Physics p2 June
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
melting point
temperature at which the solid state and liquid state of a substance are in equilibrium
Boiling point
temperature at which the vapour pressure of a substance is equal to the atmospheric pressure
vapour pressure
pressure experienced by a vapour of a substance in equilibrium with the liquid
substances with strong intermolecular forces have:
high melting and boiling points with low vapour pressure
AX’2; E’0
linear
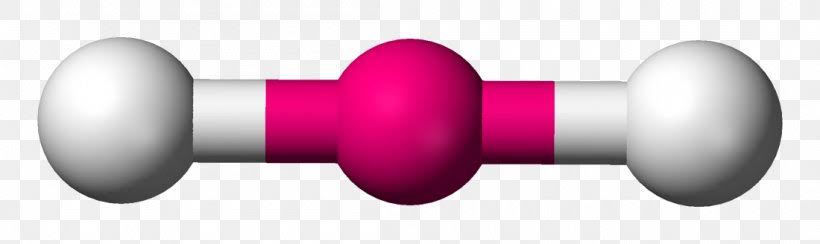
AX’3; E’0
Trigonal planar
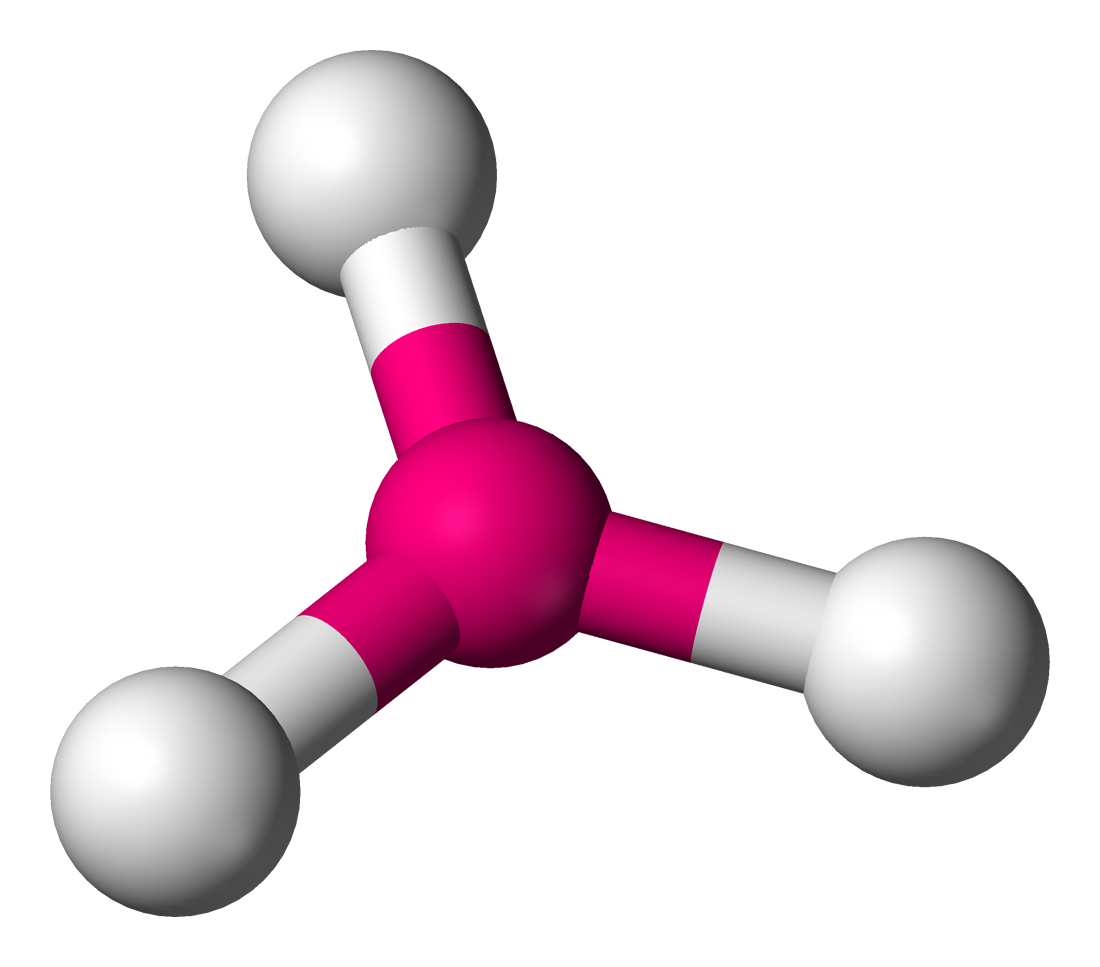
AX4’; E’0
Tetrahedral
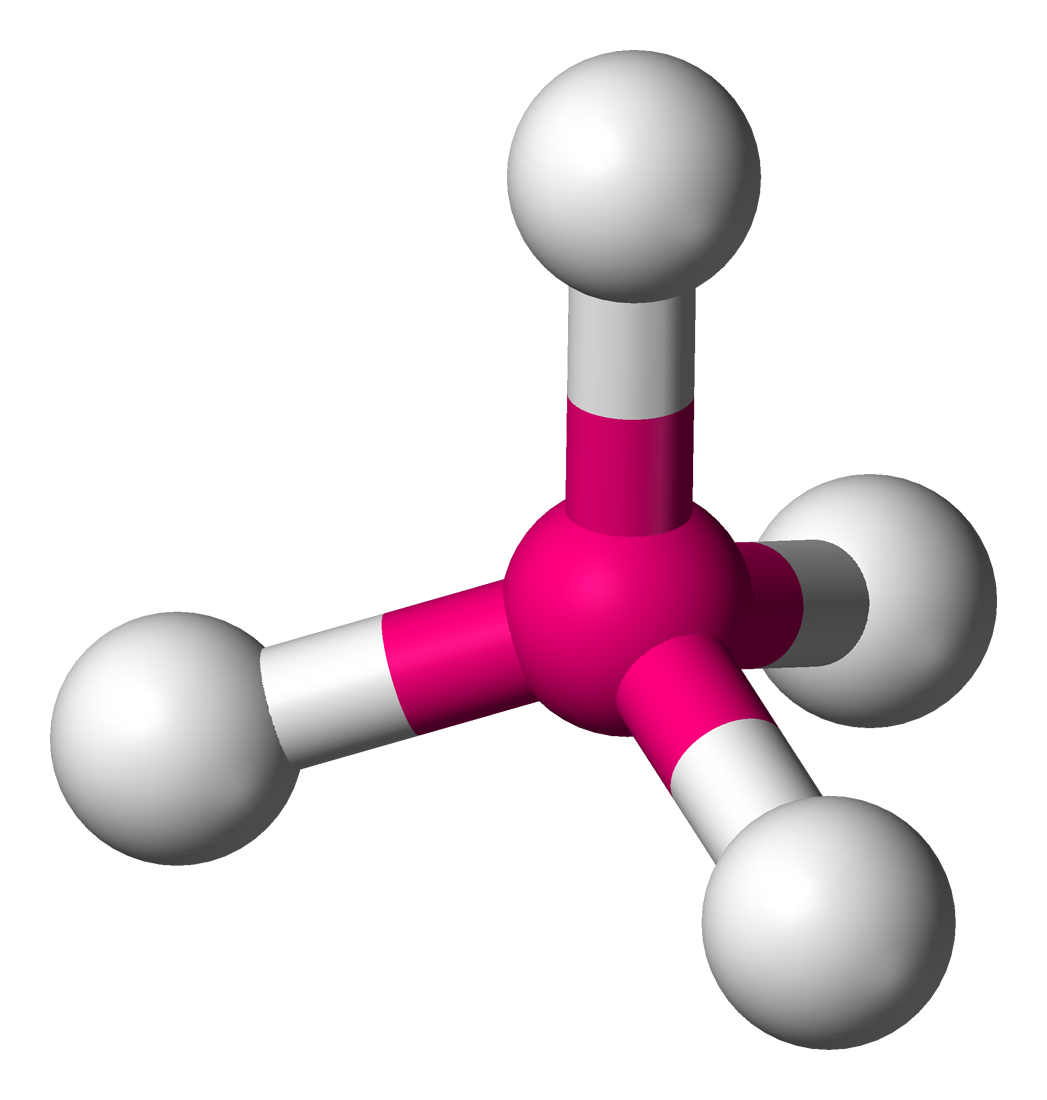
AX’5; E’0
trigonal bypyramidal
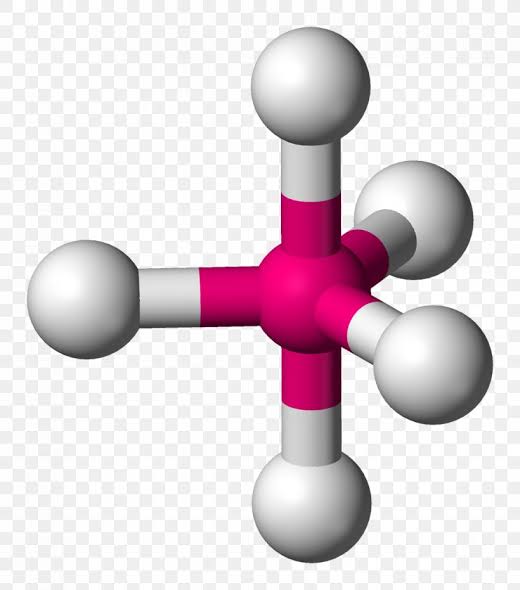
AX’6; E’0
Octahedral
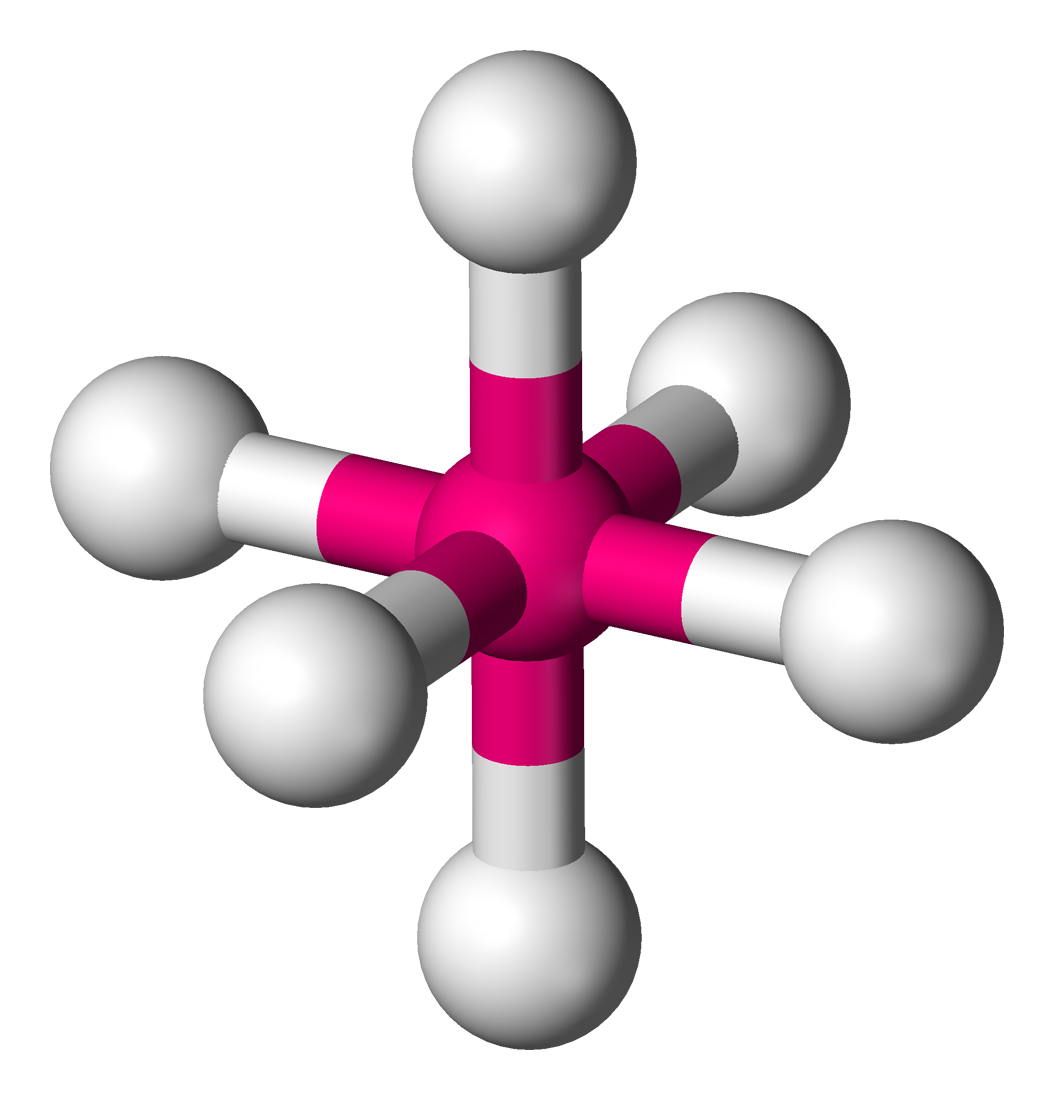
AX’2; E’2
Bent/angular/v-shape
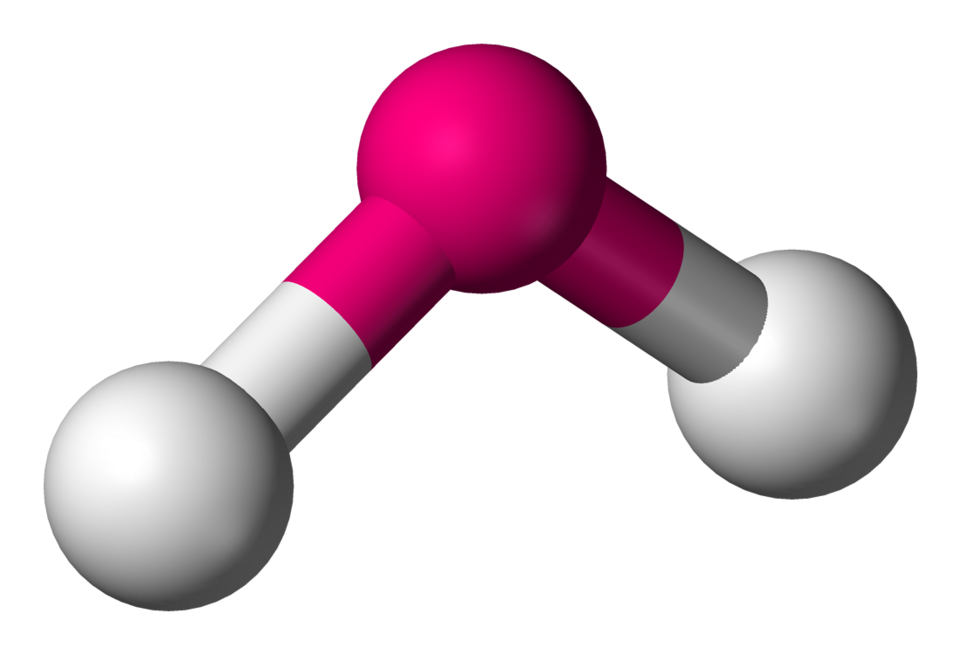
AX’3; E’1
Trigonal pyramidal
Strongest intermolecular force
hydrogen bond
weakest intermolecular force
London forces
ion dipole force
occurs when a dipole approaches a positive or negative ion
