H & I III: Cellular Regulation (Breast Cancer)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Cellular regulation
- functions carried out in a cell to keep homeostasis
Cancer
- umbrella term
- abnormal cell reproduce and rapidly spread —>disease
What is the second leading cause of death worldwide after cardiovascular diseases?
- cancer
Cancer patho
- Changes/damage to cells
- Caused by Inherited traits, Errors in cell division, Environmental factors
- Effects of aging
- Cancers named by body part origin, cell type
Metastasis
- spread through the body, blood, lymphatic system
Primary and secondary tumors
- Primary: tissue from which it started (parent tissue)
- Secondary (metastatic): cancer cells move from primary location
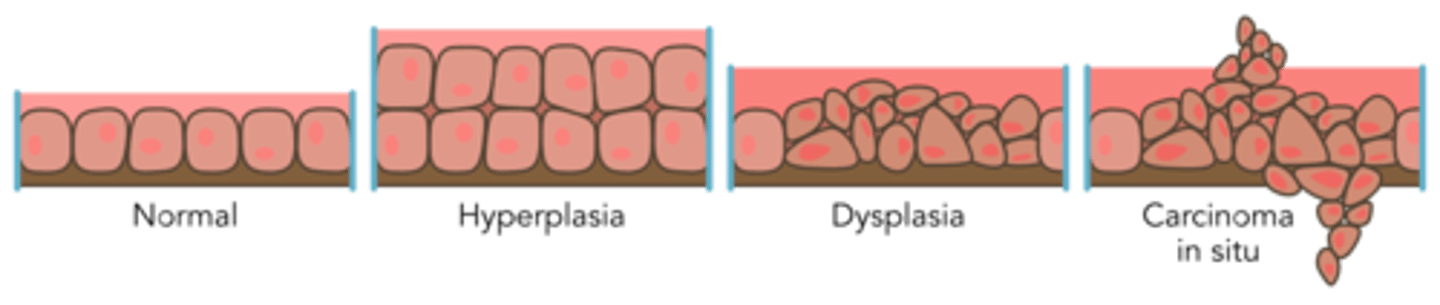
Progression to malignancy
- hyperplasia
- dysplasia
- carcinoma in situ
Malignant cells
- no apoptosis (no programmed cell death)
- angiogenesis (cancer cells have their own blood supply that they created--this is not good)
Benign
- no cancerous
- tumor cells grow locally
- no spreading or metastasis
Malignant
- cancer cells invade the tissues nearby
- cells enter blood vessels
- metastasize to different places
Cancer Epidemiological and Etiological Risk Factors
