Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What kind of symetery?
Bilateral Symmetry
What do they have as their head?
Cephalization
Distinct Front
Sensory Organ
What kind of cell layers?
Triploblastic
Ectoderm
Mesoderm
Endoderm
What kind of skeleton?
Hydrostatic Skeleton
What kind of nervous system?
Cerebral Ganglia
Lateral and Transverse Nerve Cords
What does it lack?
It lacks a cavity containing the internal organs (acoelomate) instead it is imbedded in the mesoderm
How do they reproduce?
Monoecious
How do they reproduce Asexually?
Fission
Regeneration
How do they reproduce Sexually?
Cross-Fertilization
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - How do they survive?
Found in Fresh Water and are free-living carnivores
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - What do they have as sensory organs?
Auricles (structure like an ear) and oceili (simple eyes)
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - What kind of muscles?
Long and Circular Muscles
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - What kind of digestion?
Incomplete Digestion
Muscular Pharynx and Intestines
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - How do they reproduce Asexually?
Fission
Class Turbellaria (Planarians) - How do they reproduce Sexually?
Penis-fencing
They have a genital pore and penis
Class Trematoda (Flukes) - What are they?
Parasite
Class Trematoda (Flukes) - How do they eat?
Using 2 suckers that attach/move
Pharynx and Intestines
Class Trematoda (Flukes) - What excretory organ do they have?
Protonephiridia that consists of “Flame Cells”
Class Trematoda (Flukes) - What kind of skin do they have?
Tegument (Tough living outer covering that replaces typical skin)
Class Trematoda (Flukes) - How do they reproduce?
Monoecious
Class Trematoda (Flukes) Clonorchis - Where can they be found?
Human Liver
Class Trematoda (Flukes) Schistosoma - Where can they be found?
Human Blood
Dioecious
Gynaecophoric Canal (Long longitudinal groove on belly)
Class Trematoda (Flukes) Fasciola - Where can they be found?
Sheep liver
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - What are they?
Parasites that have no digestion
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - What do they have as skin?
Tegument
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - What kind of body do they have?
Strobila (long segmented body)
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - What kind of head do they have?
Scolex (head of a tapeworm with specialized organs like hooks and suckers
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - How do they reproduce?
Proglottids (Each segment contains it’s own reproductive system and can break off and looks like rice-like segment)
Self-Fertilization
Cross Fertilization
Class Cestoda (Tapeworm) - What is an example?
Taenia Pisiformes
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What are they?
Parasites can be found in fresh and salt water and in soil
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of body do they have?
Pseudocoelomate (fluid-filled body cavity called a pseudocoel, which is not completely lined by mesoderm)
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of Skeleton?
Hydrostatic Skeleton
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of Cell Layers?
Triploblastic
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of digestion?
Complete Digestion
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - Symmetry?
Bilateral Symmetry
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of skin do they have?
Cuticle (Tough flexible exoskeleton that is primarily made up of cross-linked collagen)
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of muscles?
Longitudinal Muscles
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) - What kind of reproduction?
Dioecious (Mostly)
Spicule (paired, needle-like, chitinous copulatory organs found in males, used to grasp the female's vulva during mating to hold it open and facilitate sperm transfer)
Genital Pore (the external opening for the reproductive system)
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) Ascaris Lumbricoides - Facts?
“Giant Intestinal Roundworm”
25% Worldwide
Resilient Eggs (250,000 per day)
Poor sanitation
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) Necator Americanus - Facts?
“Hookworm”
Dogs → Humans
28,000 Eggs per day
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) Enterobius Vermicularis - Facts?
“Pinworms”
Eggs → Anus → Night
Common in U.S.
16,000 Eggs per day
Phylum Nematoda (Roundworms) Trichina - Facts?
Pigs → Humans
Larvae encyst (Invade skeletal muscle after hatching to form protective cysts)
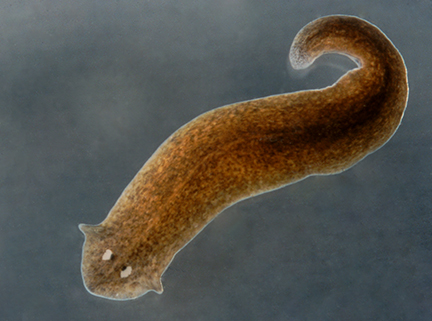
What organism is this?
