Missed Psych Soc
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:20 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
three major psychotherapy
humanistic
cognitive behavioral
psychoanalytic theory (talkative)
cognitive behavioral
psychoanalytic theory (talkative)
2
New cards
cognitive behavioral therapy
tries to change negative thoughts and behaviors into maladaptive behaviors
3
New cards
humanistic therapy
tries to empower individual into self-actualization
4
New cards
talkative/psychoanalytic therapy
tries to uncover unconscience rooted in childhood that shape behaviors
5
New cards
emotion
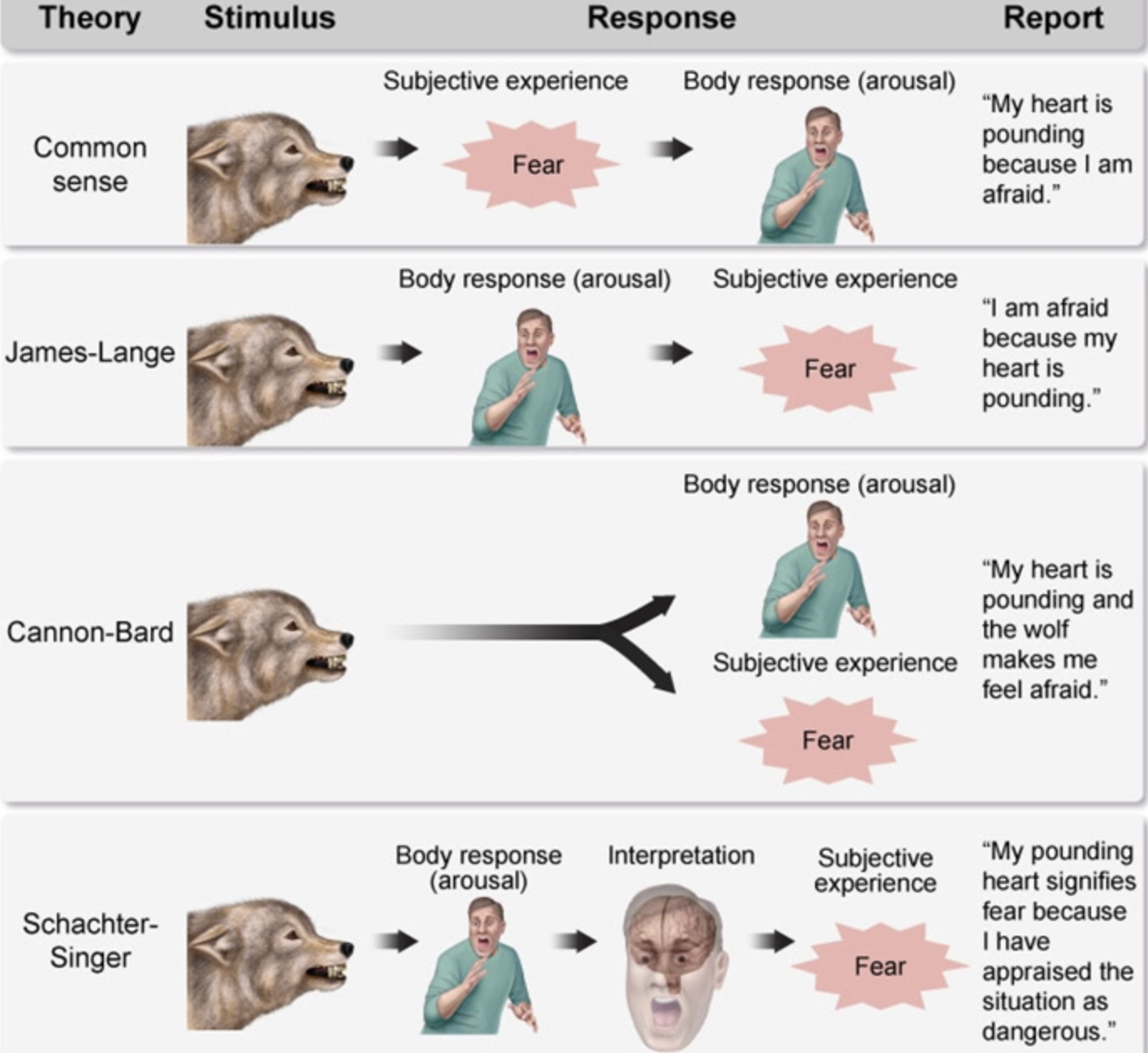
6
New cards
cognitive dissonance
state of discomfort that results in motivation to reduce the conflict by aligning thoughts and behaviors
\
* basically needs to pick on in order to properly reduce discomfort
* i.e will not choose to accept an diagnosis that you cannot get pregnant while maintaining the idea you need a child and will not adopt
\
* basically needs to pick on in order to properly reduce discomfort
* i.e will not choose to accept an diagnosis that you cannot get pregnant while maintaining the idea you need a child and will not adopt
7
New cards
major sociology theories
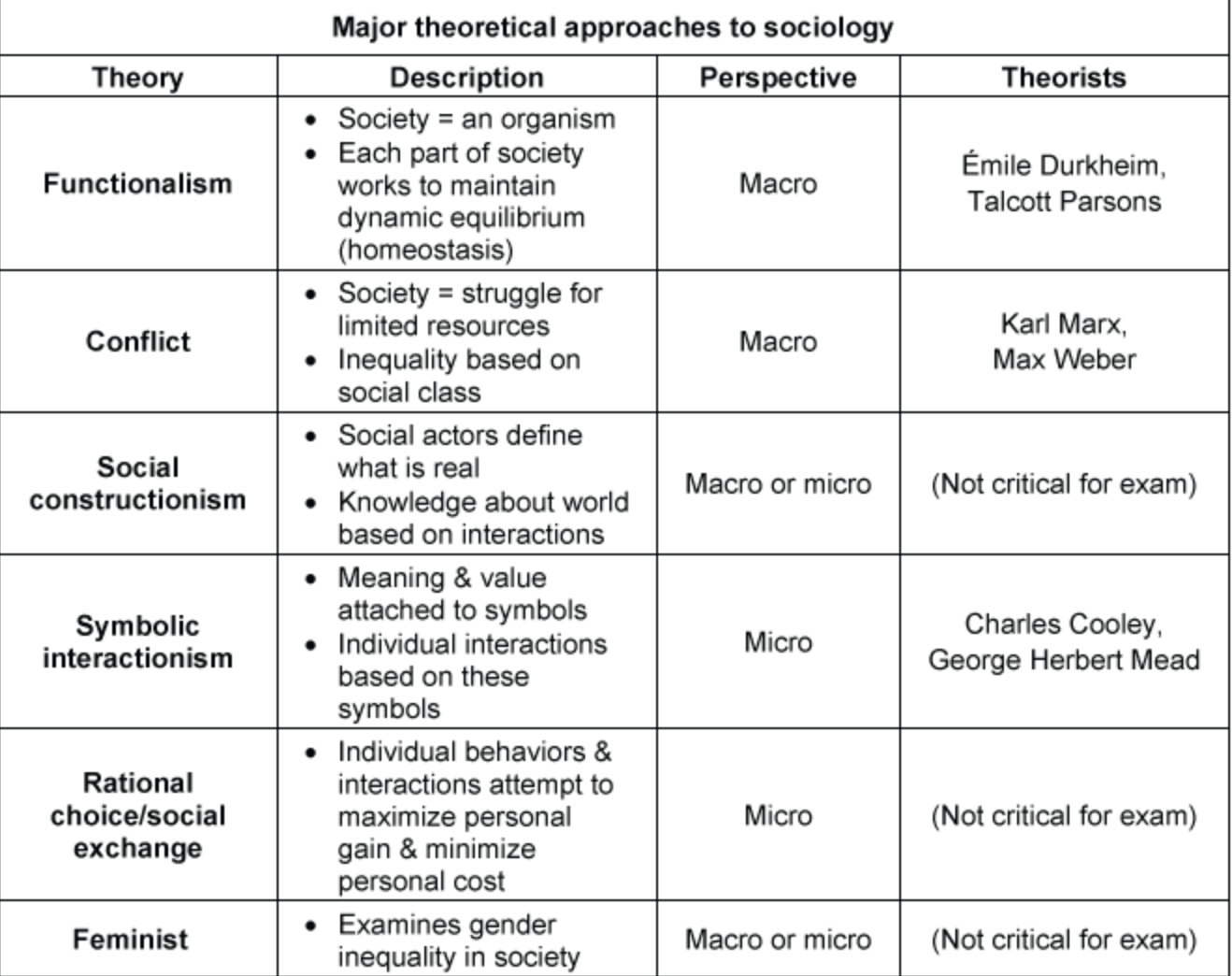
8
New cards
power vs authority
power is the ability to control or influence others
\
authority whether others believe that that power is legitimate
\