- Common risk factors
- Genetics
- Smoking (lung cancer)
- Alcohol consumption (liver, esophagus)
- Excess body weight
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Dietary habits
- Viruses (HPV, Hep B, Hep C, EBV, lymphoma, HIV--Kaposi sarcoma)
Cancers common in those assigned female at birth
- Breast
- Lung
- Colorectal
- Uterine
- Melanoma
Cancers common in those assigned male at birth
- Prostate
- Lung
- Colorectal
- Bladder
- Melanoma
Cancer impact on overall health
- Pain
- Infections
- Gastrointestinal: Malnutrition, Elimination
- Lymphedema
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Fertility
Cognitive
- Sleep disturbances
- Stress
- Meds
- Delirium
- Concentration problems
- Decreased organizational abilities
- Impaired memory
Fatigue
- Anemia
- Meds
- Emotions—anxiety, fear
- Inflammatory function
- Sleep disturbances
Oncologic complications
- Hypercalcemia
- Spinal cord compression
- Superior vena cava syndrome
- Malignant pericardial effusion
- Tumor lysis syndrome
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
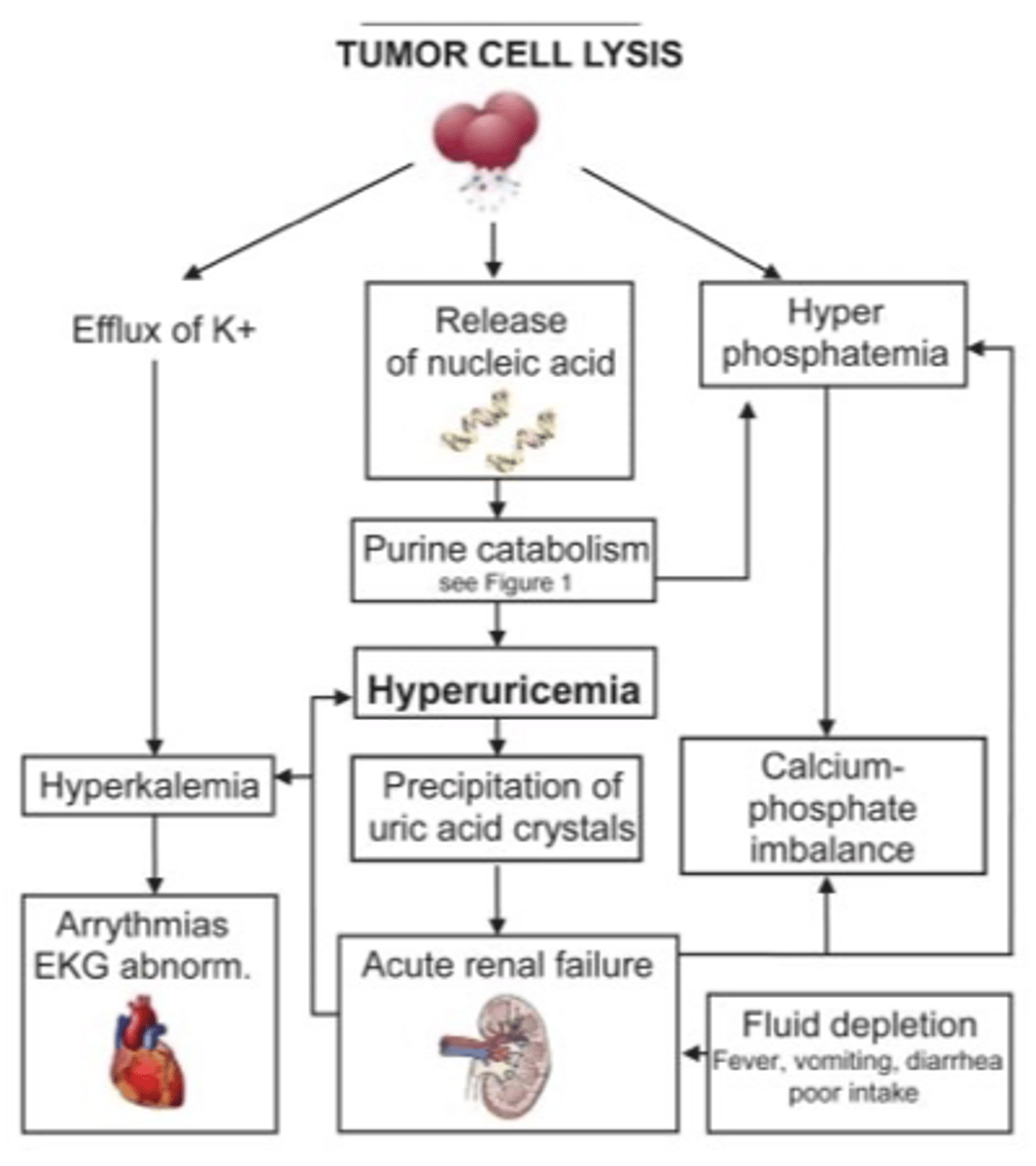
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
- impacts electrolytes
