CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 14: Coordination and response
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
nerve impulse
an electrical signal that passes along nerve cells called neurones
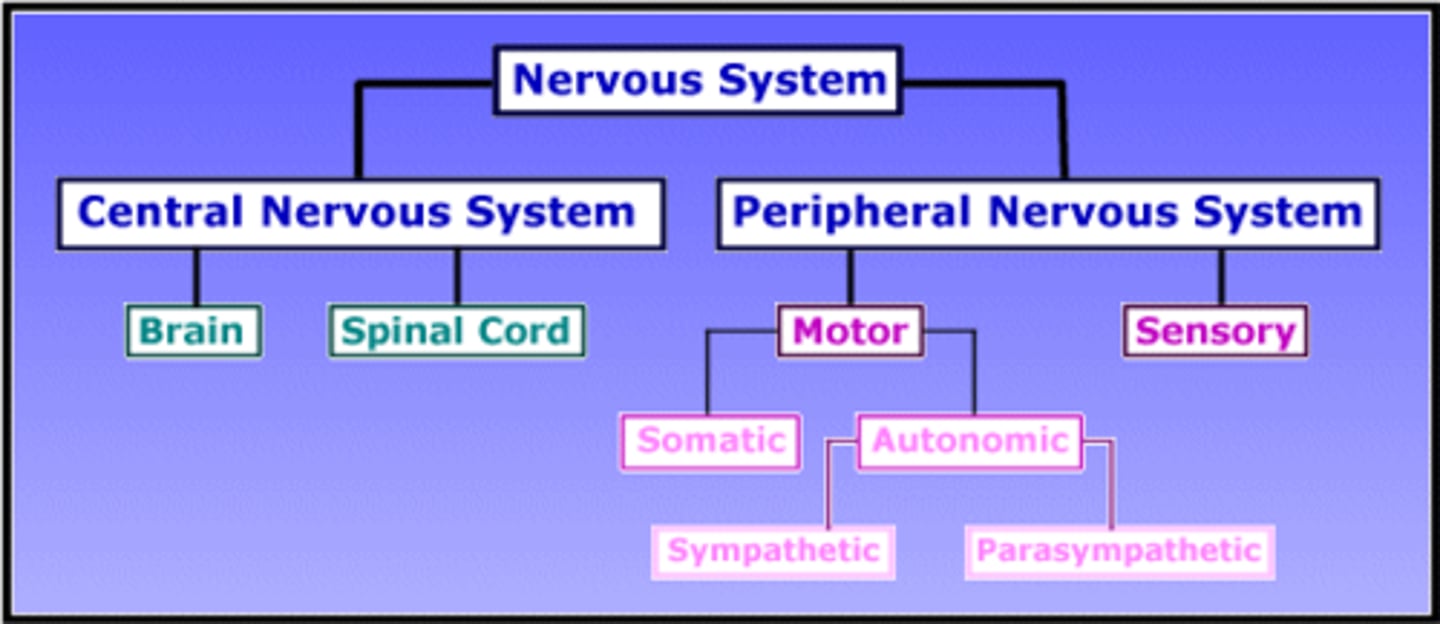
human nervous system
Central nervous system: made up of two organs, spinal cord and brain
Peripheral nervous system: connected to the limbs, linked with central nervous system
voluntary actions
Requires decision making from the brain, is slower compared to involuntary action as it requires impulse to travel to brain
involuntary actions (reflex)
