Anatomy Part #1
5.0(2)Studied by 134 people
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Last updated 2:19 PM on 3/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
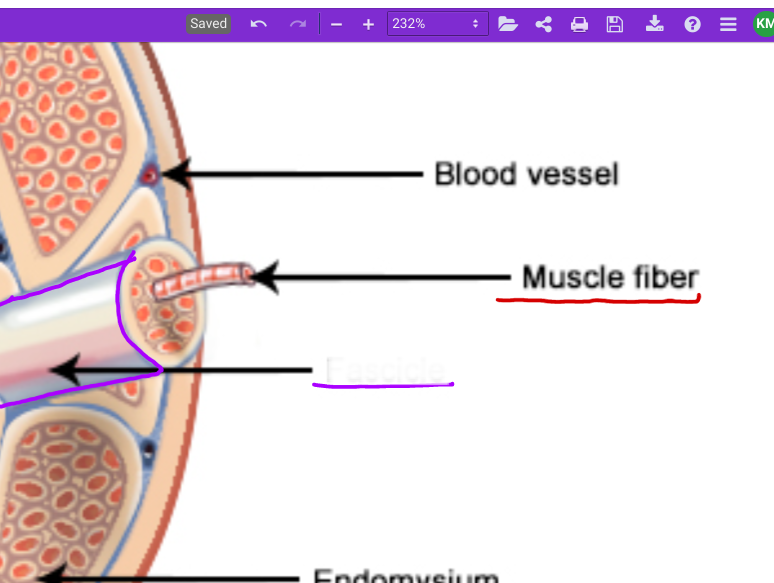
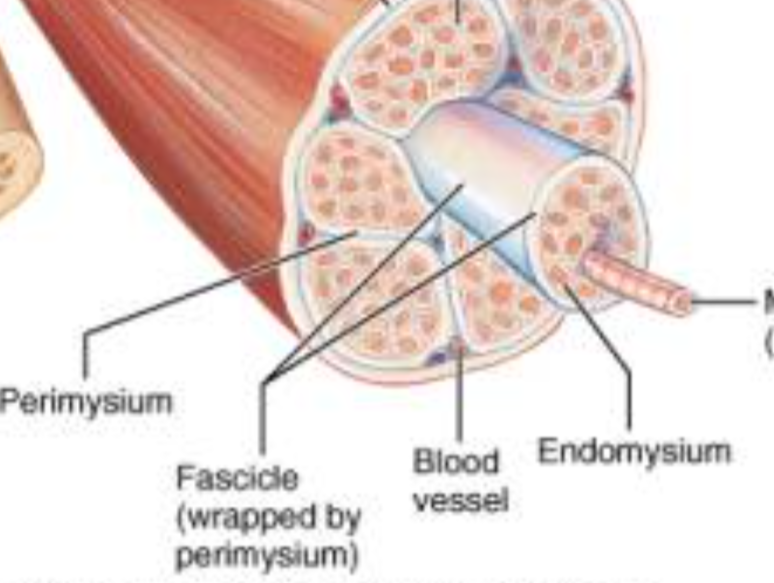
Muscle fiber (red)
elongated multi nucleate cell; has a banded (striated) appearance
2
New cards
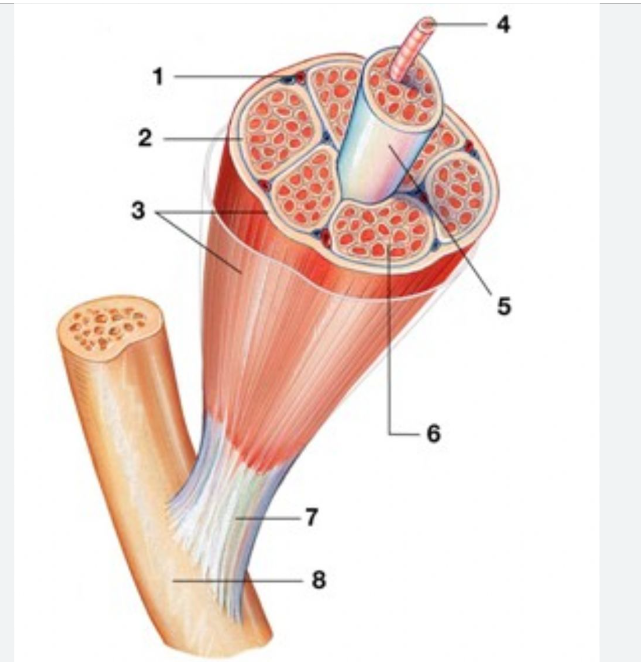
Endomysium (between fibers) #6
Individual muscle fiber is surrounded by a fine sheath of connective tissue consisting of areolar and reticular fibers.
3
New cards
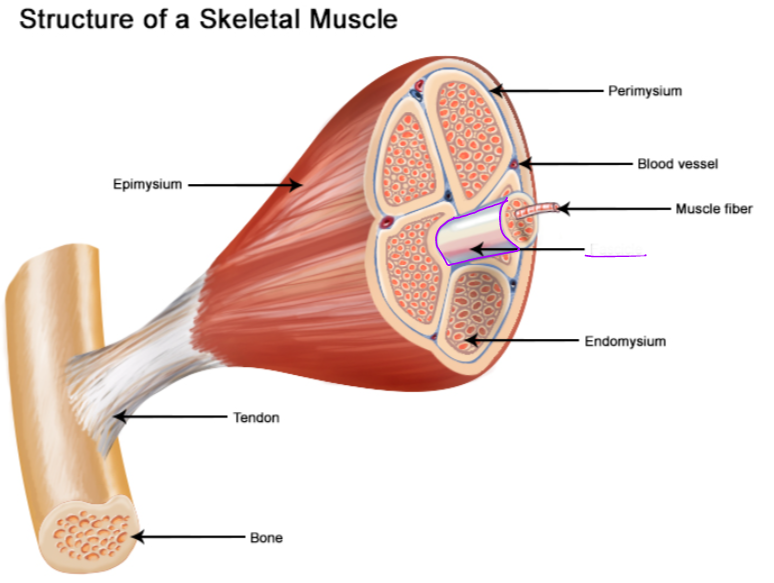
Fascicle (purple)
bundle of muscle cells, segregated from the rest of the muscle by a connective tissue sheath (perimysium)
4
New cards
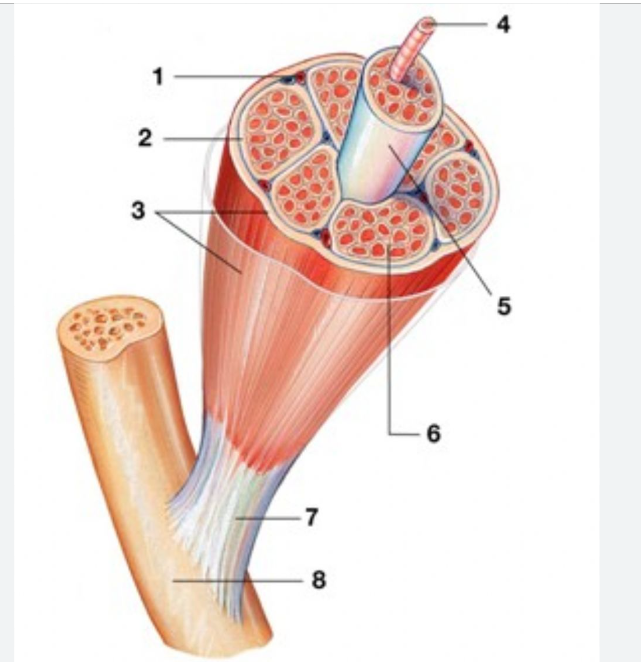
Perimysium #2
Surrounding each fascicle is a layer of fibrous connective tissue
5
New cards
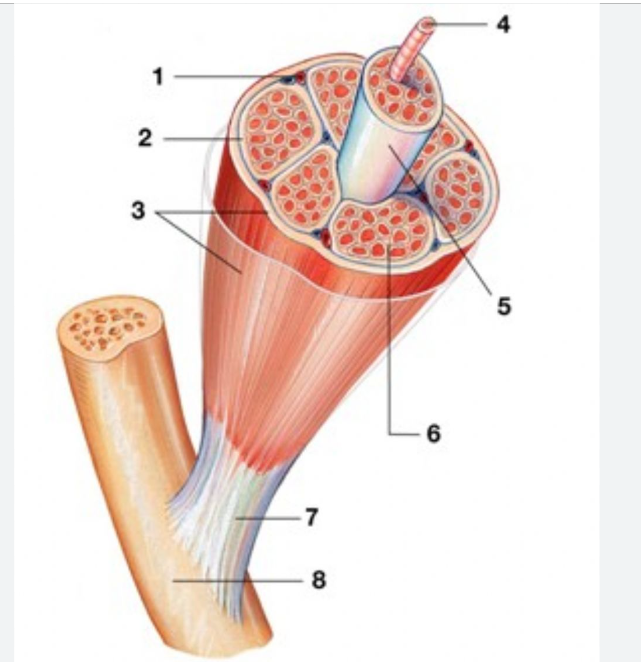
Epimysium #3
An “overcoat“ of dense irregular connective tissue surrounds the whole muscle.
6
New cards
epi-
outside
7
New cards
\-mysium
muscle
8
New cards
peri-
around
9
New cards
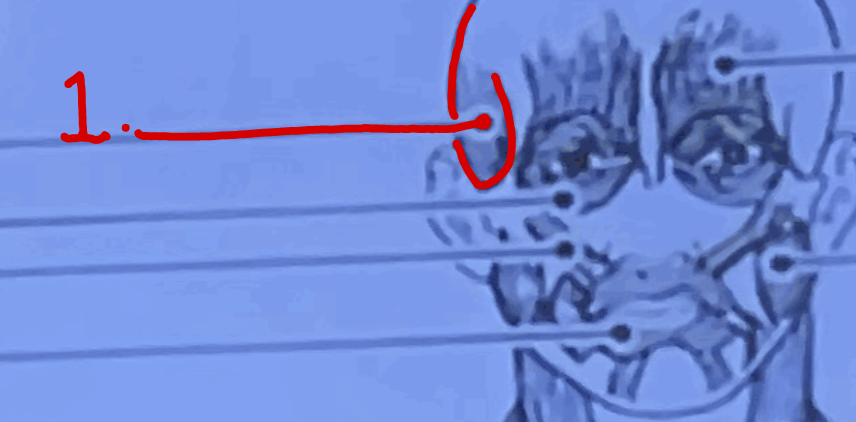

What is this muscle?
