marine biology 2 redo
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/329
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:48 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
330 Terms
1
New cards
virus
non-cellular particles containing nucleic acid but unable to reproduce unless infecting living cells
2
New cards
prokaryote
an organism made up of cells with a cell wall, cell membrane, lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
3
New cards
microbial loop
the process where viruses infect bacteria and microbes that form phytoplankton, which eventually burst and release DOM that is eaten by bacteria and microbes, which is eaten by zooplankton and can reach small fish and whales
4
New cards
metagenomics
the study of nucleic acids from environmental samples, including the identification of new species and interactions between species
5
New cards
stromatolite
massive calcareous skeletons formed by cyanobacteria
6
New cards
frustule
the siliceous, box-like cell wall of diatoms
7
New cards
zooxanthellae
dinoflagellates that live within the tissues of reef corals and other marine animals
8
New cards
pseudopodia
a thin or blunt extension of the cytoplasm
9
New cards
lichen
the symbiotic association between fungi and green algae or cyanobacteria
10
New cards
bacteria
cyanobacteria domain
11
New cards
eukarya
protista domain
12
New cards
protista
diatom kingdom
13
New cards
protista
dinoflagellate kingdom
14
New cards
protista
foraminiferan kingdom
15
New cards
protista
radiolarian kingdom
16
New cards
protista
ciliate kingdom
17
New cards
eukarya
fungi domain
18
New cards
virus
capsid of protein, sometimes lipids
19
New cards
virus
infect all marine organisms, release dissolved organic matter from destroyed cells
20
New cards
bacteria
prokaryotic, unicellular, some form colonies
21
New cards
bacteria
cell wall of peptidoglycan containing muramic acid, chains of amino sugars
22
New cards
bacteria
essential role in nutrient cycles (autotrophs, heterotrophs, nitrogen fixers), components of detritus, some cause diseases, symbiotic in many organisms, some produce blooms
23
New cards
archaea
prokaryotic, unicellular
24
New cards
archaea
cell wall made up of variety of compounds but no muramic acid
25
New cards
archaea
autotrophs, heterotrophs, nitrogen fixers
26
New cards
diatoms
eukaryotic, unicellular, some form chains, mostly planktonic
27
New cards
diatoms
cell membrane secretes frustules of silica, pectin
28
New cards
diatoms
important primary producers, frustules are components of siliceous sediments
29
New cards
dinoflagellates
eukaryotic, unicellular, 2 flagella, mostly planktonic, some bottom-dwelling
30
New cards
