Lady bits lecture - 80085
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
produce and transport ova
transport sperm
fertilize and accommodate fetus until birth
three super general tasks of the female repro system
Ovaries, genital tract, mammary gland
three "structural units" included in the female repro system
ovary
_________: s paired organ with both endocrine and exocrine function in the form of female hormones and ova production
female hormones
ova
The ovaries have both endocrine (_____________________) and exocrine (________________) functions.
uterine tube/oviduct
The conduit for the oocyte, spermatozoa and zygotes
uterus
the place for implantation of the "conceptus"
cervix
the terminal end of the uterus and barrier during pregnancy
vagina
copulatory organ and aid for expulsion of urine
cortex (peripheral aspect)
which part of the ovary houses follicles?
medulla
which part of the ovary is in the center (normally) and is highly vascular?
ovulation fossa, cortex on the inside
whats weird about the mare ovary? (we know this y'all)
Chromosomal sex determination
There are 3 "tiers" of sex determination,
Tier 1 = __________________
Genetic sex determination
There are 3 "tiers" of sex determination,
Tier 2 = __________________
hormonal sex determination
There are 3 "tiers" of sex determination,
Tier 3 = __________________
SRY
the _________ gene is the primary determinant of male sex in mammals
initiates testis development by upregulating SOX9
How does the SRY gene determine male sex?
promotes sertoli cell differentiation
What does SOX9 do?
DAX1
what is an antagonist to SRY and SOX9, leading to ovary development of male-to-female sex reversal?
RSPO1
what positively regulates WNT4 expression in the XX gonads, ensuring proper ovarian development?
suppresses male specific genes in the ovary
What does WNT4 do?
FOXL2
what is vital for the maintenance of ovarian function?
false: it can lead to testis like cells even in adult females
true/false: the loss of functioning FOXL2 can cause ovarian cell to become testis like, but only in immature and developing mammals
female is born with all her oocytes
oocytes dont reach haploid unutil time of ovulation
What two reasons contribute to why there is no need for a "blood Oocyte layer"?
yolk sac, ovarian cortex
In the beginning of primordial germ cell migration
the Oogenia migrate from the _______ into the ______ and then begin to multiply by mitosis
4-5th month
at what point during human fetal development do some oogenia enlarge and become primary Oocytes? (first stage meiotic division)
7th month
at what point in human fetal development are primary oocytes encapsulated by a single layer of follicular cells, and form a primordial follicle? (arrest of 1st meiotic division)
AMH
what hormone do male sertoli cells produce in the testicle to inhibit female duct formation?
where the oocyte resides
what is a follicle?
a single cell with DNA inside a follicle
What exactly is an oocyte?
true
true/false: At tertiary follicular stage Meiosis I is always complete, but Meiosis II may not be complete
before birth
A 2n Oogonium undergoes mitosis and arrests in prophase 1 as a 2n primary Oocyte...
does this happen before birth or after puberty?
after puberty
a 2n primary Oocyte restarts meiosis and divides into 1n secondary oocytes
does this happen before birth or after puberty?
ovulation and sperm entry
What is the step directly after a 1n secondary Oocyte is made and paused in mataphase II?
meiosis and fertilization, leading to a fertilized egg
What happens after ovulation and sperm entry into a secondary oocyte?
primordial follicle
if you have a primary oocyte surrounded by simple squamous epithelium... what type of follicle do you have?
primary follicle
if you have a primary oocyte surrounded by simple cuboidal epithelium... what type of follicle do you have?
secondary follicle
if you have a primary follicle, stratified cuboidal epithelium and a zona pellucida... what type of follicle do you have?
zona pellucida
amorphous substance between the oocyte and corona radiata
ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, ZP4
what glycoproteins does the zona pellucida contain to act as "gate keepers" to regulate sperm binding?
tertiary follicle
if you have a secondary ovum (at ovulation), an antrum (fluid filled cavity), granuosa cells and theca cells, and the presence of a corona radiata and zona pellucida... what type of follicle do you have?
(we'll cover what this shhtuff means later)
FSH
growth of the secondary follicle stage is stimulated by what?
theca cell layers (interna and externa)
what are the stromal cells surrounding the follicle called?
theca interna
what thecal layer is the vascularized cellular layer?
theca externa
which thecal layer is basically just fibrous connective tissue?
stratum granulosum and theca
what are the two main structures of the ovarian follicle?
granulosa cells,
cumulus oophorus (type of ganulosa cell),
corona radiata (type of granulosa cell),
zona pellucida
what make up the stratum granulosum?
