Pharmacokinetics Metabolism and Excretion
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Drug elimination is an?
Irreversible Process
What are the 2 Steps to Drug Elimination?
metabolism (biotransformation)
And/or excretion
The effect that a drug has on the body is therefore not only dependent on its pharmacological actions but also?
On how the Body handles it.
the main sites of metabolism and excretion are?
Metabolism = Liver
Kidneys = Excretion
The products of metabolism are generally more?
Water soluble than the Original Compound
Drug metabolism involves two types of reactions known as?
Phase 1 & Phase 2
Phase 1 reactions involve the?
Involve the enzymatic introduction of a functional group which generally make the molecule less lipophilic,
and so reduces the possibility of its reabsorption in the renal tubules
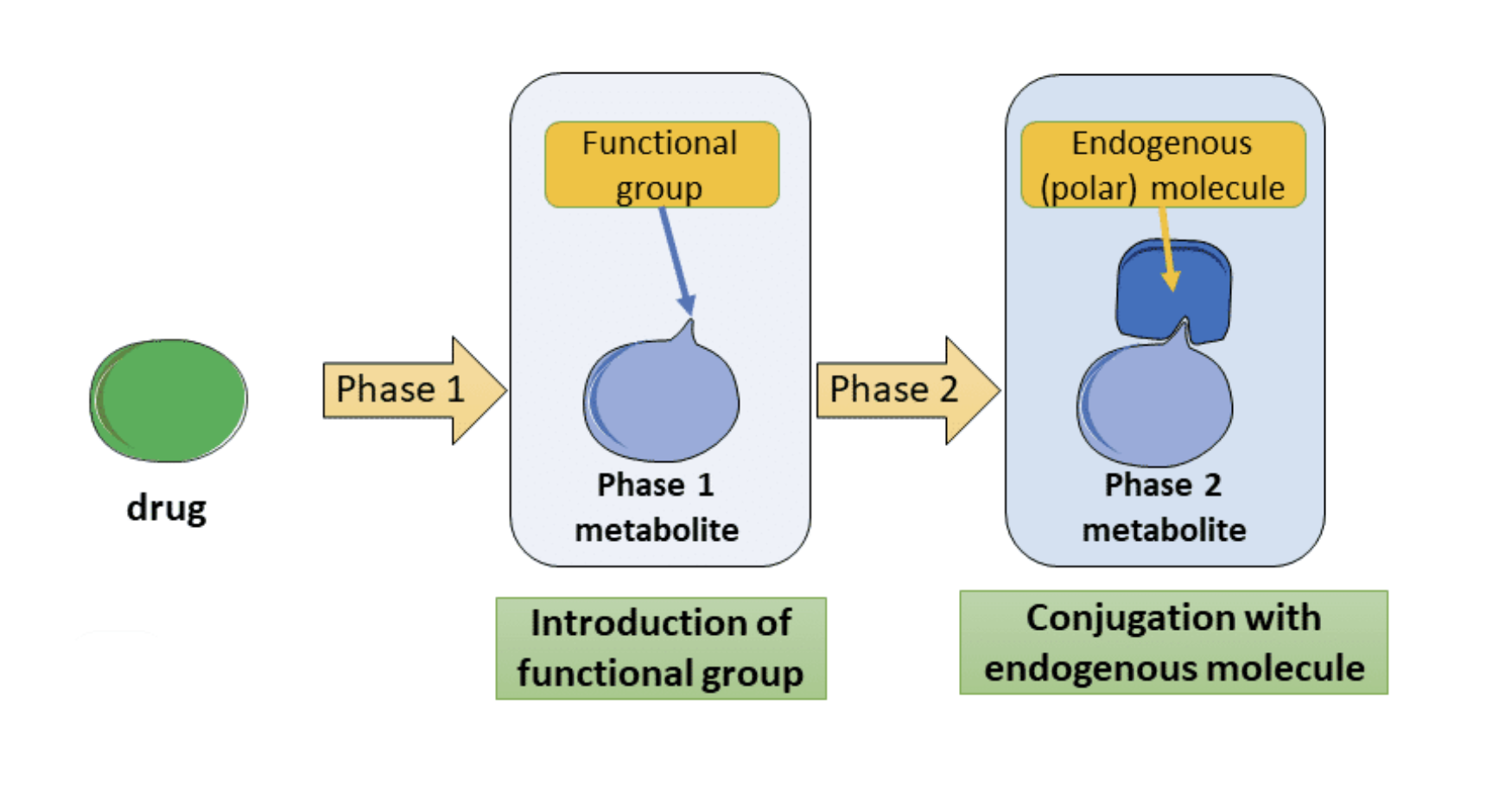
Phase 2 reactions involve?
