Biology cells and control topic test
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are meristems?
An area in a plant that contains undifferentiated cells in plants
Describe the term asexual reproduction
When there is one parent and the offspring is genetically identical to it

What happens in interphase?
-DNA is copied
-Chromosomes start to become visible

What happens in prophase?
-Each chromosome consists of two chromatides
-Spindle fibres start to form
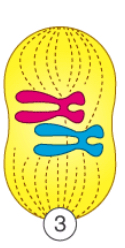
What happens in metaphase?
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
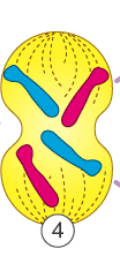
What happens in anaphase?
-The chromatids separate
-One from each pair is pulled to each pole of the cell
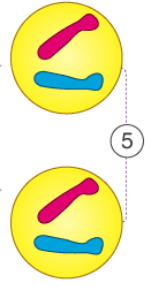
What happens in telophase?
-Spindle fibres disappear
-A new nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes
What happens in cytokinesis?
A cell membrane divides the cells
Explain the term cell differentiation
The process by which unspecialised cells develop into specialised cells
How is a red blood cell specialised?
-No nucleus so there is more space for haemoglobin
-Biconcave shape increases area for oxygen absorption
How is a striated muscle cell specialised?
-Lots of mitochondria to supply all the ATP needed for contraction
-Multinucleate because one nucleus can’t handle producing enough proteins to support the cells size and contraction
How is a nerve cell specialised?
-Myelin sheath insulates axons to speed up signal transmission
-Long axons to carry signals over long distances
How is a fat cell specialised?
-Extendable membrane allows the cell to grow as it stores more fat
-Fewer organelles most of the cell is devoted to fat storage rather than other tasks
Define growth
An increase in the amount of cells an organism has
How is growth measured in plants?
-Increase in length
-Finding the plants dry mass
How is growth measured in animals?
-Increase in body mass
-A growth curve or percentile graph
Define mitosis
A type of cell division that produces two genetically identical diploid daughter cells
Give two reasons why synapses are used in the nervous system
-Allow communication between neuron’s
-Ensure one way transmission
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
-Insulate axon
-Speed up nerve impulse transmission
What is the function of the axon?
To carry electrical impulses away from the cell body
What is the function of the dendrites?
To receive electric signals from other neurones
What is the function of the axon terminal?
To release neurotransmitters into the synapse
Define neurotransmission
The process of sending signals between neurones
What are embryonic stem cells?
Undifferentiated cells found in embryos that can develop into any type of cell in the body
What are adult stem cells?
Undifferentiated cells found in certain tissues of the body that can develop into some types of specialised cells
State some uses of embryonic stem cells
-Drug testing
-Tissue repair
-Research into development
What two organs make up the central nervous system?
-Brain
-Spinal cord
What are the moral and ethical implications of therapeutic stem cell research?
-Destruction of embryos
-Embryos can’t consent
-Financial exploitation of women who donate
Describe 2 physiological problems with using stem cells
-Risk of tumours
-Immune rejection
What are the 4 senses and their receptors?
-Sight: eyes
-Hearing: ears
-Taste: tongue
-Smell: nose
-Touch: skin