(4 terms... but two of them are technically specifics)
cumulus oophorus
the granulosa cells associated with the oocyte to form the projection
(the projection???)
corona radiata
the single layer of granulosa cells that immediately surrounds the oocyte
convert androgens to estrogens
Produce other hormones to nuture the developing gamete
What do granulosa cells actually do?
leydig cells in testicle
what are the male equivalent of the theca interna cells in a female?
sertoli cells (nurture the seminiferous tubules)
what are the male equivelant of granulosa cells in the female?
LH, androgens
The theca interna cells are induced by ______ to produce _______
granulosa cells
after androgens are released by theca interna cells, they are absorbed by what?
hilus
depression where vessels and nerves enter an organ (specifically here the ovary)
ovarian artery, ovarian branches of uterine artery
broad ligament
the blood supply to the ovary is the _____ and the ___________________
these arteries enter the hilus of the ovary from the _______________
blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics, elastic and reticular fibers
the medulla of the ovary contains what?
corpus hemorrhagicum
post ovulatory structure that is the remnant of a tertiary follicle containing a blood clot
corpus luteum
post ovulatory structure that acts as a temporary endocrine organ
granulosa lutein cells (internal)
theca lutein cells (external layer)
what two cell types are found in a corpus luteum
produce progesterone and convert androgens into estrogen
what do the granulosa lutein cells of a corpus luteum do?
produce progesterone, androgens and some estrogens
what do the theca lutein cells of the corpus luteum do?
corpus albicans
structure that occurs when a corpus luteum is replaced by a fibrous connective tissue (a scar)
Atretic follicle (degenerated)
If you see a follicle whos zona pellucida has thickened and folded and who's basement membrane between the granulosa and theca cells has also thickened...... what type of follicle is this?
atresia occurs until the follicle disappears
What happens if a follicle does NOT maturate and ovulate?
infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus
What are the three parts of the oviduct?
fimbria
finger-like projections only found in the infundibulum of the oviduct
ampulla
where in the oviduct dos fertilization occur?
(HELLA IMPORTANT)
isthmus
where does sperm capacitation occur?
(^sperm undergo changes that allow them to penetrate the egg)
peg cells
non ciliated secretory cells in the oviduct that provide nourishment for the ovum
to propel the ovum towards the uterus
why do we have ciliated columnar epithelium cells in the oviduct?...
less,
thickens
as you move towards the uterus through the oviduct,
the mucosal folds become [more/less] numerous and the smooth muscle layer [thickens/thins]
endometrium,
myometrium,
perimetrium
what are the names in the uterus of the tunica mucosa, tunica muscularis and tunica serosa/adventitia respectively?
epithelium and lamina propria (made of functional and basal zones)
what makes up the endometrium?
stratum vasculare
feed the fetus
the inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers of the myometrium are separated by _______ which functions to "_________ ___ ______"
caruncles
thickened endometrium only found in cattle with extensive vascular beds and fibrocytes
false
true/false: caruncles have endometrial glands
cotyledon
the caruncle in a cow is the attachment site for what specific part of the fetal placenta?
placetome
when a fetal cotyledon and maternal caruncle join, they form a _______________
all nutrition (vasculature and otherwise) passes through here
what is the function of a placentome?
top third is stratum compactum,
middle third is stratum spongiosum,
(both of the more superficial thirds together make the functional zone)
deep third is the basal zone
If you divided the endometrium into thirds, what would each third be called? (roughly)
cervix
what structure provides a physical barrier to the uterus during pregnancy to protect the fetus from ascending infection?
mucous secretion, physical interdigitation of folds
what two features help the cervix to form that protective barrier?
stratified squamous
ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
what type of epithelium does the cervix in dogs have?
In cows and horses?
true
true/false: the cervix contains longitudinal mucosal folds. These include primary folds with secondary folds budding off of them and tertiary folds budding off of those.
