Week 12: Chronic Neurological Disorders
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Amyotrophy
progressive wasting of muscle tissues
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
-loss and hardening of nerves on the sides of spinal cord
-leads to destruction of upper and lower
-sensory neurons remain intact
Early s/s of ALS:
EARLY
-muscle twitching/weakness
-tripping
-slurred speech
Late s/s of ALS:
-spasticity
-atrophy
-dysphagia
-flaccid quadriplegia
-inability to move diaphragm
Huntington's Disease (HD):
hereditary neurodegenerative disorder that gradually destroys brain cells leading to problems with muscle coordination, cognitive decline, psych problems
Huntington's inheritance pattern:
-autosomal dominant pattern
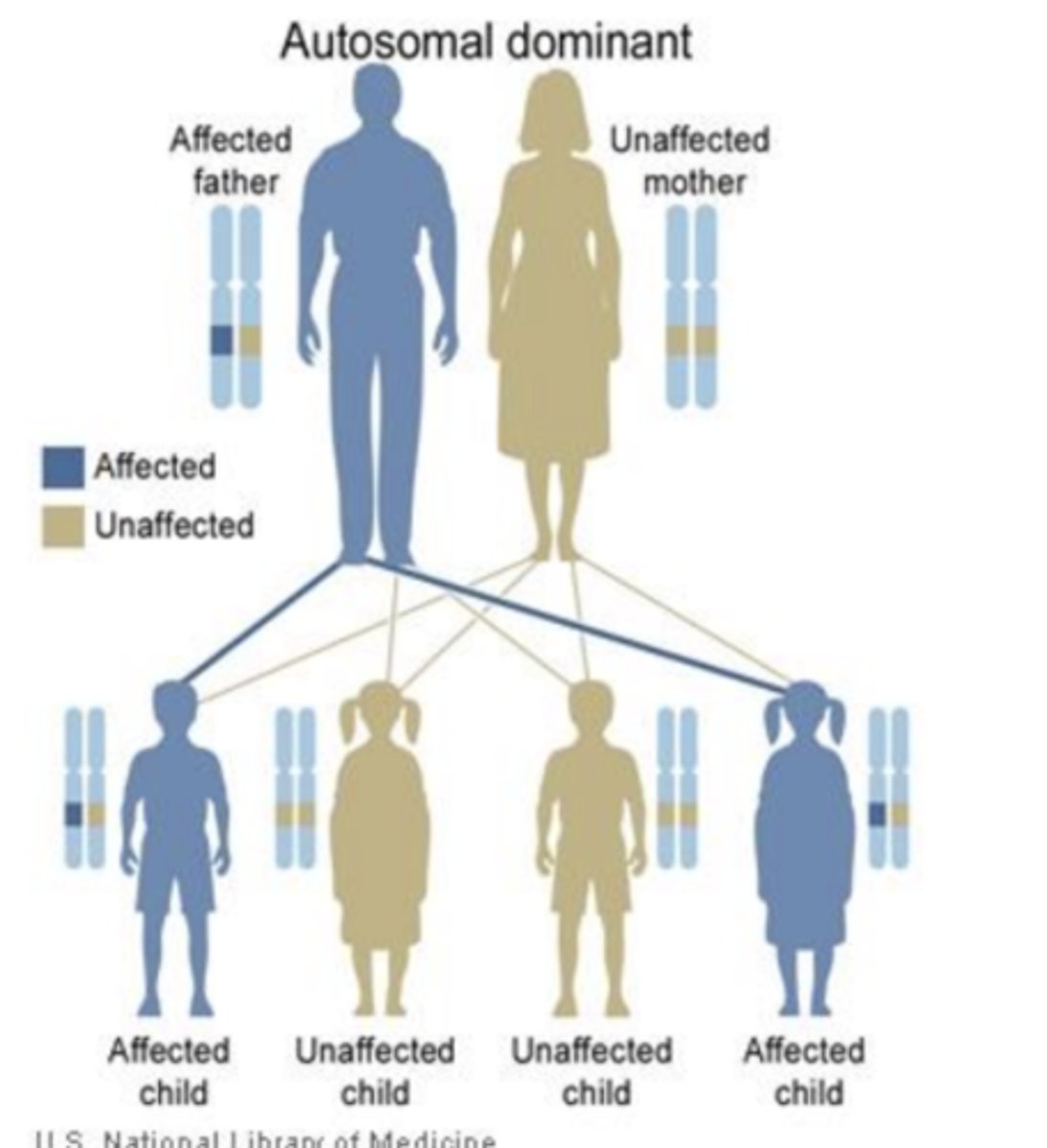
S/s of Huntington's disease:
-clumsy, restless, twitches, muscle spasms
-difficulty walking
-chorea (uncontrollable twisting movement)
-trouble with memory
-anxiety, OCD, depression, psychosis
Relationship between Dopamine and Huntington
EXCESS dopamine in HD
-explanation for chorea
-Tetrabenazine med used to decrease dopamine
Nursing considerations for Huntingtons:
-caregivers need to monitor for suicide/mental health problems
-supplemental nutrition (due to patient always in motion)
-administer Tetrabenazine and Haldol to suppress chorea
-very big fall risk
Myasthenia Gravis
chronic, autoimmune, neuromuscular disease that causes fluctuating weakness in skeletal muscles
-"least devastating" of all diseases in unit
S/s of Myasthenia Gravis
-generalized fatigue
-ocular muscles weakness (Ptosis)
-oropharyngeal muscle weakness (bad swallowing, chewing, speaking)
Nursing considerations for myasthenia gravis:
-the severity of muscle weakness fluctuates and improves with rest
-Ptosis is the most common symptom
-things that worsen MG (not taking meds, fatigue, emotional stress, certain meds, heat, pregnancy)
Myasthenia crisis
-TOO LITTLE MEDICATION
when muscle weakness in chest wall fails resulting in respiratory failure that requires tempo mechanical ventilation
Pyridostigmine bromid (Mestinon)
prevents the breakdown of Ach in the neuromuscular junction
-Ach inhibitors
Nursing considerations for Mestinon:
-must be administered ON TIME
-difficult to achieve right dose
-watch for s/s of CHOLINERGIC CRISIS (overstimulation)
Cholinergic chrisis
-TOO MUCH MEDICATION
-overdose of Ach inhibitors
-causes profound weakness
S/s of Cholinergic chrisis
DUMBBELLS
-defecation
-urination
-miosis and muscle weakness
-bradycardia
-bronchospasm
-emesis
-lacroimation (tearing)
-lethargy
-salivation
Antidote for cholinergic crisis
ATROPINE
Which disease indicated a Thymectomy?
