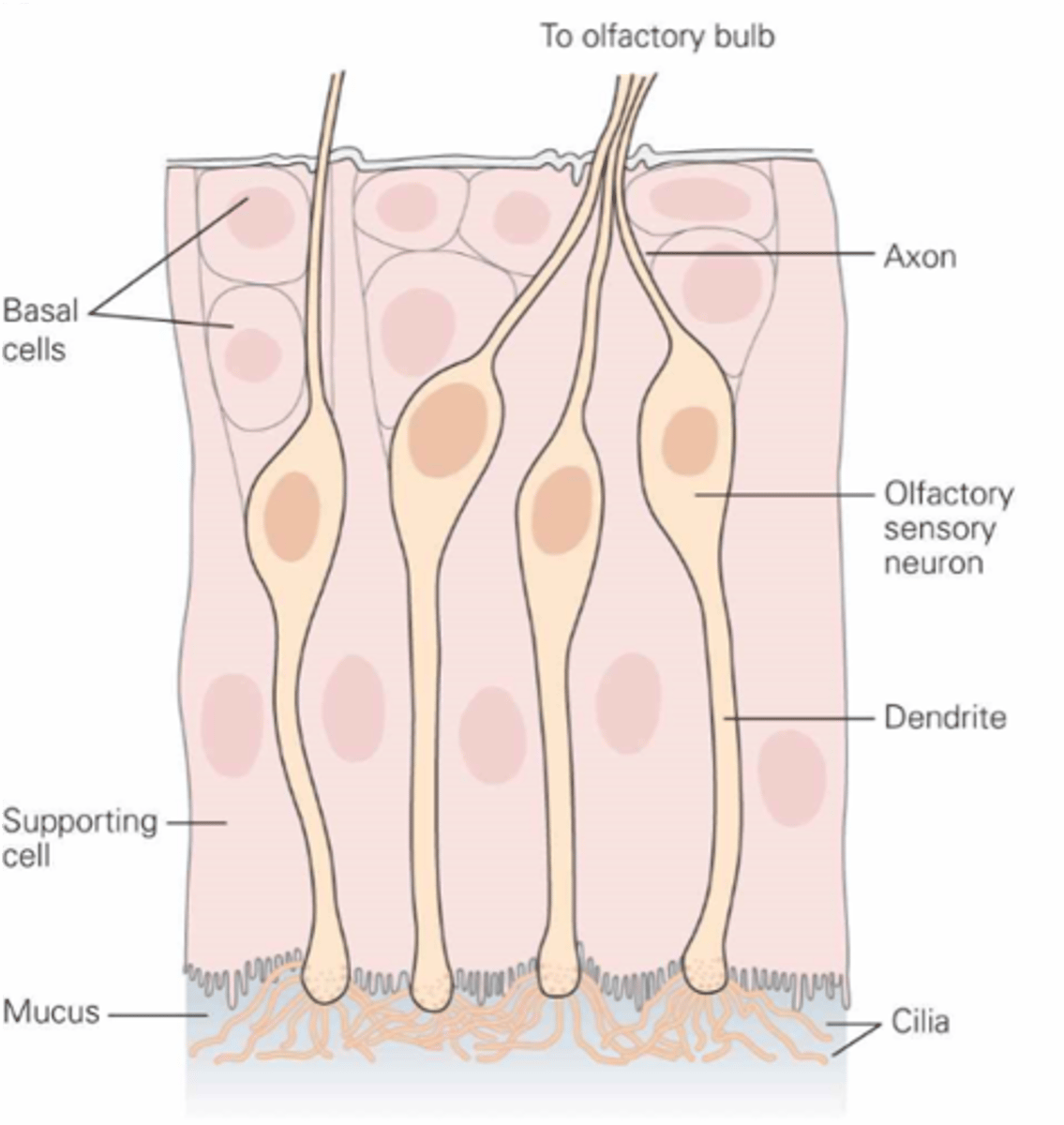
Bipolar chemoreceptive neurones
What are the olfactory receptor cells?
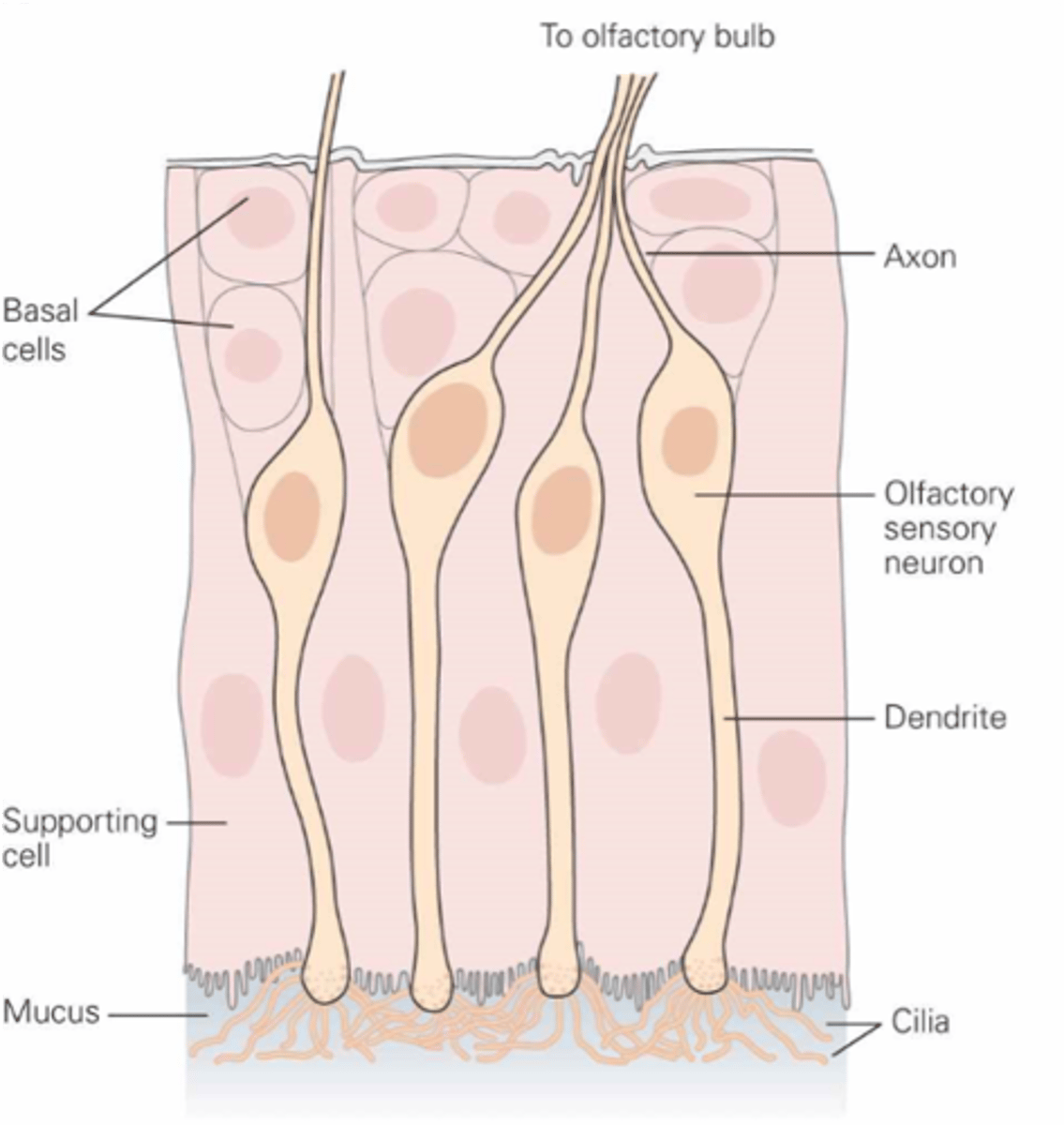
Dissolve, mucus
Odorants must ________ in the ______ layer to reach olfactory receptor cells