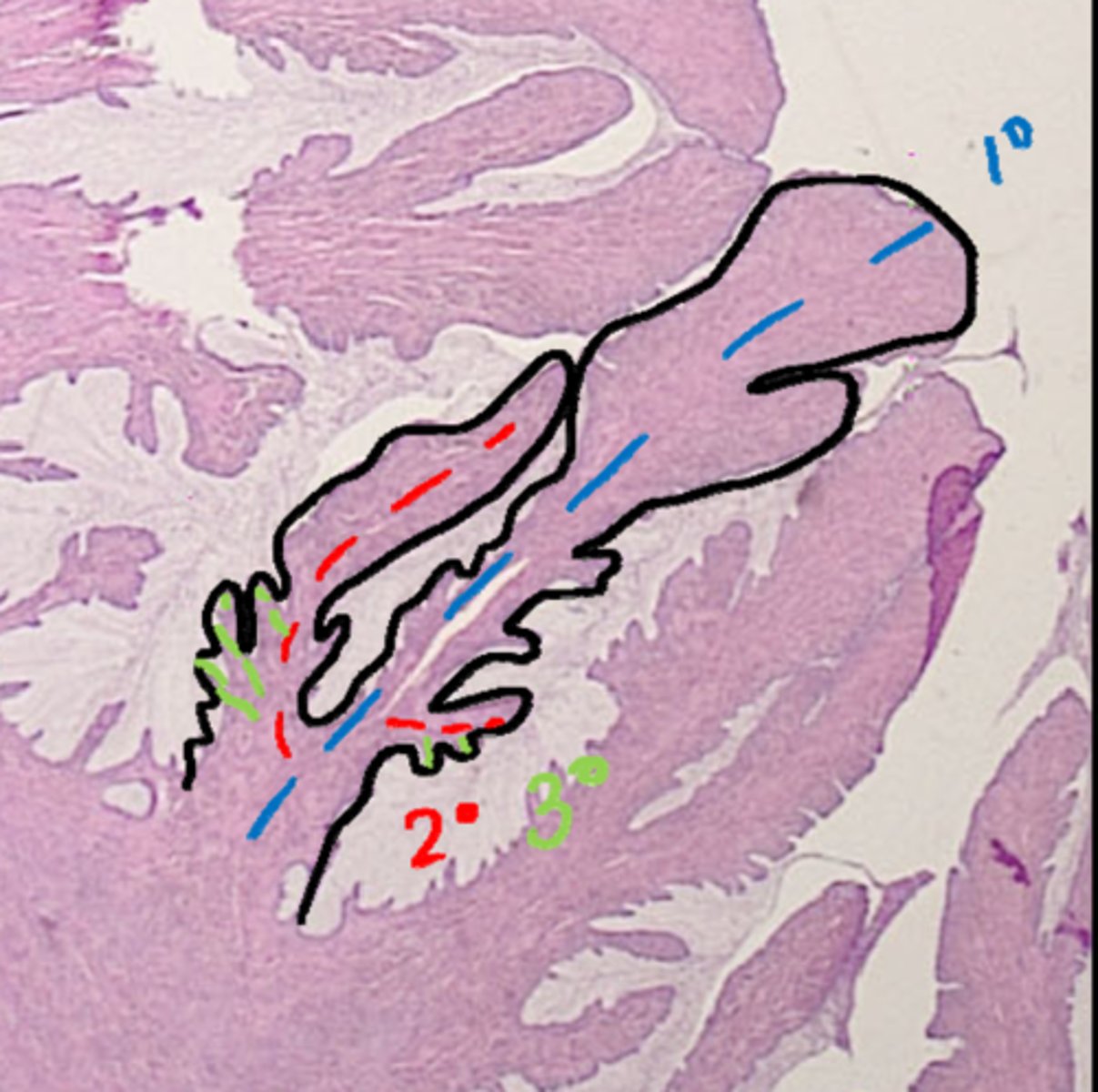
vagina
____: a copulatory organ for mating and birth canal during parturition
(NOTE: acidic in humans to prevent infection... not necessarily in animals)
false: longitudinal folds are in the vagina, just not as pronounced as the cervix
true/false: the cervix ends and the vagina starts at a point where the longitudinal folds in the cervix abruptly end.
true
true/false: the stratified squamous epithelium in the vagina will change thickness and keratinize dependant on different parts of the estrous cycle
thicker,
thinner
the epithelium in the vagina is a lot [thicer/thinner] close to proestrus,
and a lot [thicker/thinner] at the end of estrus
proestrus
period of the estrous cycle before sexual receptivity, accompanied by vulvar swelling and bloody vaginal discharge.
estrogen
proestrus is a time of rising ______ levels to prepare the reproductive tract for breeding
estrus
period of sexual receptivity in the female
the first day the female stands,
day of the LH surge
progesterone, estrogen
behaviorally, estrus begins when?
Hormonally estrus begins when?
regardless, it is marked by rising _____ levels and decreasing _______ levels.
diestrus
7-9 days after LH surge (in a dog) this stage starts and it lasts until birth or until progesterone returns to a basal level.
anestrus
period of time between the end of estrus and start of next proestrus
FSH,
rising estrogen,
LH surge,
Progesterone
what is the dominant hormone during anestrus?
What hormone marks proestrus?
What about estrus?
Whats dominant during diestrus?
Estrous is the estrous cycle.
Estrus is a PART of that cycle
What is the difference between estrous and estrus
parabasal, intermediate, superficial
what are the three types of cells found on vaginal cytology?
parabasal
small, uniform, round, non keratinized cells with small amounts of cytoplasm found o f vaginal cytology
intermediate
cells on vaginal cytology with nuclei similar to parabasal cells, but that have variable amounts and shapes of cytoplasm
superficial
cells on vaginal cytology with pyknotic (tiny) nuclei and abundant angular cytoplasm
(as time goes on they may develop vacuoles)