- Rapid release of intracellular components in response to chemotherapy; (cells are dying, not doing to correctly, cellular components are being released, overwhelming the kidneys)
- Hallmark signs: hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia; can cause acute kidney injury and cardiac arrest
- Treat with IV fluids, allopurinol, and IV sodium bicarbonate
Tumore Lysis Syndrome image
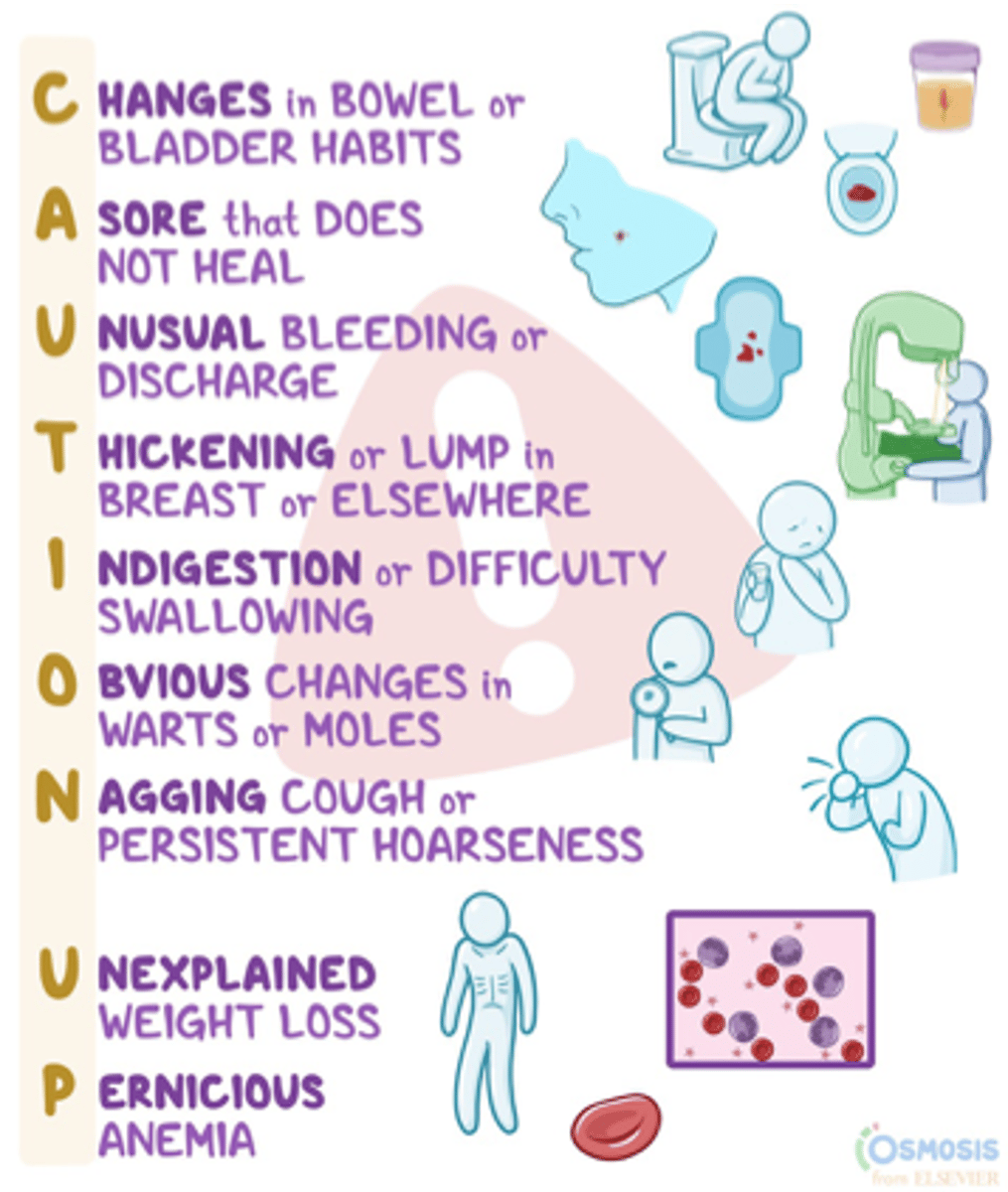
General manifestations of cancer
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Palpable masses
- Swelling
- Pain
- Skin changes
Cancer diagnostics
- Imaging tests
- Bone scans
- Angiography
- Biopsies
- Tumor markers
TNM
- T: tumor
- N: lymph node status
- M: metastasis
TNM staging
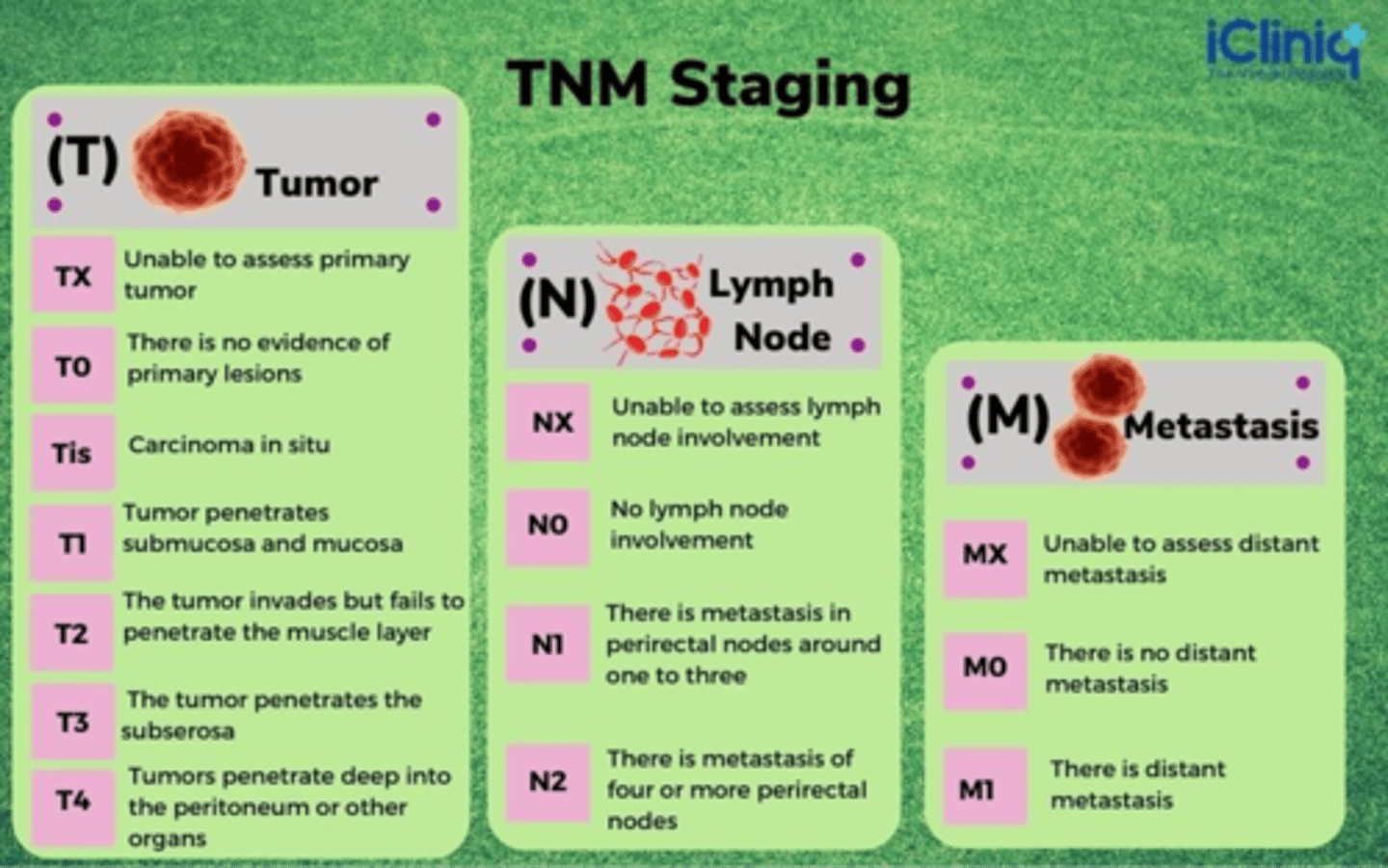
TNM staging and 5 -year survival rate
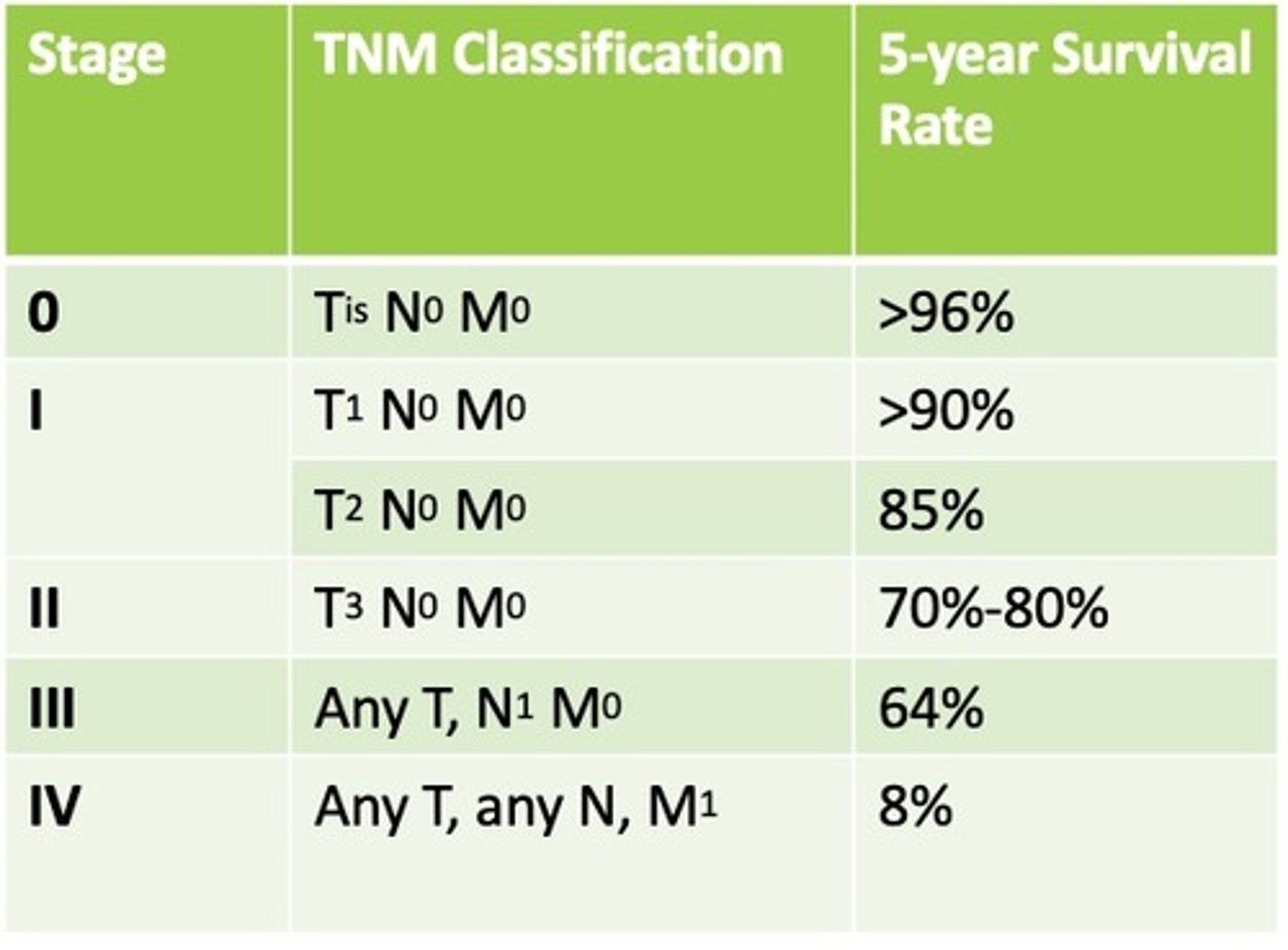
Cancer staging
- TNM (tumor, node, metastasis)
- Stages 0-IV (stage 4 is BAD)
- Additional terms: In situ, Localized, Regional, Distant, Unknown
Chemo PPE

Neutropenia
- Decrease in neutrophils based on the absolute neutrophil count (ANC)
- Usually seen within 1-2 weeks of last chemotherapy dose
- Classic signs of infection (e.g. fever, pain, redness, swelling, pus) may not be present
- Neutropenic fever (≥100.4° F [38° C] and a neutrophil count <500/µL) is a medical emergency.