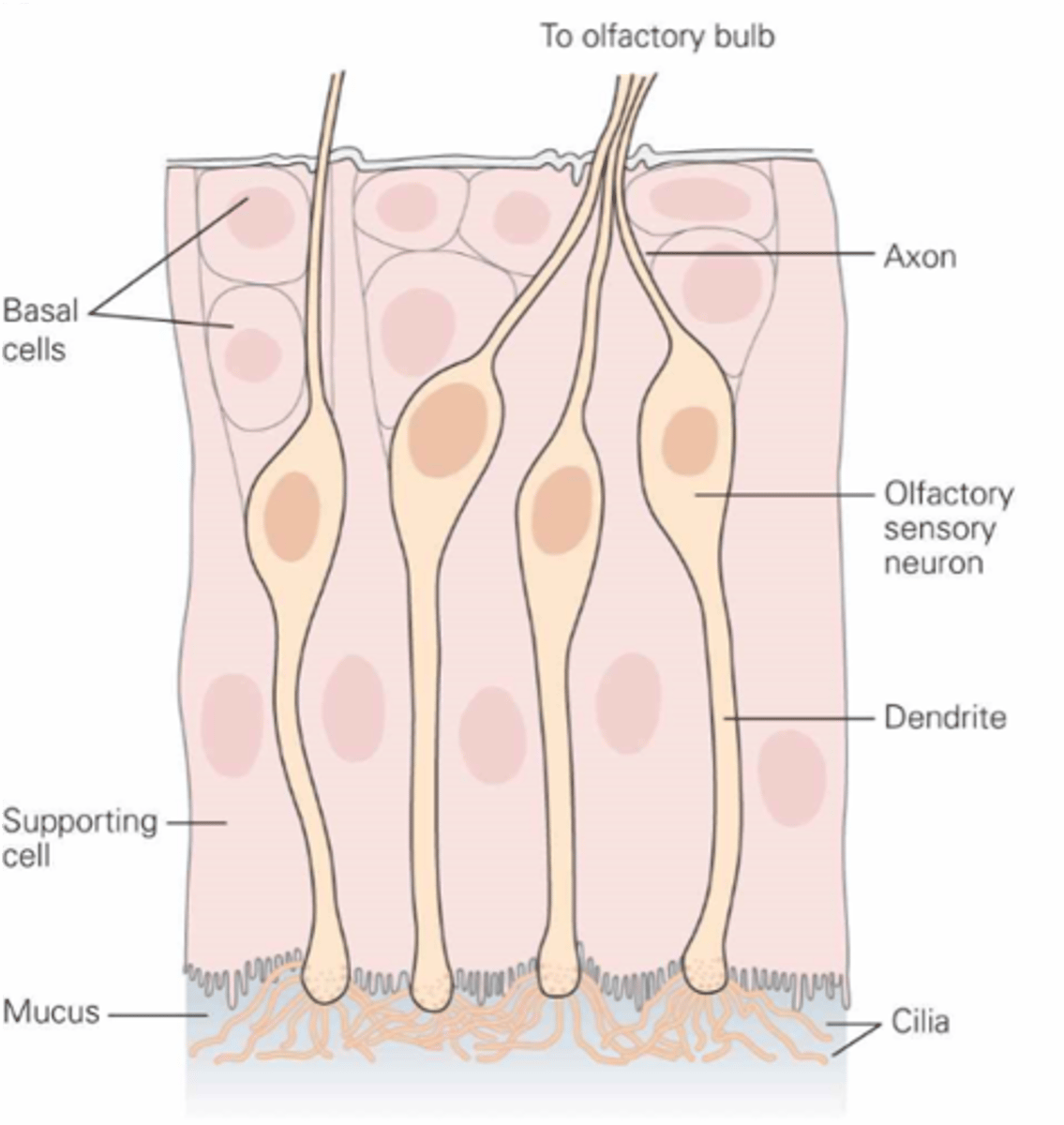
Within the cilia at the end of the dendrite
Where are transduction machinery found?
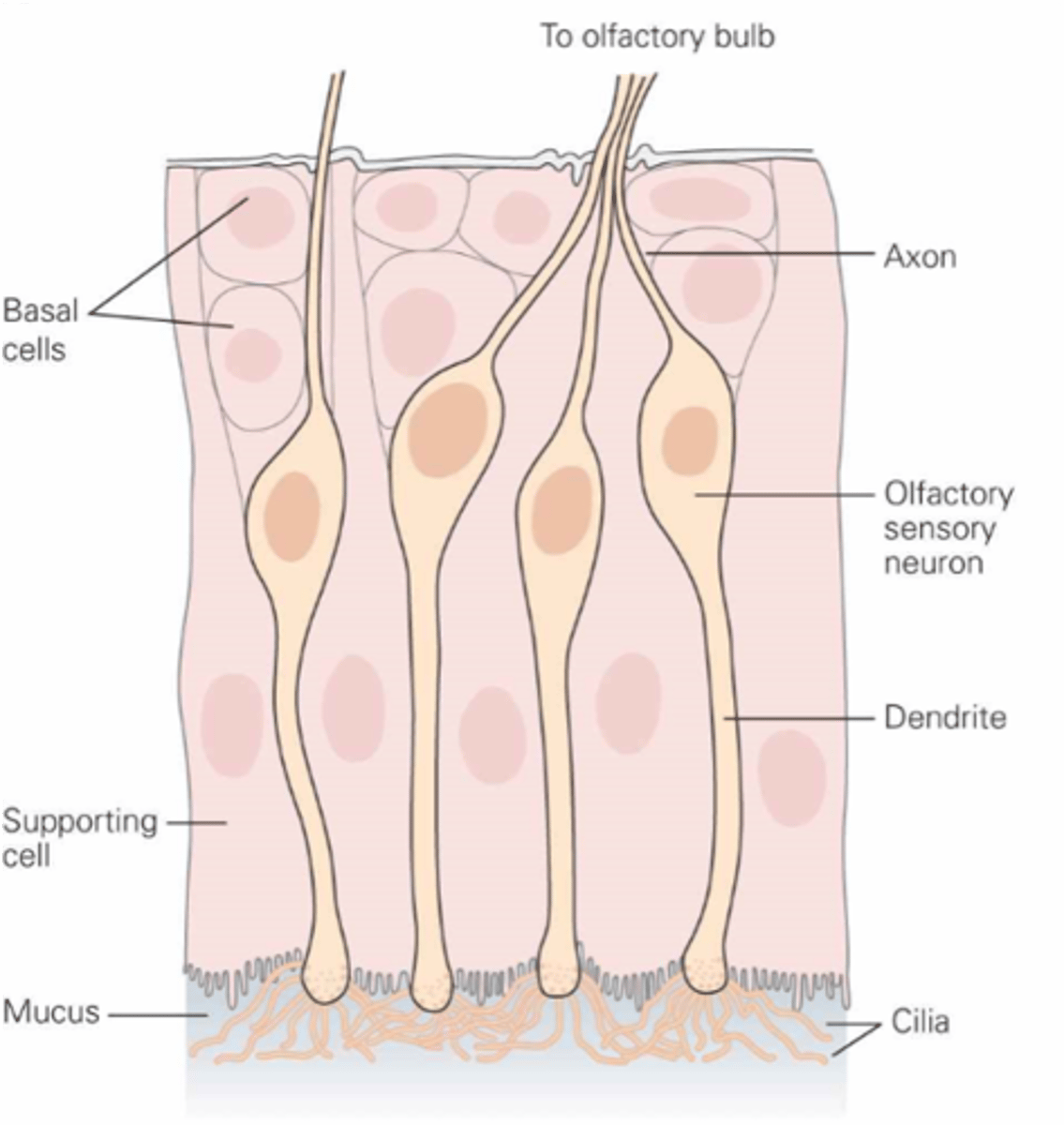
The axon of the olfactory receptor cell
What is the primary afferent neuron?
