BACILLUS
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Bacillus anthracis
A 53-year-old Sheep farmer presents with a 2-week history of a 4.5 cm circular skin lesion of black eschar surrounded by vesicles and edema.Culture and gram stain shows gram positive bacilliin chains.
What is the organism most likely causing the disease?
C. Bacillus cereus
The health department is notified of a small outbreak of patients who sought medical help afteran episode of abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting in 6 members of a party of 20 who ateat a restaurant 4 hours before. The food was served family style with the 'usual fixings',including sauteed chicken, eggrolls, fried noodles and fried rice. What is the most likely causative agent?
A. Clostridium perfringens
B. Clostridium botulinum
C. Bacillus cereus
D. Bacillus anthracis
E. Staphylococcus aureus
F. I don't know
C. Inhibition of acetylcholine release
A 42-year-old woman is brought to the ED with rapid onset of ptosis (droopy eyelids), double vision, slurred speech, and difficulty swallowing or speaking, as well as difficulty breathing and onset paralysis on both sides of the body, starting at the neck. On questioning about her last food items, she reports drinking home-made carrot-juice about 24 hours ago. Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action ofthe offending Toxin?
A. Inhibition of GABA release
B. Destruction of membranes by lecithinase
C. Inhibition of acetylcholinerelease
D. Polyclonal activation of T cells by superantigen
E. Blockage of proteintranslation via EF2
F. I don't know
Staph aureus
C. perfringens
C. difficile
B. cereus
Main cause of GI symptoms
T
Bacillus are Aerobic spore formers (t/f)
Anthrax
Bacillus anthracis causes
Bacillus spp.
Clostridium spp.
BC
Spore forming
Erysipelothrix spp.
Listeria spp.
Corynebacterium spp.
ELC
Non-spore forming
Rhodococcus spp.
Actinomyces spp.
Nocardia spp.
RAN
