HSCI 100 Immune system
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Infectious agents
Microbes: microscopic organisms such as bacteria and viruses that can cause disease
Pathogens: microscopic organisms + fungus, parasites and prions(misfolded proteins)
Infection: when pathogen colonizes a tissue that can support its
growth
A pathogen is contagious if it can spread
the 3 lines of immune defense
1. Non-specific physical and chemical barriers
2. Non-specific inflammatory response and
proteins
3. A specific and adaptive or learned response
from the T and B cells
Innate
first 2 lines of defense
No memory (does not “learn”)
Non-specific
Fast
Adaptive/Acquired
3rd line of defense
Memory (learns)
Primed
Specific
Slow (days to weeks)
1st line of defense
physical and chemical barriers:
tears, skin, saliva, large intestine, respiratory tract, stomach and bladder.
2nd line of defense
internal defenses
Inflammation
Cellular phagocytosis
Natural killer cells
Complement system
Organs of the immune system
Lymphatic organs
Primary– Red bone marrow, Thymus gland
Secondary– Lymph nodes, spleen, Peyer’s patches, tonsils, and appendix
Red bone marrow
– Blood cell production
– Some white blood cells mature there
– More bones in children have red marrow and it
decreases as we age
Thymus gland
located in chest cavity behind sternum
Largest in children, shrinks as we age
Immature T cells move from the bone marrow to the thymus where they mature and likely stay
→Only T cells that recognize ‘non-self’ antigens will become active. Self-recognizing T cells are eliminated
Lymph nodes
oval shaped structures found along the lymphatic vessels filled with B cells, T cells and macrophages
Spleen
In the upper left region of the abdominal cavity
– Filled with white pulp that contains B and T lymphocytes and red pulp which is invovled in recycling dead red blood cells
Peyer's patches
clusters of lymphoid tissue in the small intestine monitoring intestinal bacteria
Appendix
small finger like projection near start of large intestine. Vestigial organ that has lymphoid tissue role early in life, but becomes non-essential
The second line of defense:
phagocytic white blood cells
Neutrophils and macrophages both leave circulation and move into
tissue
Extravasation/diapedesis (leukocytes pass through the walls of blood vessels into surrounding tissues)
The second line of defense: inflammatory response
4 symptoms of inflammation: redness, heat, swelling, and pain
-mast cells and basophils releases compounds like histamine that trigger inflammation and allergic reactions.
-pus is mostly dead neutrophils
if neutrophils can’t fully control the damage, cytokines
(secreted by lymphatic cells)
promote more white blood cells in that area
third line of defense:
B and T cells adaptive and specifi
attacks when 1st and 2nd defense fails
Relies on antigen recognition
• Many B and T cells are generated in response to existing antigens
• Attacks cancer cells
B cells
matures in the bone marrow, and recognize antigens directly on pathogens (antibody-mediated immunity) and produce antibodies to fight infections
T cells
produced in the bone marrow, matures in the thymus and respond directly to
antigens presented by other cells (cell-mediated immunity). T cells can either kill infected cells directly or help regulate the immune response.
Antibody-mediated immunity by B cells
the production of antibodies by B cells in response to foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruse
results in clonal expansion
plasma cells are the most activate b cells
other b cells become memory cells which result in long term immunity
plasma cells undergo apoptosis after infection, but memory cells survive
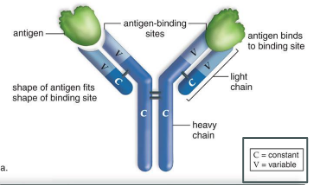
antibody structure
Y-shaped protein assemblies:
2 heavy chains
– 2 light chains
– Joined by disulfide bonds
The end of the two arms are the variable regions that bind to
specific antigens
-by binding to the antigen, it marks it as a foreign entity to be destroyed.
Cell-mediated immunity by T cells
-Each t cell has a receptor called TCR that will recognize an antigen with the help of an antigen-presenting cell(APC)
-The antigen presenting cell(APC) engulfs the antigen and breaks it into small peptides and presents it on its surface. They do this using (MHC) proteins, allowing T cells to recognize and respond to pathogens
-Clonal expansion of T cell prompt helper T cells to recruit B cells and activate cytotoxic T cells (which kill infected cells) and memory T cells(which “remembers” antigens)
-after infection helper T cells and killer T cells undergo apoptosis, but memory T cells survive.
Acquired immunity
-ability to combat infectious diseases and cancer
-long lasting
-depends on clonal selection and production of memory B and T cells
-Immunization can happen naturally or artifically (through vaccines)
Clonal selection: the four predictions
process in the immune system where specific B or T lymphocytes are activated by antigens
1) Each lymphocyte has a unique receptor
2) The receptor must bind to an antigen for activation
3) Activated lymphocytes create clones
4) Clones produce identical receptors and antibodies specific to the antigen.
Allergies
Hypersensitivities to harmless substances
-Immediate allergic responses are caused by the IgE antibodies that attach to mast cells and basophils. This causes histamine to be released, causing allergy reactions.
-Delayed allergic responses are initiated by memory T cells
autoimmune disease
when killer T cells or antibodies attack the body’s own cells
Examples: Lupus, diabetes
Immunodeficiency disease
when the immune system is compromised and thus unable to defend the body against disease
Examples:
AIDS:
HIV infects macrophages and helper T cells
SCID:
Severe combined immunodeficiency