Conjugation Reactions
that generally result in inactive products which are more hydrophilic (water soluble)
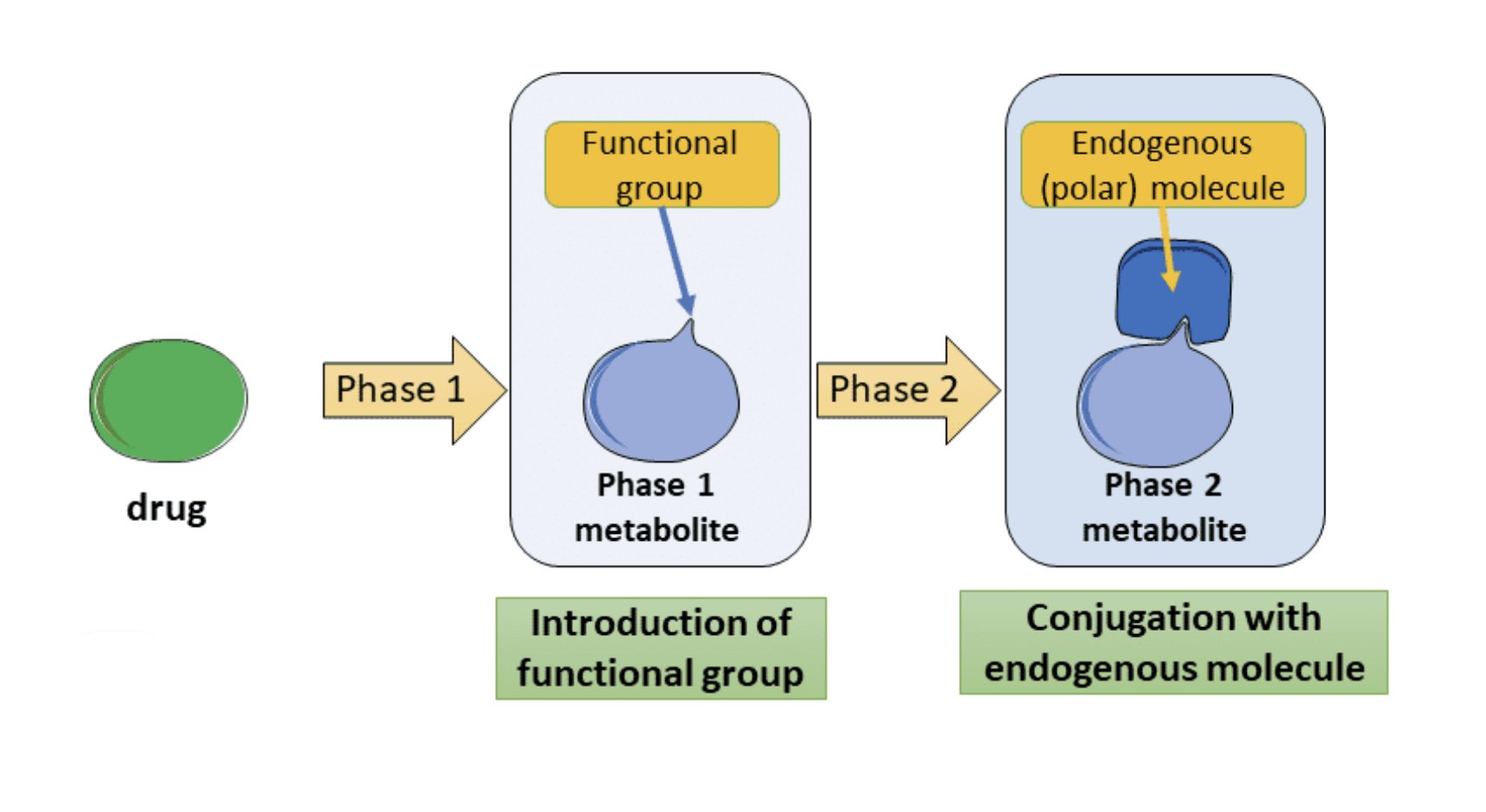
The metabolites from phase 1 reactions may be pharmacologically less active but the?