Temporalis
10
New cards
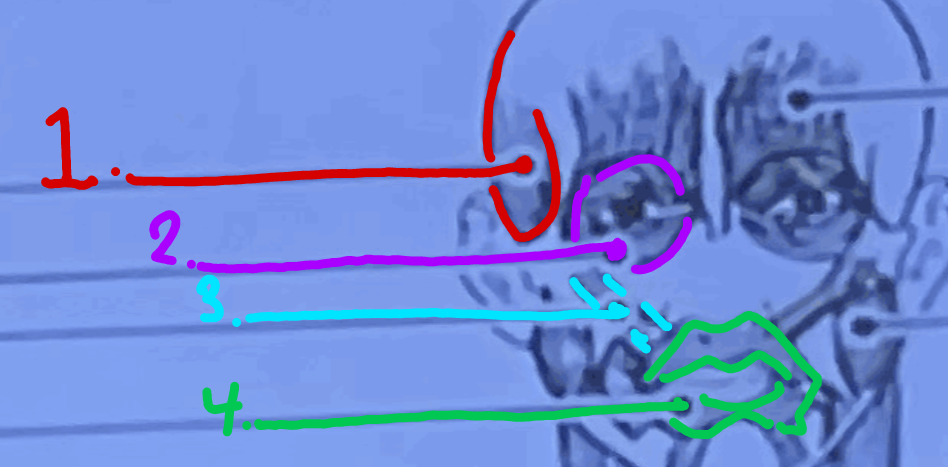
What is purple muscle called?
Orbicularis Oculi
11
New cards
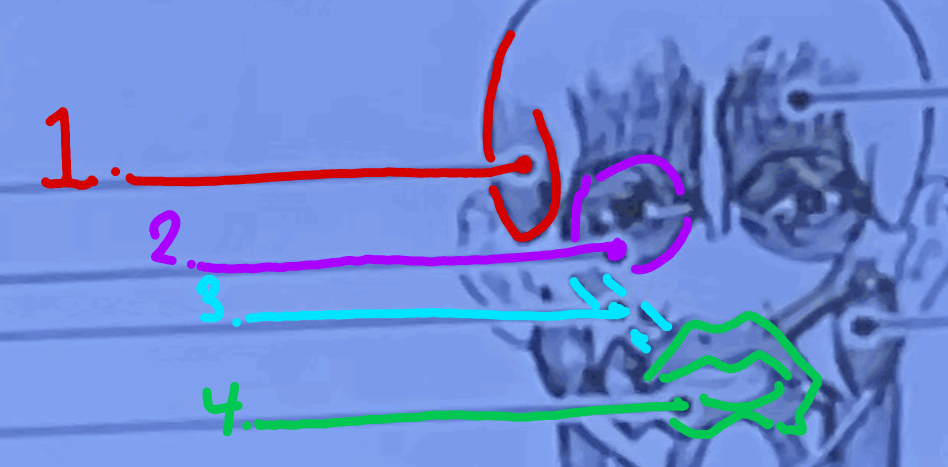
What is the blue muscle called?
Zygomaticus
12
New cards
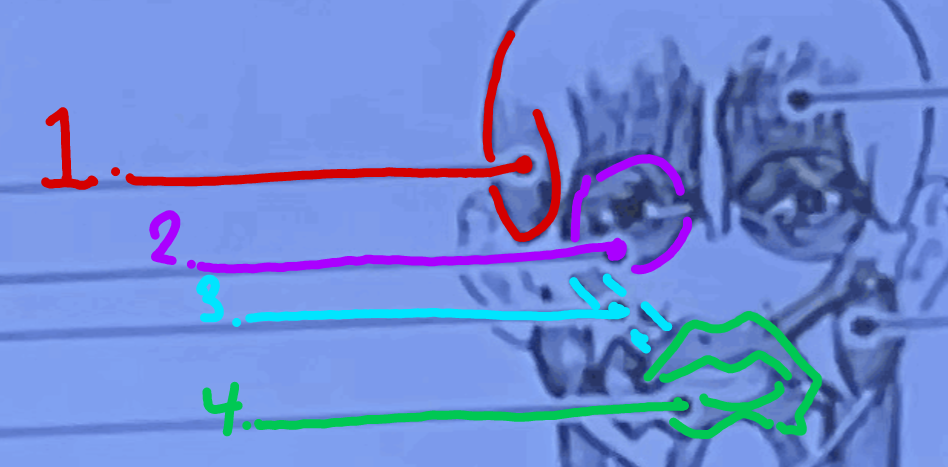
What is the green muscle called?
Orbicularis Oris
13
New cards
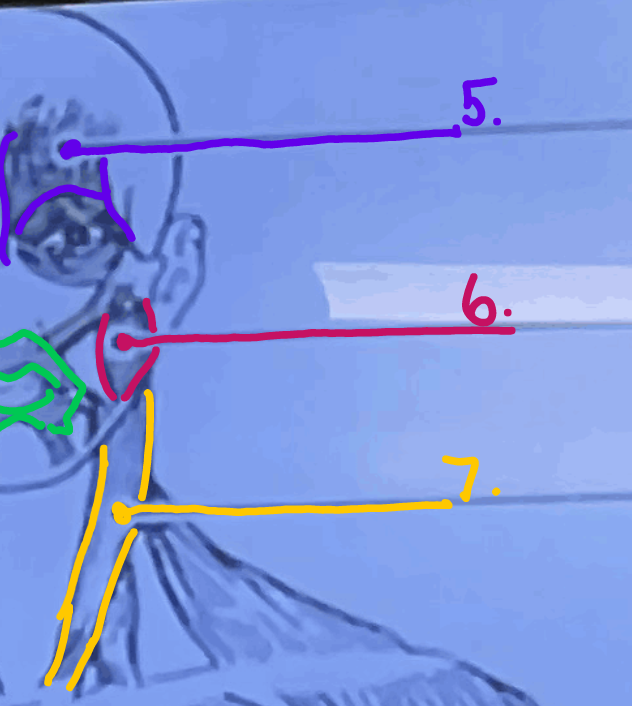
What is #5 muscle called?
Epicranius, frontal belly
14
New cards
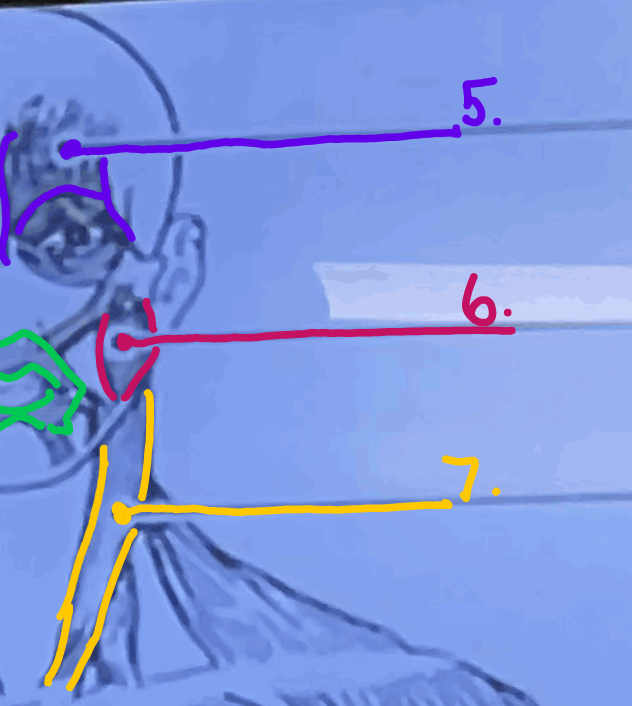
What is #6 muscle called?
Masseter
15
New cards
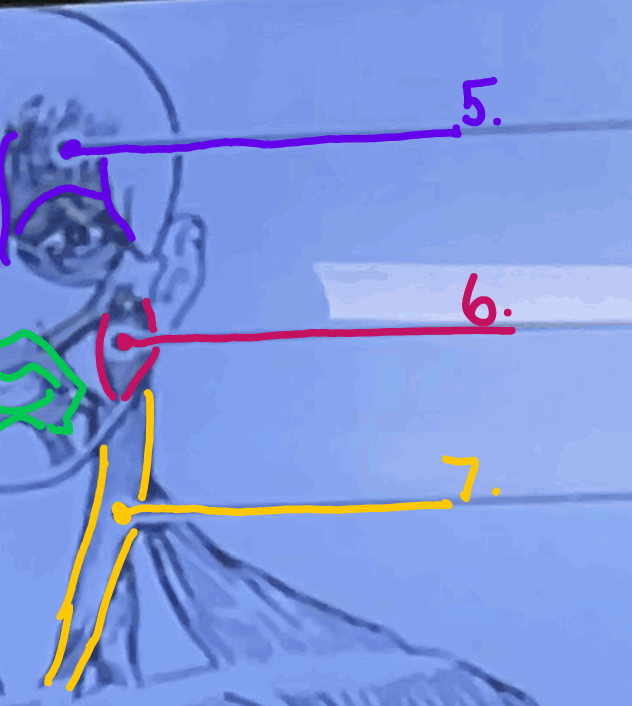
\#7?