Branching
Bacillus is SPORE FORMING
Bacillus is non-spore forming (t/f)
T
Bacillus are rod-shaped organisms; can be isolated from soil (t/f)
F
Bacillus are aerobic / Facultative anaerobes (t/f)
Bacillus are aerobic / Facultative aerobes (t/f)
T
Bacillus produces spores aerobically & anaerobically (t/f)
PERITRICHOUS FLAGELLA
Bacillus are motile with -
Bacillus anthracis & Bacillus mycoides
Bacillus are motile with PERITRICHOUS FLAGELLA except for
Catalase +
Ferments Glucose
Biochemical test for Bacillus:
Catalase :
Ferments :
-5°C
Bacillus can survive in temp as low as
75°C (heat stable)
Bacillus can survive in temp as high as
Bacillus cereus
what is the most clinically significant Bacillus group
B. anthracis
B. cytotoxicus - heat-tolerant, a probiotic
B. weihenstephanensis - cold-tolerant
B. thuringiensis - crystal-forming
B. mycoides
B. pseudomycoides
B. toyonensis & morphologic variants,
Bacillus cereus group is the most clinically significant species:
Halophilic 7% NaCl
Bacillus anthracis is Halophilic (-)
Agent of Bioterrorism
Bacillus anthracis is famously known as
Fried rice Bacillus
Bacillus cereus is famously known as
Hay Bacillus
Bacillus subtilis is famously known as
Flat sour spoilage
Biological indicator of autoclave
Bacillus stearothermophilus is famously known as
Insect pathogen
Bacillus thuringiensis is famously known as
Glucose, maltose, sucrose B
GSM
Bacillus anthracis produces acid from
T
Bacillus anthracis is non-motile (t/f)
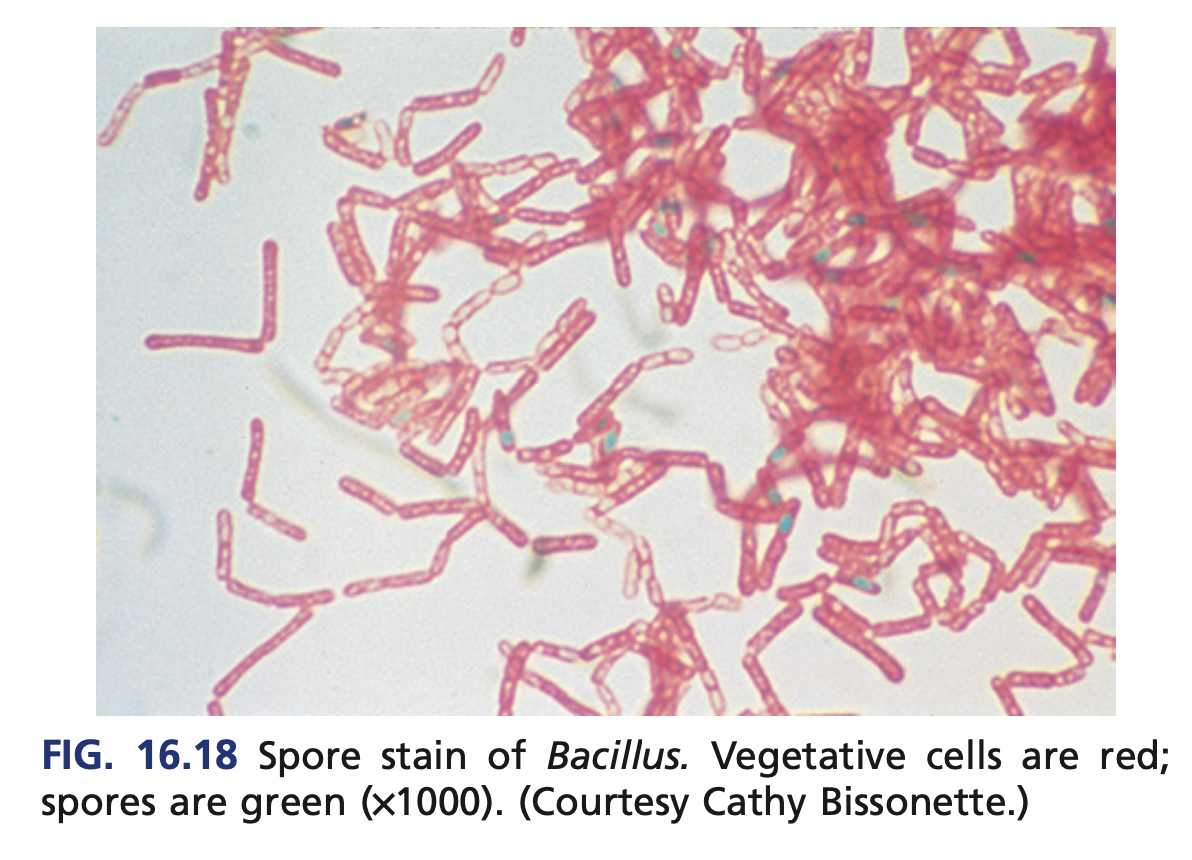
oval centrally located spores
Bacillus anthracis’ spores are
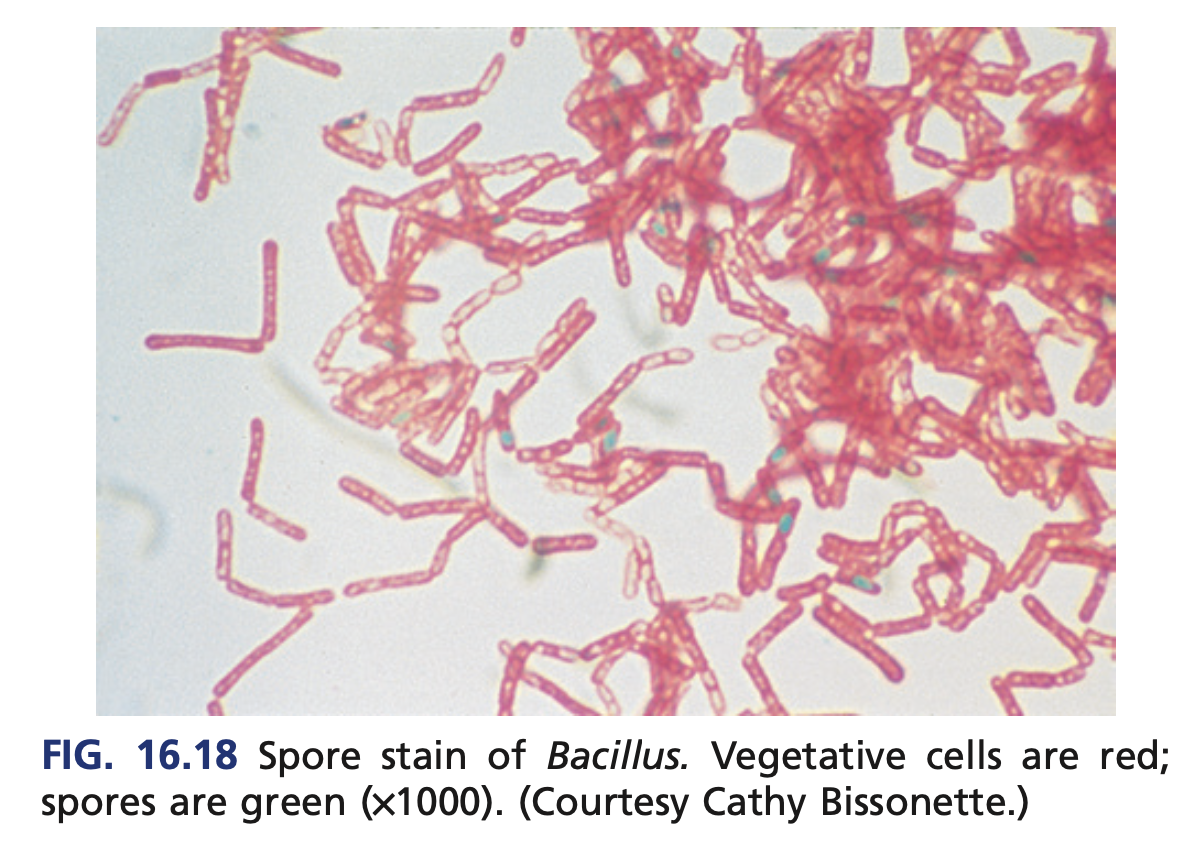
Malachite green
Bacillus anthracis’ oval centrally located spores is visualized using
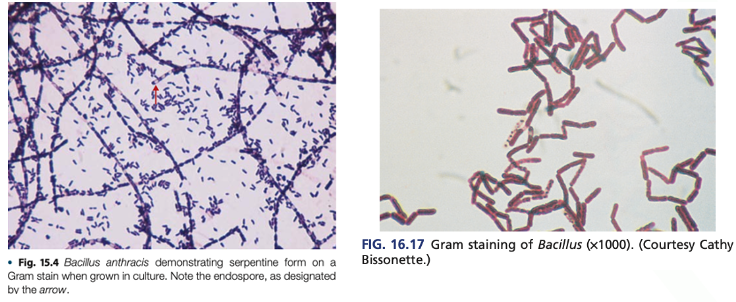
Boxcar / DIsjointed Bamboo morphology
Fishing rod / Serpentine appearance
Morphology and Colonial Characteristics
Bacillus anthracis on Gram stain
opaque zone around the colonies
