Vesicle transport
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
On the importance of the vesicle transport system:
-proteins that function on or within the endomembrane system, the plasma membrane, or are secretory proteins are targeted to their respective final destinations via ( )
-phospholipids also move through the cell in ( )
transport vesicles
transport vesicles
moving “cargo” ( ) out of the cell from inside the cell is ( ), occurs though ( ) of vesicles from internal sources with the plasma membrane
proteins and other molecules
exocytosis
fusion
moving “cargo” into the cell from the outside is ( ), occurs through ( ) of vesicles from the plasma membrane
endocytosis
budding
phospholipids and some proteins are transported via transport vesicles, orientation remains ( ), so ( )
conserved- inside in, outside out
topology (organization/arrangement of features on each surface) is conserved
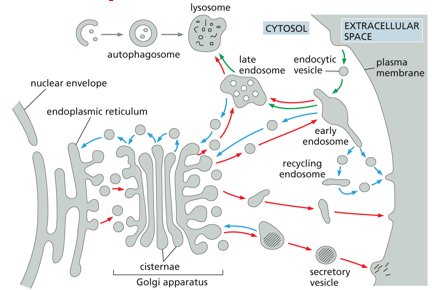
secretory pathway ( )-molecules are transported from ( ), through ( ), to ( ) or via ( ) to ( )
red arrows
ER
Golgi
plasma membrane
endosomes
lysosomes
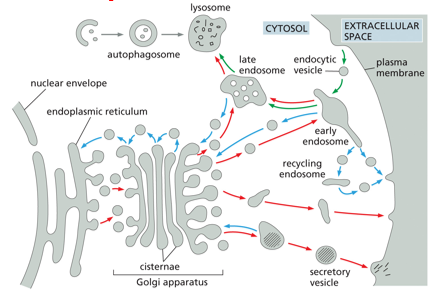
endocytic pathway ( )- molecules are ingested in ( ) derived from the ( ) and delivered to ( ) and then to ( )
green arrows
endocytic vesicles
plasma membrane
early endosomes
lysosomes
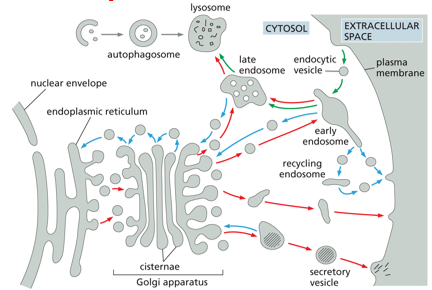
autophagy ( )- ( ) engulfed into autophagosome and go to ( )
gray arrows
cytosolic components
lysosomes
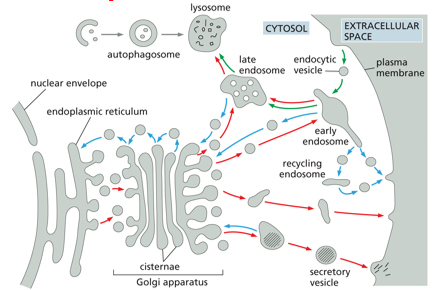
retrieval pathways ( )- endocytosed molecules are retrieved from ( ) and returned to the ( ), ( ) , or ( )
blue arrows
endosomes
cell surface
Golgi
ER for reuse
Different transport vesicles utilize different ( ) proteins.
-( ) mainly for movement from ER to ( )
-( ) mainly for movement from Golgi apparatus to ( )
coat
COPII (red)
COPI (blue)
COPII vesicle formation in ER is initiated by ( ) on ( ) by ( )- ( ) then becomes membrane bound by a ( )
guanine nucleotide exchange
Sar1 (a small G-protein)
Sar1-DEF
Sar1
amphipathic a-helix
membrane bound Sar1-GTP recruits COPII coat proteins ( ) and ( ) , ( ) specifically interacts with transport sequences on cargo proteins,
cargo receptors these specific protein-protein interactions determine which protein go into vesicles
Sec23
Sec24
Sec24
The COPII proteins ( ) form a cage-like multimer
-forms around the vesicle as directed by ( )
-similar for COPI and clathrin coats
-not all coats form like this
Sec 13/31
Sec 23/24
COPII-coated vesicles bud off the ER membrane with contents to be ( )
transported
receptors specifically interact with ( ), cargo proteins specifically interact with ( )
Sec24
receptors
this is how cargo proteins are loaded into the vesicles, so vesicles have cargo to be transported
-only ( ) that have ( ) are loaded into COPII vesicles to leave the ER
1)cargo proteins interact with cargo receptors, which also have exit signals that
2)target them and the cargo to the correct vesicles
correctly folded proteins
exit signals
COPII-coated vesicles bud off of the ER membrane-with ( )
coat proteins ( ) after vesicle buds from donor membrane
this is the same for ( ), ( ), and ( )
contents to be transported
dissociate
COPI
COPII
clathrin coated vesicles
polymerization of actin filaments occurs near the vesicle neck, helping push the budding vesicle away from the ( )
plasma membrane
( ) molecules assemble into a spiral around the neck of the forming bud and recruit other proteins to the bud neck, which, together with dynamin, ( ) the interacting lipid bilayers. the newly formed vesicle then pinches off from the ( )
dynamin
destabilize
membrane
what does the monomeric GTPases Rab do?