Sternocleidomastoid
16
New cards
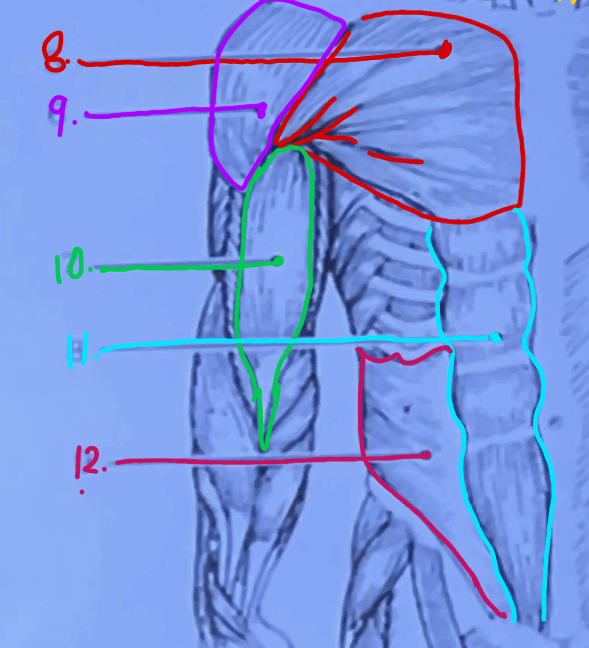
What is #8?
Pectoralis Major
17
New cards
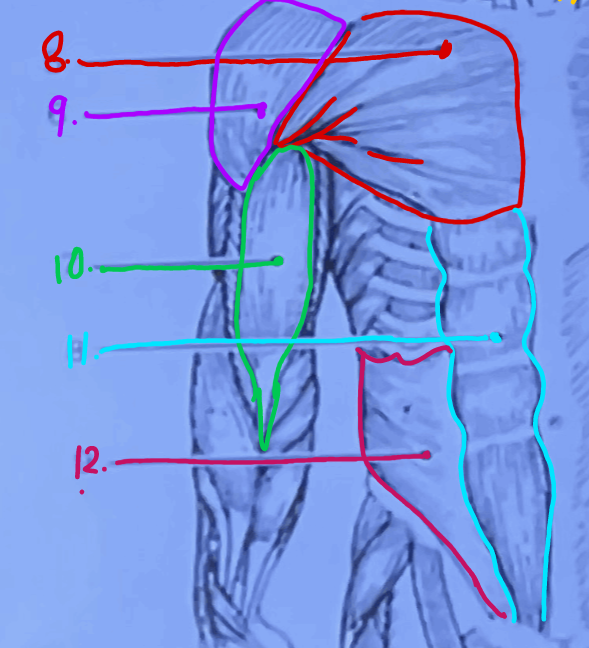
What is #9?
Deltoid
18
New cards
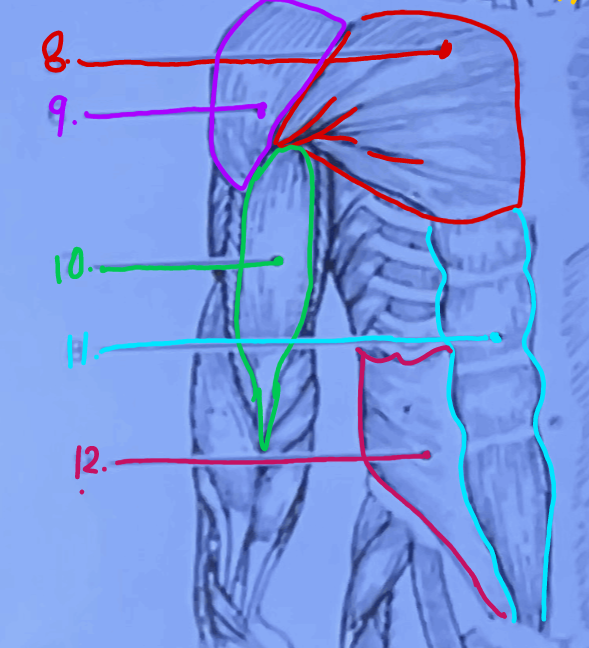
What is #10?
Biceps Brachii
19
New cards
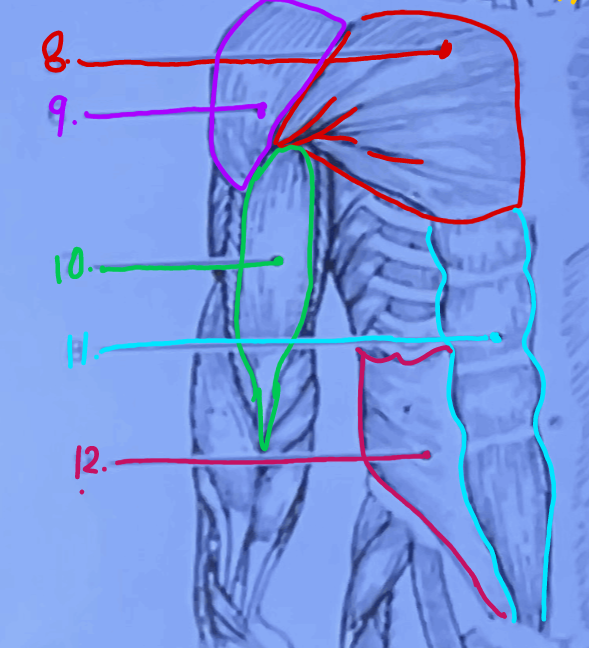
What is #11?
Rectus abdominis
20
New cards
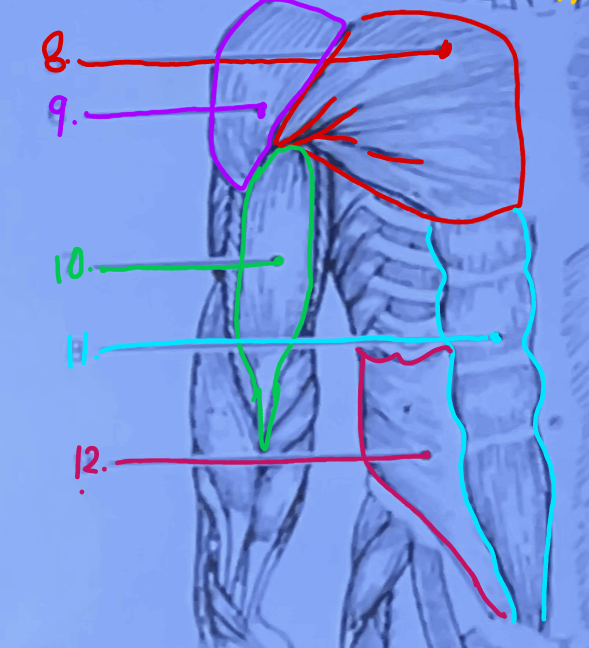
What is #12?
Internal oblique
21
New cards
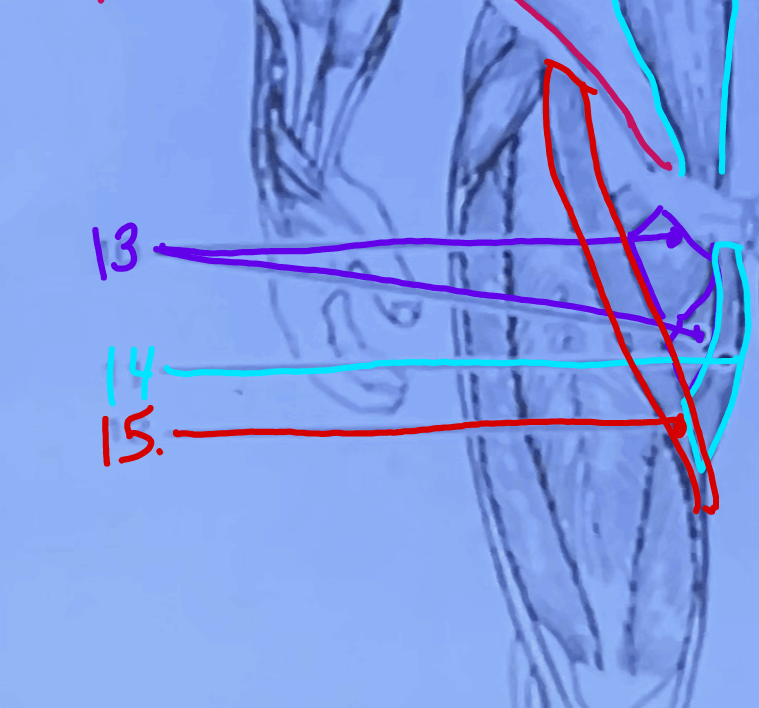
What is #13?
Adductor Longus
22
New cards
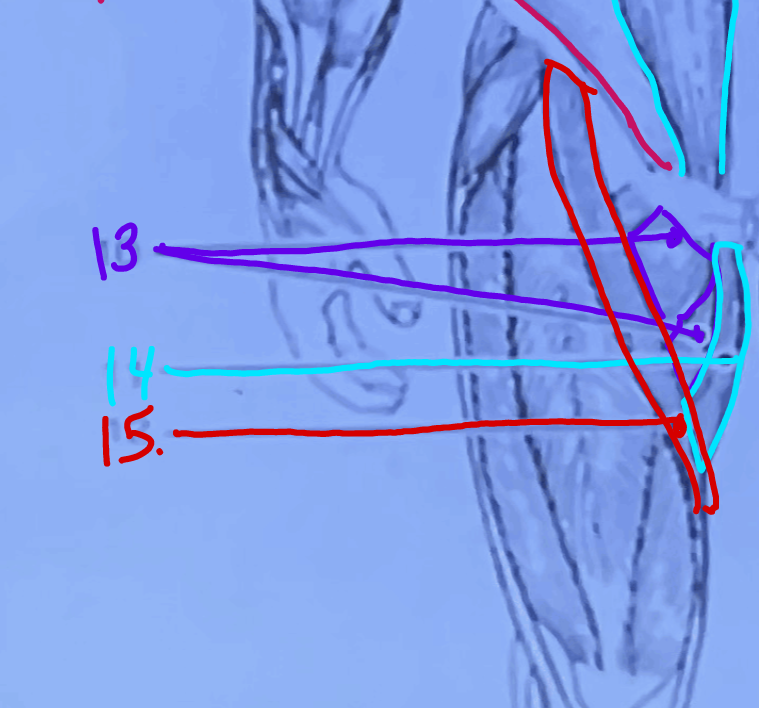
What is #14?