Morphology and Colonial Characteristics
Bacillus anthracis on Lecithinase test/ Egg Yolk Agar + result
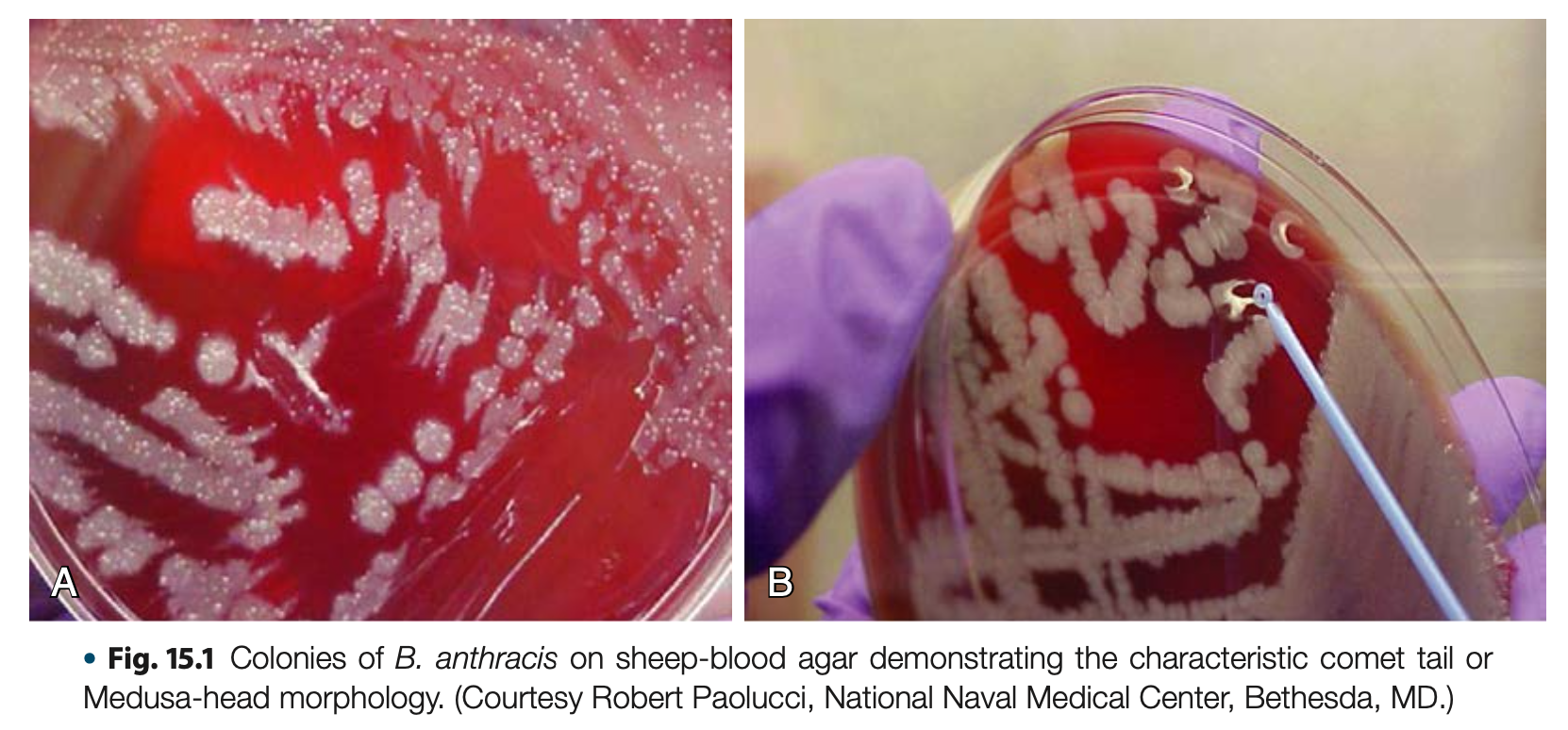
Comet tail /Medusa head / Ground glass colonies
Morphology and Colonial Characteristics
Bacillus anthracis on 5% SBA (non-hemolytic) colonies
string of pearls
Morphology and Colonial Characteristics
Bacillus anthracis on Mueller-Hinton agar and a 10 U penicillin disk
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis has a D-glutamase capsule which is not a polysaccharide unlike other
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis has a D-glutamase capsule which is a polysaccharide unlike other (t/f)
M’ Fadyean Capsular Stain / McFadyean stain
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis has a D-glutamase capsule which is not a polysaccharide unlike other which is visualized using
Protective Antigen (PA)
Edema Factor (EF)
Lethal Factor (LF)
LEP
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis has exotoxin with 3 components
