RLE: Maternal serum screening
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Alphafetoprotein
A protein produced primarily by the fetal liver and yolk sac during development.
Alphafetoprotein
Measured during the second trimester or usually 13–32 weeks gestation
Alphafetoprotein
Helps detect:
Neural tube defects (e.g., spina bifida, anencephaly) → ↑ AFP
Abdominal wall defects (e.g., gastroschisis) → ↑ AFP
Chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome) → ↓ AFP
Chorionic Villi sampling
a prenatal diagnostic test used to detect chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders in a developing fetus. It involves collecting a small sample of chorionic villi — finger-like projections from the placenta that share the fetus’s genetic makeup.
Chorionic Villi sampling
This screening is usually performed between 10–13 weeks of gestation
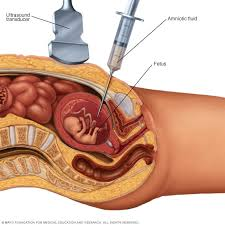
Aminocentesis
A prenatal diagnostic procedure used to analyze fetal cells and amniotic fluid for genetic, chromosomal, and neural tube abnormalities. It’s one of the most definitive tests for fetal health and development.
Aminocentesis
→ A thin needle is inserted into the amniotic sac through the abdominal wall under ultrasound guidance.
→ A small amount of amniotic fluid is withdrawn — this fluid contains fetal cells and proteins.
→ These cells are cultured and analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities, genetic mutations, and biochemical markers.
Percutaneous Umbilical blood sampling
Also called cordocentesis — is a specialized prenatal diagnostic test that involves collecting fetal blood directly from the umbilical cord to assess for genetic, hematologic, and infectious conditions.
Percutaneous Umbilical blood sampling
→ Performed by inserting a thin needle through the mother’s abdomen into the umbilical vein, guided by ultrasound.
→ It allows direct access to fetal circulation, making it one of the most precise methods for evaluating fetal health.
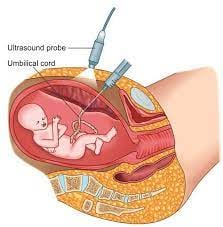
Percutaneous Umbilical blood sampling
this method is typically done after 18–19 weeks of gestation