Gracilis
23
New cards
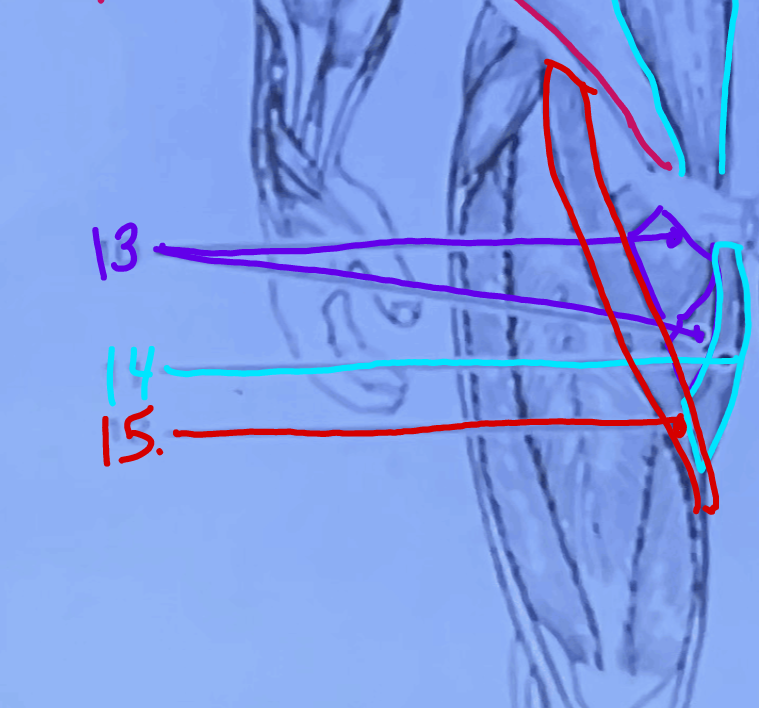
What is #15?
Sartorius
24
New cards
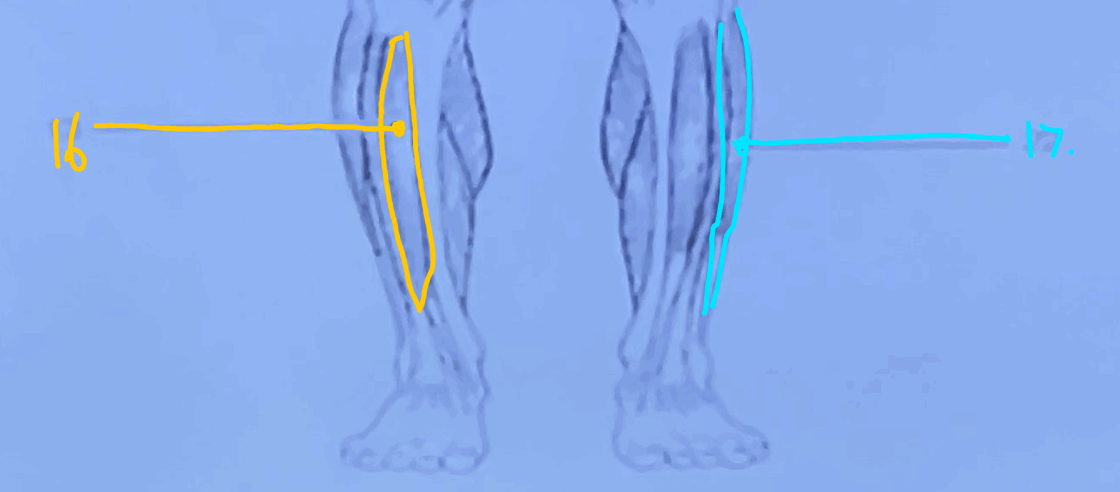
What is #16?
Tiblias Anterior
25
New cards
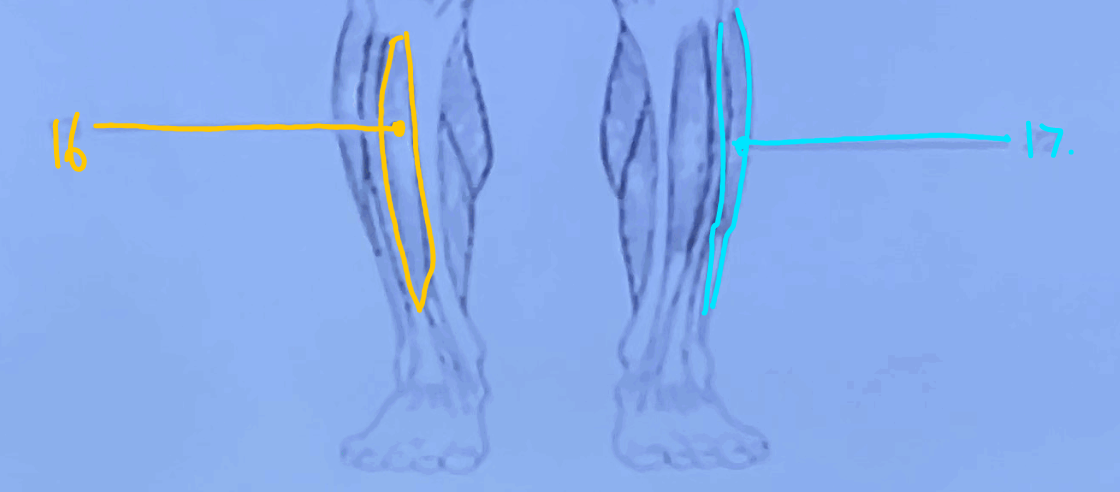
What is #17?
Gastrocnemius
26
New cards
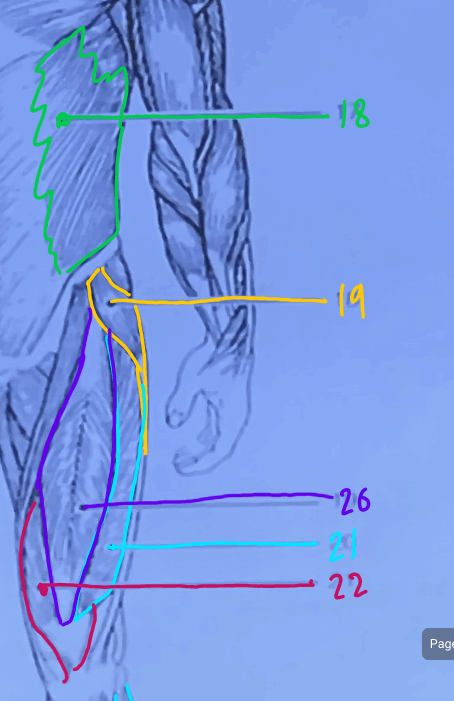
What is #18?
external oblique
27
New cards
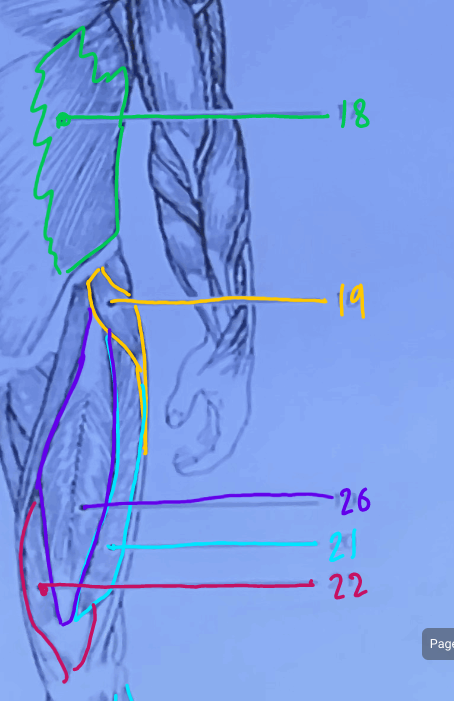
What is #19?
Tensor Fasciae latae
28
New cards
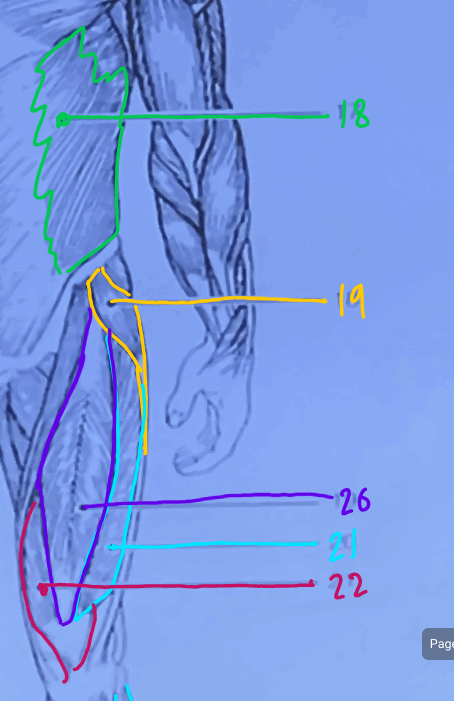
What is #20?
Rectus Femoris
29
New cards
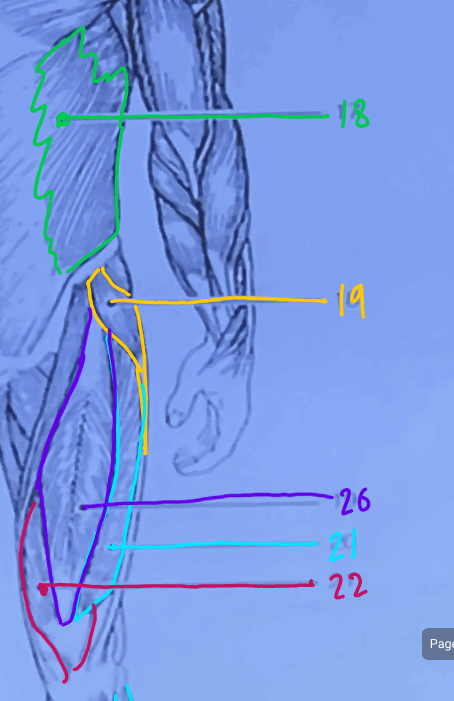
What is #21?
