W2 - Blood pressure
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
blood pressure
differences in BP drive blood flow
the heart generates pressure in the arteries
blood flows from high pressure (arteries) to low pressure (veins)
blood is opposed by resistance
BP ↓ as it overcomes resistance to drive blood flow
BP is pulmonary circulation (↓P) is much lower than in the systemic circulation (↑P)
Arterial blood pressure
BP in elastic arteries is pulsatile due to the action of the heart
gives rise to two diff. pressures in the arteries
systolic pressure:
peak pressure in the large arteries when ventricles contract
normal range 95-140 mmHG (avg. 120 mmHg)
diastolic pressure:
lower presser in the arteries due to ventricular relaxation
normal range 60=80mmHg (avg, 80 mmHg)
Pulse pressure
throbbing sensation associated with a “pulse”
waker as move away from the heart
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
120mmHg = 80mmHg = 40 mmHg
Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
average pressure in arteries over cardiac cycle
a better indication of perfusion of tissue
average between systole and diastole
MAP = diastolic + (1/3 x pulse pressure)
MAP = 80mmHg + (1/3 × 40) = 93mmHg
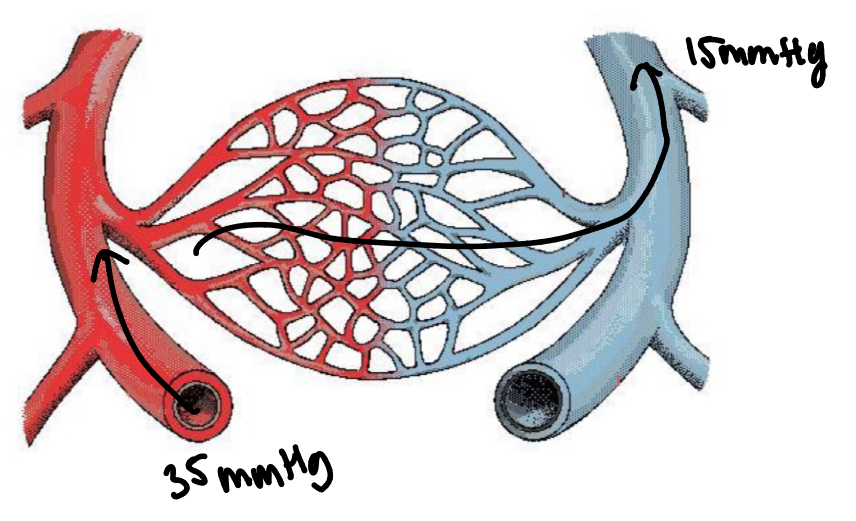
Capillary BP
changes as move through the capillary bed
35mmHg at arterial end
15mmHg at the venous end
low pressure is required to prevent damages of thin-walled delicate capillaries
venous BP
relatively constant, doesn’t change significantly with cardiac cycle
pressure in venules/veins - 15mmHg
pressure in vena cava = approaching 0mmHg
small pressure gradient
how does blood return to the heart
muscular pump (skeletal msucle)
respiratory pump (pressure changes in thorax and abdomen)
valves to prevent backflow