regulate intracellular vesicle traffic
These are events at target membranes-preparation to “catch” incoming vesicles
1)Rab-GEF exchange GTP to Rab (a small G-protein), causes conformation change in Rab5- (2) exposing amphiphilic a-helix and attached lipid
-Rab proteins are held in membranes by covalently attached lipid- so they are anchored membrane proteins and a-helix
3) Rab stimulated PI kinase to tri0phosphorylate PI, which binds to Rab effector proteins
4)Rab proteins recruit Rab effector proteins (including tethering proteins) and PI(3)P to specific areas of the target membrane for “catching” vesicles
5)Rab proteins and phosphorinostiol phosphate PI(3)P PLUS tethering proteins and other Rab effector proteins form a “Rab membrane area” that will tether vesicles to target membranes
( ) on vesicle specifically target and “tether” vesicle to target membranes by interacting with tethering proteins (on surface of target membrane)
Rab proteins
t-snares ( ) and v-snares ( ) to drive vesicle fusion, whereupon GTP is hydrolyzed by a GAP and Rab-GDP is released
target membranes
INTERACT (“dock” and twist)
( ) twisting forces membranes to fuse
tSNARE/vSNARE
( ) cation channels act as neuromuscular junctions to control muscle contraction
Acetylcholine-gated
there are several ( ) proteins ( which are small G-proteins) active at several, specific locations in cells, the presence of particular Rab proteins determines ( )
Rab
specificity of vesicle transport
Golgi apparatus modifies ( ) of ( ) , nearly all ( ) in golgi are membrane proteins
glycosylation state
cargo proteins
resident proteins
( ) of proteins on serine (Ser, S), threonine (Thr, T) hydroxylated lysine (Lys, K), occurs in golgi
O-linked (on hydroxyl, OH) glycosylation
glycosylations added in ER are modified in ( )
golgi apparatus
specific glycosylation patterns provide ( ) on proteins so that they are ( )
specific tags
targeted for specific functions and locations
polysaccharides form rigid 3D structures which can be recognized by ( ) for ( )
specific molecular interactions
specific functions
( ) are formed from golgi apparatus-derived vesicles and sometimes plasma membrane derived vesicles for endocytosis or phagocytosis
lysosomes
lysosomes are proteolytic digestive ( )
organelles
during acid hydrolases proteins use ( ) to digest other molecules in an acidic environment
these proteins are ( ) by a ( ) that is recognized by ( ) that are ( )
water
specifically directed to the lysosomes
“tag“ (a modified sugar attached)
receptors in the vesicles (from the Golgi)
directed to the lysosomes
lysosomes digest material from three sources:
what are they?
microorganism from outside cell (eg bacteria) by process of phagocytosis
macromolecules from outside the cell by process of endocytosis
parts of cell itself (eg mitochondria) by process of autophagy
Peroxisomes:
functions:
-( ) through oxidation reactions, producing hydrogen peroxide as a byproduct- which must be removed or it damages cells
-( ) in the liver and kidneys ( ) that enter bloodstream ( )
- convert ( )
-role in ( ) in the liver ( )
breaking down fatty acids and other molecules
detoxification reactions
detoxify toxic substances
such as alcohol
hydrogen peroxide, a toxic byproduct of metabolism, into water
cholesterol synthesis and bile acid production
oxidative enzymes such as ( ) and ( ) at such high concentrations that they form crystalline structures
catalase
urate oxidase