Vastus Lateralis
30
New cards
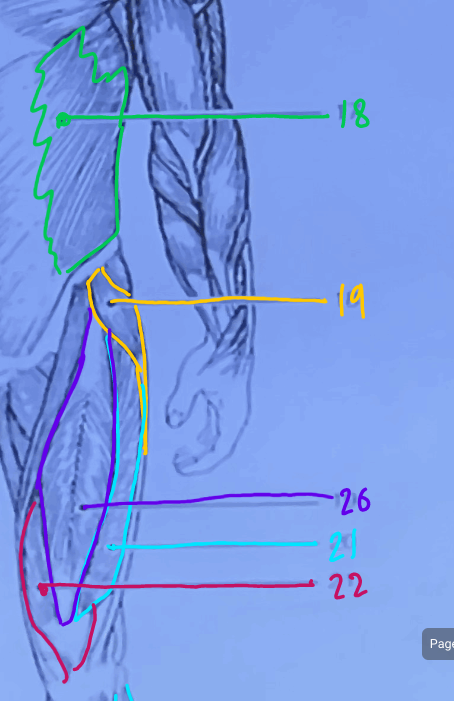
What is #22?
Vastus medialis
31
New cards
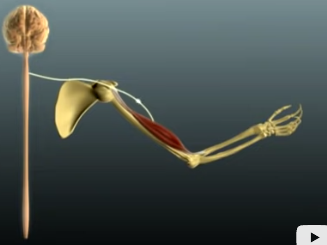
1st Event at the NMJ?
**AP travels the link down the neuron to the axon terminal.**
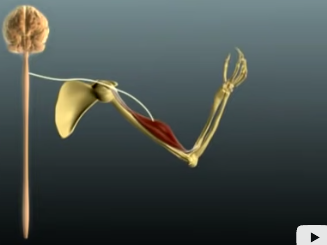
32
New cards
NMJ Step 2:
**Voltage-gated calcium channels open and calcium ions diffuse into the terminal.**
33
New cards
NMJ Step 3:
**Calcium entry causes synaptic vesicles to release acetylcholine via exocytosis**
34
New cards
NMJ Step 4:
**AcH diffuses across the synaptic cleft and vines to the AcH receptors which contain Ligand-gated cation channels**
35
New cards
NMJ Step 5:
**These ligand-gated cation channels open**
36
New cards
NMJ Step 6:
**Sodium ions enter the muscle fiber potassium ions exit the muscle fiber. The greater end of flux causes the membrane potential to become less negative.**
37
New cards
NMJ Step 7:
Once the membrane potential reaches its threshold value an Action potential (AP )propagates against the sarcolemma
38
New cards
Neuromuscular Junction
area where the axon terminal of a motor neuron meets a motor end plate of a muscle fiber
39
New cards
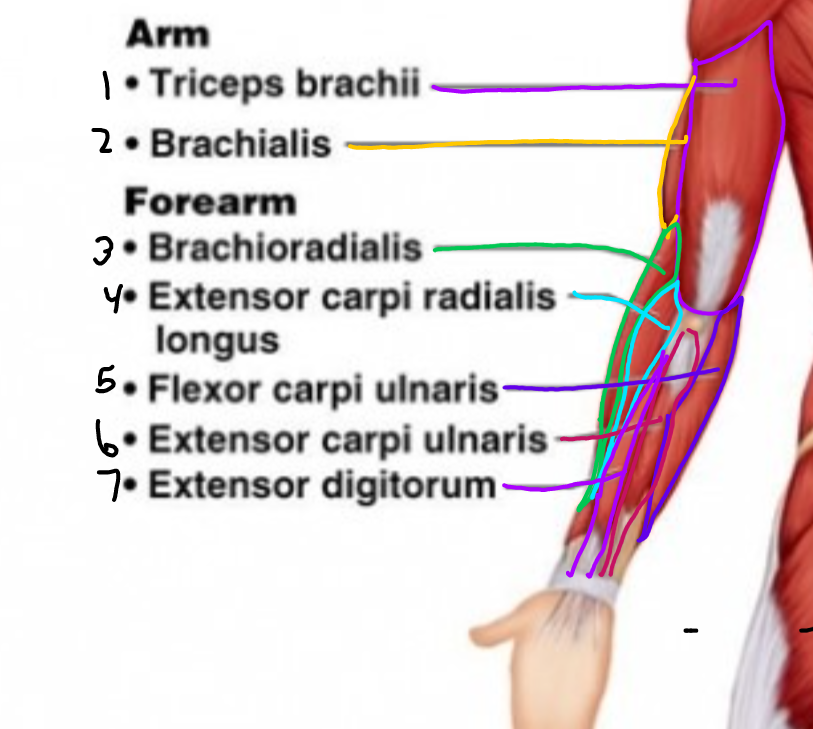
\#1?
Triceps Brachii
40
New cards
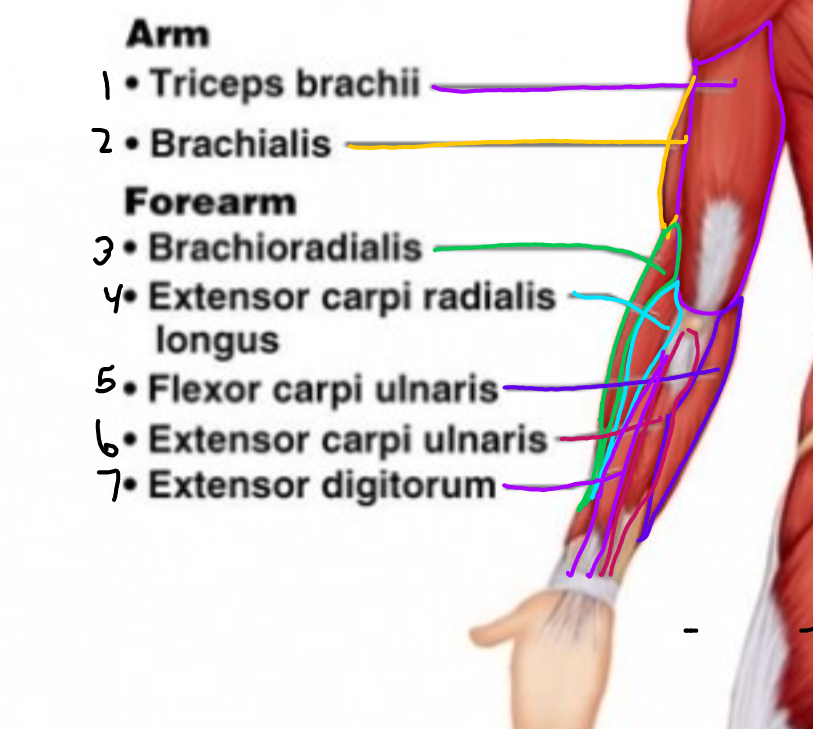
\#2?
Brachialis
41
New cards
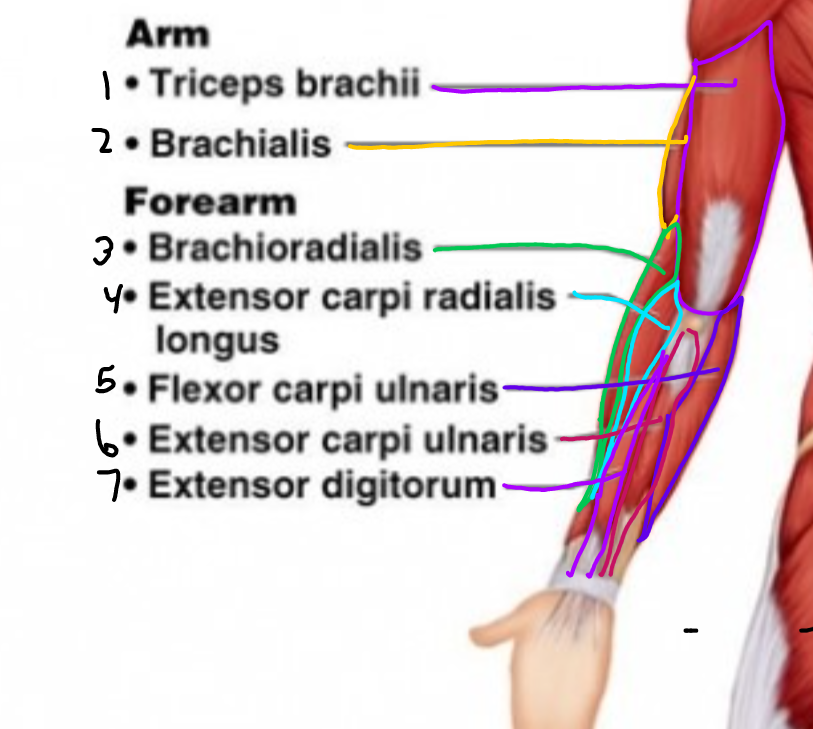
\#3?
Brachioradialis
42
New cards
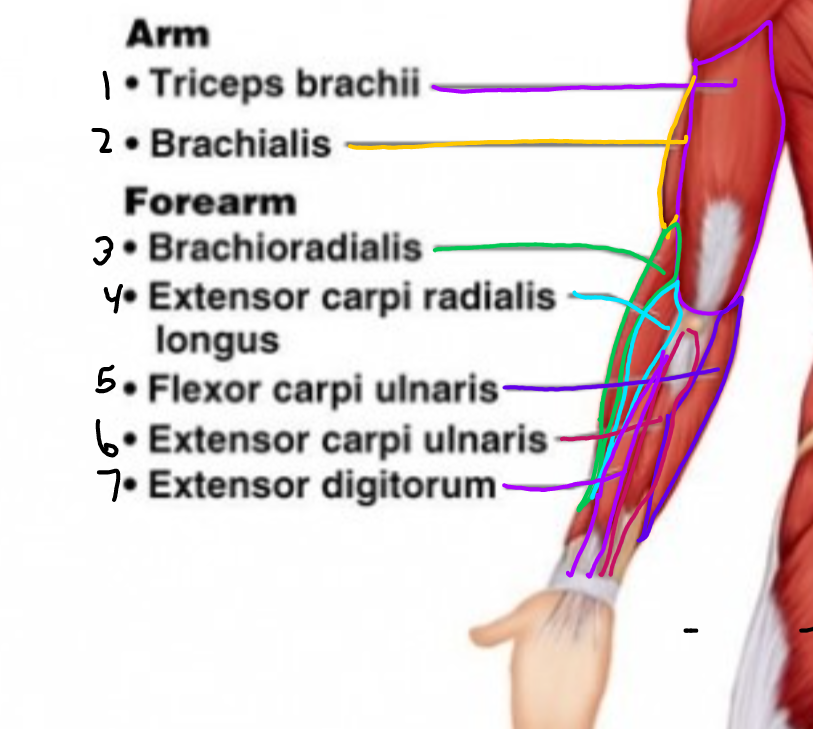
\#4?