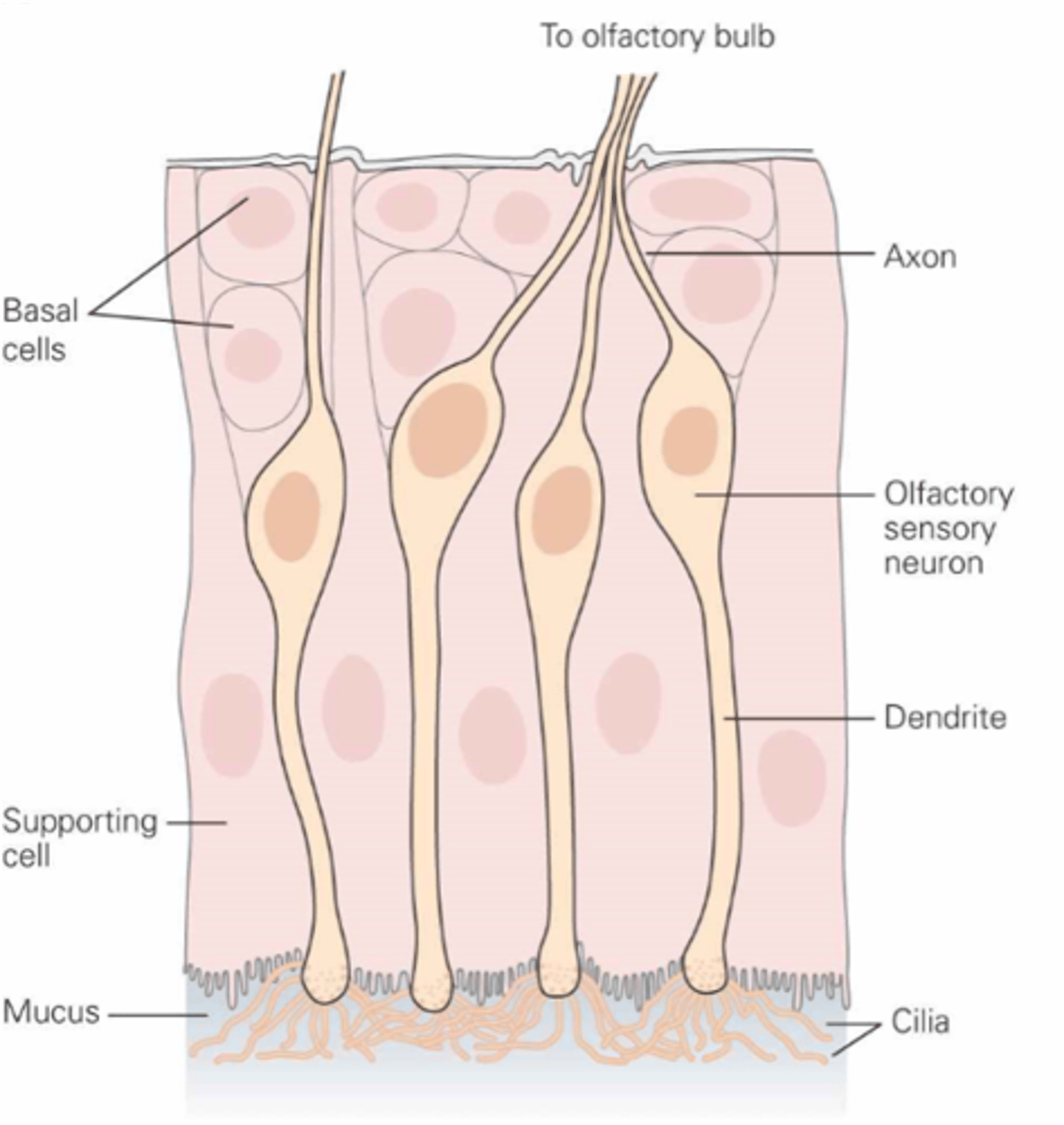
Thin, unmyelinated
The axons are ___, ______________
Replaced
Olfactory receptor cells are regularly ____________
Regularly replaced
Olfactory receptor cells are one of the few types of neurones that are _________ ____________ in adults
350
Around how many odorant receptor proteins (ORs) do humans have?
One odorant receptor
