Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
List the boiling points of the carboxylic acid derivatives from lowest to highest.
aldehyde~ketone~acyl chloride~ester<nitrile<carboxylic acid<amide
Dipole-dipole interactions and H+ bonding increase bp.
Why does the pi bond between C and O break when the nucleophile attacks in addition elimination reaction
It is the weakest bond in the molecule.
What is the difference in nucleophilic substitution and nucleophilic addition elimination?
Substitution = Sigma bond breaks
Addition elimination = Pi bond breaks
Name the reactivity of carbonyls from least to most

Why do weaker bases form the tetrahedral faster?
Strong bases can from double bonds with the carbon and make the carbon not very electron deficient, which makes it harder for the Nu- to attack it. (resonance contributors)
weak bases are also easier to eliminate
What are the two steps of the reactions w/ negative nucleophiles?
Formation of tetrahedral intermediate
Collapse of tetrahedral intermediate
What step is added in the middle when a reaction occurs with a neutral nucleophile instead of a negative one?
Depronation of the protonated tetrahedral intermediate.
When acyl chlorides react with an ether they give an . . .
ester and HCl
When acyl chlorides react with H2O they give an . . .
alcohol and HCl
When acyl chlorides react with an amine they give an . . .
Amide and CH3NH+3Cl-
How many amines are required to react with an acyl chloride to give an amide?
2 because another amine is needed to react with HCl to give a corresponding salt
What are the three main reactions Esters undergo?
Hydrolysis, transesterficaiton, and aminolysis
What are the types of hydrolysis ester can undergo?
Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis of ester w/ tertiary alkyl group
Hydroxide - Ion Promoted Hydrolysis of an Ester
Which ester reaction is slow, needs a catalyst, and converts 1 compound into 2 without alcohol?
Hydrolysis
Which ester reaction is slow, needs a catalyst, and uses alcohol to convert 1 compound into 2 compounds?
Transesterification
Which ester reaction is not slow, does not need a catalyst, forms amide and alcohol and increases rate with heat?
Aminolysis
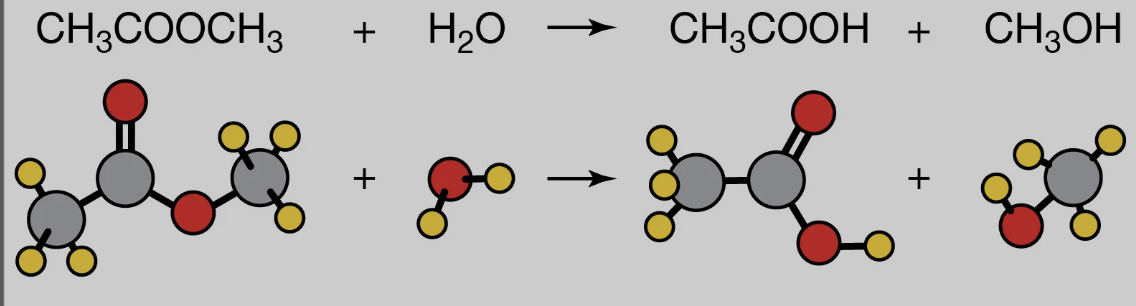
Name reaction
Hydrolysis of Ester
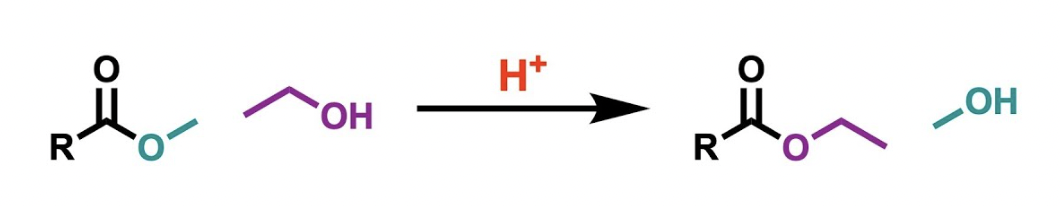
Name reaction
Transesterification
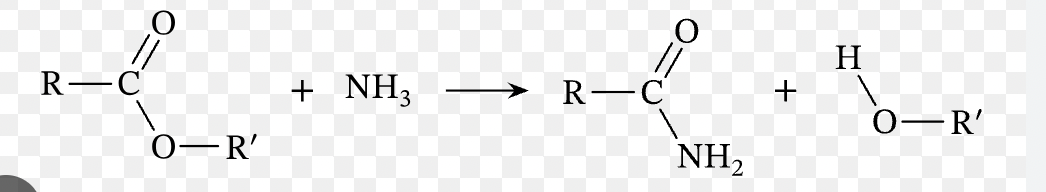
Name reaction
Aminolysis of an ester
Do weaker or stronger bases make for better leaving groups?
Weaker
In hydrolysis of an ester, the relative amount of intermediates depends on:
pH of solution
pKa of intermediate
In hydrolysis of an ester, how do you drive forward to a carboxylic acid?
Periodically remove alcohol
Use excess water
In tranesterfication how do you drive the reaction forward?
Excess alcohol
The acid catalyst in transesterification has 2 purposes:
Protonate carbonyl oxygen and increase the susceptibility of carbonyl carbon to nucleophilic addition.
Protonate the leaving to make it a better leaving group.
What are the three types of hydrolysis for an ester
Hydroxide-Ion Promoted
Hydrolysis of Ester w/ 3° alkyl group
Hydrolysis of Ester w/ 1° and 2° alkyl group
Is water or hydroxide ion a better nucleophile?
Hydroxide ion
Compare acid catalyzed and OH- promoted hydrolysis.
Acid Catalyzed isn’t reversible.
OH- only promotes hydrolysis.
Why do amides not undergo addition-elimination without catalyzation?
Until amino group is pronated, it is stronger than OH-.
When amides react with water what do they form? What about when they react with alcohol?
Water → Carboxylic Acid
Alcohol → Ester
Whats formed by mixing 2 carboxylic acids?
Acid Anhydrides
How do acid anhydrides react w/
Alcohol
H2O
Amine
Alcohol: Ester and Carboxylic Acid
H2O: 2 Carboxylic Acid
Amine: Amide & carboxylate ion
When acid anhydrides and amines react, how many amines must be used?
2
Nitriles are even more resistant than amides, which means they need to be in the presence of what?
Heated acid
How can a alkyl halide turn into nitrile?
SN2 reaction (-C=N/DMF)
How do you convert a nitrile into a 1° amine?
with H2/Raney NIckel
Acid catalyzed hydrolysis of a nitrile produces what?
Carbox. Acid
Carbox. Acids react w/ alcohol to form:
What is this reaction called?
Ester and Water
Fischer’s Esterification
How is fischers esterification drove to the right?
Excess alcohol
Carb. Acid + Amine is an Acid-Base reaction, what needs to be done in order to form the amide?
Add heat (225°C). If not heated it will produce an ammonium caboxylate salt
Why do dicarboxylic acids have 2 pKa values?
Protons are lost one at a time and it is harder for 2nd proton to be lost because the compound is negative.
How does the number of carbons relate to the acidity?
More carbons = Less acidic
When dicarboxylic acids are heated, what do they do?
Readily lose H2O
How do you form anhydrides?
React dicarb. acids and acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride
To activate carbox. acids OH is made into a better leaving group, how can you do this?
Use thionyl chloride
Use Phosphorous Trichloride
Use phosphorous pentoxide