PROTECTIVE ANTIGEN + LETHAL FACTOR= DEATH (Necrosis)
PLDn
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis
PROTECTIVE ANTIGEN + LETHAL FACTOR=
PROTECTIVE ANTIGEN + EDEMA FACTOR= EDEMA (swell)
PEEs
Virulence Factor
Bacillus anthracis
PROTECTIVE ANTIGEN + EDEMA FACTOR=
Cutaneous Anthrax
Pulmonary / Inhalation (Woolsorter’s / Ragpickers’ Dx) Anthrax
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
Injectional Anthrax
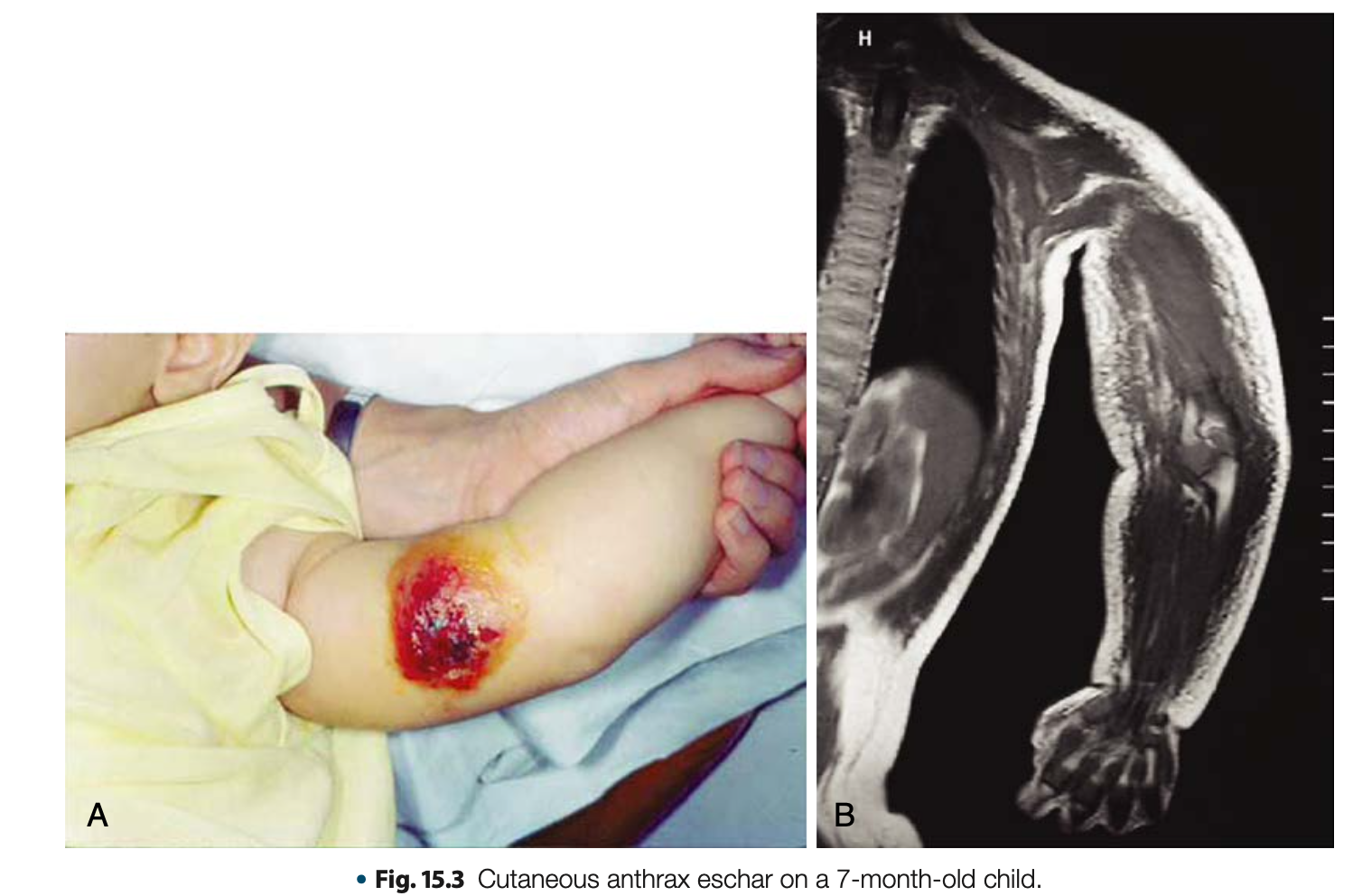
Diseases Associated in Bacillus anthracis
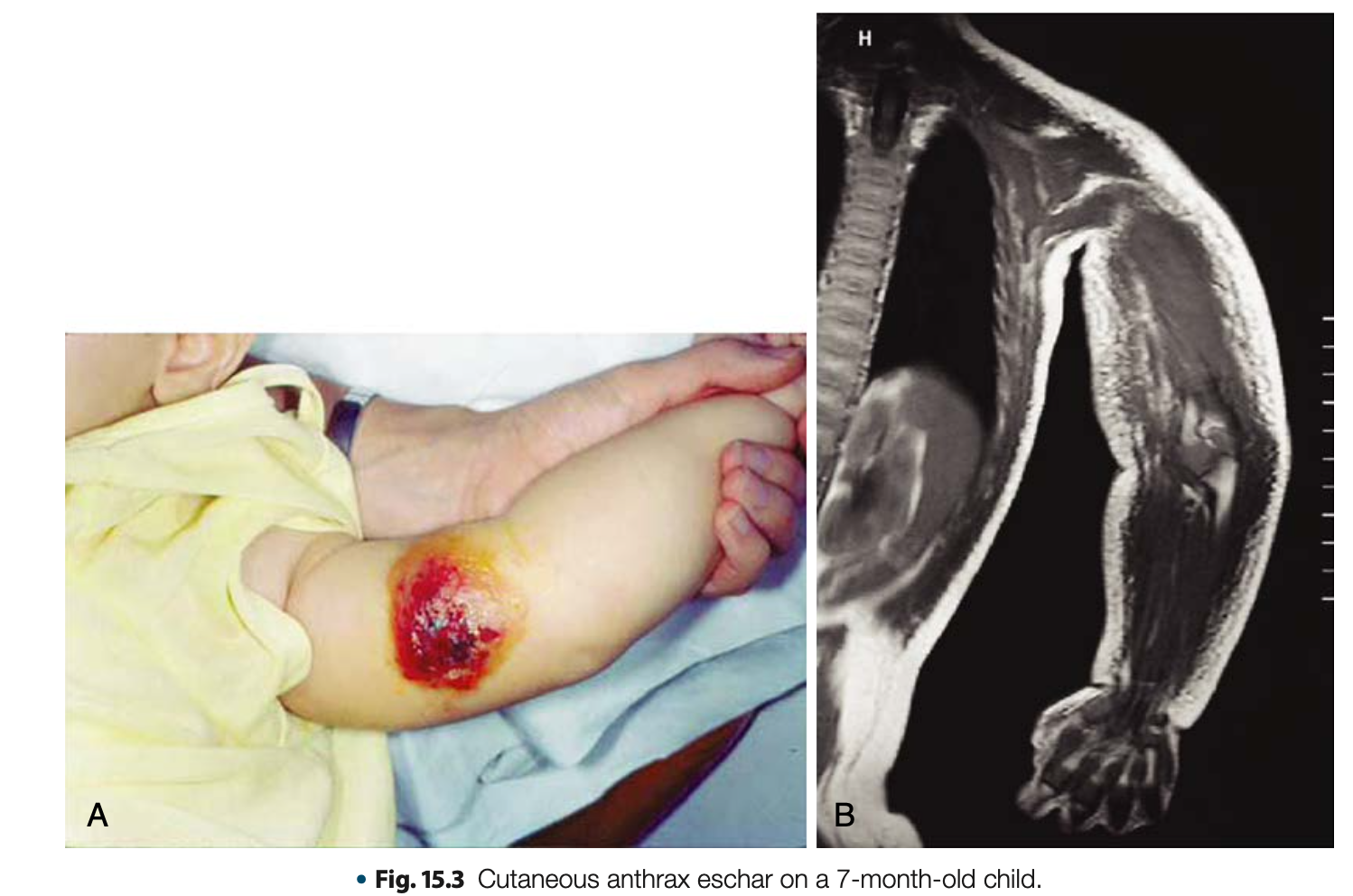
Cutaneous Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
MOST COMMON, LEAST SEVERE
Cutaneous Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
May develop BLACK ESCHAR at the site of entry
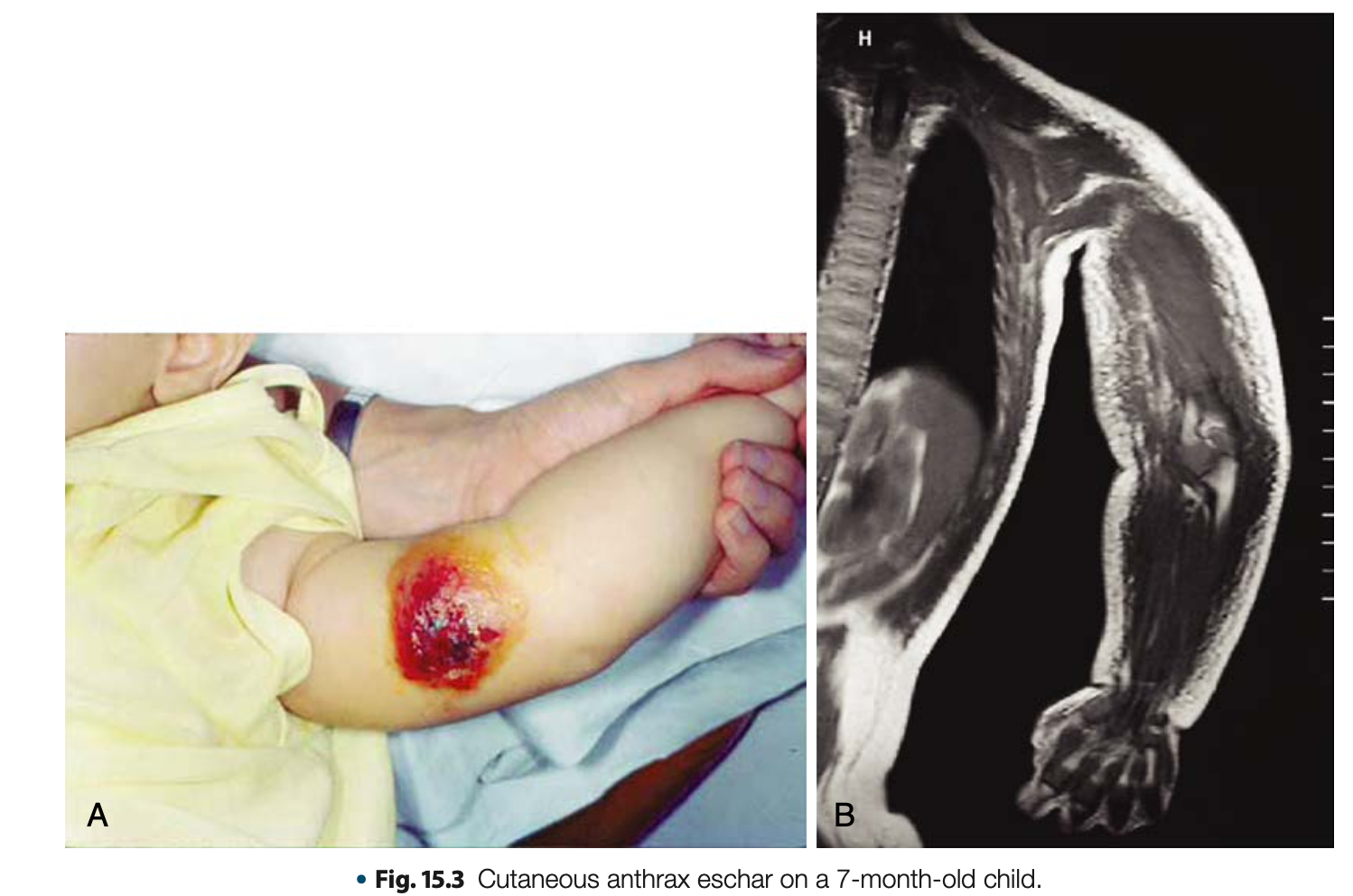
Cutaneous Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
The organisms enter through skin penetration (cut, open wound, etc.)