Does not require decision making, is fast as impulse does not require to travel to brain
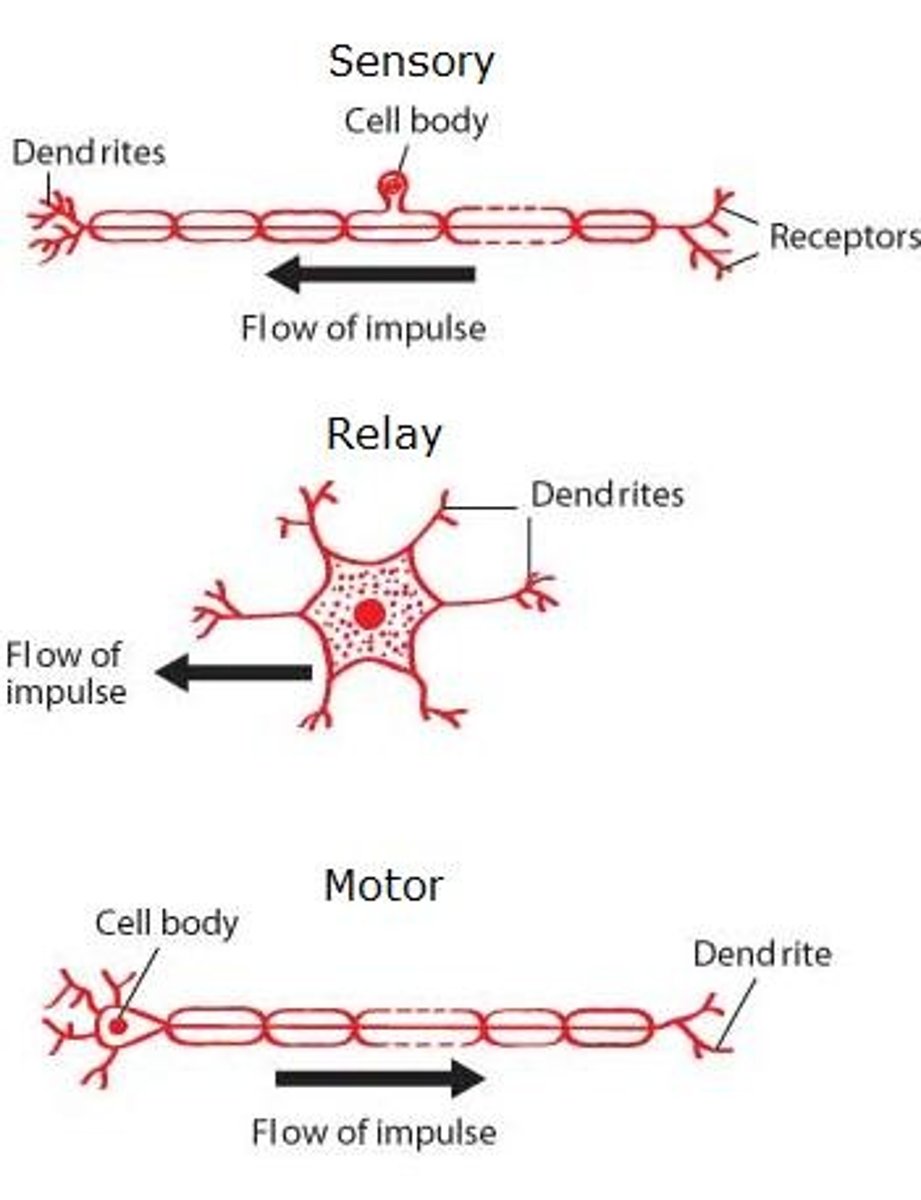
Sensor, relay, and motor neurons
Sensory neurone detects stimuli and transfer impulse through sensory neurone and relay neurone in brain transfers signal to motor neurone that sends the impulse to the effector in which a response is made
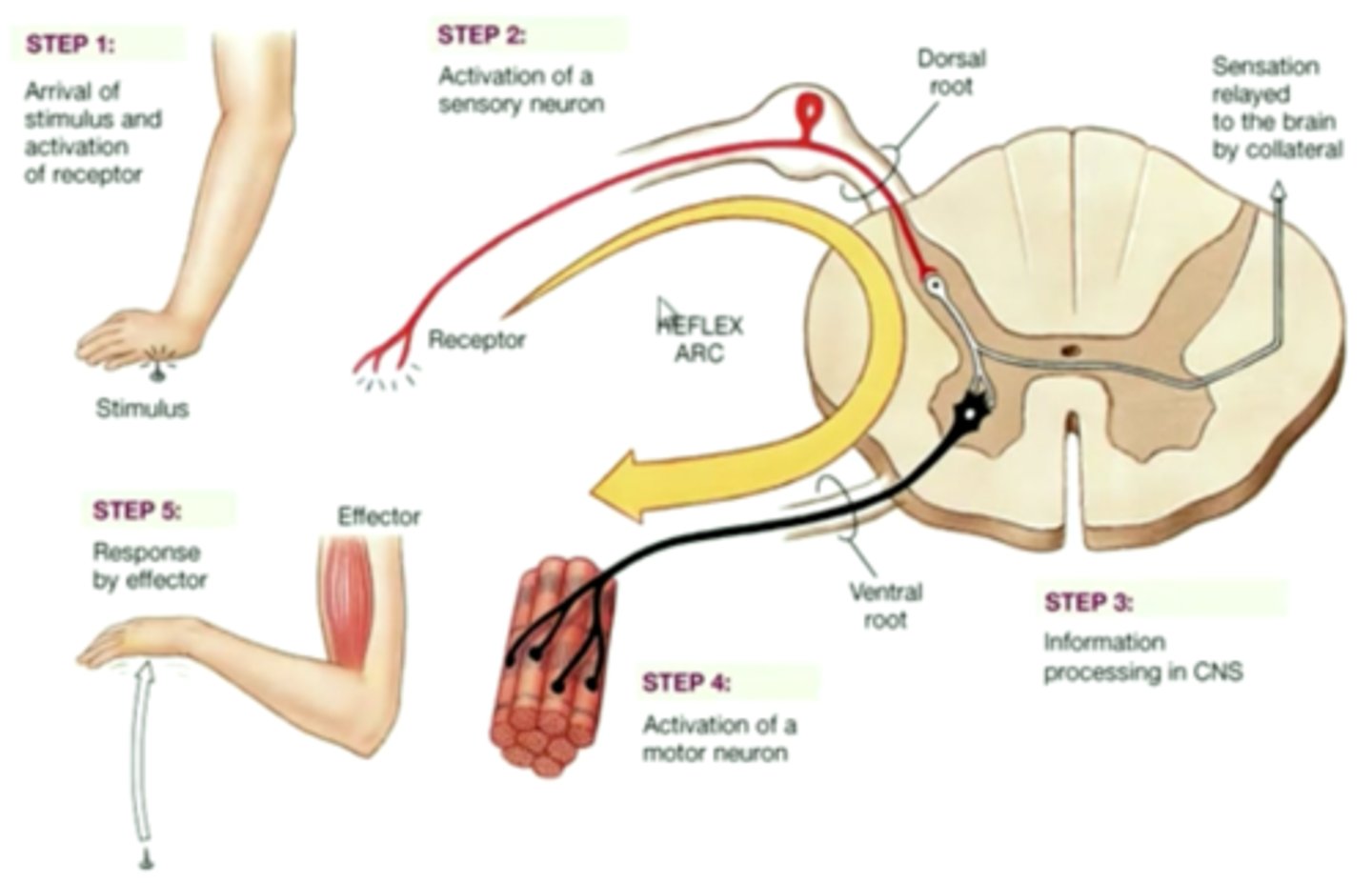
simple reflex arc
receptor, sensory neurone, relay neurone,
motor neurones and effector
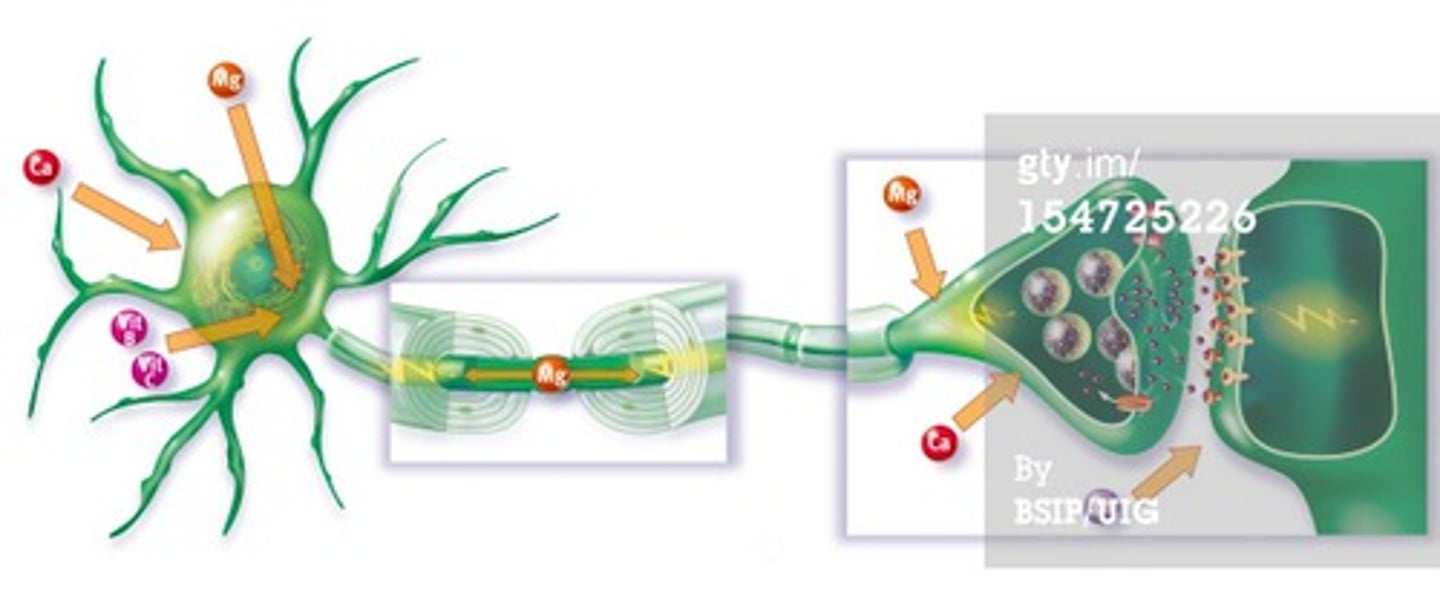
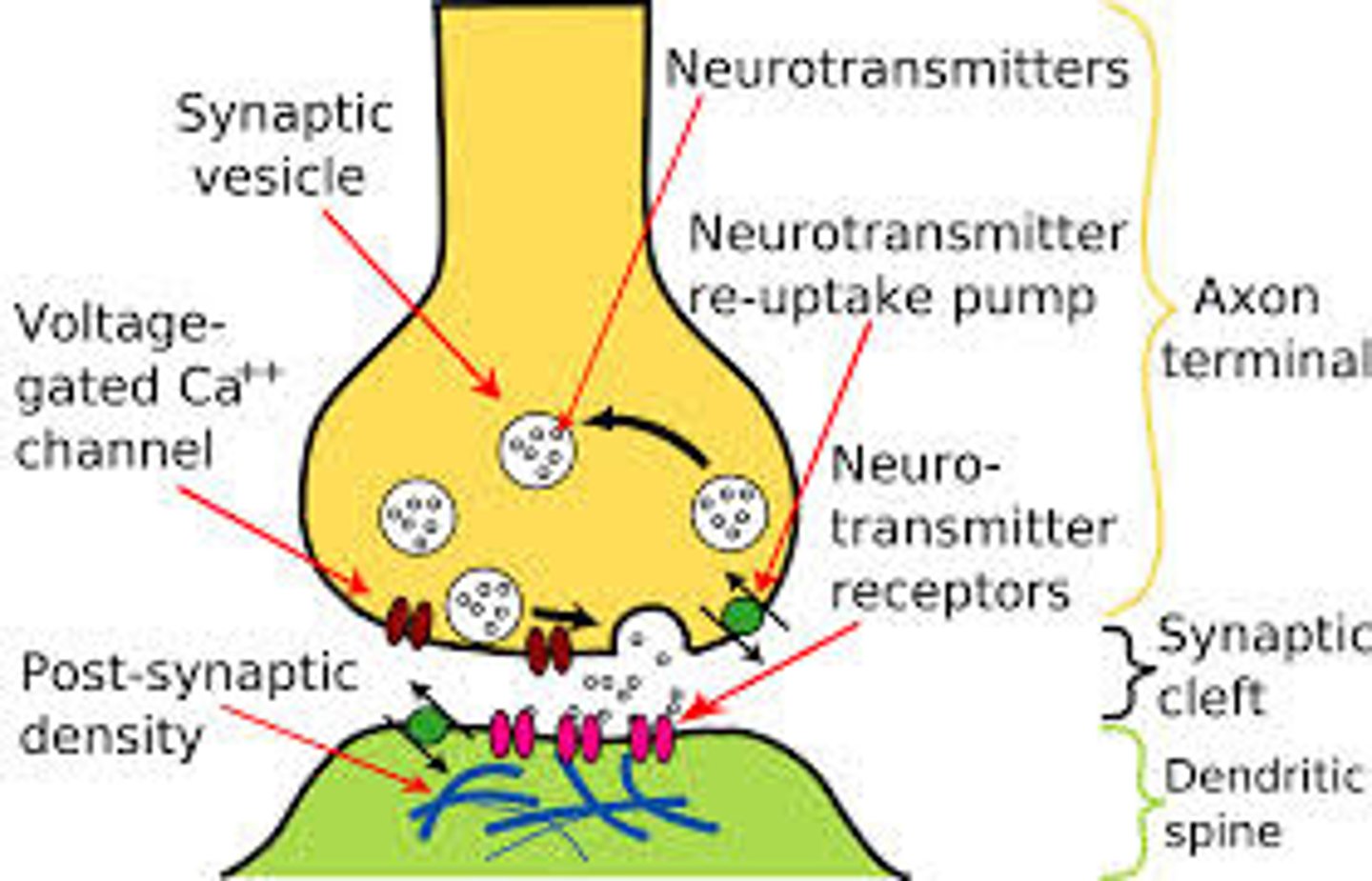
synapse
a junction between two neurones