- Blood cultures should be drawn STAT and antibiotics started within 1 hr
Neutrophil count
- Normal 2200-7700 cells/µL (1 × 109/L)
- Neutropenia ANC <1000 cells/µL
- Severe neutropenia ANC <500 cells/µL
Neutropenic precautions

Chemotherapy
- Chemicals used for systemic therapy
- Goal: prevent cancer cells from multiplying, invading, and metastasizing to distant sites
- Can offer cure, control, or palliative care
Chemo: cure, control, palliation
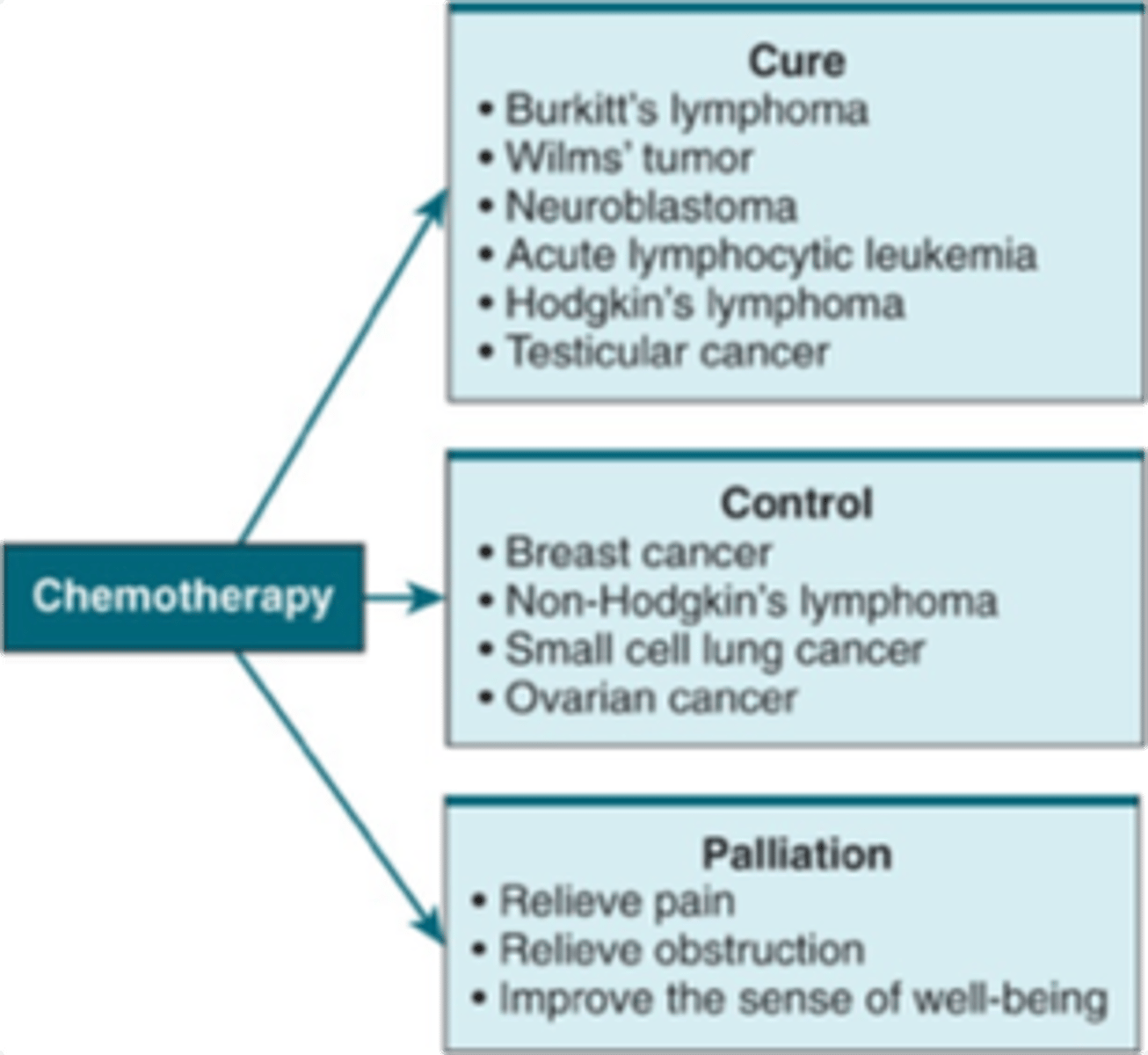
Radiation
- May be used by itself or with chemotherapy or surgery
- To treat primary tumors
- For palliation of metastatic lesions
- Internal radiation (brachytherapy)
- Implantation or insertion of radioactive materials into or close to tumor
Breast cancer
- Irregular, disorganized mass of uncontrolled cell proliferation that arises from breast tissues.