authority whether others believe that that power is legitimate
9
New cards
flash bulb memory
memory that is vivid, detailed and type of autobiographical explicit memory that is emotional and distinct to an individual
* tend to be far less accurate/consistent than people remember
* tend to be far less accurate/consistent than people remember
10
New cards
best way to train new behavior (operate)
continuous reinforcement
11
New cards
best way to maintain learned behaviors (operate)
variable ratio schedule
12
New cards
OCD behaviors (operate)
cleaning in OCD acts as a negative reinforcement because removes the unwanted anxiety stimulus -- encourages the behavior to continue
13
New cards
life course appraoch
holistic framework to understand how psychological, biological, and sociocultural factors across a lifetime can affect health outcomes
14
New cards
postive symptoms of schizophrenia
hallucinations
dellusions
disorganized thought
disorganized speech
dellusions
disorganized thought
disorganized speech
15
New cards
negative symptoms of schizophrenia
apathy
social withdrawl
flat effect
lack of speech
anhedonia
social withdrawl
flat effect
lack of speech
anhedonia
16
New cards
core vs peripheral nations, good and resources
peripheral send resources→ core nations
core send goods → peripheral
core send goods → peripheral
17
New cards
stereotype boost
positive stereotype improves preformance
18
New cards
hypothalamus, emotion
