WJEC AS Chemistry Unit 2.2 - Rates of Reaction
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Collision Theory
For an effective collision to occur, the particles collide with;
The minimum amount of energy (greater than or equal to Ae)
Correct orientation
Any factor which increases the frequency of effective collisions increases reaction rate
Calculating rates
Change in x/time
Calculating rate from a graph
Gradient
Factors that affect the rate of reaction
Concentration
Temperature
Particle size
Catalysts
Light
How concentration affects the rate
Increasing conc/pressure increases the rate of reaction
More molecules in a given volume. Distances between molecules are reduced so there is an increase in the number of collisions per unit time. Greater chance that the number of effective collisions increases, the rate of reaction increases
How temperature increases the rate of reaction
increasing temp increases the rate of reaction
Increase in KE of the molecules and so they will move faster. This means that more molecules will have enough energy to react on collision. Reaction rate will increase
How particle size affects rate
reducing size increases the SA of the molecules
Molecules closer together
Increase in number of collisions per unit time
Reaction rate will increase
How catalysts affect rate
Increases the rate of chemical reaction without undergoing a permanent change itself
How light affects rate
Some reactions are much more vigorous when carried out in bright light
Activation energy
The minimum energy required to start a reaction by breaking of bonds
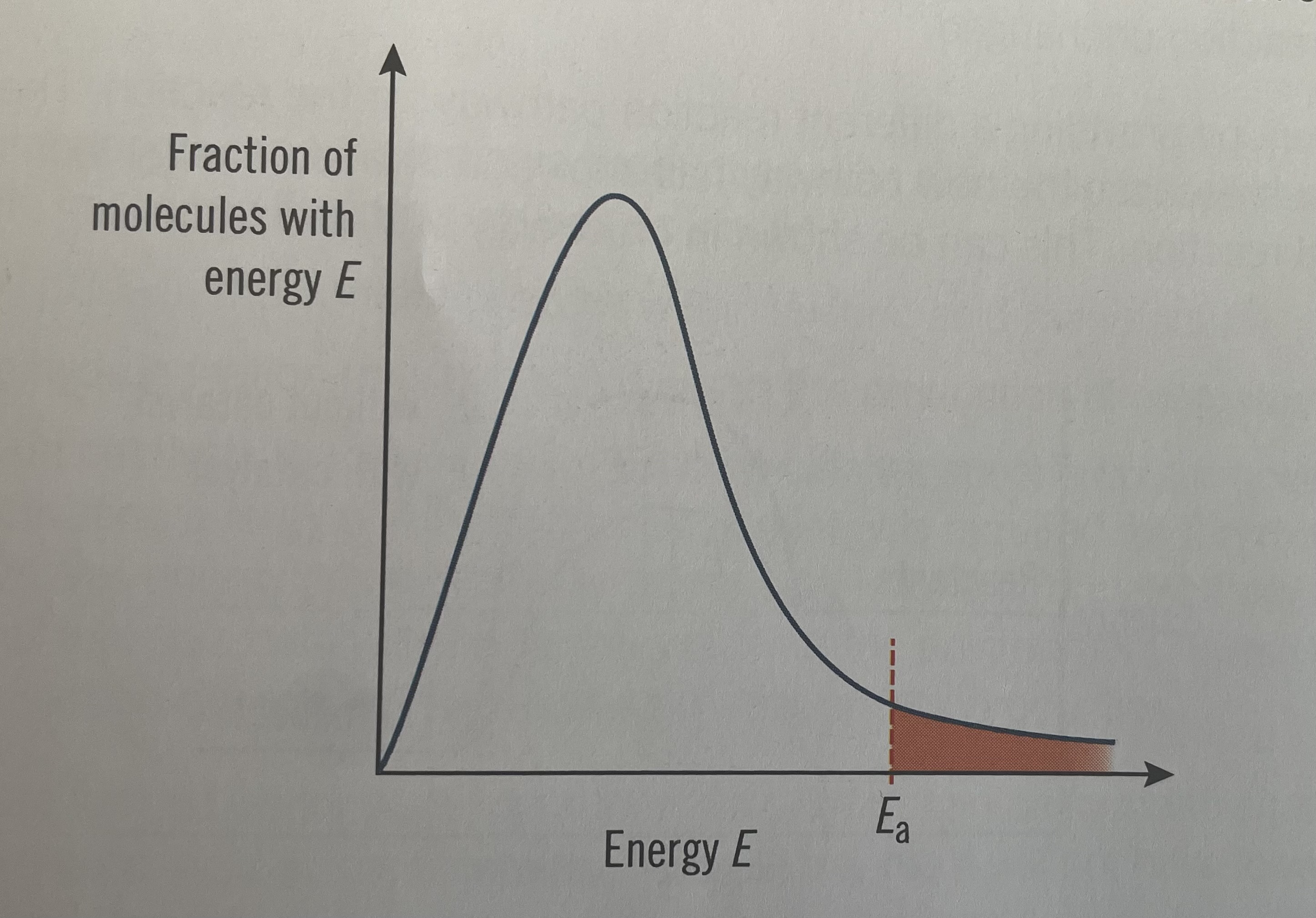
Boltzmann energy distribution curve
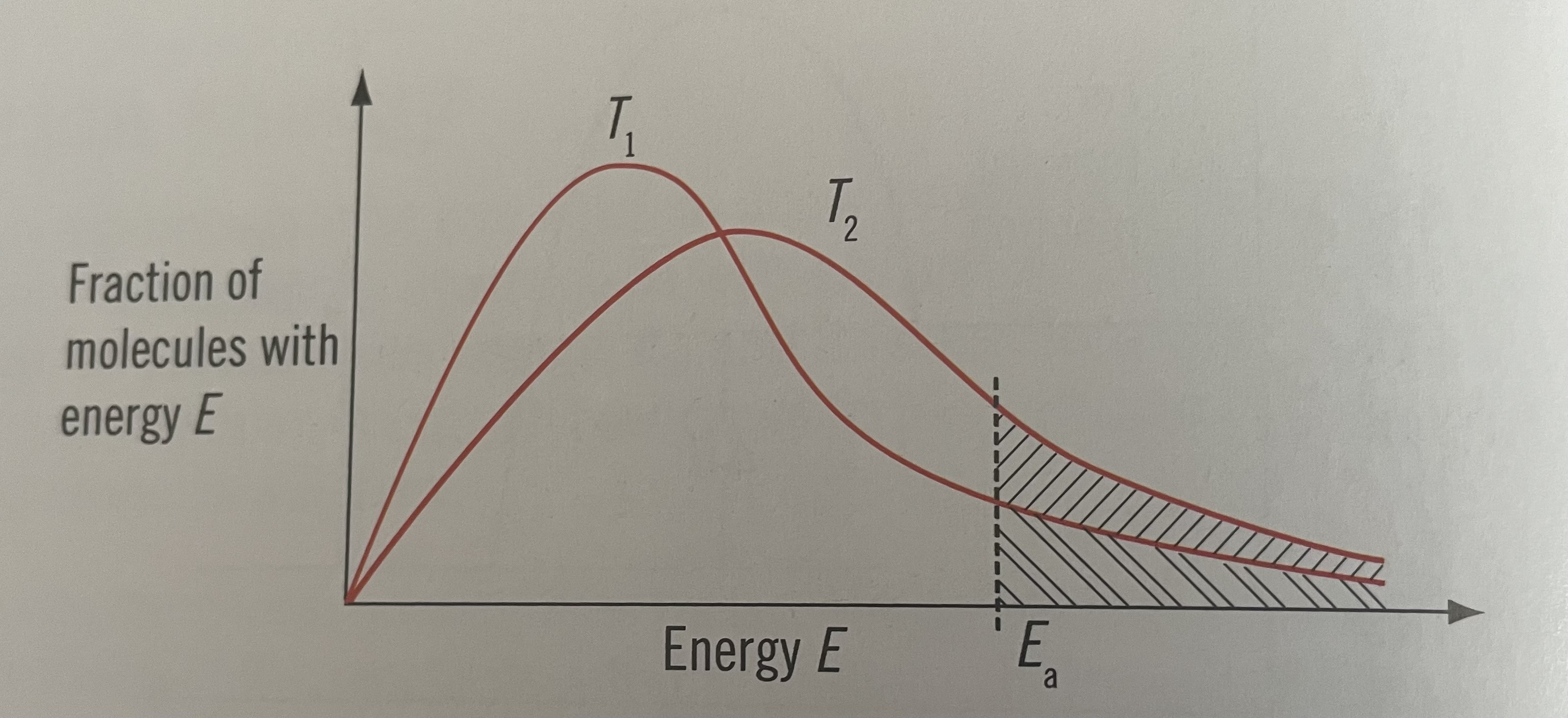
Boltzmann energy distribution curve at a higher temperature
curve moves the right towards higher energies
Curve is flatter
At the higher temperature, more molecules have energy greater than or equal to Eact so the frequency of effective collisions increases and so does the rate
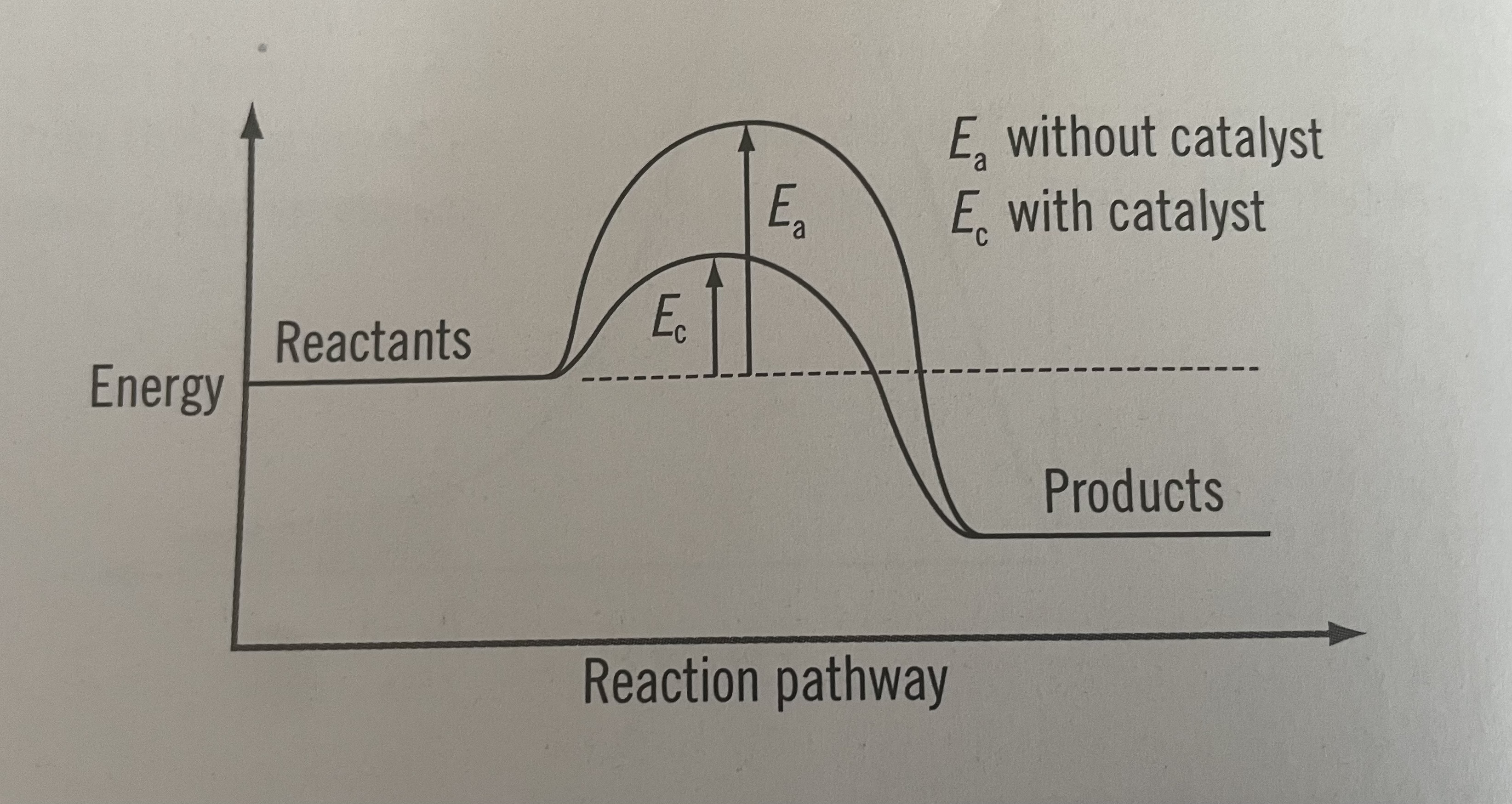
Catalysts
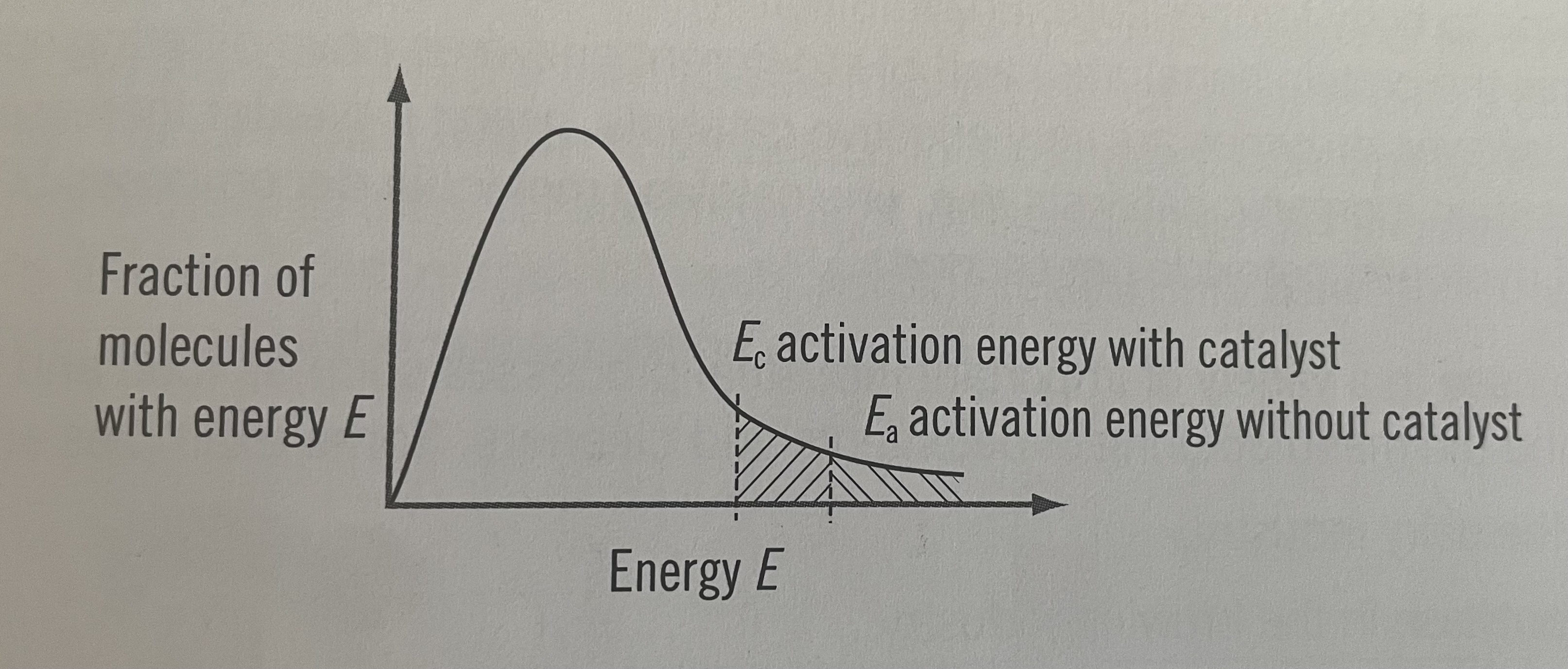
Provide an alternative route with a lower activation energy
Substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without being used up in the process
Energy profile diagram with catalyst
Boltzmann energy distribution curve with a catalyst
Types of catalyst
Homogenous
Heterogeneous
Homogenous catalysts
Catalysts in the same state as the reactants
Heterogenous catalysts
Catalyst is in a different state from the reactants
Enzymes
Biological catalysts
Methods of studying rates of reaction
Change in gas volume
Change in gas pressure
Change in mass
Colorimeter
Colorimetry to study rates
used when one of the reactants or products in a reaction is coloured, meaning there is a change in colour as the reaction proceeds
The intensity of the colour at any time is related to the concentration of the coloured substance