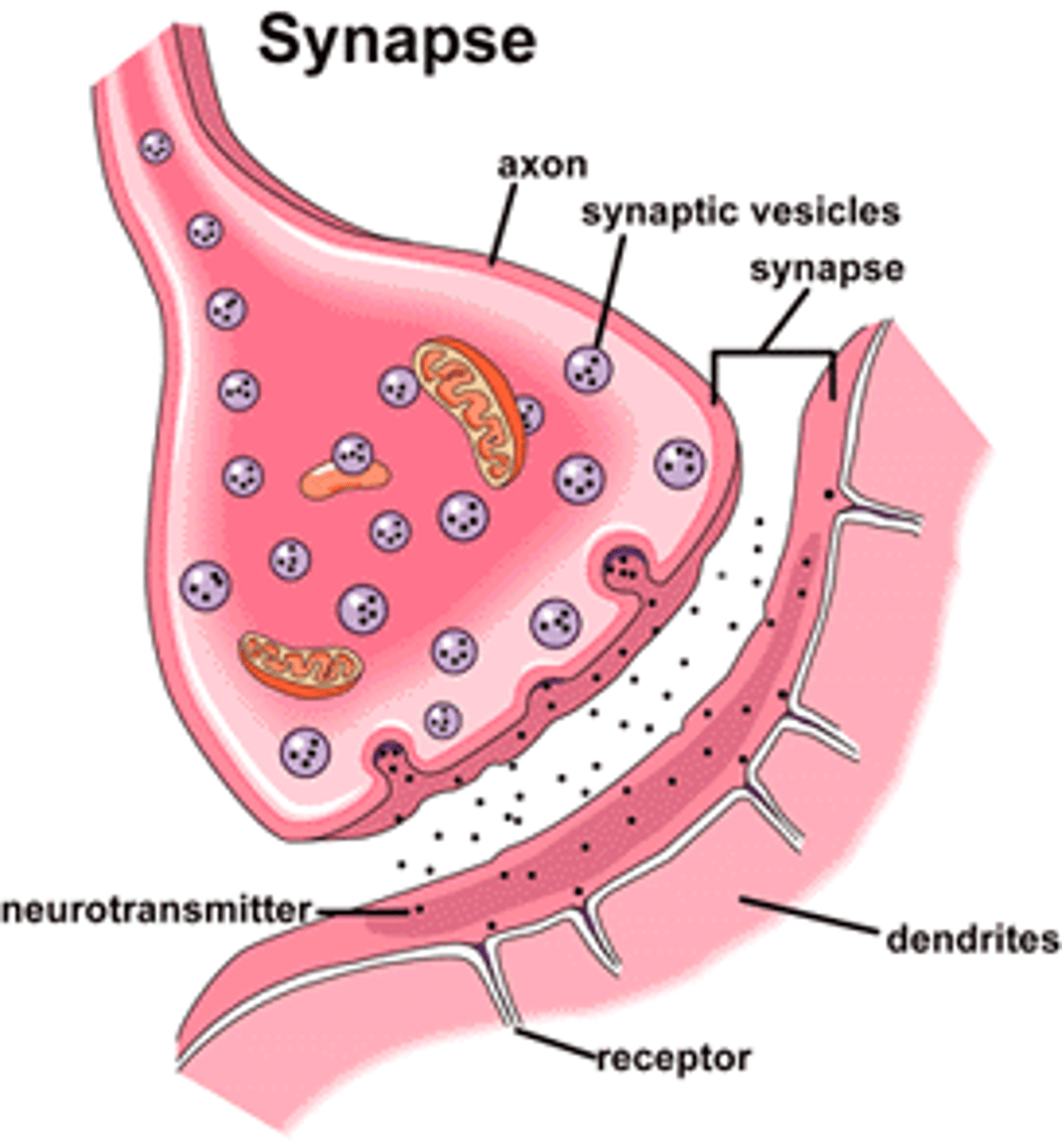
How impulses travels
an impulse triggers the release of a neurotransmitter from vesicles into the synaptic gap, the neurotransmitter diffuses across to bind with receptor molecules, in the membrane of the neurone after the synaptic gap, causing the impulse to
continue
Sense organs
groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli: light, sound, touch, temperature and chemicals
Eye structures
- cornea - refracts light
- iris - controls how much light enters pupil
- lens - focuses light onto retina
- retina - contains light receptors, some sensitive to light of different colours