regulates physiological component of emotion
19
New cards
neuroleptics
used to treat schitzophrenia, used to reduce positive symptoms but can possibly worsen negative symptoms
20
New cards
atypical anitpsychotoic
used to treat schitzophrenia, used to reduce positive symptoms, can also help improve negative symptoms in some cases
21
New cards
structural functionalism assumes two types of functions in society
manifest and latent fucntions
22
New cards
deficits in visuospatial skill usually attributed to damage in
right hemisphere
23
New cards
short term memory duration
15-30 seconds
24
New cards
retroactive interference
new information interferes w old information
25
New cards
place theory
where on basilar membrane the vibrations occur
high frequency at base
low frequency at apex
high frequency at base
low frequency at apex
26
New cards
operationalization
variable is something that is not typically directly measured by now defined into something that can be measured
* dependent variable
* dependent variable
27
New cards
incentive theory
organisms are motivated to act in order to obtain external rewards
28
New cards
smoking explains in terms of incentive theory
person is motived to continue to smoke because it is an immediate reward, know it is bad for health but wants instant gratification
29
New cards
approaches to aging
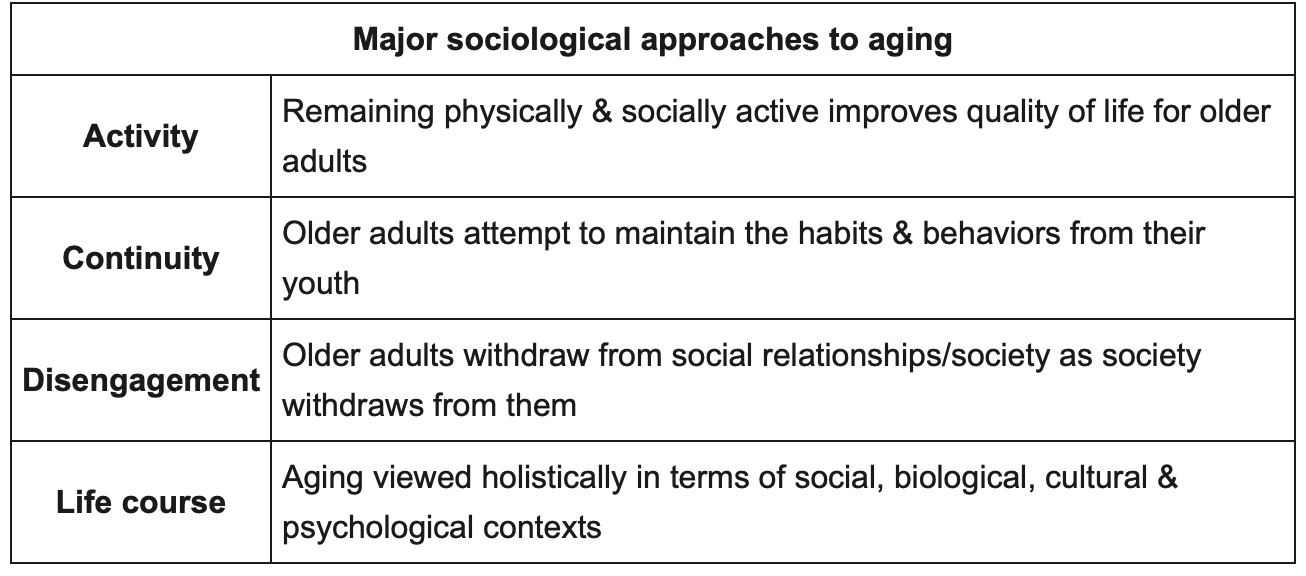
30
New cards
total fertility rate