ion induced dipole forces
an ion affects the electron cloud around an atom or molecule when nearby causing a temporary dipole
dipole dipole forces
attraction between slightly positive atom in a polar molecule and another polar molecule
dipole induced dipole forces
a polar molecule can induce a temporary dipole in a non polar molecule or atom
induced dipole/ London forces/ dispersion
when two non polar atoms of noble gasses or molecules approach each other, there's a slight rearrangement of their electron clouds, A weak, short, temporary dipole is formed, which comes and goes and alters direction
hydrogen bond
This is an exceptionally strong dipole dipole force in comparison with other Van Der Waals forces. it occurs between molecules in which hydrogen is bonded to nitrogen, oxygen or flourine
interatomic forces
bonds that hold different atoms together in a molecule
Density
number of particles per unit volume
viscosity
an indication of a liquids resistance to flow (high viscosity liquids don't flow easily)
thermal expansion
means the material expand on heating
Covalent thermal conductivity
no free electrons to help transmit heat
metalic thermal conductivity
valence electrons are free to help with the conduction of heat
solubility of a substance
is a measure of how easily a substance can dissolve in another substance
Like dissolves like
substances with the same intermolecular forces dissolve one another
Electronegativity
measure of the ability of an atom to attract a bonded pair of electrons
chemical bonding
the mutual attraction between two atoms resulting from a simultaneous attraction between their nuclei and outer shell
covalent bond
two non metal atoms in a molecule share an electron pair during the overlapping of orbitals to form a molecule
non polar covalent bond
electron density is shared equally between the atoms, the shared electron pair is distributed evenly between the two atoms where the orbitals overlap
polar covalent bond
bond in which electron density is shared unequally between the atoms, the shared electron pair is distributed unevenly between the two atoms where the orbitals overlap
molecule
group of two or more atoms covalently bonded which function as a neutral unit
ionic bond
bond between metal atoms and non metal atoms if electrons are transferred from a metal atom to a non metal atom
metalic bond
bond between metal atoms through the attractive forces between delocalised electrons and the crystal lattice of a positively charged atom rest
valence electrons
electrons found in the outermost energy level
dative covalent bonds
covalent bonds between atoms where one atom provides both electrons that are sharef
octet rule
all atoms with the exception of hydrogen and helium try to have eight electrons, in four pairs of two, surrounding them to achieve noble gas structure
VSERP
model used to predict the shape of a molecule
shape of a molecule depends on
the type of bond, number of electron pairs around the central atom and the lone pairs
Bond energy
energy needed to break one mole of a compounds molecules into seperate atoms
bond length
distance between the nuclei of the two atoms that are bonded