Extensor carpi radialis longus
43
New cards
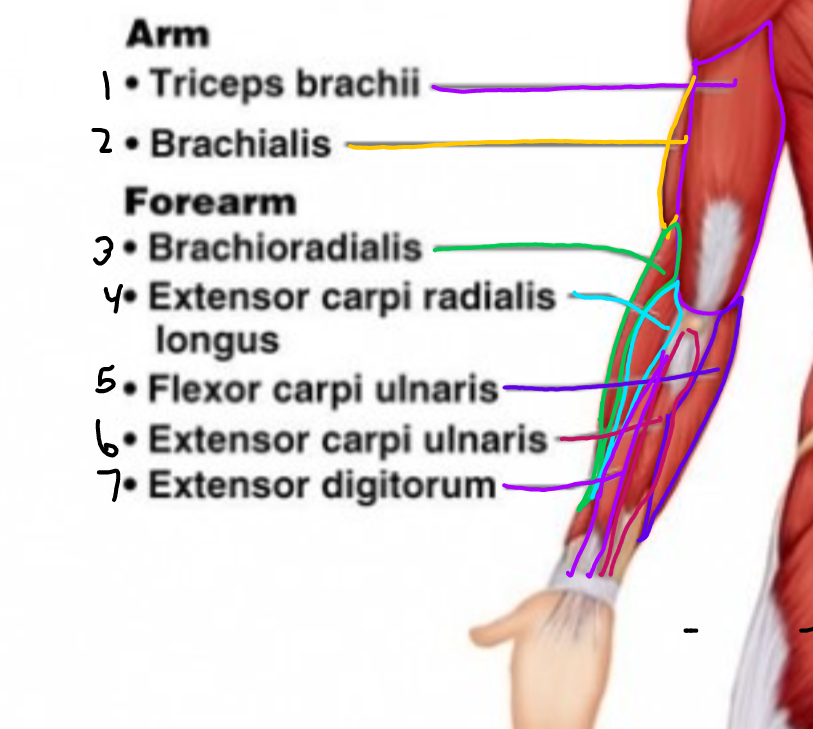
\#5?
Flexor carpi ulnaris
44
New cards
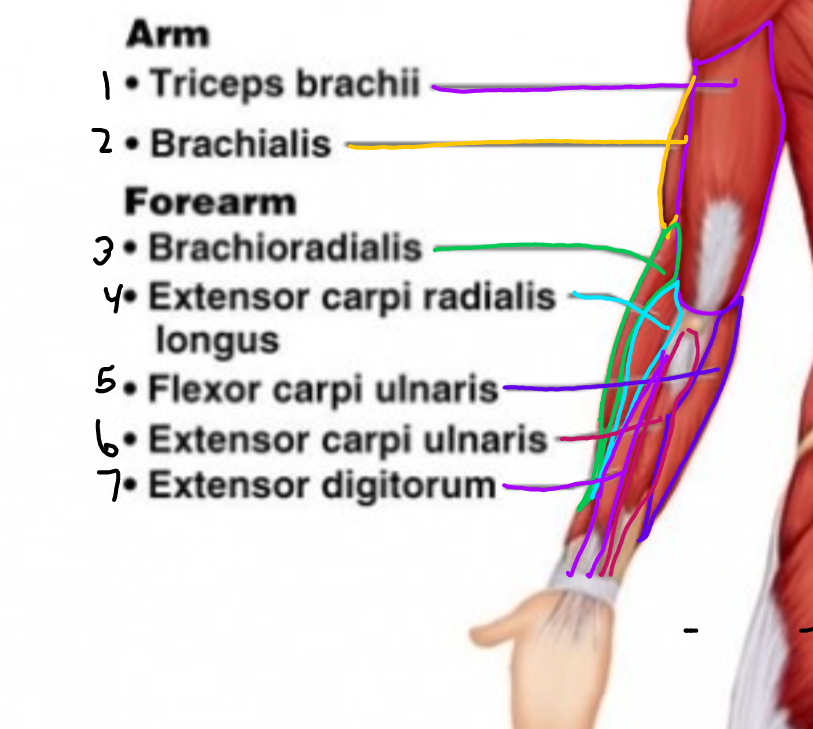
\#6?
Extensor carpi ulnaris
45
New cards
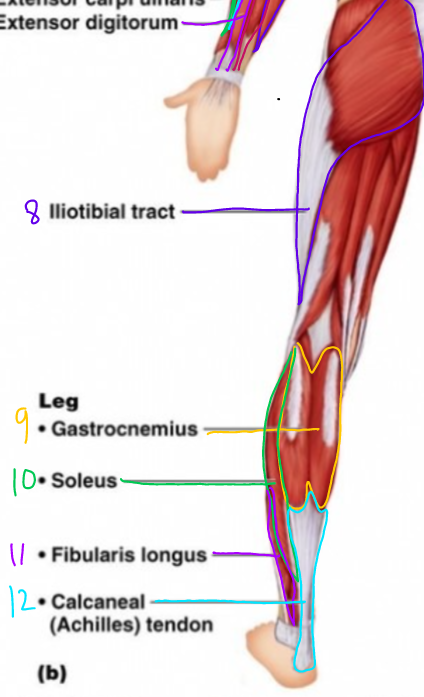
\#7?
Extensor digitorum
46
New cards
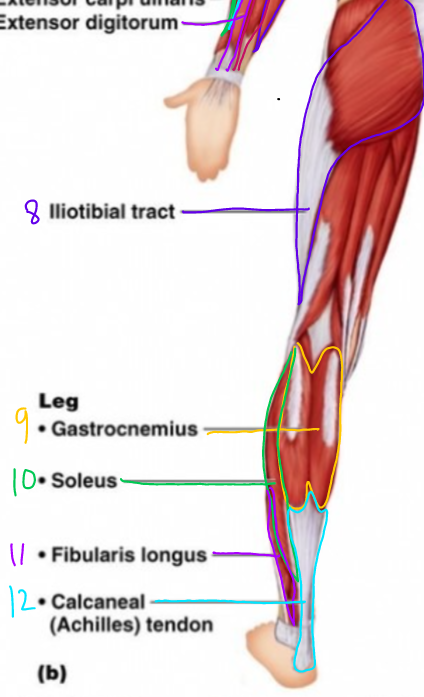
\#8?
Iliotibial tract
47
New cards
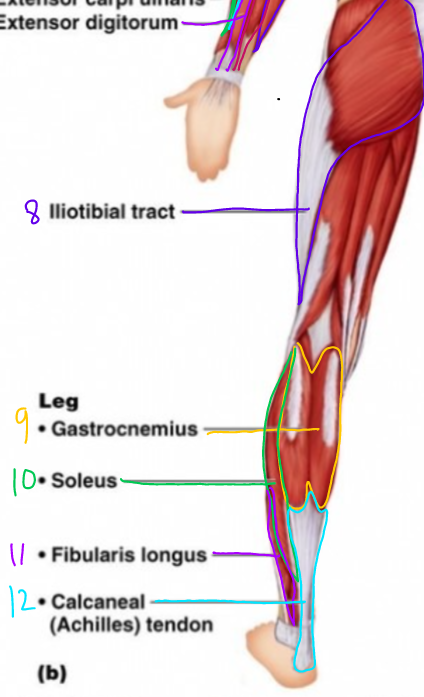
\#9?
Gastrocnemius
48
New cards
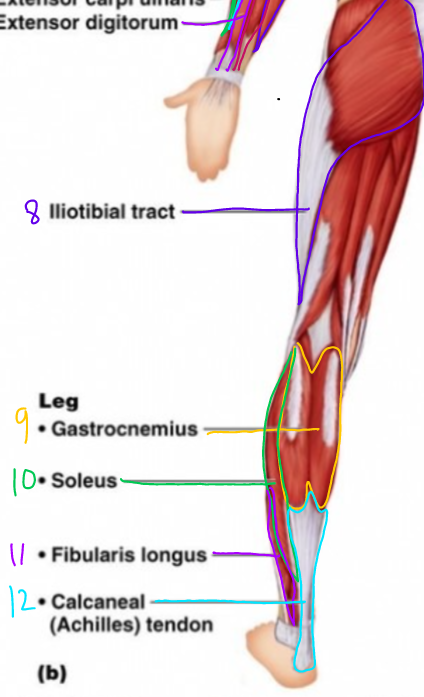
\#10?
Soleus
49
New cards
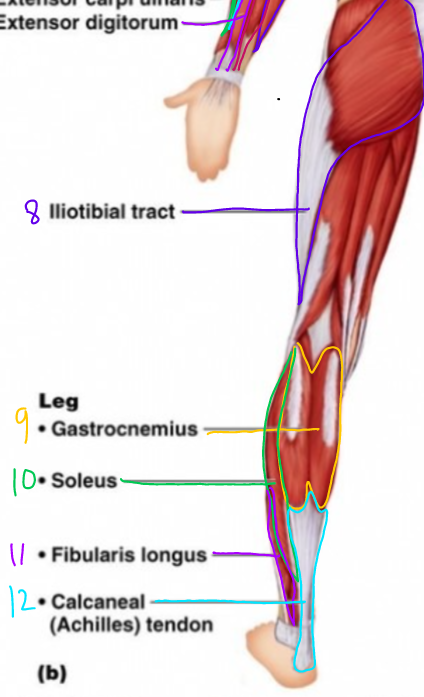
\#11?