Olfactory receptor cells only express ___ __________ __________
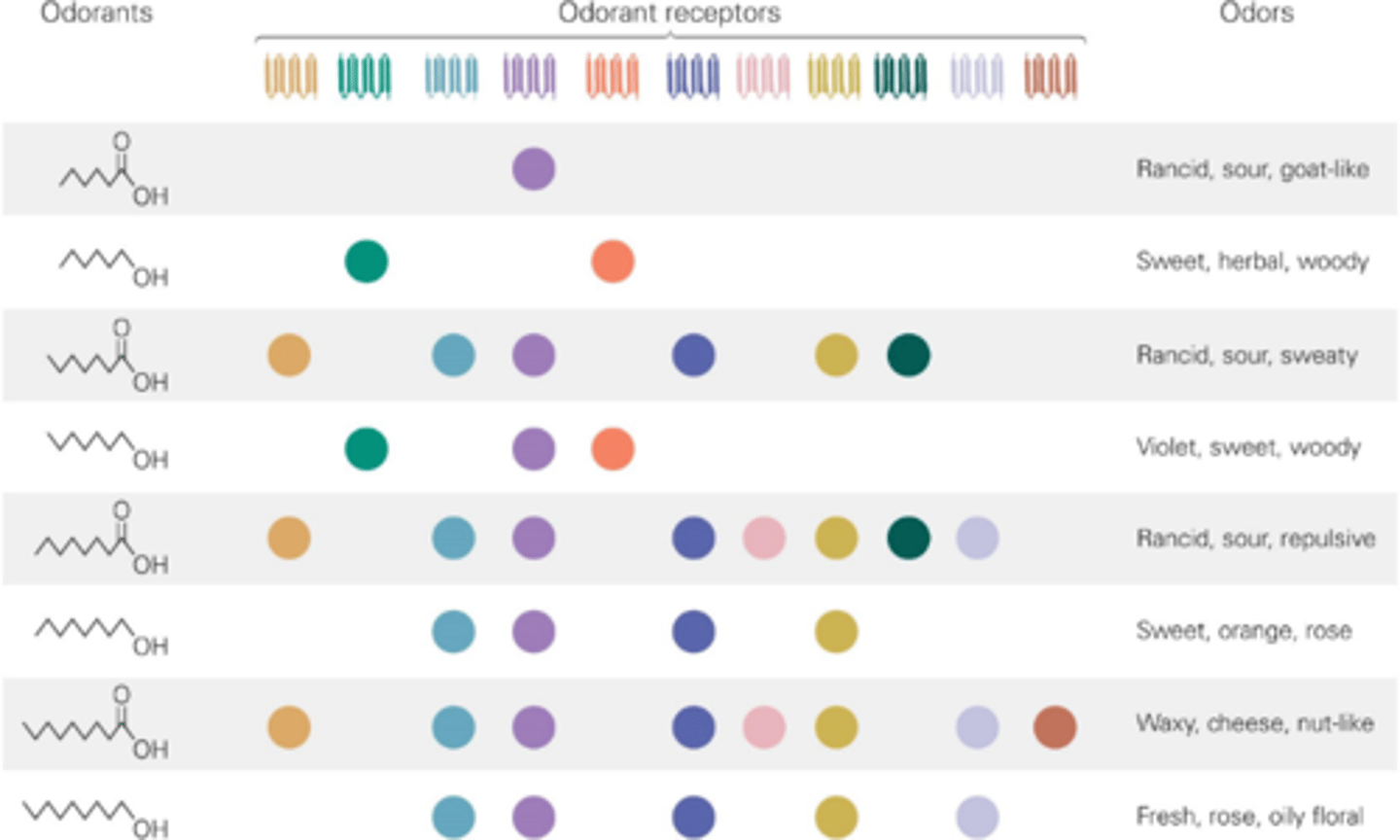
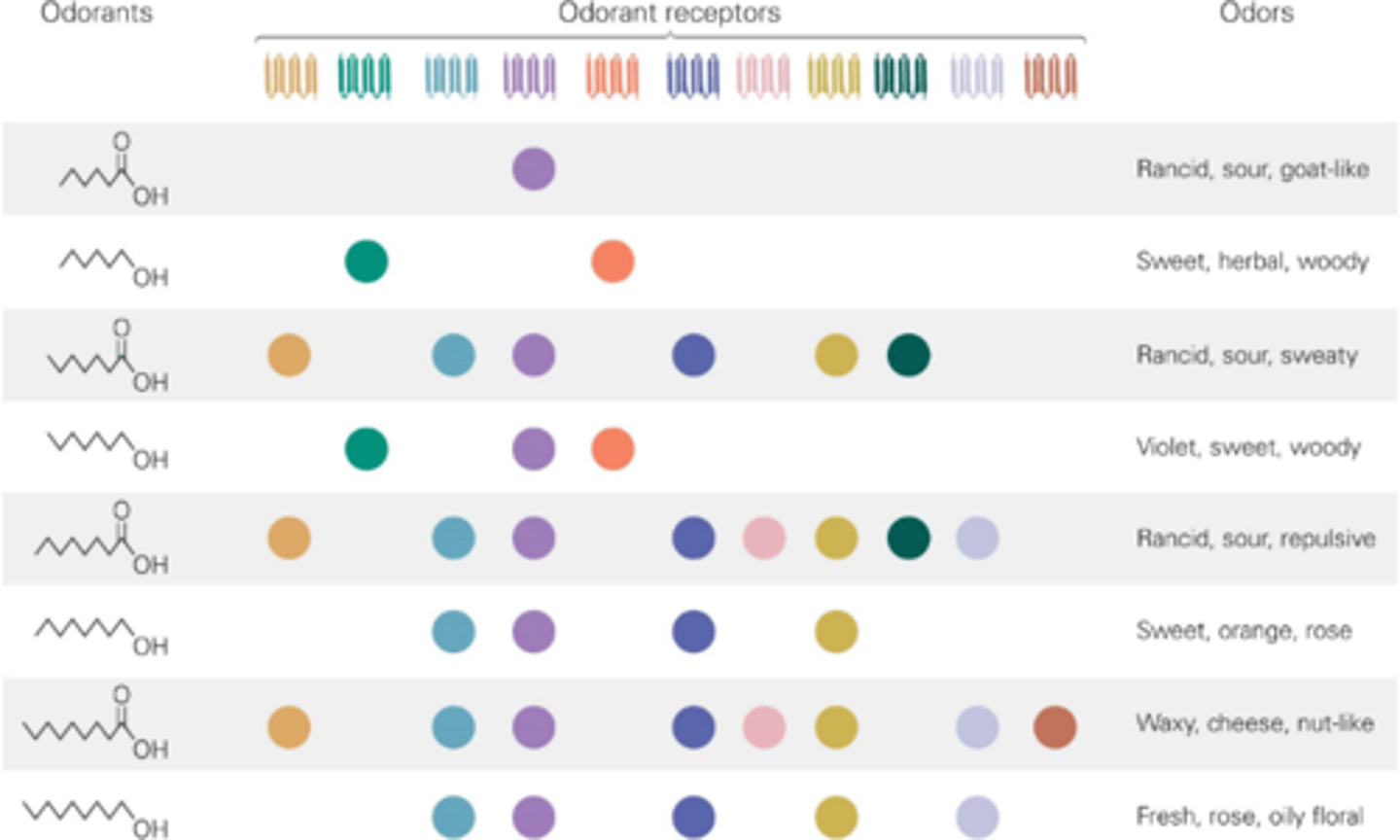
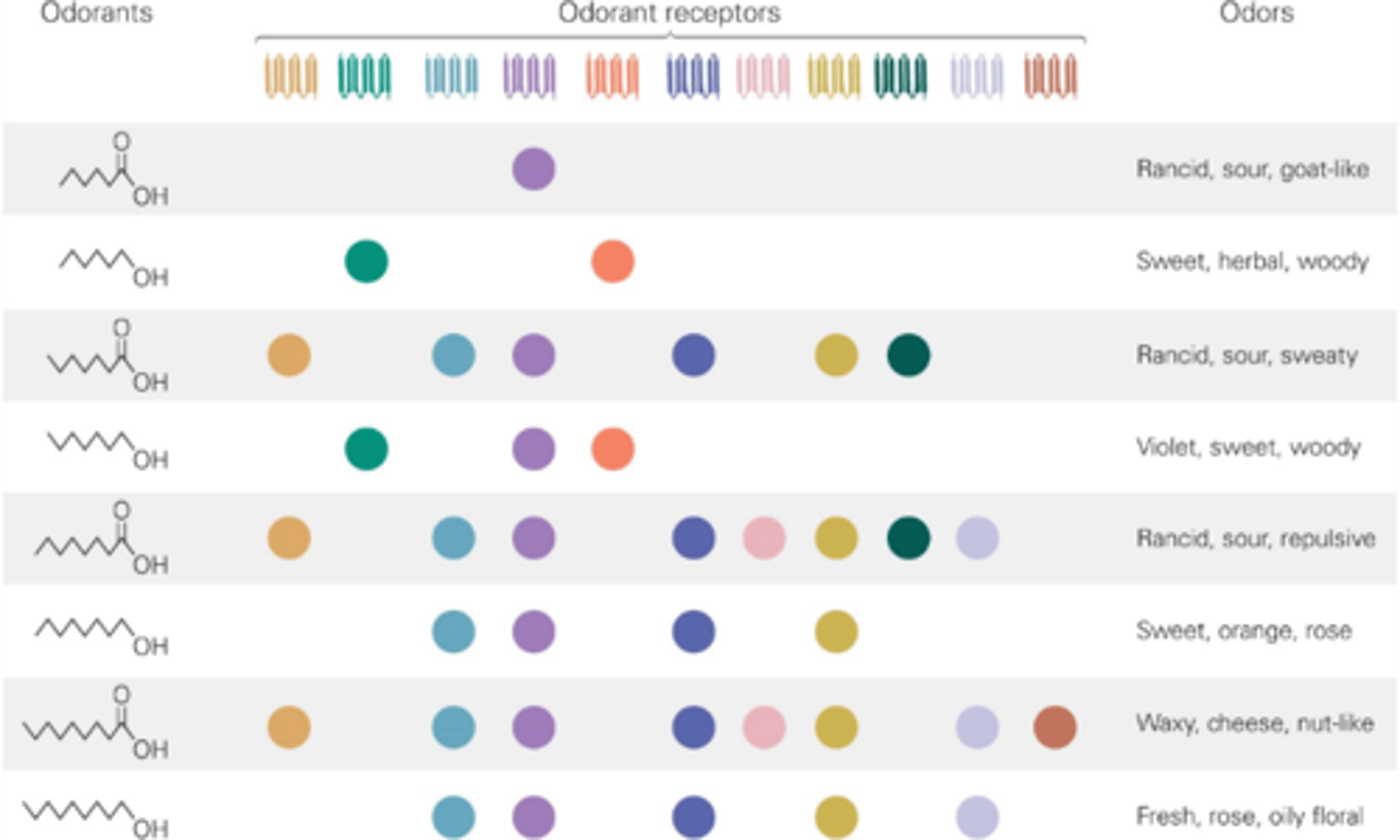
Multiple odorants
One odorant receptor can recognise _________ ___________
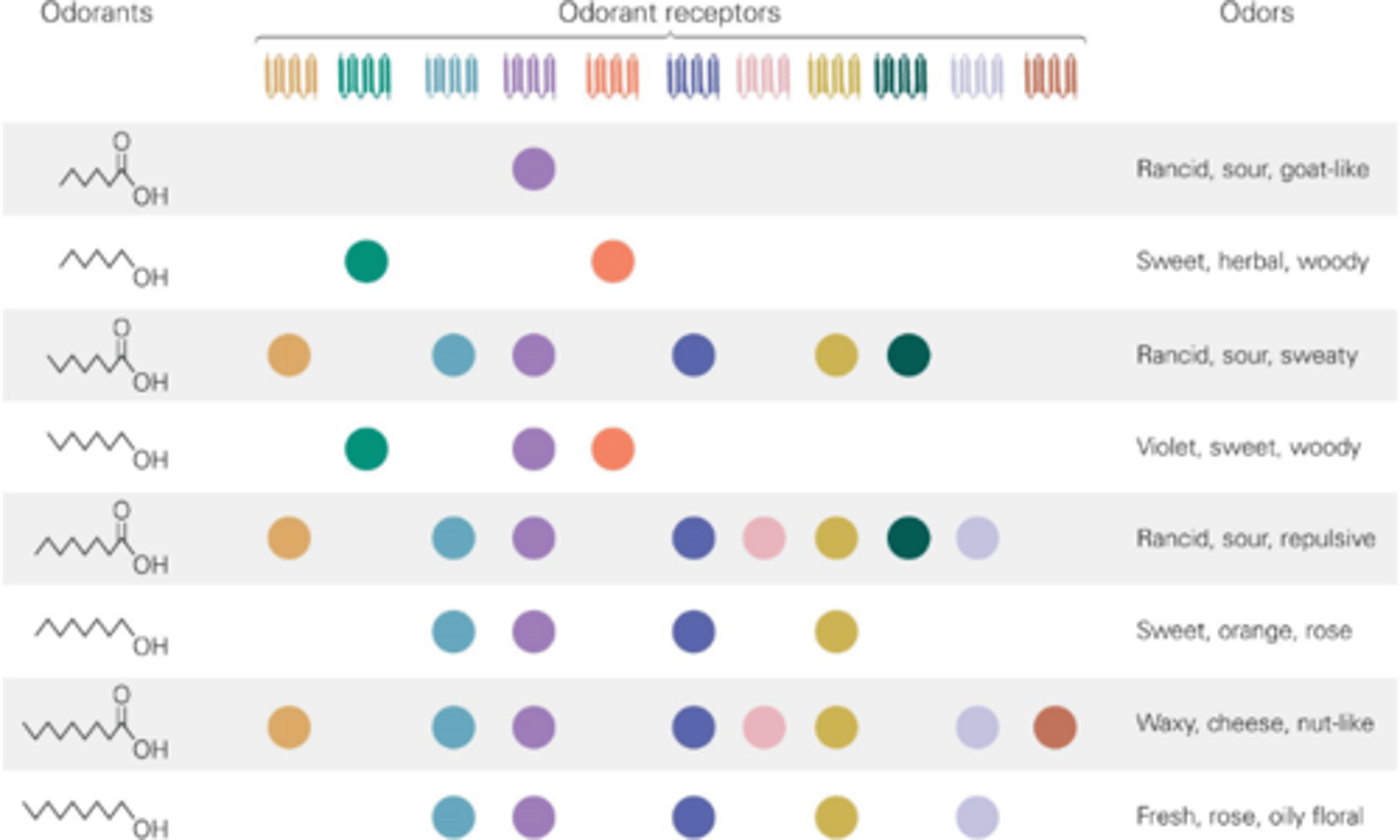
The unique combination of odorant receptors that recognise an odorant
What allows us to distinguish specific odours?