- Most common in American women except for skin cancer
- Second leading cause of death from cancer in women, behind lung cancer
Breast cancer incidence is declining due to
- decrease hormone therapy post menopause
- early detection and advances in treatment
Breast cancer risk factors that can be controlled
- exercise
- normal BMI
- alcohol
- HRT
- reproductive history (not breastfeeding, having children after 30, not having children are all KNOWN risk factors)
Breast cancer risk factors that cannot be controlled
- genetic mutations (BRCA-2)
- family history
- radiation to the chest
- menstrual history
- dense breast tissue
Breast cancer and hormonal regulation
- Estrogen and progesterone may promote tumor growth
- Increases risk for cancer
- Cancer larger and more advanced at diagnosis
- Long term estrogen alone (>15 years)
- Oral contraceptives
- Risks decrease after use
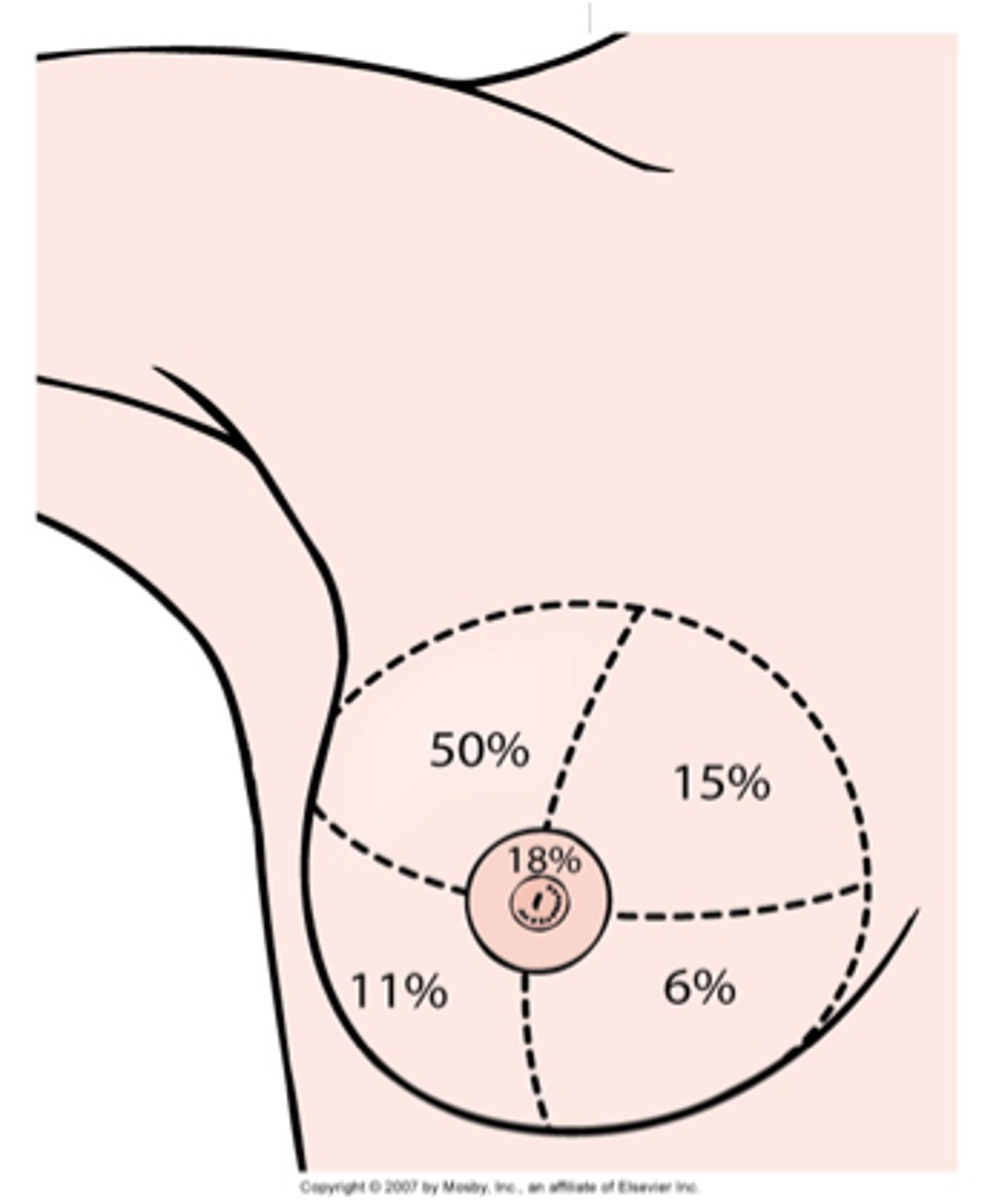
Breast cancer distribution image
Breast cancer types
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
- Lobular Carcinoma In Situ
- Invasive Lobular Cancer
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ
- breast cancer at earliest stage before breaking through the wall of the milk duct
- non-invasive
- highly treatable if detected (if not, it may spread)
Invasive ductal carcinoma
- invasive cancer
- spread beyond the ducts into other breast tissue
- most common type of breast cancer
- also the most common type to affect MEN
Lobular carcinoma in situ
- NOT BREAST CANCER
- abnormal cells in lobules of the breast
- not outside the lobules of the breast tissue
- highly treatable if detected (if not, may spread)
Invasive lobular breast cancer detection
- MRI (does not always show up on mammogram)
Screening of breast cancer
- Hx of breast disorder assists in establishing a diagnosis (mastalgia, atypical hyperplasia, intraductal papilloma)
- Presence of nipple discharge: color, consistency, from one or both breasts
- Pain
- Rate of growth of lump
- Breast asymmetry
- Correlation with menstrual cycle
Protective/preventative factors for breast cancer
- Smoking cessation.