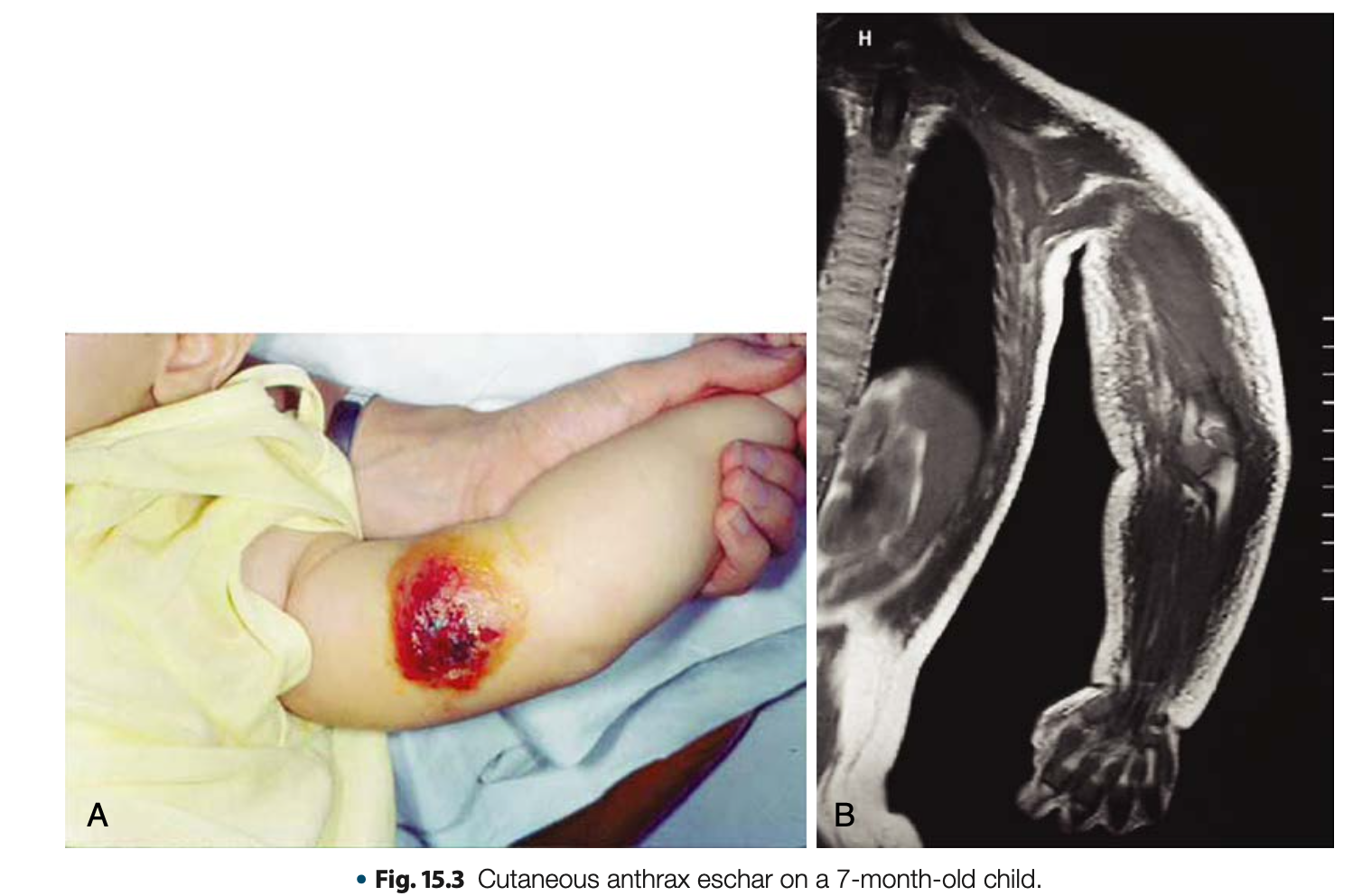
Black eschar
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
black necrotic central area or malignant pustule and it is PAINLESS and does not produce pus
Pulmonary / Inhalation (Woolsorter’s / Ragpickers’ Dx) Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
acquired through inhalation of spores during shearing or sorting of animal hair
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
MOST SEVERE FORM; LEAST COMMON
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
Ora/ oropharyngeal or gastrointestinal
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
Ingestion of improperly cooked, infected meats and ingestion of spores
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
o Bloody diarrhea and hematemesis
Injectional Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
injection of contaminated drugs of abuse, frequently heroin
Injectional Anthrax
Diseases Associated with Bacillus anthracis
characteristic lesion or eschar is absent
Bacillus cereus
Motile on BAP and beta-hemolytic
Bacillus cereus
- blood bag contaminant at RT
F
Bacillus cereus produce acid from glucose, maltose, salicin
Bacillus cereus produce acid from glucose, maltose, sucrose (t/f)

Lecithinase +
Bacillus cereus is Lecithinase + or – ?