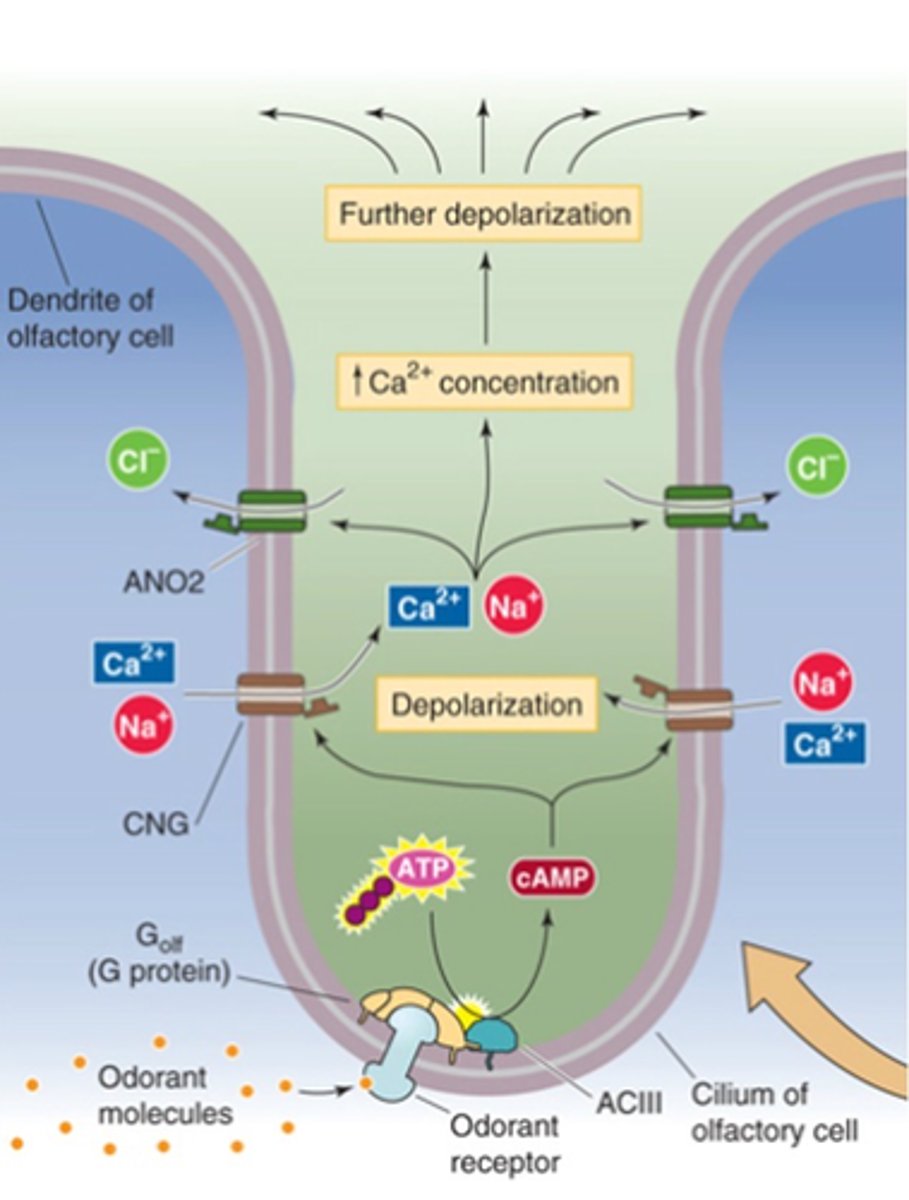
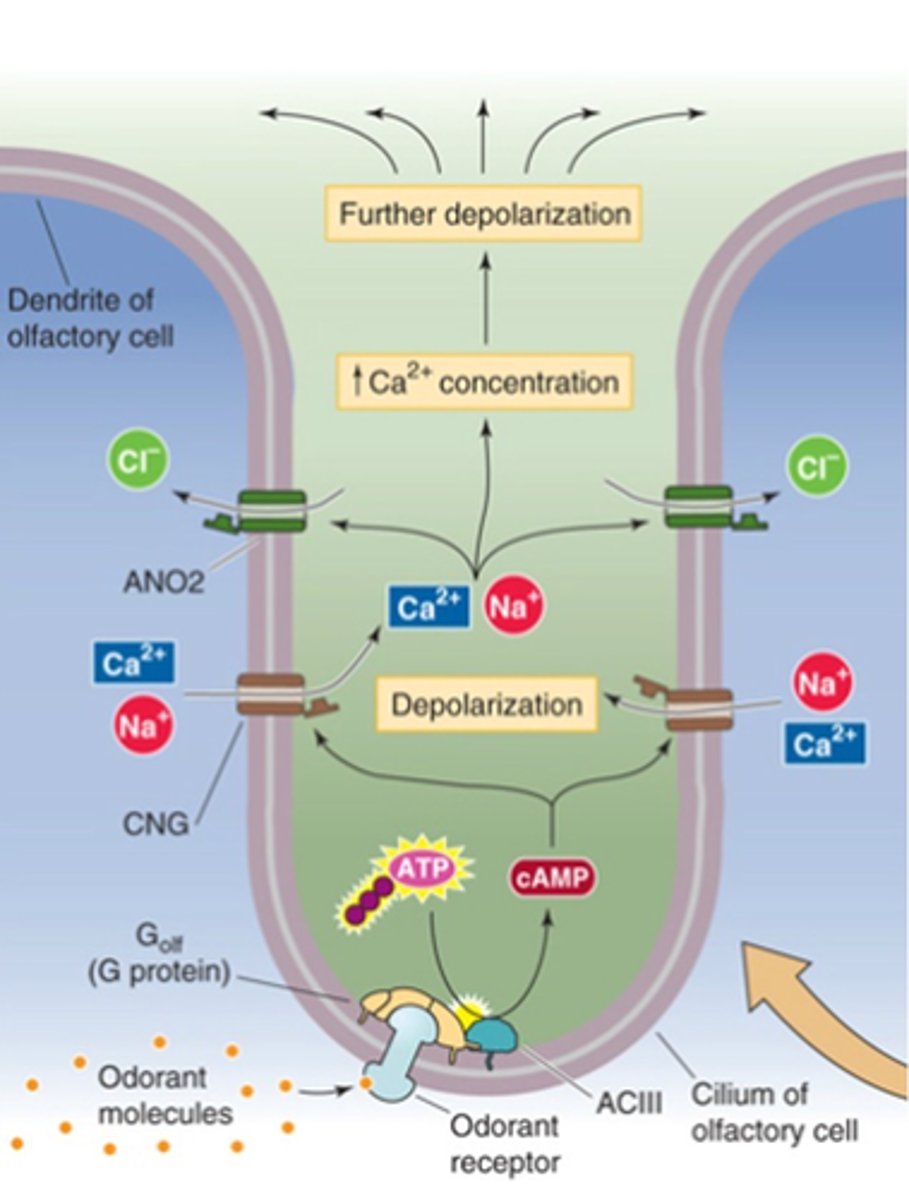
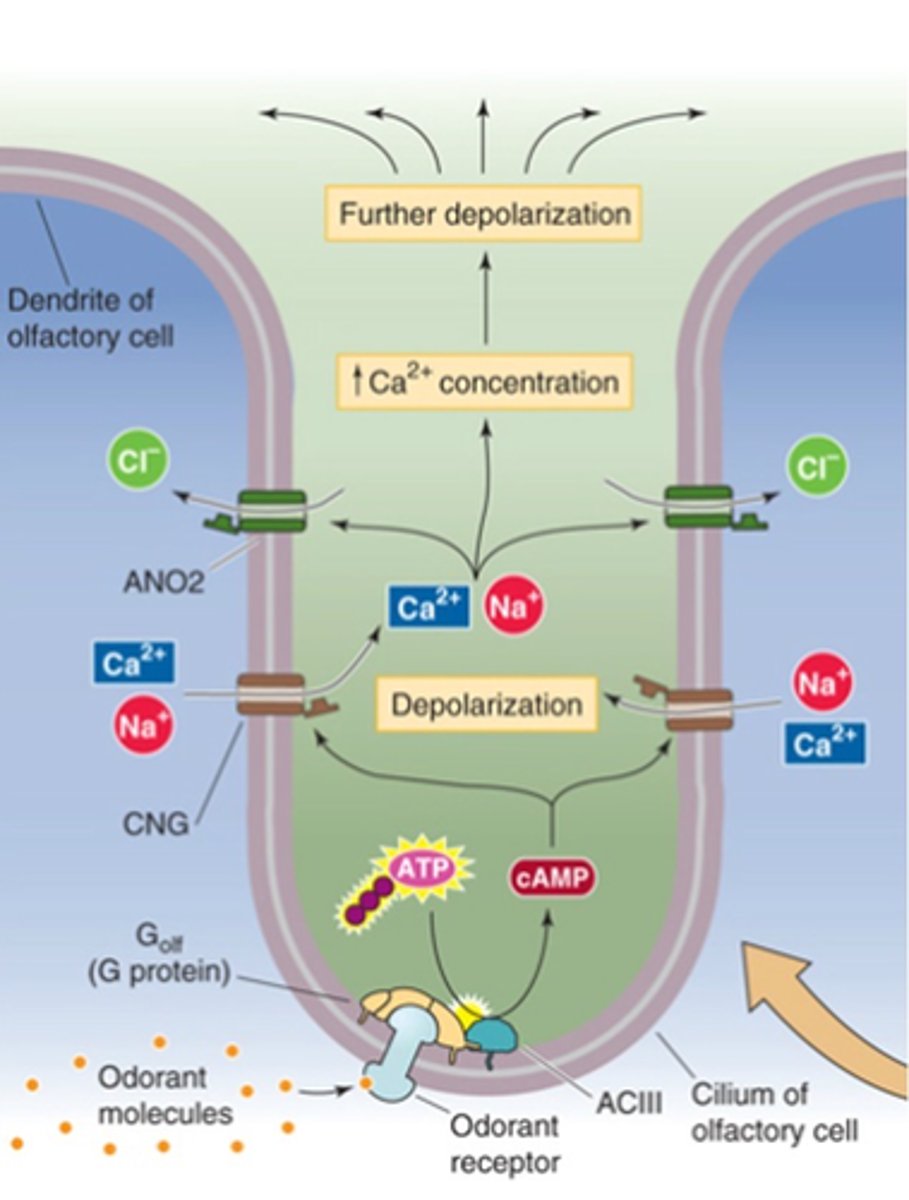
G-protein coupled receptors
Odorant receptor proteins (ORs) are _-________ __________ ___________
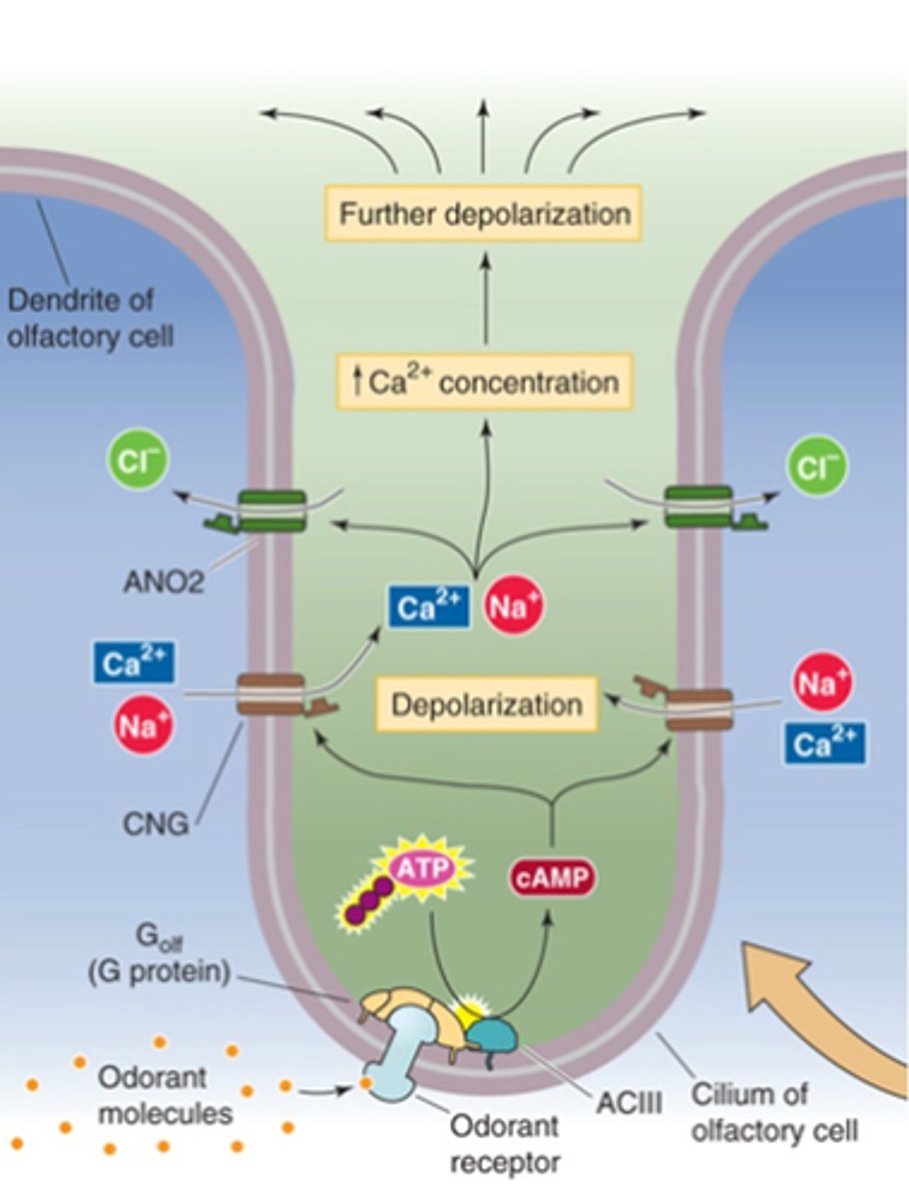
Golf
Adenylyl cyclase
cAMP
Cyclic nucleotide gated ion channels
Depolarisation
Ca2+-gated Cl- channels
Further depolarisation
Every OR uses the same downstream pathway, what is it?
~3-5%
How much of the entire genome do odorant receptor protein genes comprise?
Golfs
Transduction occurs via ....?
They cannot smell
Golf knockout mice are anosmic, what does this mean?