- optic nerve - carries impulses to the brain
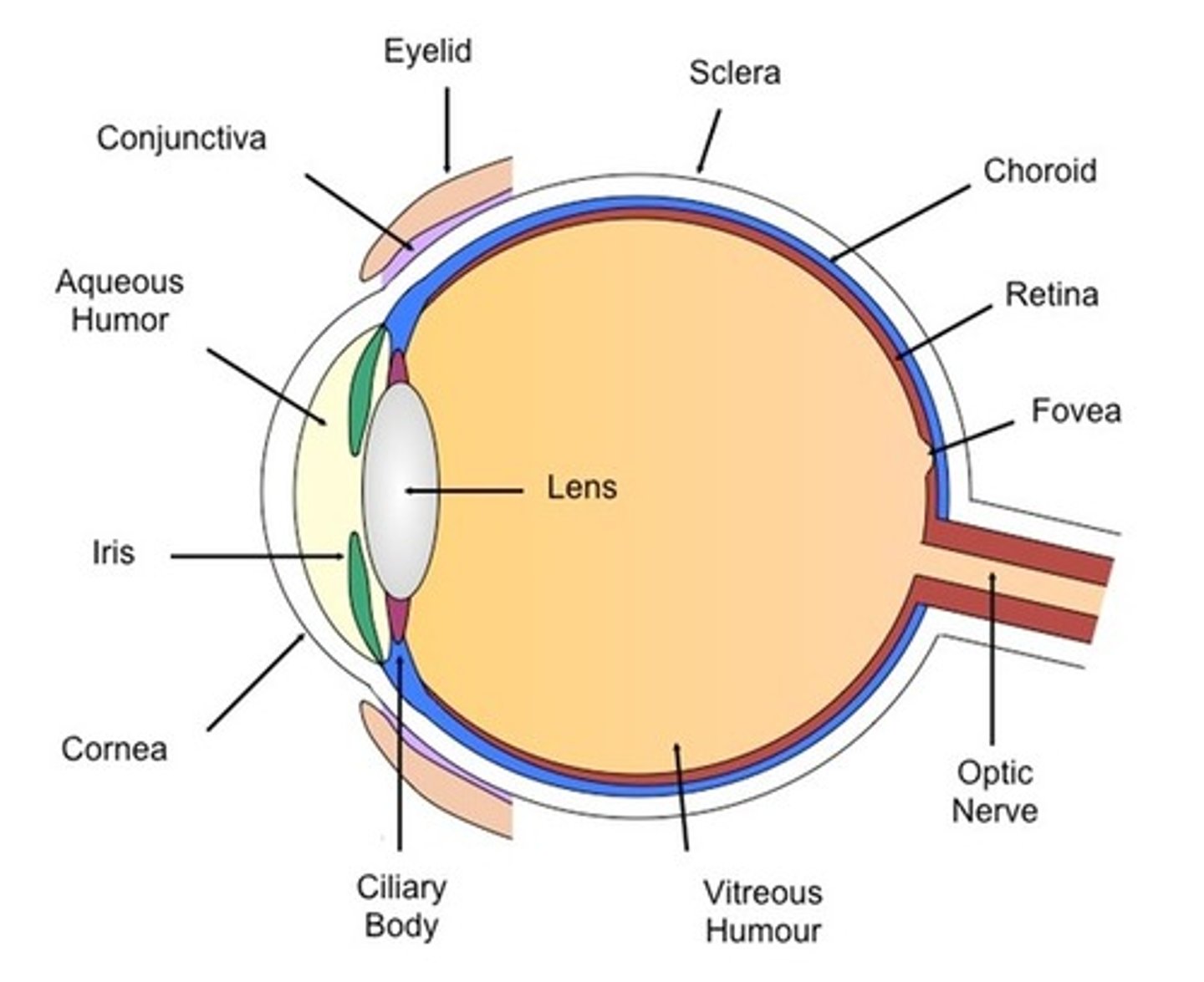
Blind spot
The exit point to the optic nerve with no light sensitive cells
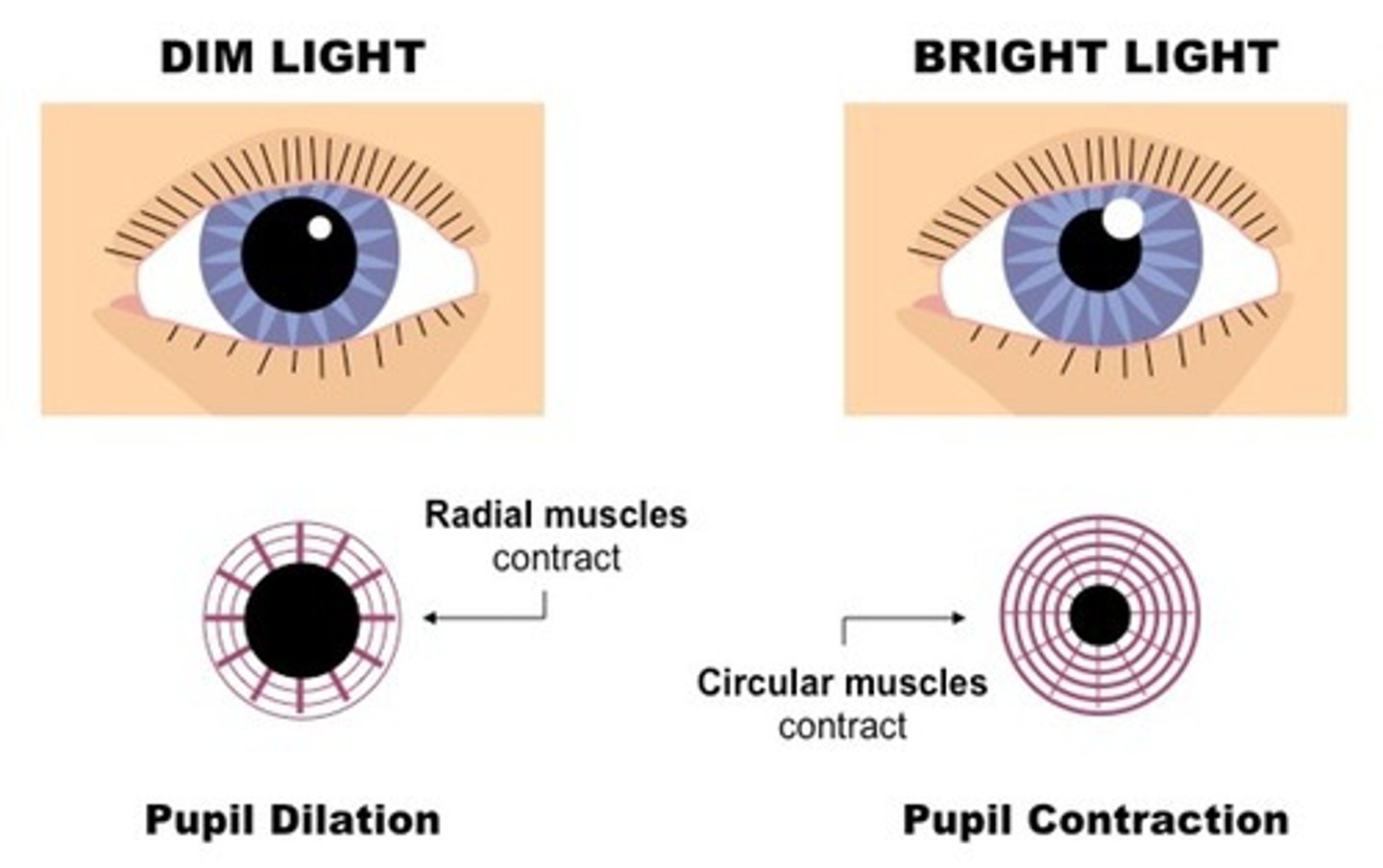
Bright light
Circular muscle contracts
Radial muscles relax
To allow less refraction to reach the retina
pupil reflex
light intensity and antagonistic action of circular and radial muscles in the iris
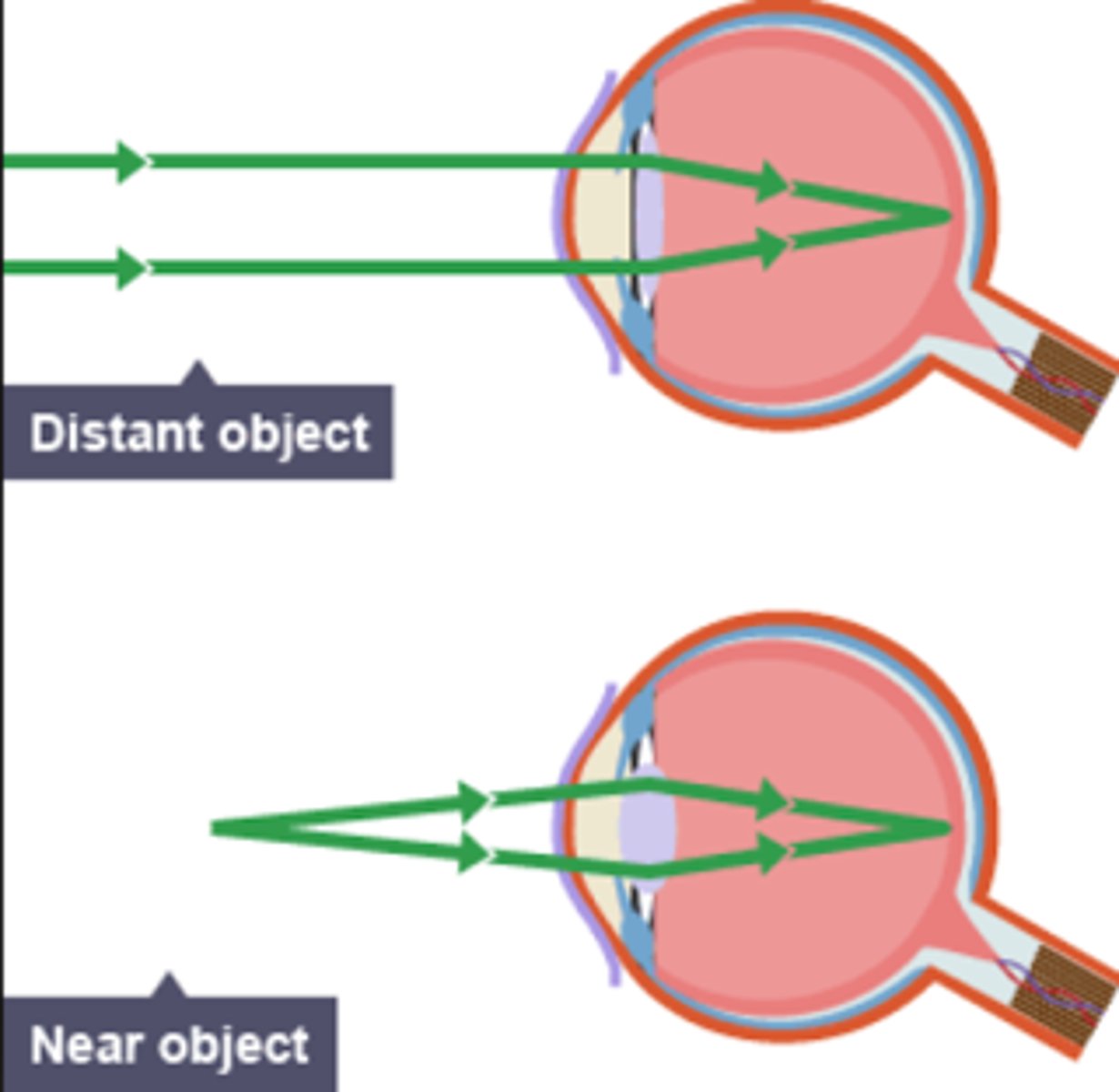
accommodation to view near objects
suspensory ligaments slacken
Ciliary muscle contracts
function of rods
More conc at edge