average number of children born per woman over the course of her lifetime
31
New cards
crude birth rate
number of live births per year for every 1,000 individuals regardless of sex
32
New cards
general fertility rate
number of live births per year for every 1000 women of childbearing age
33
New cards
age-specific fertility rate
number of live births per year for every 1000 women of a certain age
34
New cards
hindsight bias
thinking an event is likely to occur/happen after it has already occurred even if it was not likely to happen
35
New cards
gentrification, local tax
causes local taxes to expand
36
New cards
central executive, working memory
regulates attention and task switching
37
New cards
visual spatial sketchpad, working memory
employed when manipulating visual or spatial information
38
New cards
phonological loop, working memory
employed when manipulating spoken or written information
39
New cards
episodic buffer, working memory
responsible for temporal information (timeline) and integration from long term to working memory
40
New cards
motion parallex
monocular cue
foreground items appear to move more quickly than things in the background
* perceive both depth and motion
foreground items appear to move more quickly than things in the background
* perceive both depth and motion
41
New cards
retinal disparity
each eye transmits a slightly different image to the brain
binocular cue
binocular cue
42
New cards
convergence
binocular cue
the extent to which eyes turn inward to focus on, closer objects require more
the extent to which eyes turn inward to focus on, closer objects require more
43
New cards
phi phenomena
optical illusion, series of images are shown quickly and appear to be moving
44
New cards
speech shadowing
dichotic listening, repeating information in one ear while tuning information in the other ear
45
New cards
neuroimaging
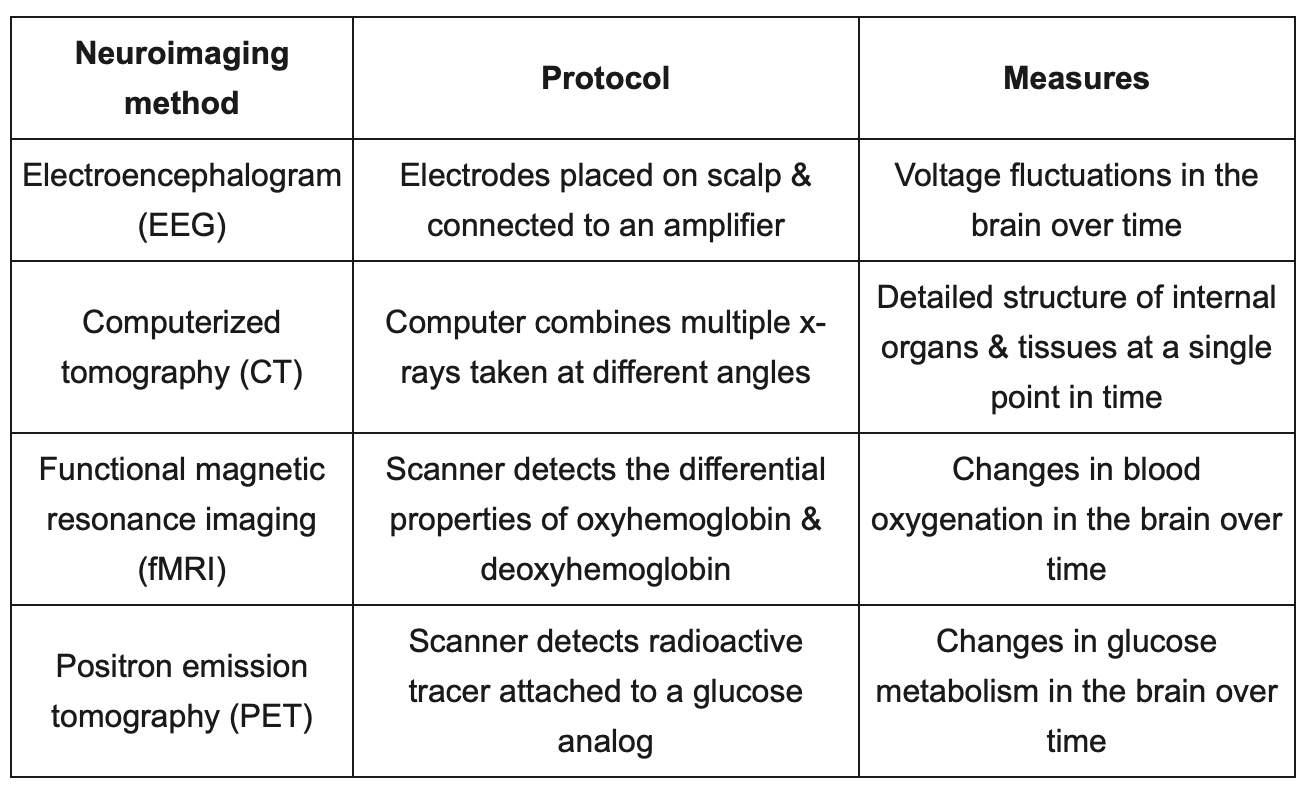
46
New cards
parietal lobe
used for processing spatial information
47
New cards
shadow the attended ear
only repeat what you hear in the specific ear assigned
48
New cards
source characteristics
about who or what is delivering information (education, prestige, trustworthiness)
49
New cards
audience characteristics
age, mood, need for cognition
50
New cards
drive
internal state individuals act to REDUCE
51
New cards
diathesis-stress model
ntegrates the influence of biological predispositions and the environment
52
New cards
Opponent process theory
for motivation is often used when speaking of addictive behaviors. Certain emotional states are followed by another emotional state that is opposite of the first. As time goes on, the second emotional state becomes stronger than the first.
53
New cards
Beck’s cognitive triad
represents three types of negative thoughts present in depression. These are thoughts about the self, the world, and the future.