- Exercise
- Decreased body fat
- Breastfeeding (Decreased risk by preventing return of menstruation and decreased exposure to estrogen)
S/S of breast cancer
- Lump or mammographic abnormality in breast; most often in upper outer quadrant - location of most of glandular tissue
- Lesion - If palpable, non-tender, non-mobile, and hard, irregularly shaped, poorly delineated
- Advanced stages (Dimpling appearance of skin, Nipple retractions, Lesions fixed to the chest, Ulcerating, fungating lesions)
Breast cancer diagnostics
Radiologic:
- Ultrasound
- Mammography
- MRI (dense breast tissue)
Tests used to predict risk and local or systemic recurrence:
- Axillary Lymph Node Analysis (ALNA)
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB)
- Tumor Size
- Estrogen and progesterone receptor status
- Cell-proliferative indices
- Genomic assays
Breast cancer: Axillary Lymph Node Analysis (ALNA)
- prognostic factor in breast cancer
- identifies if cancer has spread to the axilla on the same side as cancer --> more lymph node involvement higher risk for reoccurrence
Breast cancer interventions
- Explain breast cancer and treatment options
- Be knowledgeable about cancer treatment options and the evidence or research.
- Reduce fear and anxiety and improve coping ability
- Emotional preparation begins when tentative diagnosis of cancer is made (even when screening)
Breast cancer treatments
- radiation
- chemo
- hormone therapy
- immunotherapy/targeted therapy
- surgery
Radiation therapy
- Follows breast conserving surgery to decrease chance of local recurrence and eradicate any microscopic cancer cells
- Can be primary, adjuvant, or palliative treatment
- usually begins six weeks after surgery to allow healing
- chemotherapy is indicated, radiation follows it
- External beam irradiation delivered on a daily basis over 5 to 6 weeks to entire breast area
- A "boost" treatment may be given either before or after radiation therapy has been completed
High-dose brachytherapy
- Internal radiation
- Alternative to traditional radiation for early-stage breast cancer
- Balloon brachytherapy (MammoSite®) - recent advance: uses balloon catheter to insert radioactive seeds into breast after the tumor is removed, radiation dose is focused on area at highest risk for tumor recurrence
- Performed over 1-5 day period as outpatient
- No source of radiation remains in body between treatments or after final treatment (inserted only during)
Nursing interventions after radiation
- Use mild soap with minimal rubbing.
- Avoid perfumed soaps or deodorants.
uUse hydrophilic lotions (Lubriderm, Eucerin, Aquaphor) for dryness; check first with radiologist.
uUse nondrying, antipruritic soap (Aveeno) if dryness occurs.
- Avoid tight clothes, underwire bras, excessive temperatures, and ultraviolet light
Anti-estrogen agents: Tamoxifen
- primary hormone used in breast cancer treatment for estrogen positive tumors at all stages
- major side effect: hot flashes
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
- monoclonal antibody to HER-2
- used alone or in combination with other chemotherapy to treat clients with metastatic breast cancer or whose tumors overexpress HER-2
- these women usually have poorer prognosis
Lumpectomy along with radiation therapy
- Found to equal overall survival rate of modified radical mastectomy
- Removal of entire tumor along with a margin of normal tissue
- Contraindications: small breast size in relation to tumor (unacceptable cosmetic result); multifocal masses and calcifications; masses in more than one quadrant; central location of tumor near the nipple
Lymphatic Mapping and Sentinel Node Biopsy
- May provide the same prognostic information as the axillary dissection
- hand held probe to located the sentinel node, excises it, and has it examined by pathologist
- sentinel node is negative for metastatic breast disease, axillary dissection is not needed
- associated with a lower morbidity and a greater accuracy as compared with a complete axillary node dissection
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND)
- Removal of some or all fat-enmeshed axillary lymph node to determine extent of disease spread
Modified Radical Mastectomy
- Removal of the breast and axillary lymph nodes; preserves the pectoralis major muscle
- Selected over lumpectomy is tumor too large to excise with good margins and reasonable cosmetic result.
- Option of breast reconstructive surgery (immediate or delayed up to 6 months)
Radical mastectomy
- Removal of the breast tissue along with pectoralis major and minor muscles plus axillary lymph node dissection
Breast cancer: Post Breast Therapy Pain Syndrome (PBTPS)
- Often caused by injury to nerves during surgery (commonly intercostobrachial nerves)
- Chemotherapy and Radiation therapy can also be a contributing factor.
- Phantom breast pain: pain after mastectomy
- Symptoms lasting longer than 3month healing time: (mild to debilitating, upper arm pain, tingling sensation in the arm, continuous aching and burning, numbness, shooting pain, unbearable itching)
Post Breast Therapy Pain Syndrome (PBTPS) interventions
-ROM and exercise to affected shoulder.