Fibularis Longus
50
New cards
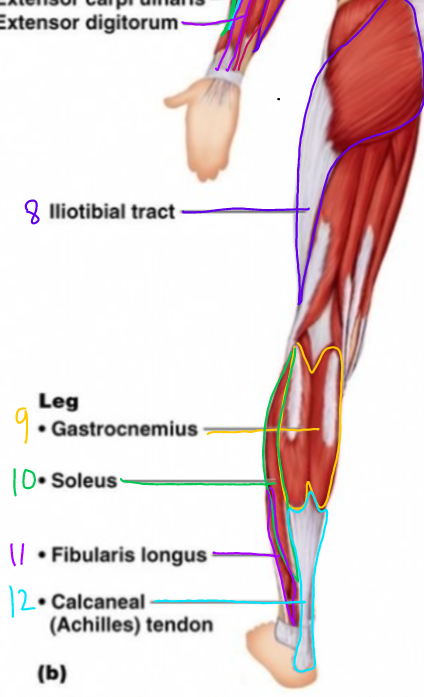
\# 12?
Calcaneal (Achilles Tendon)
51
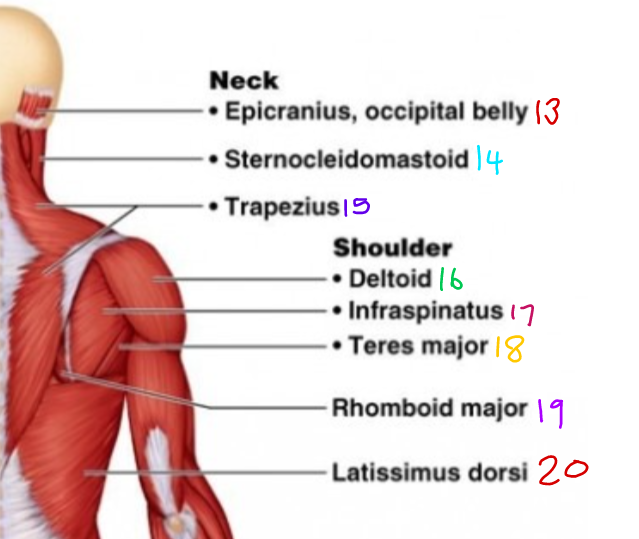
New cards
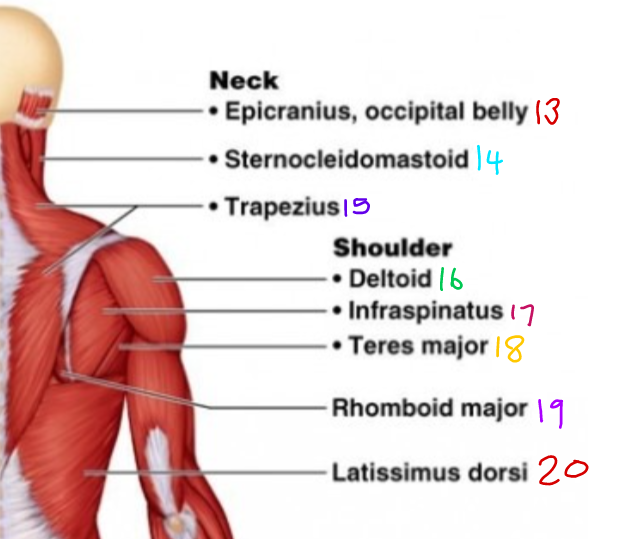
\#13?
Epicranius, occipital belly
52
New cards
\#14?
Sternocleidomastoid
53
New cards
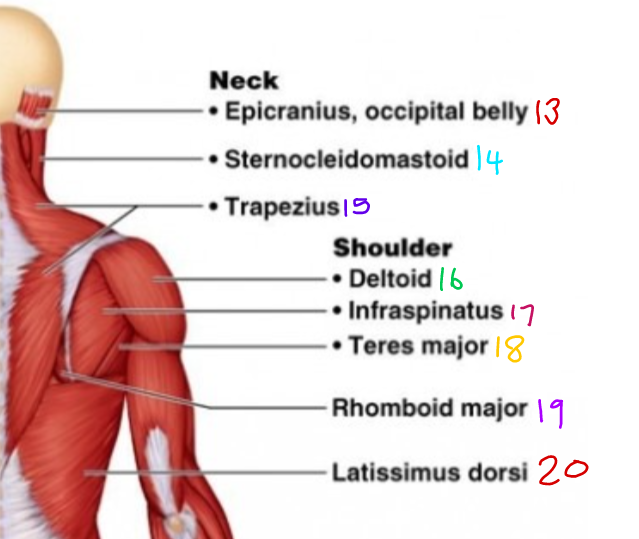
\# 15?
Trapezius
54
New cards
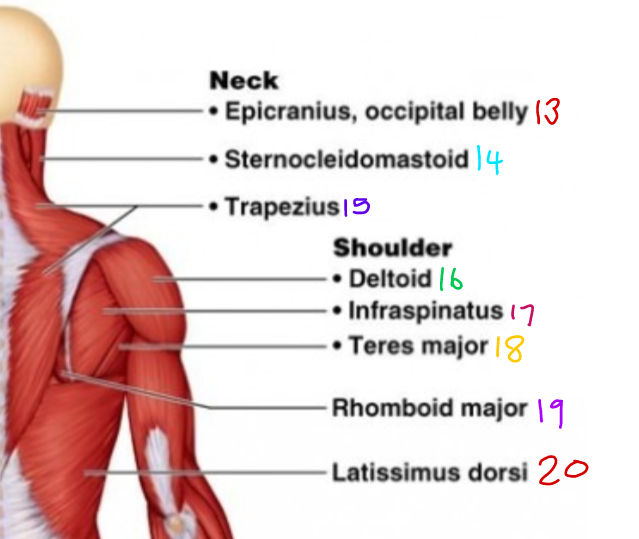
\#16 ?
Deltoid
55
New cards
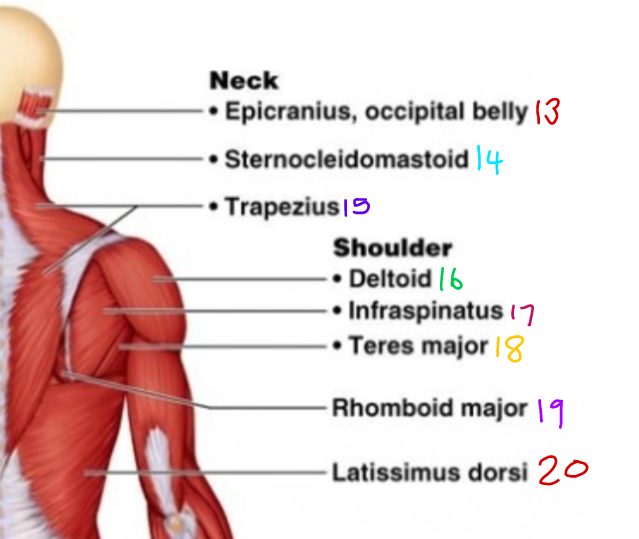
\#17?
Infraspinatus
56
New cards
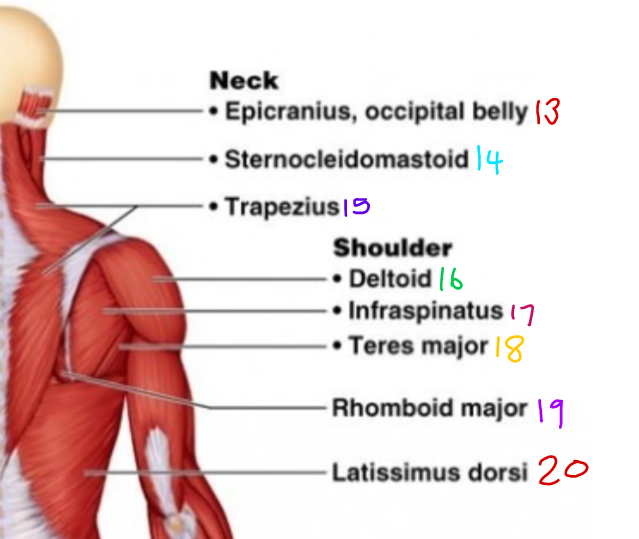
\#18?
Teres Major
57
New cards
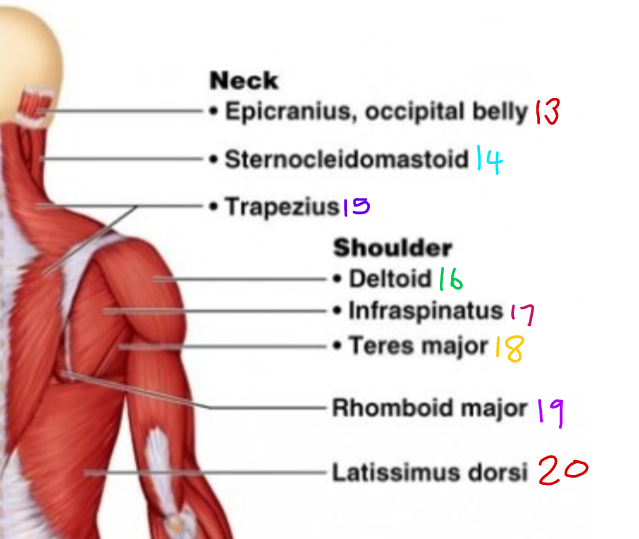
\#19?