54
New cards
learned helplessness
uncontrollable exposure to an aversive stimulus results in learned helplessness, independently of the intensity of the punishment
55
New cards
negative reinforcement
response results in escape from an aversive stimulus, it is an example of
56
New cards
humanistic perspective
explaining behavior through self-concept and incongruence
57
New cards
Long-term potentiation
process involving persistent strengthening of synapses that leads to a long-lasting increase in signal transmission between neurons
58
New cards
study that tests the encoding specificity effect is most likely to be
location of encoding and retrieval
59
New cards
primary and recency effect only take place if recall occurs
immediately after given the list
60
New cards
how sociologists differentiate the concepts of ethnicity and race
Sociologists consider ethnicity to be categorizations of people based on culture and ancestry. Sociologists consider race to be categorizations of people based on perceived physical characteristics. Both concepts are understood in sociology as complex, social categories that change over time, rather than simply biological features of human beings
61
New cards
Labeling theory
perspective on deviance that suggests labels get applied to certain groups or individuals regardless of specific behavio
62
New cards
most likely outcome of cognitive dissonance
patient changes attitude to match behavior, not vise vera (requires more work typically)
63
New cards
token economy
rewarding individuals with secondary reinforcers that can be exchanged for appetitive stimuli
64
New cards
Kohlberg moral development, precovential morality
avoid punishment
self-interest - “ill help you if you help me”
self-interest - “ill help you if you help me”
65
New cards
Kohlberg moral development, conventional morality
conformity and interpersonal accord - wanting to be good to secure approval of others
law and order - obey laws of society
law and order - obey laws of society
66
New cards
Kohlberg moral development, postconvential morality
social contract - max benefit for largest amount of ppl
universal ethics - follow own ethics above all else
universal ethics - follow own ethics above all else
67
New cards
cultural transmission
passing of information from older to younger generations
68
New cards
identity development theory
psychological progress of individuals based on their level and commitment and exploration
69
New cards
identity diffusion
low commitment low exploration
ppl have no idea where they are going/uncomminted to a career or future
ppl have no idea where they are going/uncomminted to a career or future
70
New cards
identity forecolsure
high commitment low exploration
accepted the identity they have been assigned
accepted the identity they have been assigned
71
New cards
identity moratorium
low commitment high exploreation
trying new activities and thinking of new career path, no decisions yet
trying new activities and thinking of new career path, no decisions yet
72
New cards
identity achievement
high commitment high exploration
explore their options and feel confident about their future and career
explore their options and feel confident about their future and career
73
New cards
convenient sampling
nonrandom generation of study population
74
New cards
social desirability bais
participants to overemphasize postive aspect and downplay or underreport negative aspects
75
New cards
compliance
public conformity while in private truly disagrees
76
New cards
conformity vs obedience
obedience is behavior according to the commands of others
77
New cards
informational vs normative social influence
informational, conforms due to uncertainty and believes whoever is in the group knows best
normative, conforms due to desire to be accepted (often when ppl are similar and want to be accepted by group)
normative, conforms due to desire to be accepted (often when ppl are similar and want to be accepted by group)
78
New cards
generalizability
external reliability
79
New cards
regression of the mean
extreme data points eventually begin to move towards mean after repeated measurements (an athlete who preforms amazing one game is likey to underperform the next)
80
New cards
stressors limited to few ppl
daily hassle and personal life event
81
New cards
stressors limited to many ppl
ambient (environmental), catastrophe
82
New cards
sick role theroy
illness is a socially expectable form of deviance
* right to be exempt from social roles
* obligation to make every effort to get better as soon as possible
* right to be exempt from social roles
* obligation to make every effort to get better as soon as possible
83
New cards
borderline personality disorder
instability in mood and sense of self/relationshps
mood reactivity, fear of abandonment
impulsive or reckless behavior
suicidal thoughts
mood reactivity, fear of abandonment
impulsive or reckless behavior
suicidal thoughts
84
New cards
avaiblity huristic
how quickly something can come to memory (see shark attack in news, assuming it is common)
85
New cards
representative heuristic
how well something matches a metal prototype (see woman in scrubs, assume she is a nurse not a surgeon)
86
New cards
illness experience, symbolic interactionist theory
how individuals understand and cope with chronic illness that impacts daily life and self-identity
87
New cards
illness work
gathering information bout illnessi
88
New cards
everyday work
daily activities that do not directly involve managing illness but are impacted by illness
89
New cards
biographical work
making sense of the illness for oneself and others (explaining to coworkers and friends)
90
New cards
somatic symptom disorder
express distress regarding one or more bodily symptoms
* bodily symptoms are associated with psychological factors
* bodily symptoms are associated with psychological factors
91
New cards
taste aversion, classical conditioning
develops after just one pairing, long duration (as opposed to other forms of this conditioning)
92
New cards
stage 2
newly industrializing
death rate declines as food, medicine, and sanitation become available
death rate declines as food, medicine, and sanitation become available
93
New cards
affinal relatioship
via marriage
94
New cards
consenguinal
via genetic relationship (biological parents)
95
New cards
fictive relationship
social ties are not affinal or consenguinal
96
New cards
emotional social support
love affinity belonging
97
New cards
esteem, social support
encouragement and confidence
98
New cards
tangible, social support
money resources food
99
New cards
informational, social support
advice, informaiton
100
New cards
companionship, social support
mere presence