dinoflagellates
cell membrane secretes cellulose plates (thecae)
31
New cards
dinoflagellates
primary producers, symbiotic with other organisms as zooxanthellae, red tides, many are bioluminescent, some cause diseases
32
New cards
foraminiferans
eukaryotic, unicellular, bottom-dwelling, planktonic
33
New cards
foraminiferans
cell membrane secretes calcium carbonate shell (test)
34
New cards
foraminiferans
heterotrophs, tests are components of calcareous sediments
35
New cards
radiolarians
eukaryotic, unicellular, some colonial, mostly planktonic
36
New cards
radiolarians
cell membrane secretes silica skeleton
37
New cards
radiolarians
heterotrophs, skeletons are components of siliceous sediments
38
New cards
ciliates
eukaryotic, unicellular, planktonic, bottom-dwelling
39
New cards
ciliates
cell membrane made up mostly of lipids
40
New cards
ciliates
heterotrophs, some associated with marine animals
41
New cards
fungi
eukaryotic, unicellular or multicellular, mostly bottom-dwelling
42
New cards
fungi
cell wall of chitin and other compounds
43
New cards
fungi
decomposers, many cause diseases, symbiotic with algae or cyanobacteria in lichens
44
New cards
virus
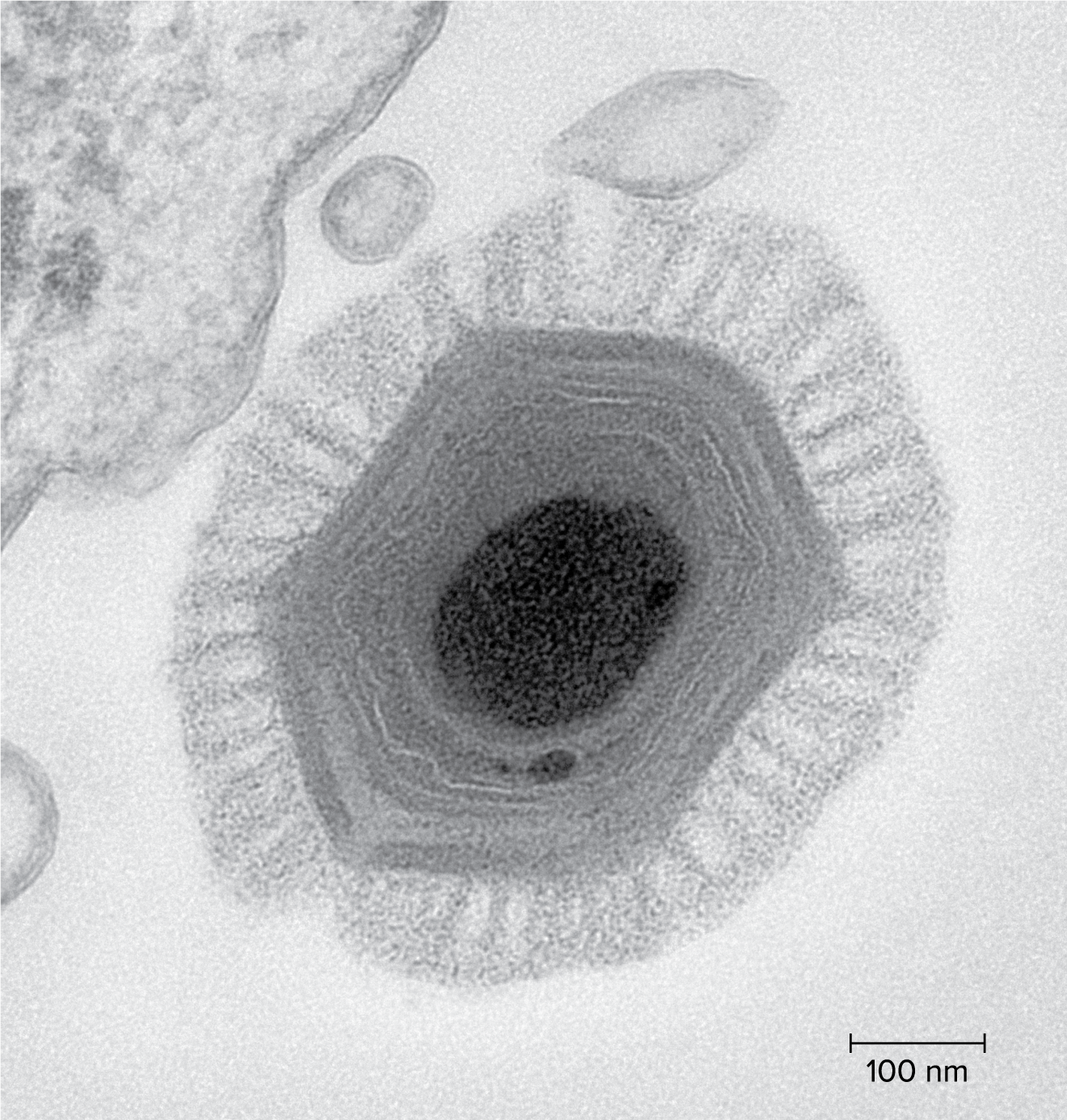
45
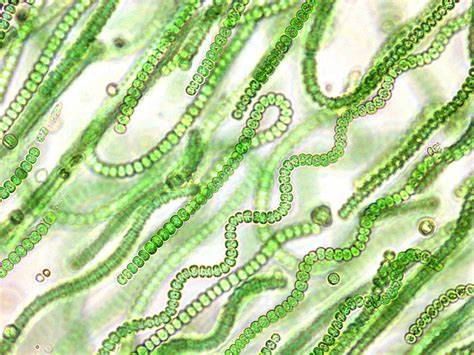
New cards
archaea
46
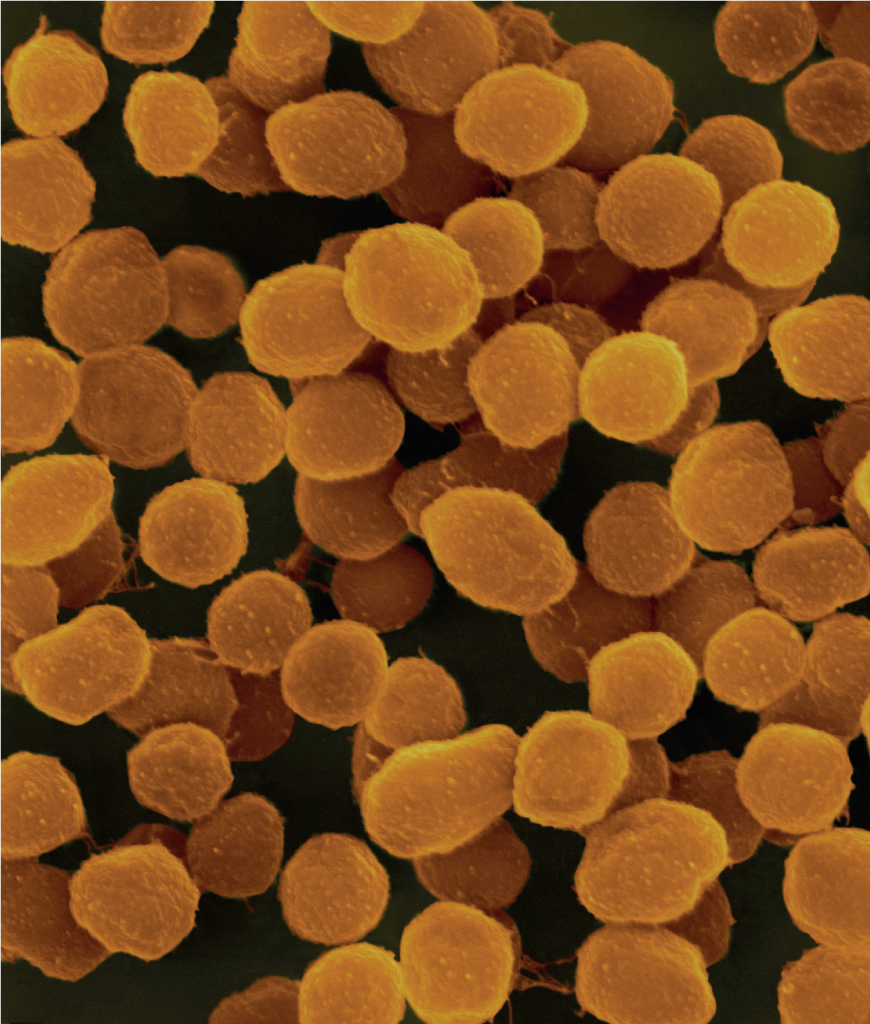
New cards
bacteria