Planarians
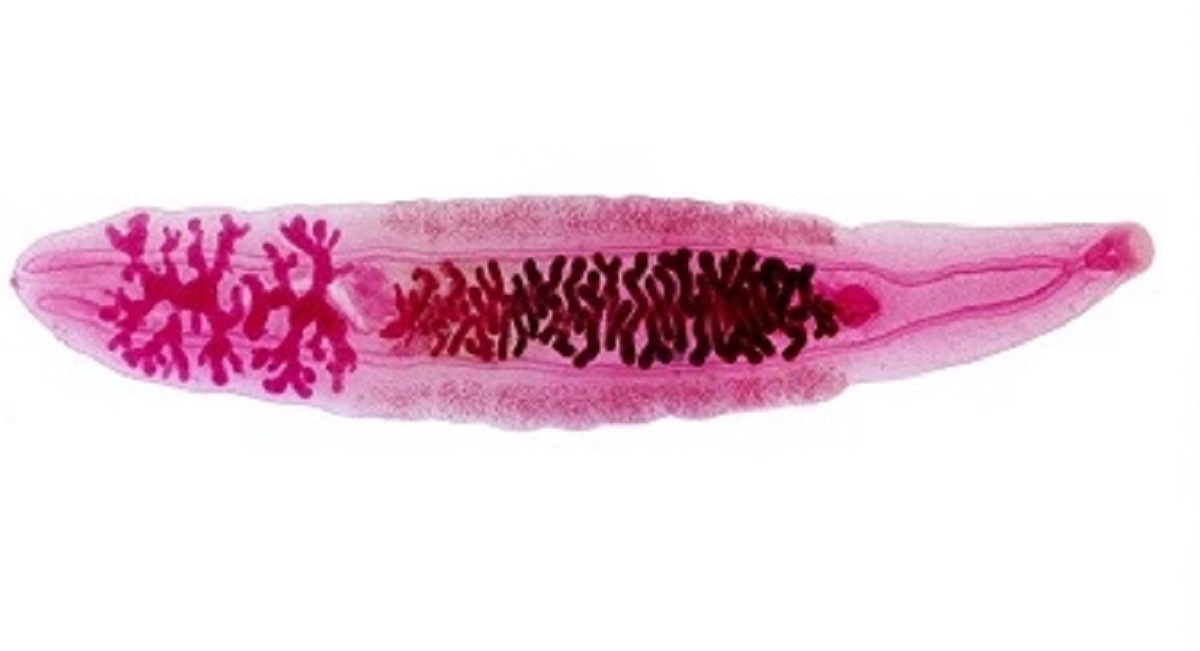
What organism is this?
Clonorchis (Liver Fluke)
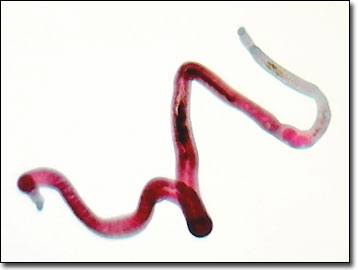
What organism is this?
Schistosoma (Human Blood Fluke)
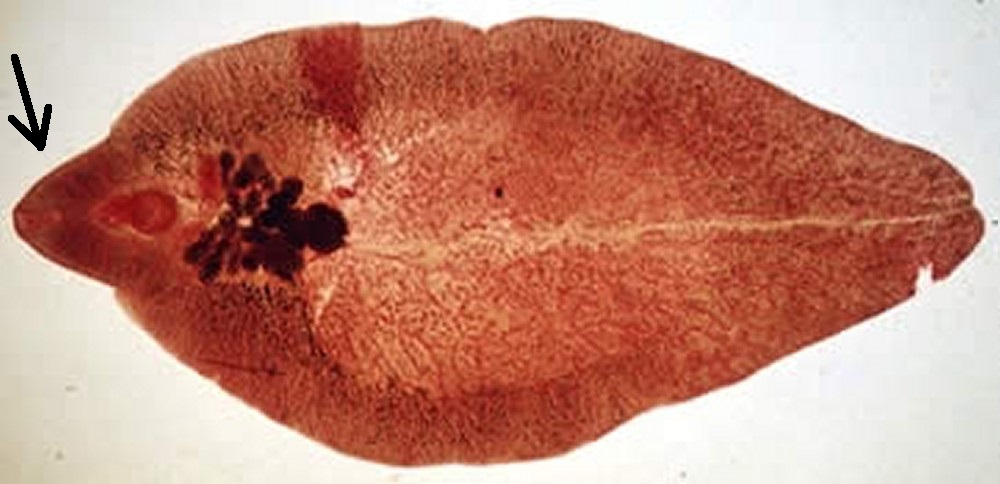
What organism is this?