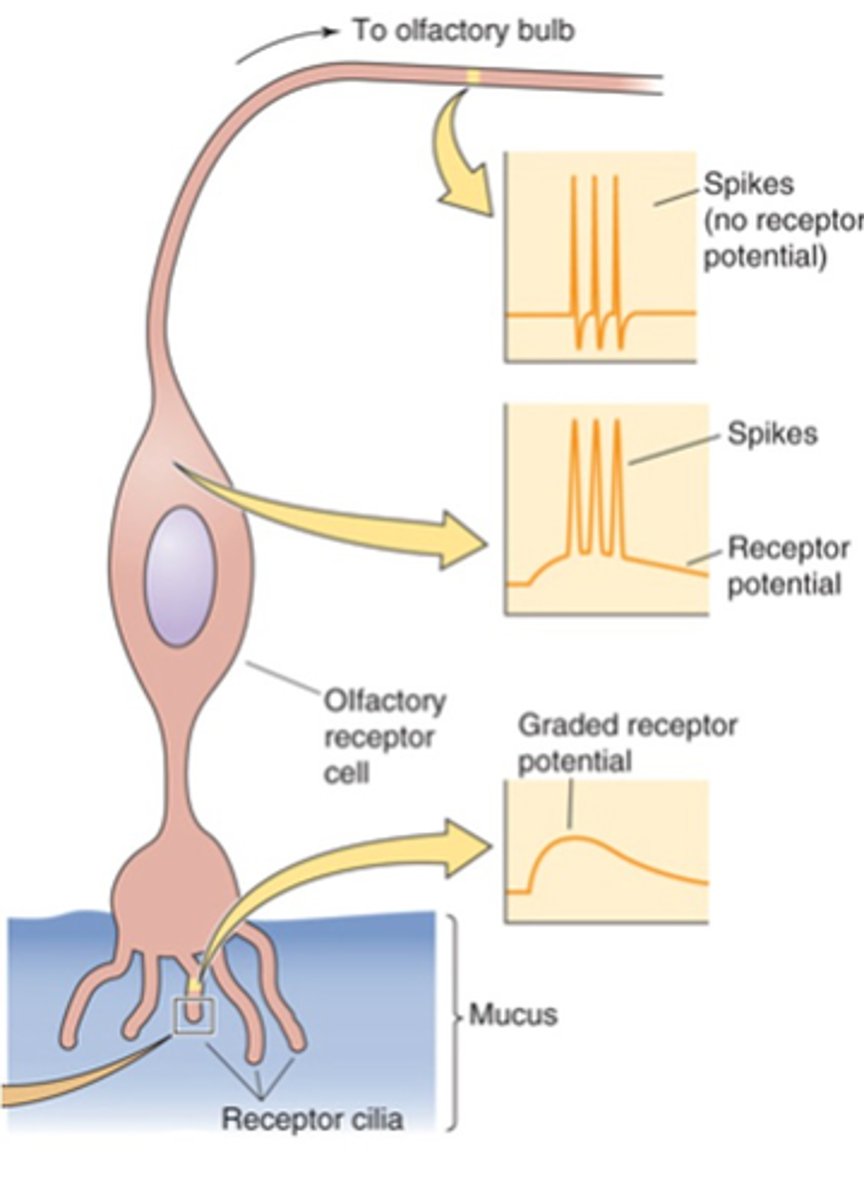
Action potentials
What do receptor potentials trigger?
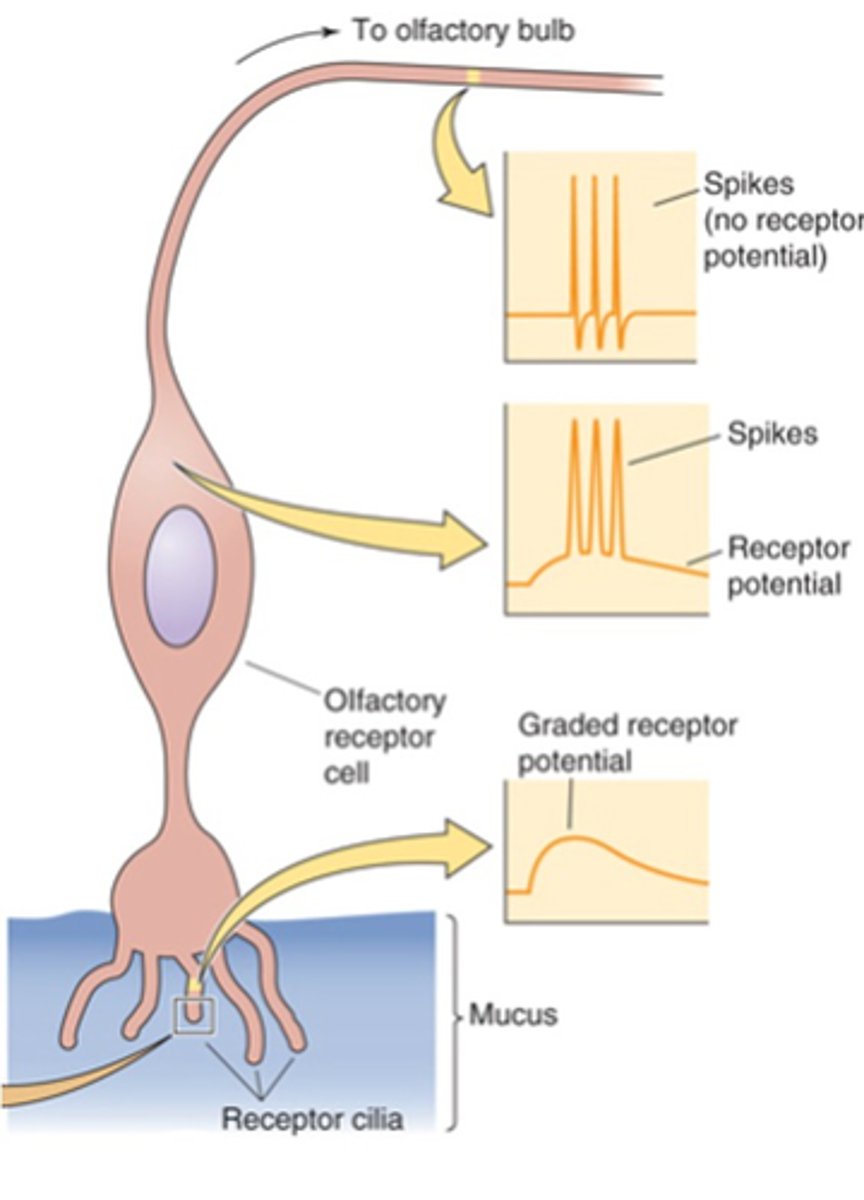
Threshold for action potential firing reached
Large enough receptor potential = ?
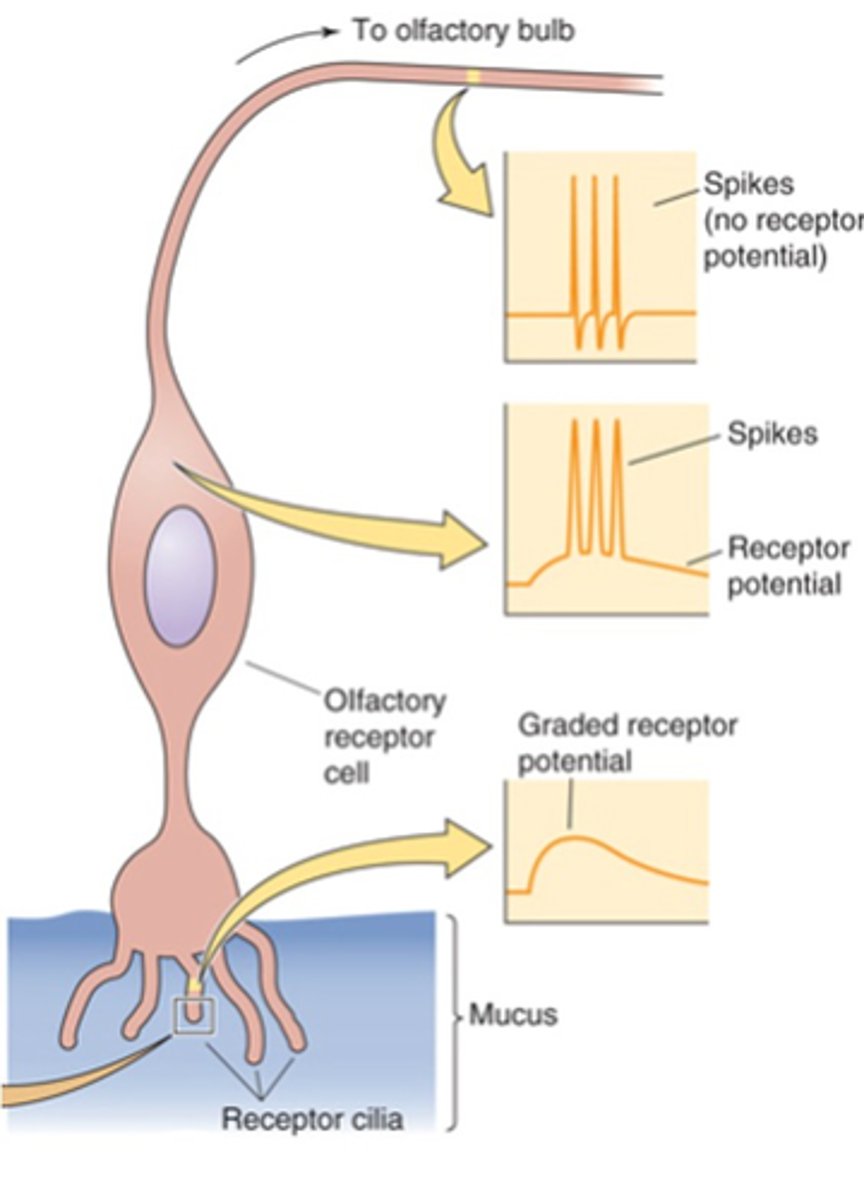
Large, increased
Intense stimulus = _____ receptor potential = ____________ action potential firing rate
Only one type of olfactory receptor
Each glomerulus of the olfactory bulb receives input from ...?