Rhomboid Major
58
New cards
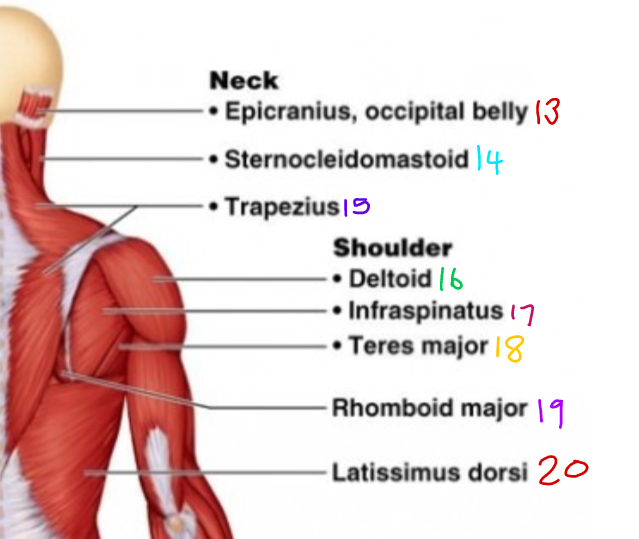
\#20?
Latissimus Dorsi
59
New cards
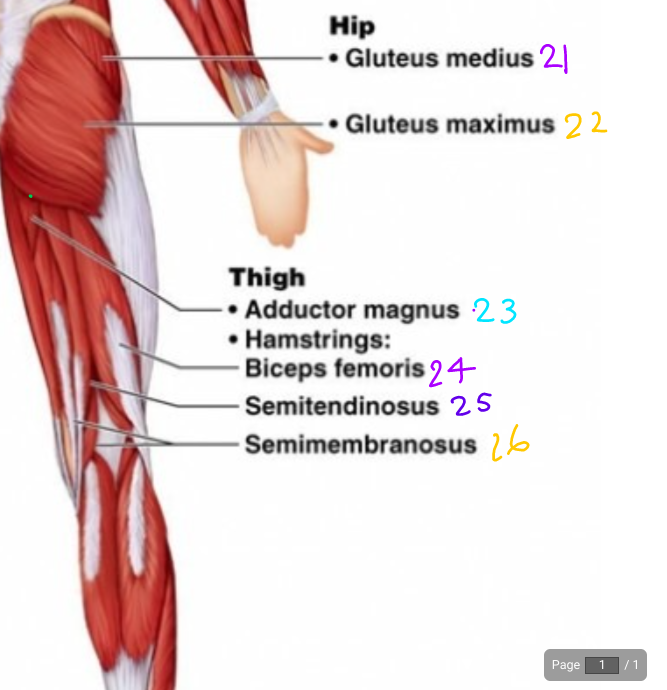
\#21
Gluteus Medius
60
New cards
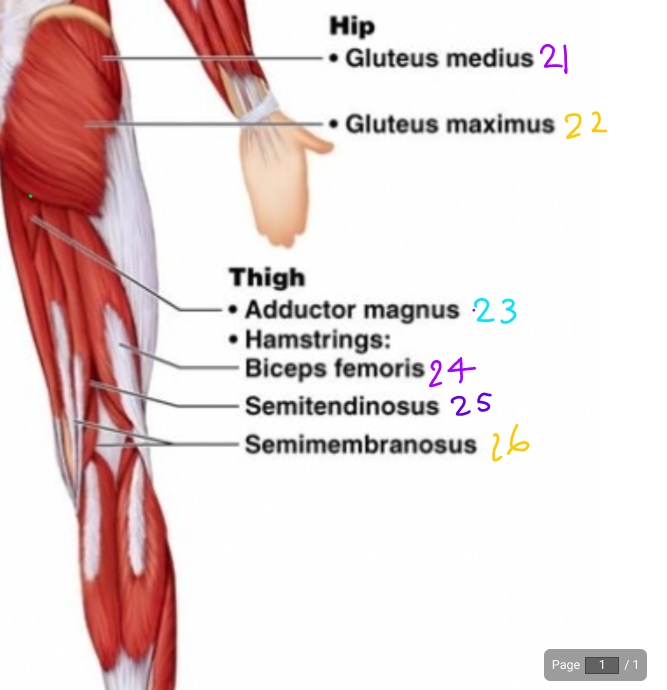
\#22?
Gluteus Maximus
61
New cards
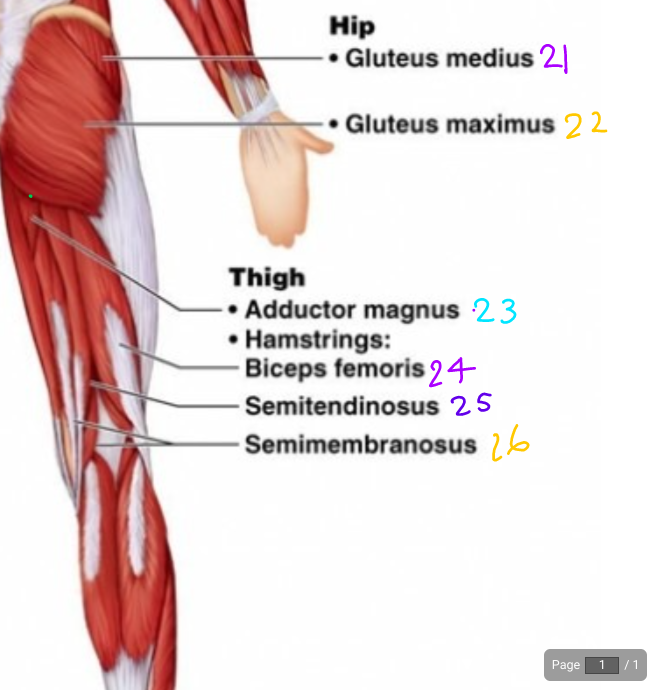
\#23?
Adductor magnus
62
New cards
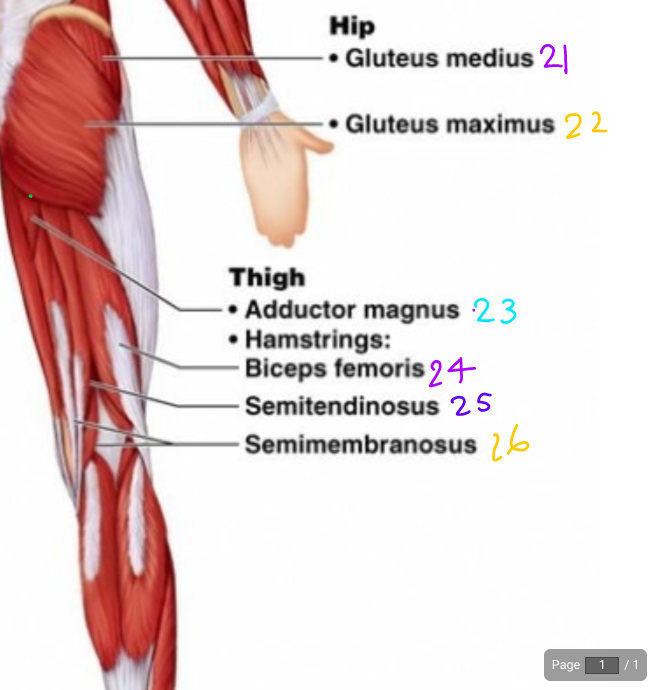
\#24?
Biceps Femoris
63
New cards
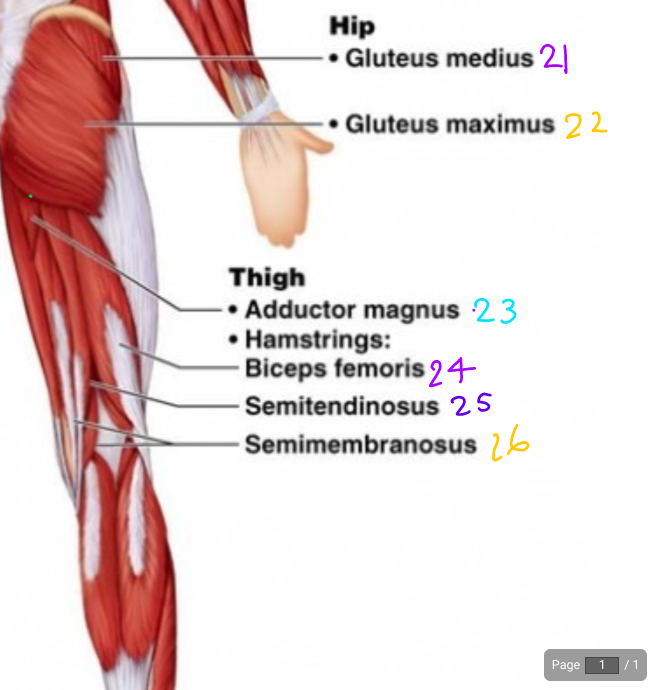
\#25
Semitendinosus
64
New cards
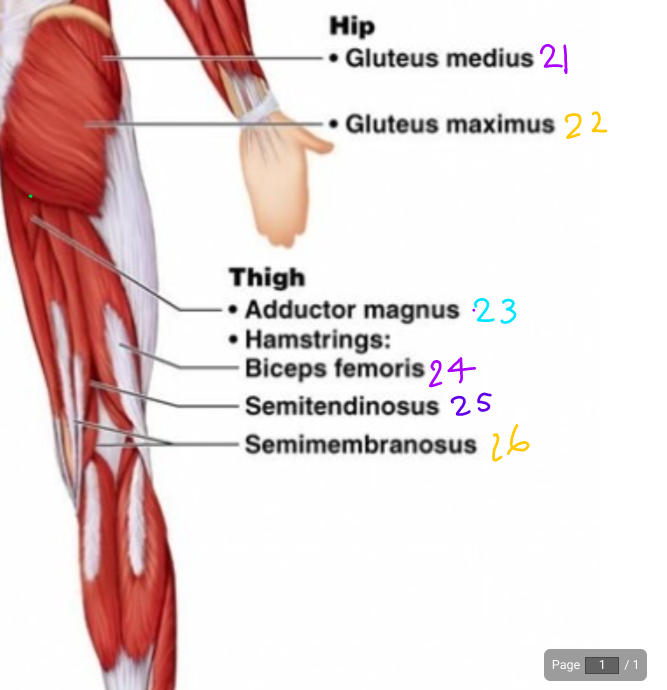
\#26?
Semimembraneous