hemolysin BL (HBL),
nonhemolytic enterotoxin (Nhe),
cytotoxin K (CytK) / Hemolysin IV
Virulence Factor
Bacillus cereus’ Toxin production are
Bacillus cereus
Commonly associated with food poisoning in rice, cereal, vegetables, and milk
Emetic Form (Rice)
Diarrheal Form ( Meat & Vegetables)
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
Forms of Infection:
Emetic Form (Rice)
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
caused by the production of HEAT-STABLE EMETIC TOXIN (Cerrulide Toxin)
Cerrulide Toxin
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
Emetic Form (Rice) is caused by the production of HEAT-STABLE EMETIC TOXIN (-)
1-6 HOURS
6 hrs
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
Emetic form (Rice) : SHORT INCUBATION (-); vomiting occurs within - hours after ingestion of contaminated food
Diarrheal Form (Meat & Vegetables)
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
caused by the production of a HEAT-LABILE ENTEROTOXIN
8-16 HOURS
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
Diarrheal Form (Meat & Vegetables) is LONG INCUBATION PERIOD (-)
Diarrheal Form (Meat & Vegetables)
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
toxin is produced when foods are left at RT
Septicemia
pneumonia
meningitis
peritonitis
Eye infections associated with trauma
Diseases Associated with Bacillus cereus
Diarrheal Form (Meat and Vegetables) is commonly associated with what diseases
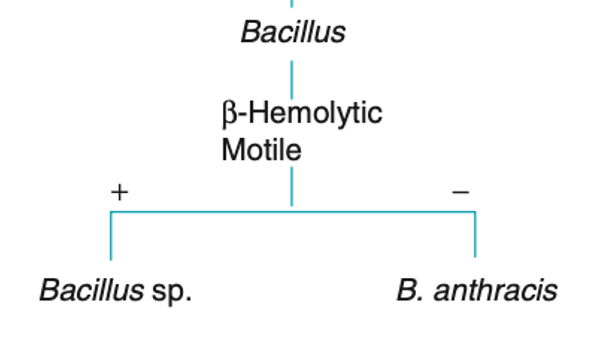
F
B. anthracis & B. mycoides is the non-motile,
B. anthracis is the only motile, Beta hemolytic on BAP (t/f)
T
Bacillus subtilis is motile & beta-hemolytic on BAP (t/f)
F
Bacillus subtilis is known to be an opportunistic pathogen
Bacillus subtilis is known to be an non-opportunistic pathogen (t/f)
T
Bacillus subtilis is Halophilic (7% NaCl) (t/f)
T
Bacillus subtilis is G+ rod in chains (t/f)
central spore
Bacillus subtilis spores
Bacillus subtilis
Common laboratory contaminant
Bacillus subtilis
Quality control for sterilization
Bacillus subtilis
CAUSES EYE INFECTION IN HEROIN ADDICT
Penicillin RESISTANT
Bacillus subtilis Penicillin R or S
Guthrie Test
Bacillus subtilis is used in what test which is a microbiological test for
phenylketonuria
phenylketonuria
Guthrie Test is a microbiological test for
Mannitol Egg Yolk Polymyxin B Agar
Bacillus subtilis selective media for isolation is
FLAT SOUR SPOILAGE
Bacillus stearothermophilus is famously known as
AUTOCLAVE (no gas but with acid)
Bacillus stearothermophilus is a biological indicator of
Bacillus stearothermophilus
- FLAT SOUR SPOILAGE in canned goods
Bacillus stearothermophilus
-biological indicator of AUTOCLAVE; no gas but with acid
Bacillus thuringiensis
- pesticides and insecticides, wound, burn, and pulmonary disease
- an insect pathogen