ch5 - osmosis
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is a solution
mixture made up of a solute (e.g. glucose), dissolved in a solvent (e.g. water)
What does water potential mean
pressure exerted by water molecules against a membrane (or container)
What symbol and unit is used for water potential
symbol - Ψ
unit measured in - kiloPascals (kPa)
What is the water potential of pure water
0 kPa
What happens to water potential when solutes dissolve in water
decreases/ the value for water potential becomes more negative as more solutes dissolve in water
What does high water potential mean
solution has a high water concentration/ little solute dissolved in it
What does low water potential mean
solution has a low water concentration/ lots of solute dissolved in it
What is osmosis
net movement of water molecules down a water potential gradient (from area high water pot. to area of lower water pot.) across a partially permeable membrane until equilibrium is reached
Is osmosis a passive or active process
passive process as it does not require added energy in the form of ATP hence molecules move due to kinetic energy
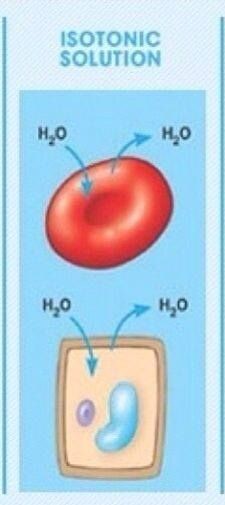
What is an isotonic solution
when water potential is the same in the solution and inside the cell hence there is no net movement of water into or out of the cell
In isotonic solutions what happens to animal cells and plant cells
animal cells = stays the same size
plant cells = stays the same size
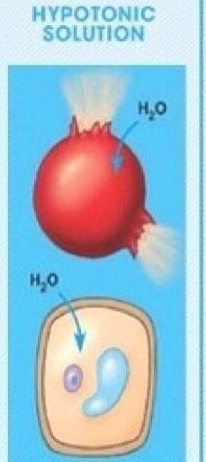
What is a hypotonic solution
when there is higher water potential outside the cell hence water molecules move into the cell
In hypotonic solutions what happens to animal cells and plant cells
animal cells = swell and burst
plant cells = swell becoming turgid
Why do plant cells not burst in hypotonic solutions
Because plant cells have cell wall
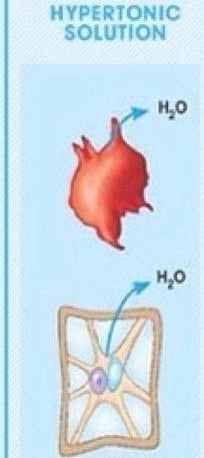
What is a hypertonic solution
when there is a lower water potential outside the cell hence water molecules move out the cell
In hypertonic solutions what happens to animal cells and plant cells
animal cells = shrink (crenation)
plant cells = shrink and become flaccid (plasmolysis)