Fasciola
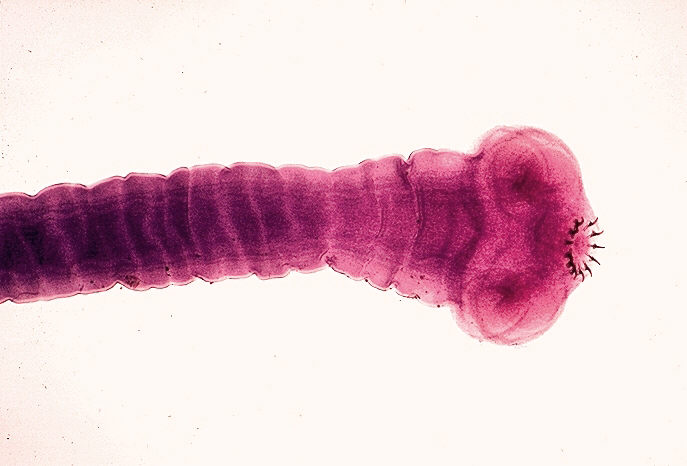
What organism is this?
Taenia Pisiformes
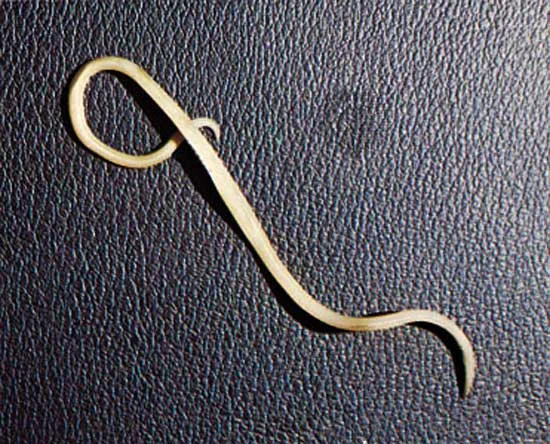

What organism is this?
Ascaris Lumbricoides (Giant Intestinal Roundworm)
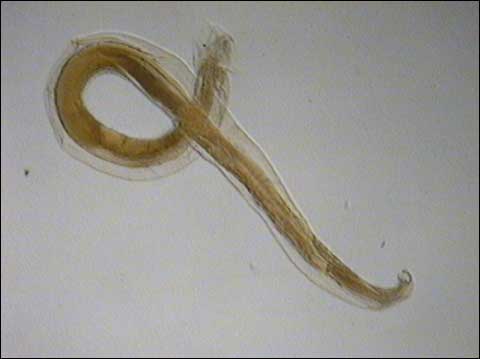
What organism is this?
Necator Americanus (Hook Worm)
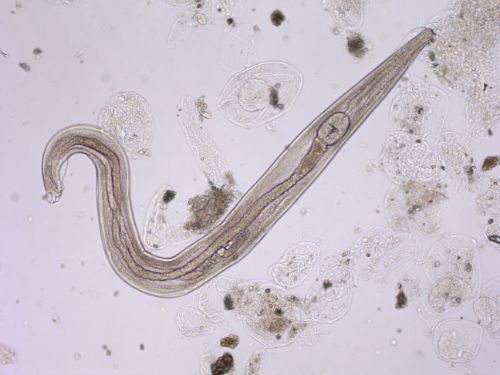
What organism is this?
Enterobius Vermicularis (Pinworm)
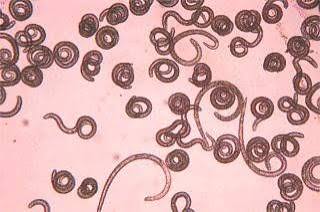
What organism is this?
Trichina