47
New cards
diatoms
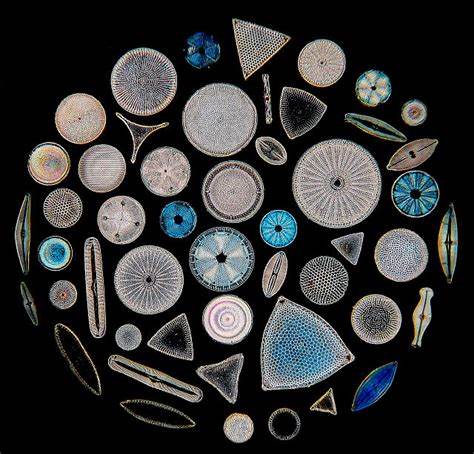

48
New cards
dinoflagellates
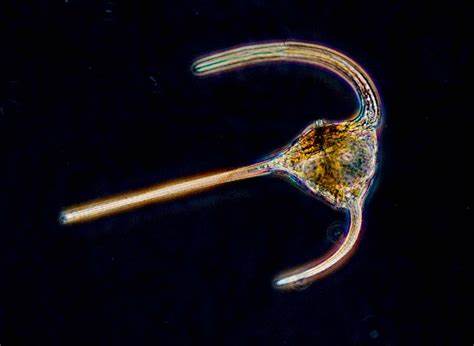
49
New cards
foraminiferans

50
New cards
radiolarians

51
New cards
ciliates
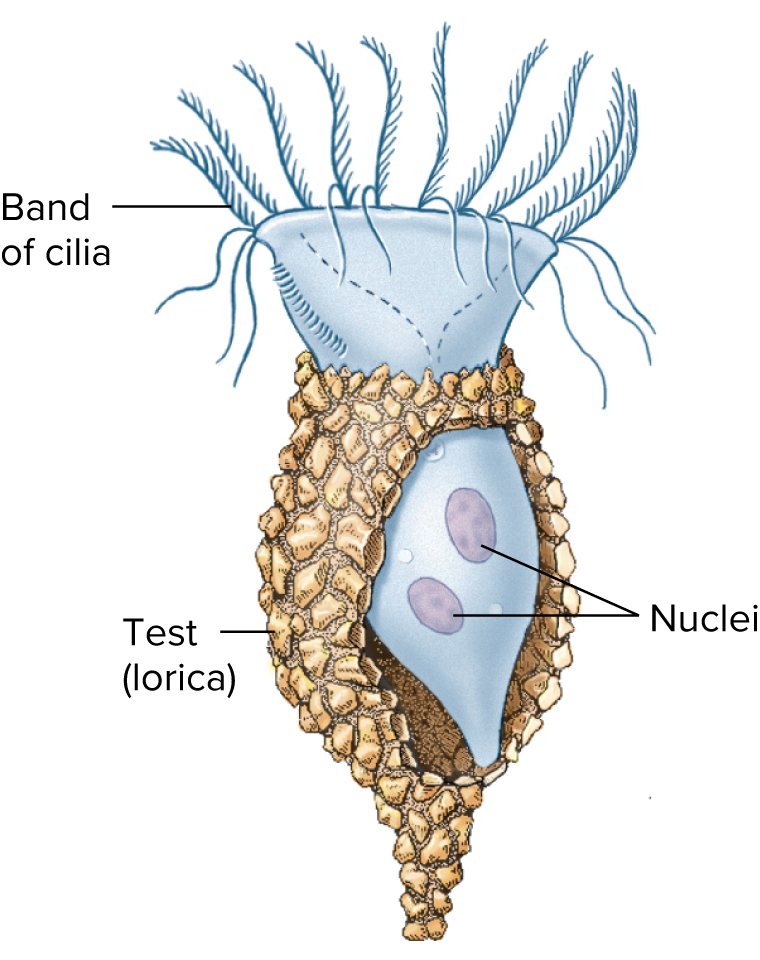
52
New cards
thallus
the complete body of a seaweed
53
New cards
blade
the leaf-like portion of the thallus of a seaweed
54
New cards
stipe
the stem-like portion of the thallus of seaweed
55
New cards
hold-fast
the root-like portion of the thallus of a seaweed
56
New cards
pneumatocyst
a gas-filled bladder in seaweeds
57
New cards
phycobilins
red algae pigment
58
New cards
fucoxanthin
brown algae pigment
59
New cards
rhodophyta
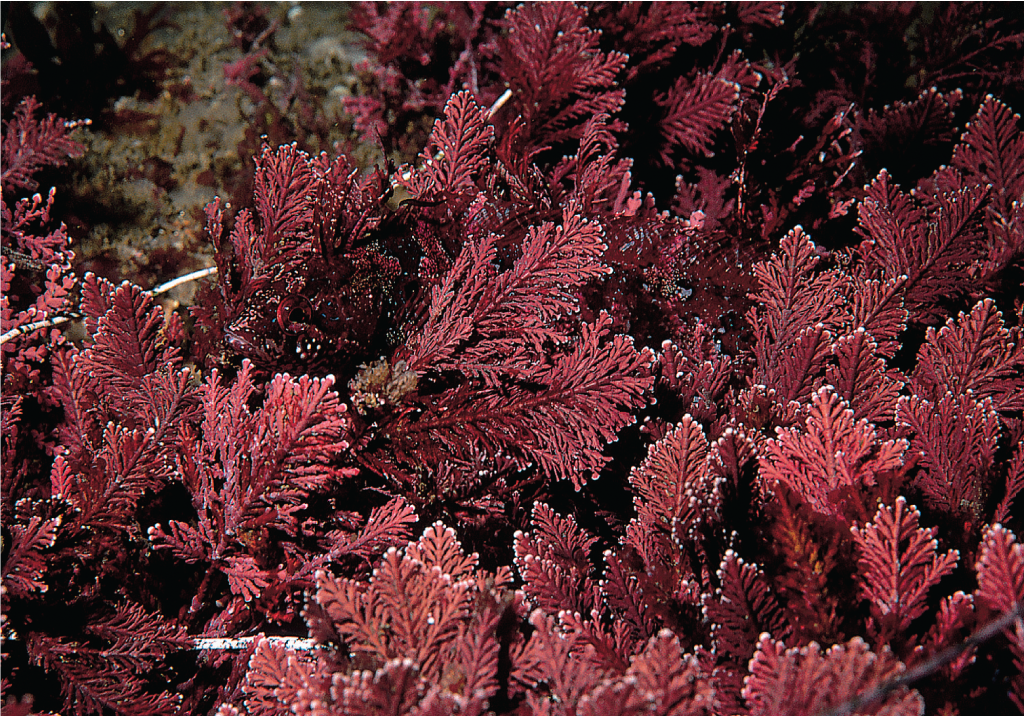

60
New cards
rhodophyta
eukaryotic, protists, multicellular, bottom-dwelling, alternation of three generations
61
New cards
rhodophyta
produce agar and carageenan for human use
62
New cards
rhodophyta
primary producers, coralline algae are important sources of calcareous deposits in coral reefs
63
New cards
chlorophyta

64
New cards
chlorophyta
eukaryotic protists, unicellular and multicellular, mostly bottom-dwelling, some planktonic, alternation of generations in many
65
New cards
chlorophyta
primary producers, calcareous algae are important sources of calcareous deposits in coral reefs
66
New cards
phaeophyta