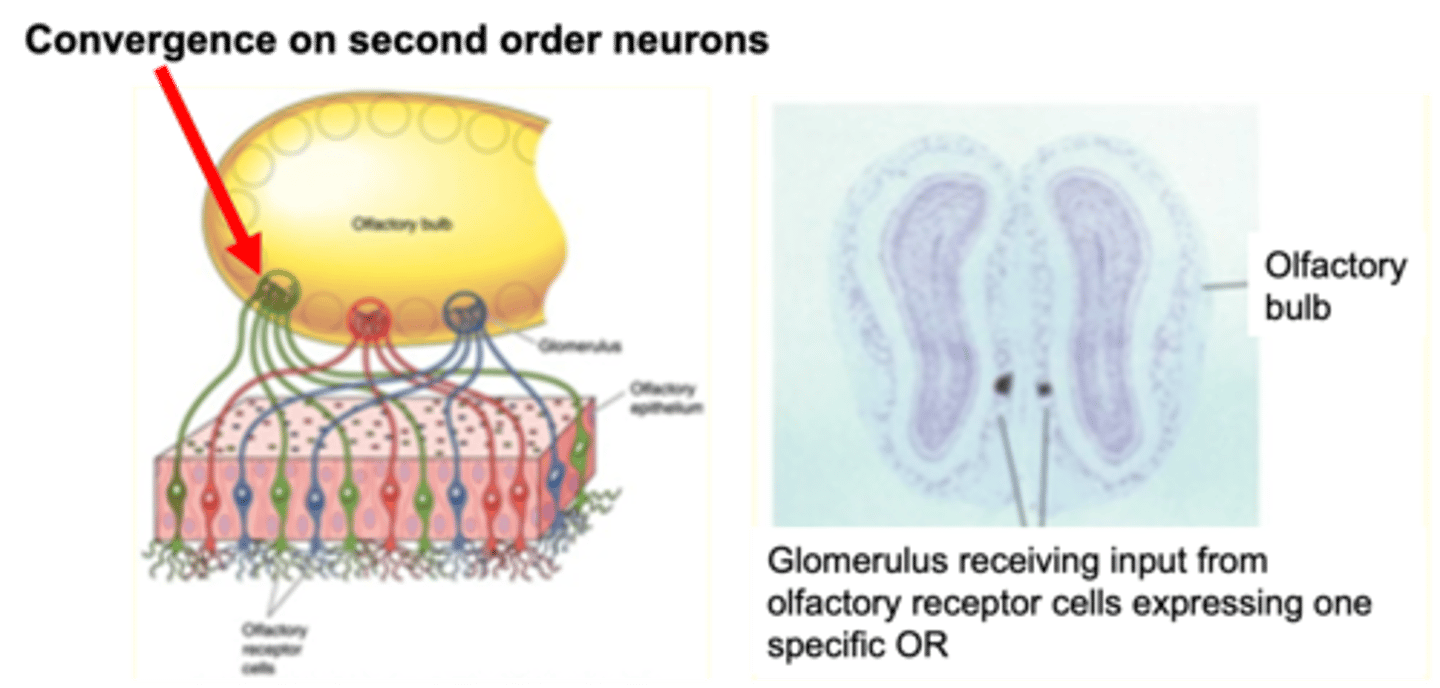
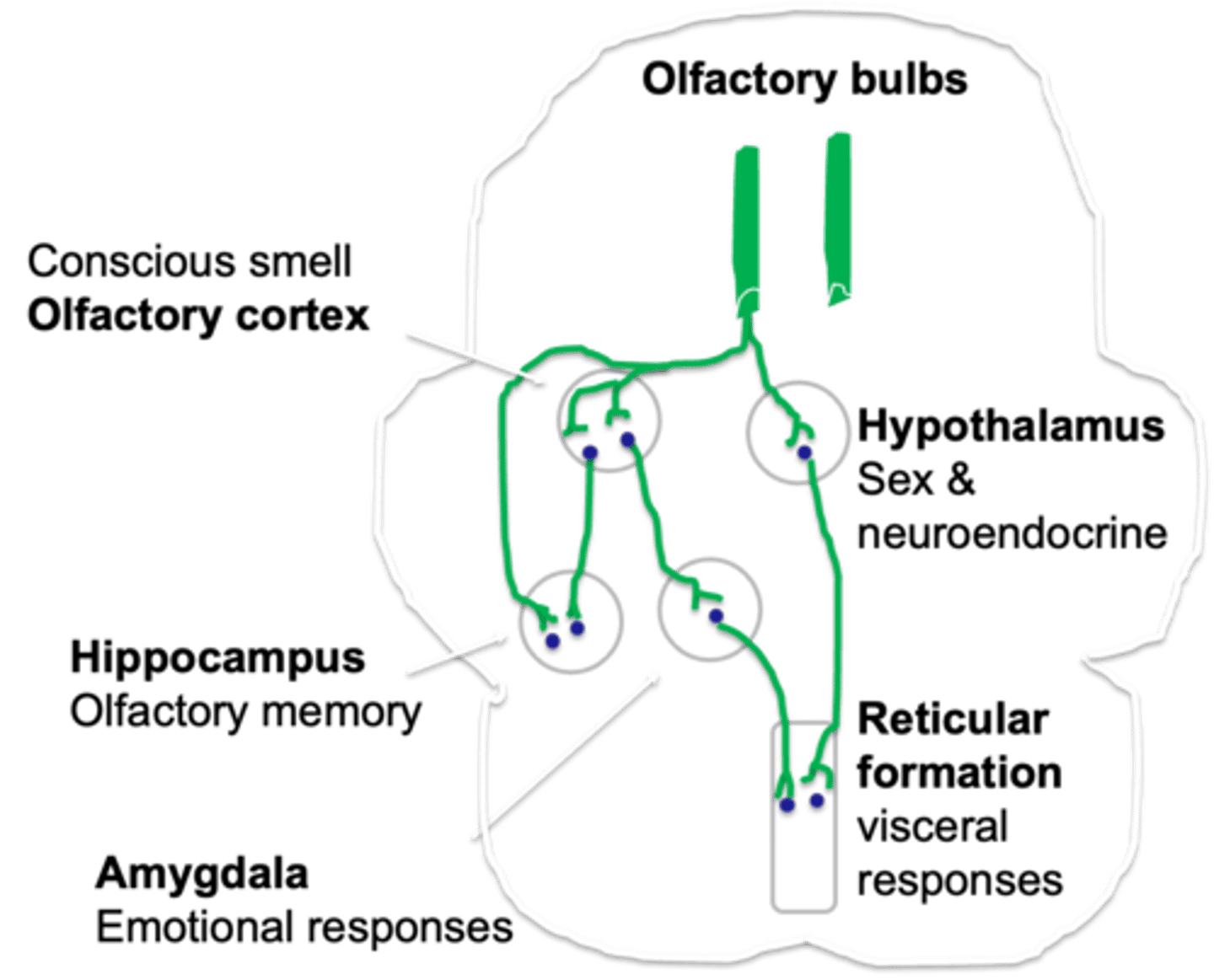
Carry information from glomeruli to various regions of the brain
What do second order neurones do?