- NSAIDS
- Narcotics
- PT
CM of colorectal cancer
- Insidious onset: symptoms often do not appear until disease is in advanced stages
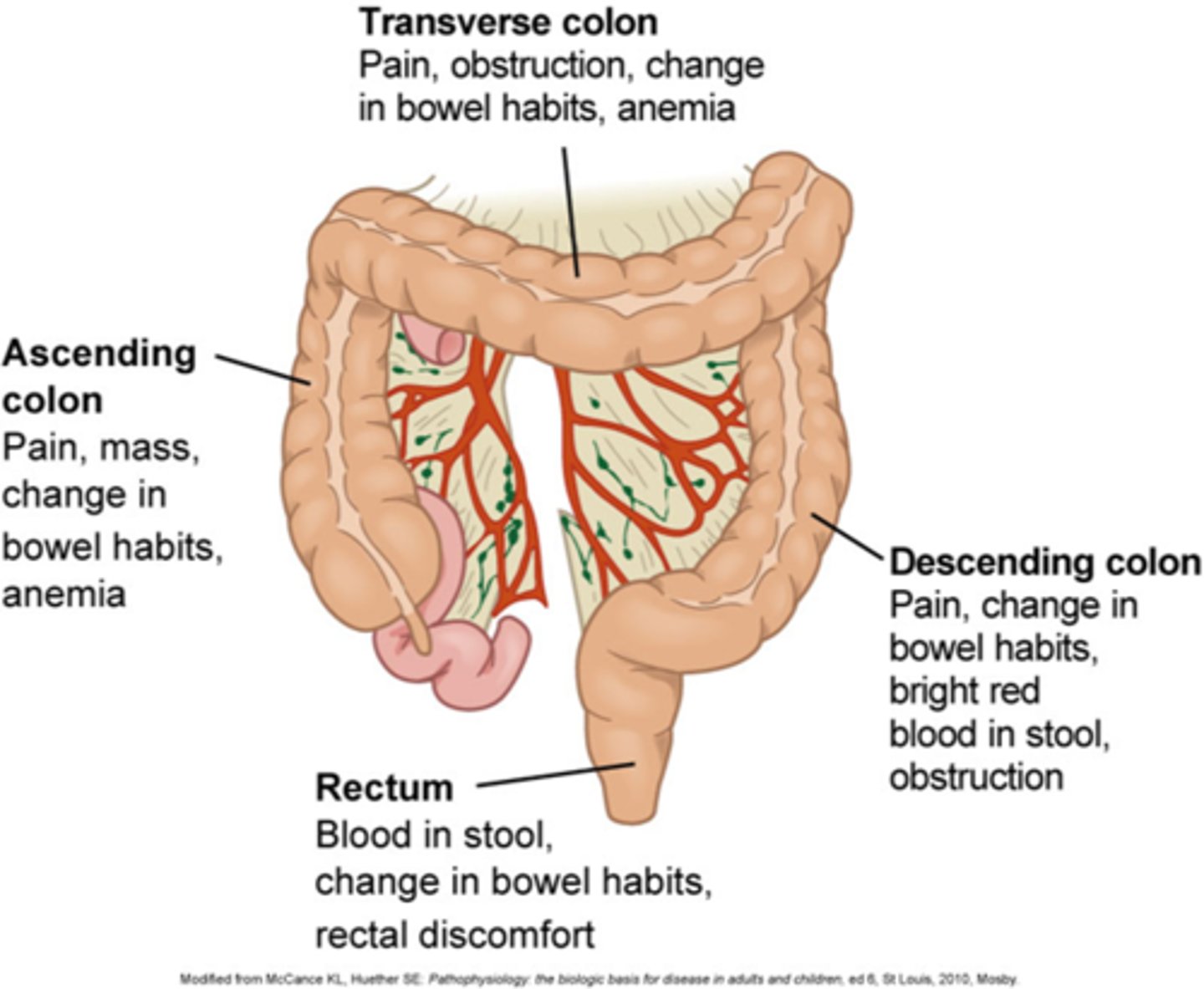
CM of early disease of colorectal cancer
Early disease:
- Nonspecific findings (fatigue, weight loss) or none at all
CM of more advanced colorectal cancer
- Abdominal tenderness
- Palpable abdominal mass
- Hepatomegaly
- Ascites
- Anemia from GI bleeding
- change in bowel habits: rectal bleeding is most common, alternating constipation and diarrhea, change in stool caliber, narrow, ribbon-like, sensation of incomplete evacuation (tenesmus)
Colorectal obstruction complications CM
- GI bleeding
- From extension of tumor and ulceration into surrounding blood vessels → hemorrhage
- Perforation
- Abscess formation
- Peritonitis
- Sepsis/septic shock
Colorectal cancer screening
- Regular screening for polyps and cancer from ages 45 to 75 years of age
- Screening after age 75 based on personal choice, life expectancy, co-morbidities, etc.
- Not recommended after age 85
- Colonoscopy every 10 years with digital rectal exam (gold standard for CRC screening because the entire colon is examined, olyps can be immediately removed & biopsied)
- Persons at higher risk should get colonoscopies earlier
- Bowel prep required