Detects low intensity
B&w kmage
function of cones
more conc at fovea
Detect high light intensity
Provides detailed colored vision
3 types of cones
Hormones
a chemical substance, produced by a gland and carried by the blood, which alters the activity of one or more specific target organs
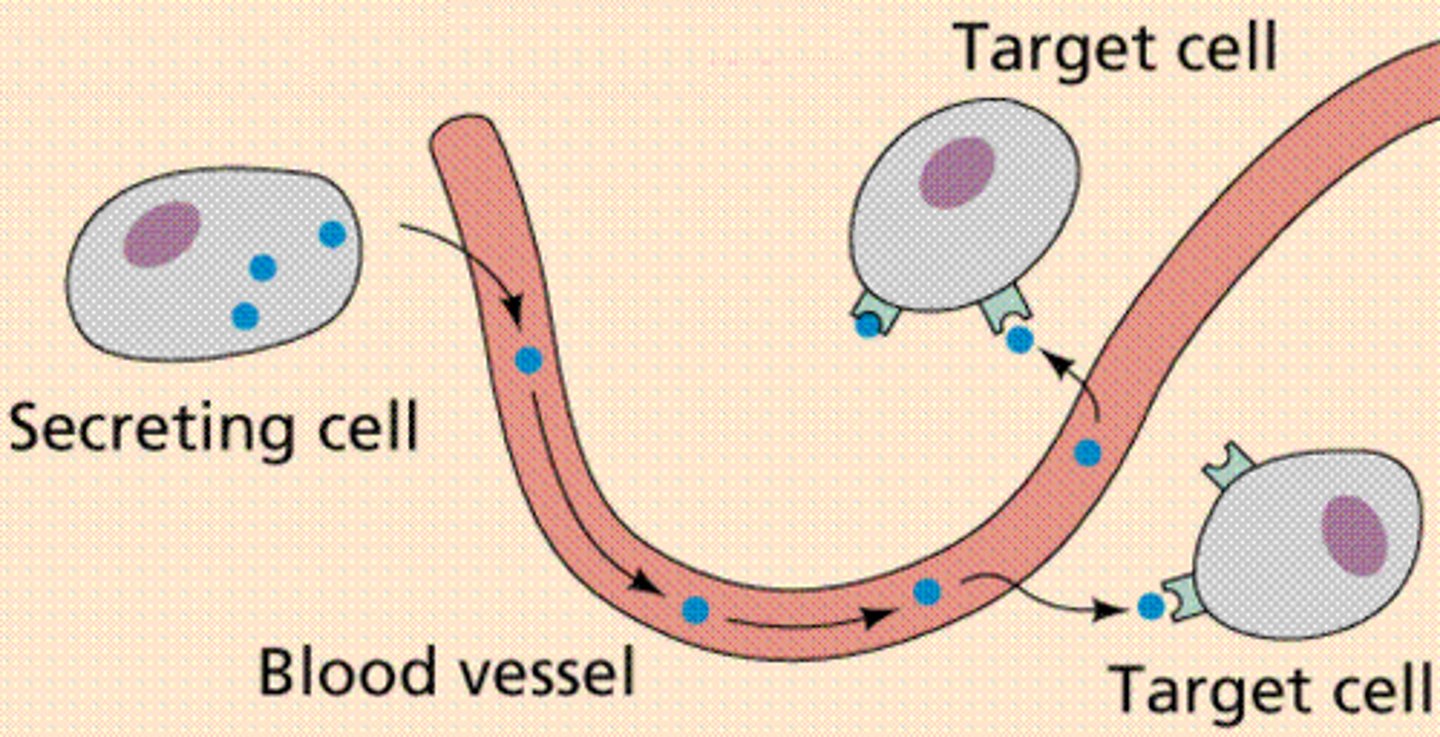
endocrine glands and secretion
adrenal glands- adrenaline
pancreas-insulin
testes-testosterone
ovaries-oestrogen
adrenaline
the hormone secreted in 'fight or flight' situations and its effects, limited to increased breathing and pulse rate and widened pupils, produced by the adrenal gland above the kidney