The Products (Metabolites) may be more Active/ Reactive
Some drugs, known as prodrugs, are administered?
administered in a pharmacologically inactive form
to facilitate absorption, and require metabolism in the body to become active.
E.G Codeine
Phase 1 reactions frequently result in the formation of?
Stable Metabolites
which may be less lipophilic
and have a lower or no pharmacological activity

Drugs can be metabolised into a products called?
Metabolites
Metabolites have pharma…
Pharmacological Activity
Metabolites can prolong the duration of effect. E.G Diazepam
Some drugs, prodrugs, are administered in an inactive form that?
Requires metabolism that to form the pharmacological active metabolite E.G Codeine
For some drugs one of their metabolites can be?
Chemically reactive
These reactive metabolites can cause?
Cellular Damage & Toxicity
When produced in high enough quantities e.g. paracetamol
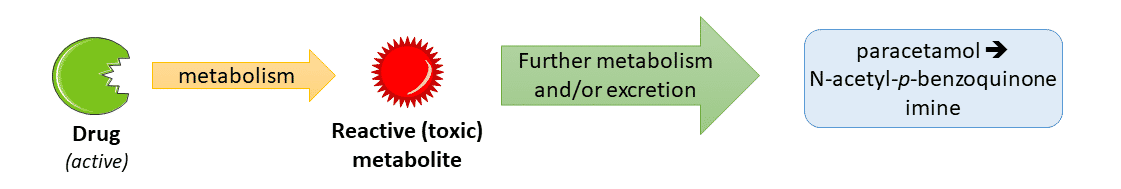
Most drugs will undergo several metabolic reactions concurrently, resulting in the formation of?
Stable, Inactive & Active Metabolites.
and sometimes reactive and potentially toxic metabolites.
The balance between these Phase 1 & 2 Metabolic pathways will determine the overall?
Biological Response to the Drug
Phase 1 reactions generally…?
Precede Phase 2 but not always
During Phase 1 reactions the chemical is converted to a more polar derivative by either?
introducing or unmasking a functional group
Phase 1 Reactions Occur Via ?
oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis.
The majority of oxidation reactions are catalysed by the?
cytochrome P450
(often referred to as CYP)
CYP is mainly involved in metabolizing?
Foreign Compounds.
How are CYP Enzymes classified?
Families
Subfamilies
Individual Enzymes
How are CYP Enzymes Families classified?
Families are Identified by a Number E.G CYP1 = Family 1
CYP1, CYP2, CYP3
How are CYP Enzymes Subfamilies classified
Subfamilies are identified by a Letter.
E.G CYP1 + A
= CYP1A
individual enzymes: Identified by a?
By a number after the Subfamily
E.G CYPA1 = A
= CYPA1A
Oxidation of foreign compounds, important for?
Drug Metabolism & Detoxification
The reactions catalysed by CYP require the drug?
NADPH
The overall reaction is shown below:
Drug +NADPH +H++O2 →Drug-OH+NADP+H2O
Reduction reactions are much less?
Less common than Oxidative Reactions
Reduction reactions are catalysed either via?
microsomal or cytosolic reductases.
Ester and amide bonds are subject to?
Hydrolysis reactions
esterases and amidases, These enzymes are found in the?
Cytosol and Various Tissues
Esterases is also found in Plasma
Local anaesthetics, for example are inactivated by?
Hydrolysis
Phase 2 reactions are conjugation reactions that involve the addition of a?
endogenous (polar) molecule which makes the drug metabolite
more water soluble and so more easily excreted in the urine or bile
The conjugates formed are usually?
Inactive
Phase 2 reactions generally take place in the?
Liver but also can Occur in the Kidneys