- Yearly tests: high sensitivity fecal occult blood test (FOBT), fecal immunochemical test (FIT), test for blood in the stool (must be done frequently to catch intermittent bleeding common with tumor)
Colon cancer diagnostics
- Blood tests
- CBC & Coagulation studies
- CMP
- Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): sometimes produced by colorectal cancer cells, but NOT a good screening tool because of a large number of false positives, may be used to monitor for disease recurrence after surgery or chemotherapy
- Tissue Biopsy (Gold Standard): confirm cancerous tissue and determine differentiation
- Imaging: MRI , CT scan & Chest X-ray to check for metastasis, tumor depth and penetration of tumor in bowel wall
Surgery for colorectal cancer
Surgical goals
1. Complete resection of tumor
2. Thorough exploration of abdomen
3. Removal of all lymph nodes that drain the area
4. Restoration of bowel continuity
5. Prevention of surgical complications
- May be treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation before surgery to shrink the tumor
Types of colectomies
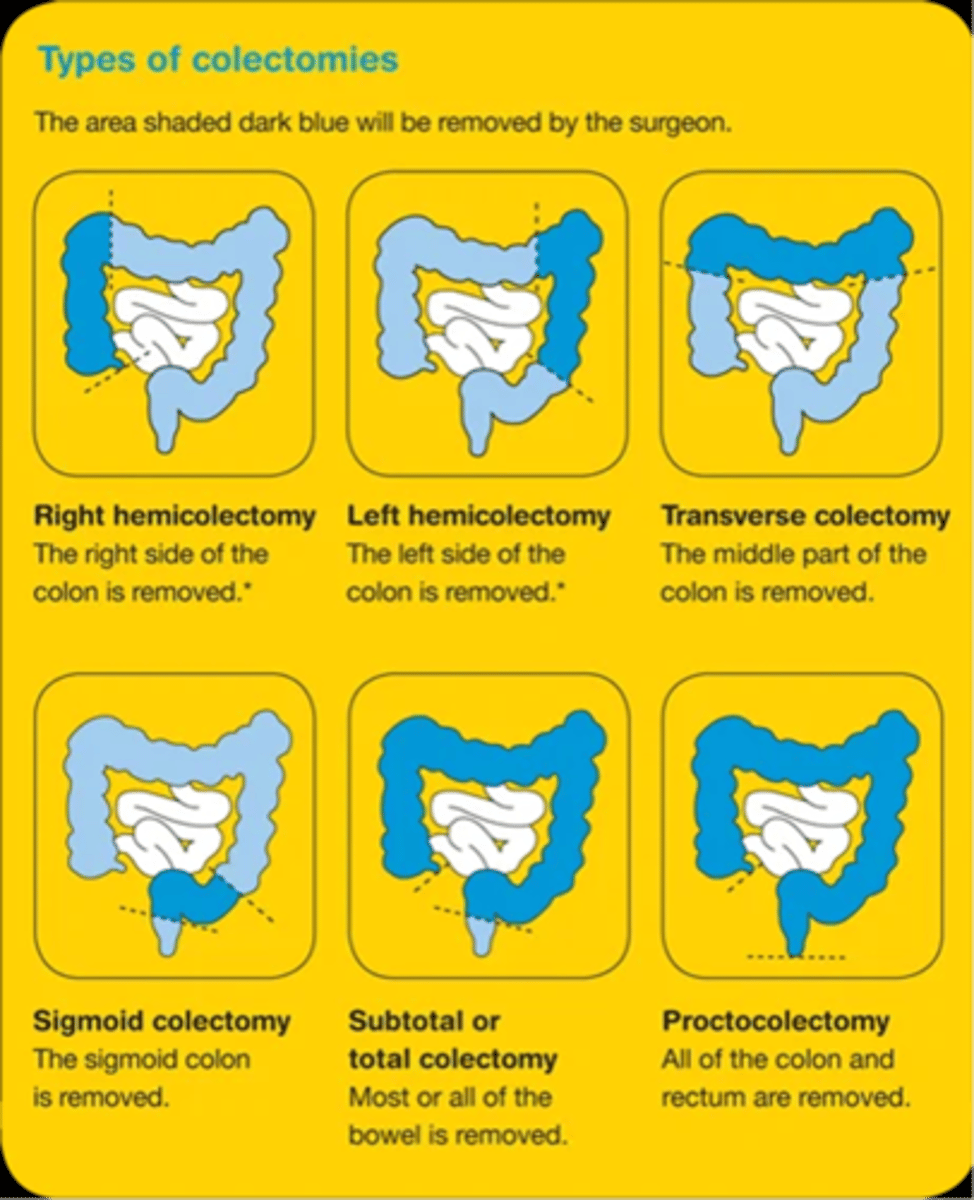
Colorectal cancer nursing assessment
- Polyps
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Medications
- Weakness or fatigue
- Pain
- Change in bowel habits
- High-calorie, high-fat, low-fiber diet
- Increased flatus
- Feelings of incomplete evacuation
- Bloody stool (hematochezia)
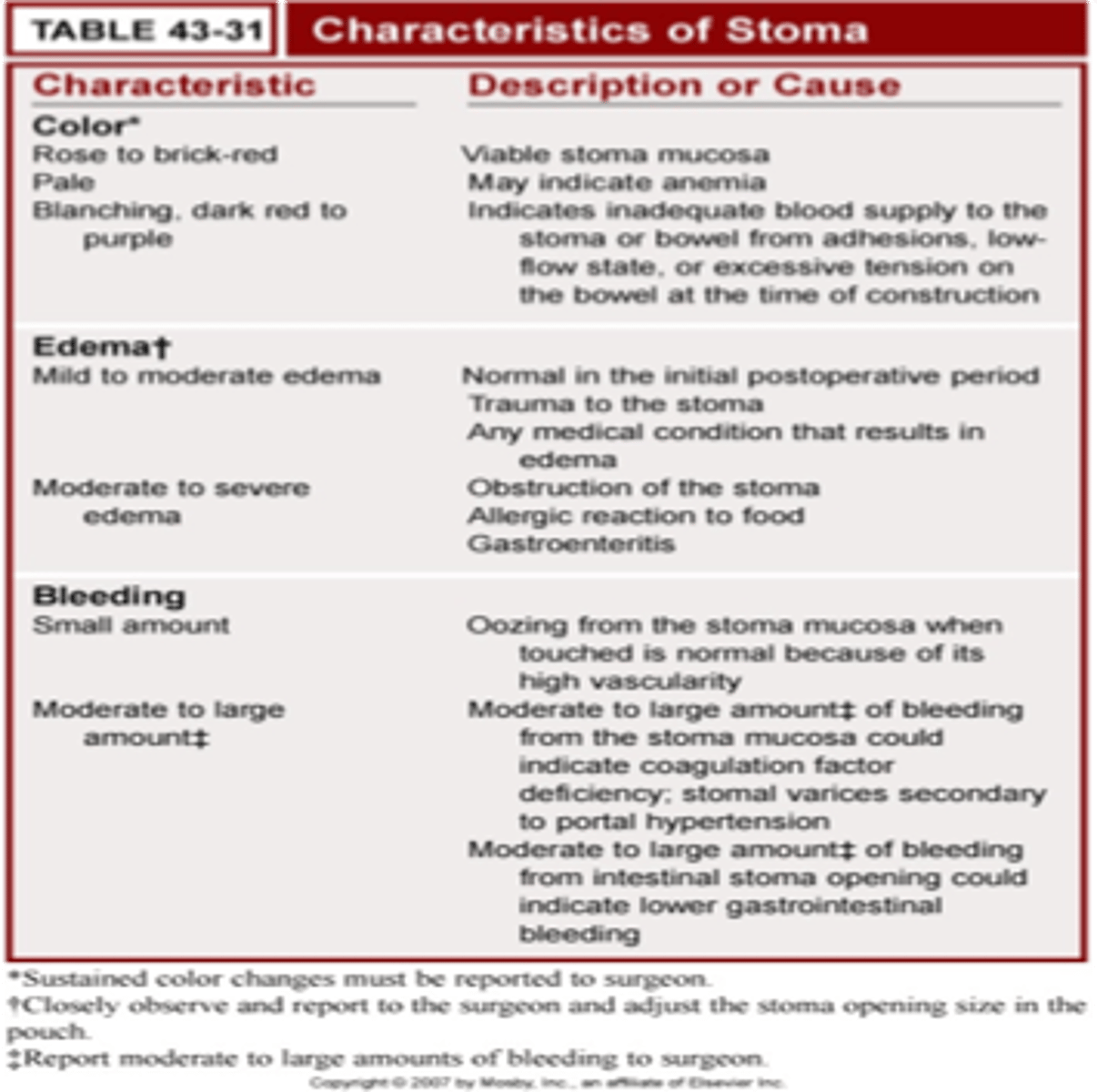
Stoma characteristics