role of the hormone adrenaline in the chemical control of metabolic activity
increasing the blood glucose concentration and pulse rate
nervous and hormonal control systems in terms of speed and longevity of action
Is slow and long lasting
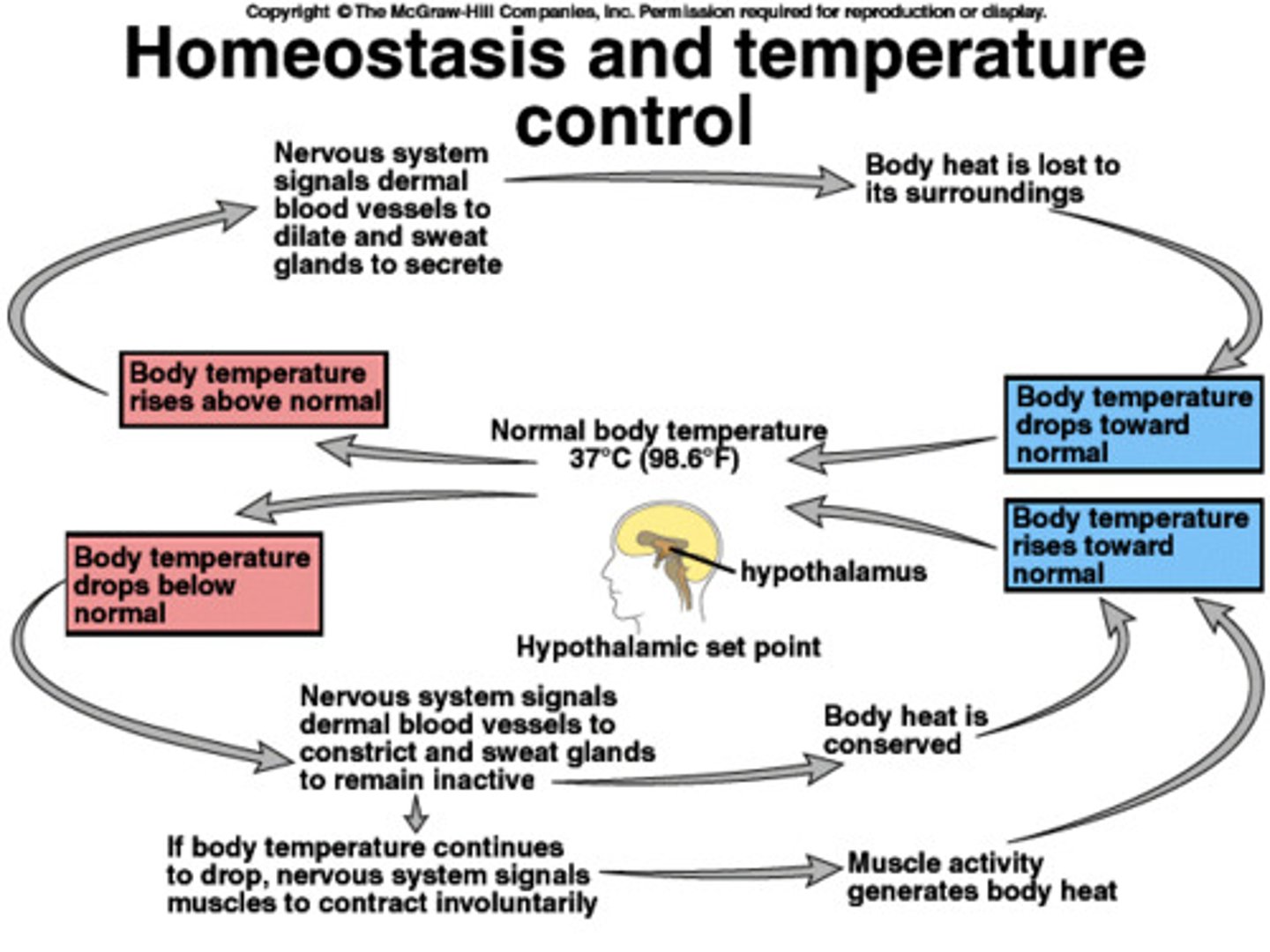
homeostasis
the maintenance of a constant internal environment by the control of internal conditions within set limits
Constant body temp
Constant metabolic rate
For optimum temperature for enzymatic activity
Avoid denature of enzymes by higher temperature above optimum
Higher temperature denature of other protein molecules such as carrier protein
High temp
Skin receptors detect
Sends electric impulses thru sensory neurone
to relay neurone in brain
To motor neurone to effector
1 sweat glands - decrease sweat production so no water evaporates
2 hair erector muscle
Contracts
Hair erects
Allowing better insulation
3 skin arteriole
Arteriole constricts
Shunt vessel dilates
Decreasing blood supply to capillaries near skin to allow less heat loss by radiation
High Blood glucose
Change is detected by pancreas
Pancreas secretes insulin
Chemical message in blood
To liver, insulin stimulates to breakdown glucose to glycogen
Phototropism
To reach light for more absorption
Reach Co2 for more photosynthesis
Reach O2 for more photosynthesis
Flower accessible to pollinators
Gravitropism
To absorb water n minerals from soil
Anchor plant in soil
Shoot light
Auxin
accumulates more in shaded side
Causes cells there to absorb more water by osmosis
More cell elongation and growth
Shoot grows and bends towards the light
Positive phototropism
Root gravity
Auxin accumulates more at lower side
Cells there absorb less water by osmosis
Less cell elongation and growth
Root grows towards gravity
Positive gravitropism