Myasthenia Graves
-1/3 of patients see no benefit from this surgery
Parkinsons Disease (PD):
a chronic progressive neurological disorder marked by:
TREMORS
MUSCLE RIGIDITY
BRADYKINESIA
-lewy bodies also contribute s/s of PD
Relationship between Dopamine and Parkinsons:
LOSS OF DOPAMINE in PD
VERY early s/s of Parkinsons
-hyposmia (reduced ability of smell)
-constipation
-REM sleep behavior (acting out dreams during sleep)
EARLY signs of Parkinsons:
-TREMOR (described as pill rolling)
-rigidity (no swinging muscles, soreness)
-dystonia (a sustained muscle contraction resulting in abnormal posturing)

LATER s/s of Parkinsons:
-bradykinesia (slow start and actual movements)
-lack of self expression w/facial movements
-dysarthria
-akinesia and freezing
-constipation
-incontinence
-postural instability
may lead to cognitive impairment
5 Stages of Parkinsons Summarized:
1: tremor of one limb
2: tremors in both limbs
3: tremors in both and impaired reflex/posture
4: akinesia and rigidity (ADLS difficult)
5: unable to walk/stand, dementia
Nursing considerations for Parkinsons:
-no cure for PD
-do not administer drugs that BLOCK dopamine receptors (antipsychotics, some antimetics)
-dont delay medications for even 5 mins
-parkinsonism hyperpyrexia syndrome
Nursing considerations for Carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet and Parcopa):
-used to treat moderate to severe motor symptoms
-after 5 years dyskinesia occurs ("on/off" time)
-should be taken on empty stomach
-takes 1-4 months for effects
Side effects of Carbidopa Levodopa:
-nausea and anorexia
-orthostatic hypotension
-somnolence
-unusual dreams (extra dopamine?)
-hallucinations
-hypersexuality
Entacapone (Comtan) and Carbo-Levo-Encant (Stalevo):
-COMT inhibitors
-inactivates dopamine
-reduces "off" s/s
-same s/s but also diarrhea and orange urination
Nursing considerations for COMT inhibitors:
-must be taken with levo
-additional s/s of diarrhea and orange urine
Pramipexole (Mirapex), Rotigotine (Neupro)
-dopamine receptor agonists
-mimics the function of dopamine in the brain
-used for moderate motor symptoms
-has longer duration of action
-treats restless leg syndrome
Side effects of dopamine receptor agonists:
-excessive daytime sleepiness
-visual hallucinations
-confusion
-impulsive behaviors like gambling, sex, shopping
-punding (repetitive organizing, like nuts and bolts)
Selegiline (Eldepryl), Rasagiline (Azilect)
-Monoamine Oxidase B inhibitor
-breaks down serotonin and dopamine
-for minimal PD sympyoms
-used with carbo/levo
Nursing considerations for MAO-B:
-do not ingest excess tyramine product (cheese, wine, dried meat)
-lots of contraindications
Parkinsons hyperpyrexia syndrome:
abrupt withdrawal of carbo/levo can lead to this
-rigidity, increase temp, reduced LOC
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
chronic, progressive, immune mediated disorder caused by demyelination of nerves in CNS
-results in disordered or lost messages
S/s of multiple sclerosis:
-unpredictable condition (s/s vary from nothing to devastating)
-numbness, tingling, burning pain
-vision problems
-weakness in arms or legs
-walking and coordination problem
-muscle spasms
Nursing considerations for MS:
-85% diagnosis occur during relapsing remitting
-MRI requires two different lesions in CNS
-take vitamin D supplements, drugs to manage symptoms
-triggers for relapse include infection, stress, change in temp
Pregnancy and MS:
-MS s/s tend to DECREASE when women are pregnant
-exacerbation rates INCREASE in the first 3-6 months postpartum