67
New cards
phaeophyta
eukaryotic protists, multicellular, bottom-dwelling, alternation of generations present in some
68
New cards
phaeophyta
produces algin for human use
69
New cards
phaeophyta
primary producers, dominant components of kelp forests
70
New cards
seagrasses

71
New cards
saltmarsh

72
New cards
mangrove
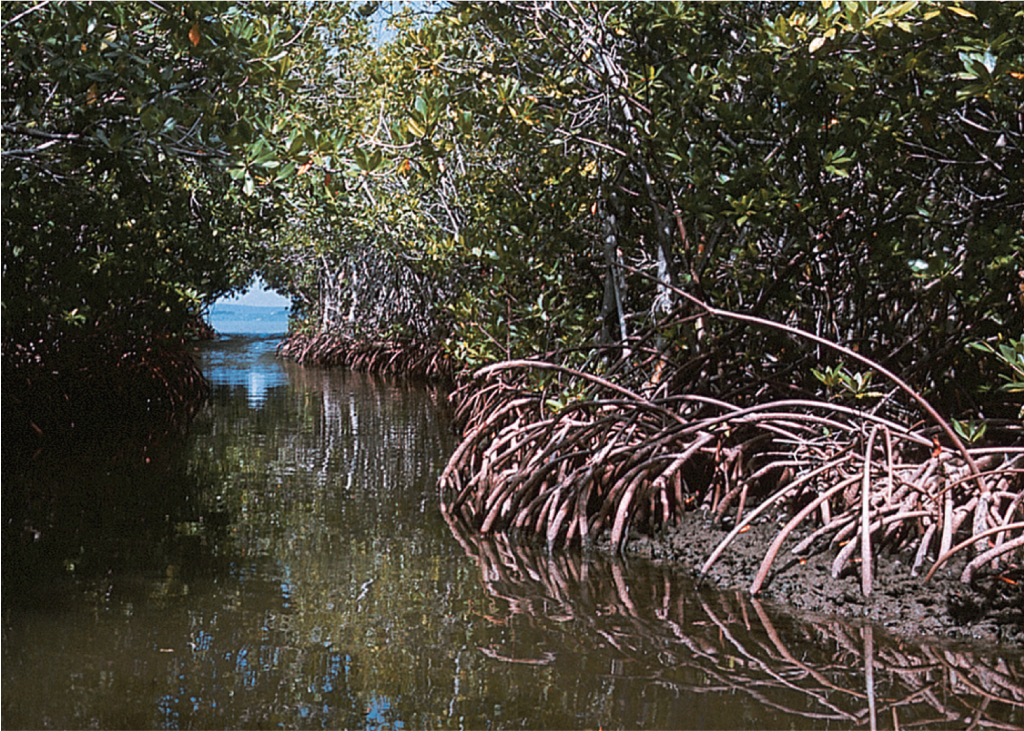

73
New cards
seagrasses, saltmarsh plants, mangroves
eukaryotic plants, multicellular, bottom-dwelling, alternation of dominant sporophyte and minute male and female gametophytes
74
New cards
seagrasses, saltmarsh plants, mangroves
dominant primary producers, nursery grounds for many species, help stabilize soft bottoms, protect coast from turbulence, food for many species in the form of detritus
75
New cards
radial symmetry
symmetry where equal parts radiate out from a central point
76
New cards
bilateral symmetry
symmetry where an organism can be divided into right an left halves that are more or less equal
77
New cards
asymmetry
having no symmetry
78
New cards
biradial symmetry
symmetry of comb jellies
79
New cards
oral
side with mouth
80
New cards
aboral
the opposite side without the mouth
81
New cards
anterior
the front of the organism
82
New cards
posterior
the back of the organism
83
New cards
dorsal
the top of the organism
84
New cards
ventral
the bottom of the organism
85
New cards
sessile
an organism that lives attached to the bottom or to a surface
86
New cards
suspension feeder
an animal that feeds on particles suspended in the water
87
New cards
filter feeder
a suspension feeder that actively filters food particles
88
New cards
deposit feeder
an animal that feeds on organic matter that settles on the bottom
89
New cards
osculum
a large opening in many sponges
90
New cards
ostia
tiny pores on the surface of sponges that allow water to enter and circulate
91
New cards
choanocyte
a flagellated, food-trapping cell of sponges
92
New cards
spicule
any of the small calcareous or siliceous bodies embedded among the cells of sponges to provide structure
93
New cards
spongin
the resistant fibers of sponges
94
New cards
amebocyte
wandering cells that secrete spicules and spongin and transport and store food particles
95
New cards
porocyte
the tube-like cell of sponges that forms ostia
96
New cards
pinacocyte
the flat cells on the outer surface of sponges
97
New cards
broadcast spawning
the release of gametes into the water
98
New cards
epidermis
the external layer of cells that form the body wall of cnidarians
99
New cards
mesoglea
the layer between the epidermis and gastrodermis in cnidarians
100
New cards
gastrodermis
the layer of cells that lines the gut in cnidarians