Diversity of Living Things
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
Biodiversity
The number and variety of species and ecosystems on Earth
Species
All organisms capable of breeding freely with each other under natural conditions
Hybridization
The crossbreeding of two different species
Morphology
The physical appearance and characteristics of an organism; also the science of the study of these physical characteristics
Evolutionary changes
A change that occurs in an entire population; usually occurs over a long period of time
Genetic diversity
The genetic variability among organisms -- usually referring to individuals of the same species
Species diversity
A measure of diversity that takes into account the quantity of each species present, as well as the variety of different species present
Structural diversity
The range of physical shapes and sizes within a habitat or ecosystem
Species interaction
Food supply, protection, transportation, reproduction, hygiene, and digestion
Biological classification
The systematic grouping of organisms into biological categories based on physical and evolutionary relationships
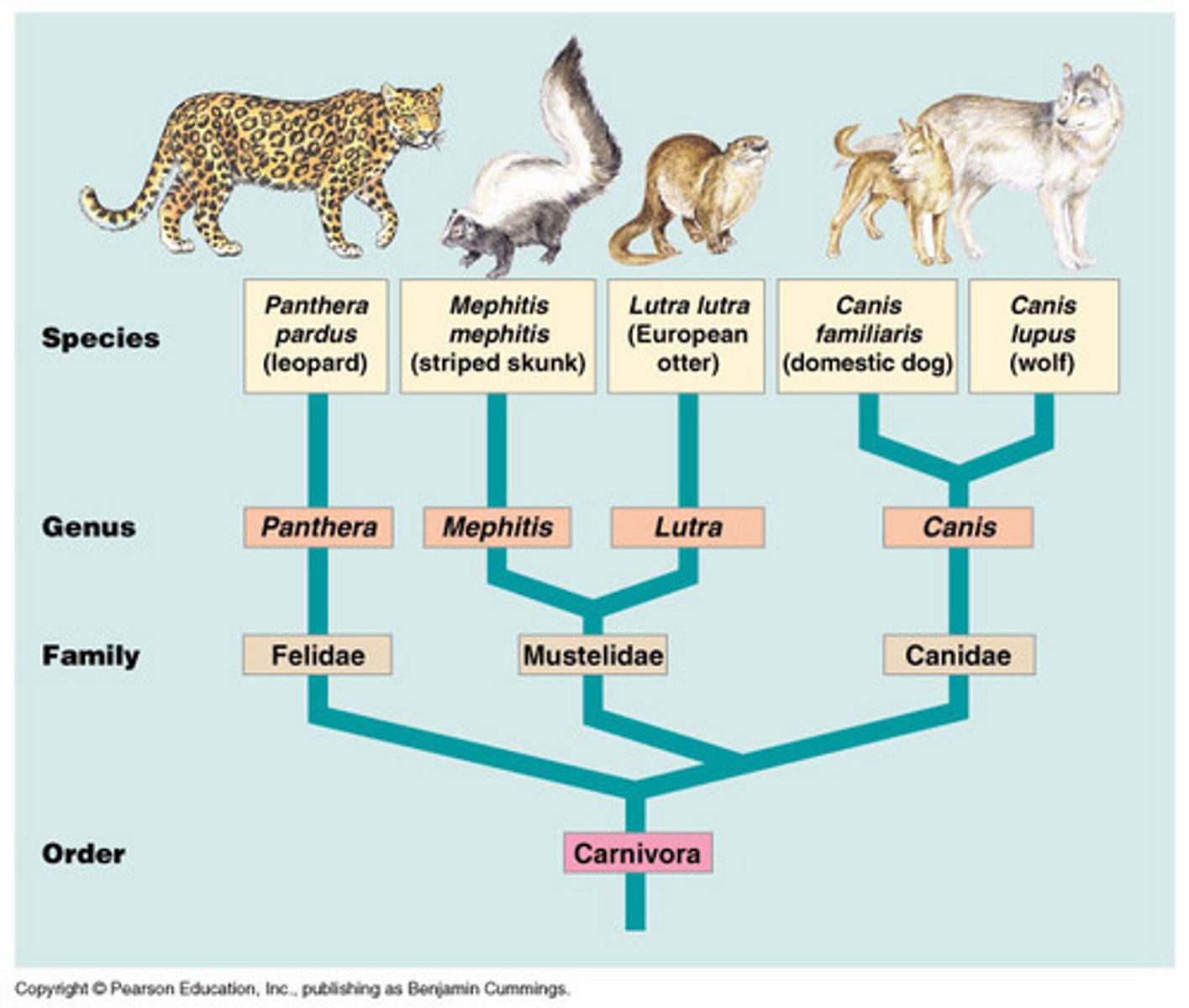
Taxonomy
The science of classifying all organisms; taxonomists classify both living and fossil species
Carl Linnaeus
A Swedish naturalist (1707-1778) who is considered to be the "father" of taxonomy; he introduced a consistent way of grouping species according to morphological similarities and established a naming system
Genus
A taxonomic level consisting of a similar group of similar species
Binomial nomenclature
The formal system of naming species whereby each species is assigned a genus name followed by a specific name
Seven taxa
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
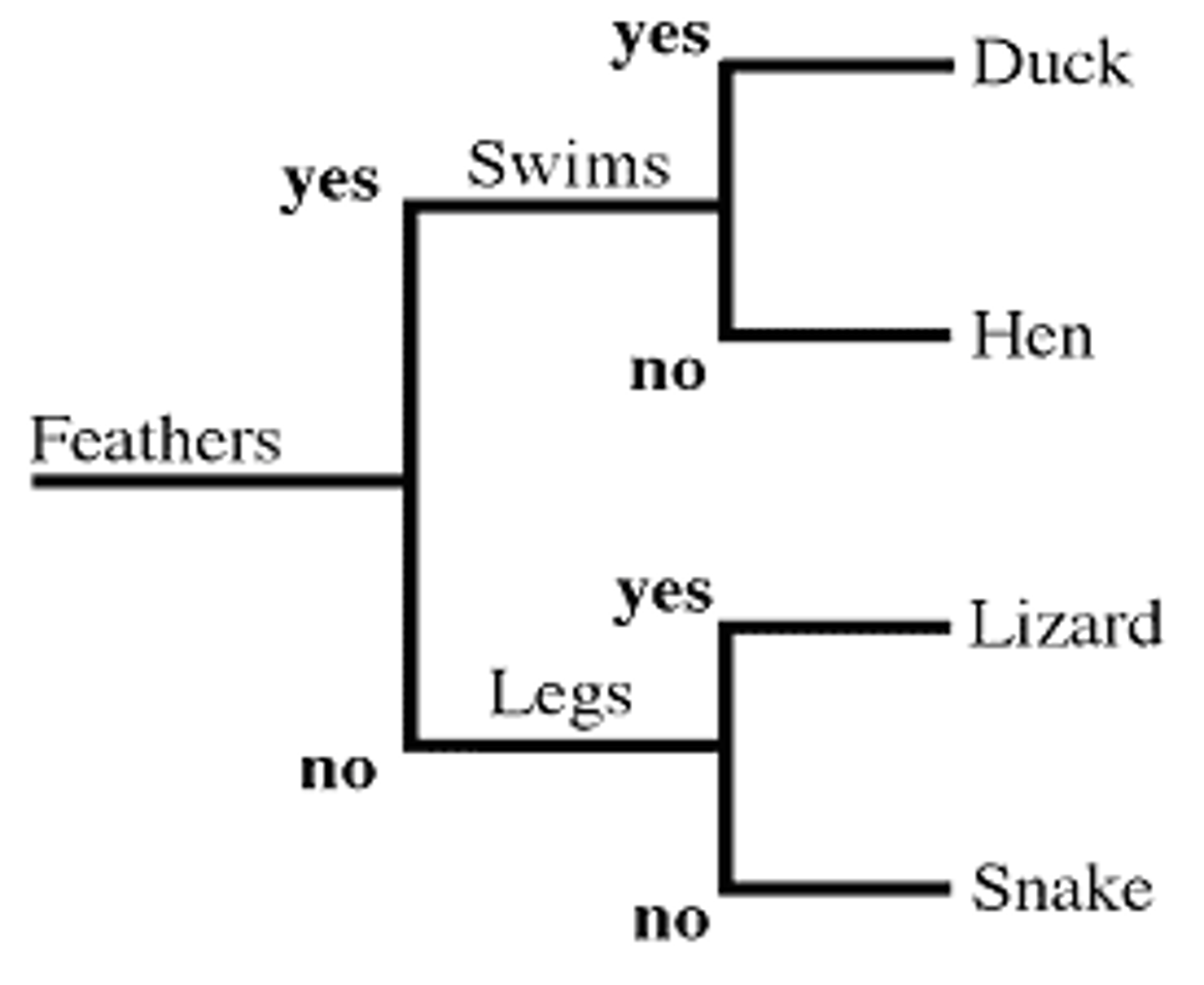
Dichotomous key
Phylogeny
The study of the evolutionary relatedness between, and among, species
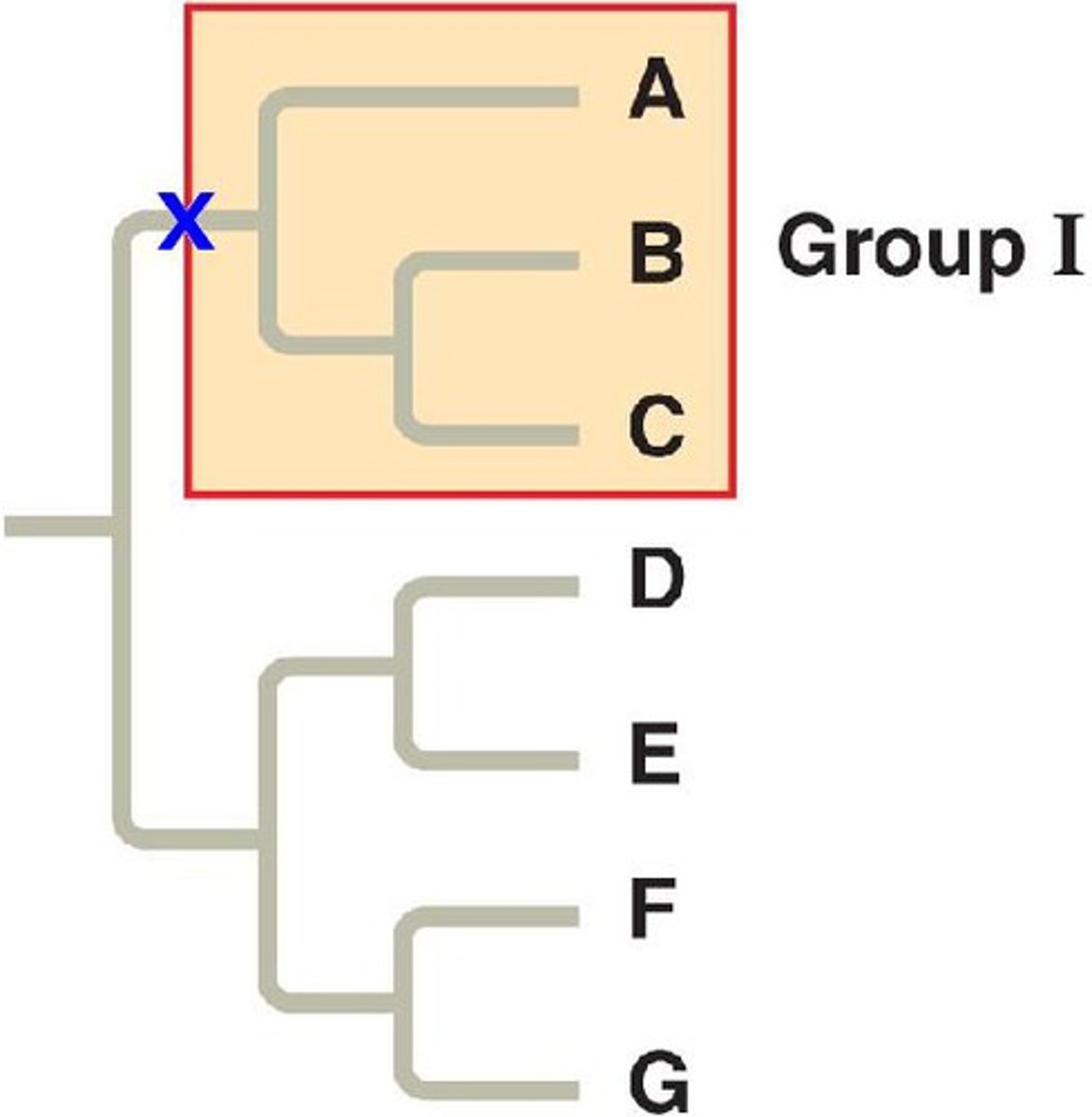
Phylogenetic tree
A diagram depicting the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups
Clade
A taxonomic group that includes a single common ancestor and all its descendants
Prokaryote
A single-celled organism that does not contain membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote
Any organism whose cells contain organelles; some eukaryotic organisms are single-celled, while others are multicellular
Six Kingdoms of Life
Eubacteria, archaea, protista, fungi, plants, and animals
Eubacteria
-Prokaryotic
-Cell walls contain a unique compound
-Cells are variable in shape and size
-Have diverse means of obtaining energy/nutrients
-All can reproduce asexually
Archaea
-Prokaryotic
-Cells walls and cell membranes have a unique structure
-Most are extremely small
-Some colonize extreme environments
-All can reproduce asexually
Protista
-Eukaryotic
-Cells have extreme diversity of cellular structure
-Some have chloroplasts and cell walls
-May be heterotrophic/autotrophic/both
-Have variable forms of movement
-Usually live in aquatic or other moist environments
-Reproduce asexually and sexually
Fungi
-Eukaryotic
-Cell wall composed of chitin
-Most are multicellular
-Cells have no chloroplasts
-All are heterotrophic
-Most are terrestrial
-Reproduce asexually and sexually
Plants
-Eukaryotic
-All are multicellular
-Cell walls are composed of cellulose
-Possess chloroplasts
-Are autotrophic and photosynthetic
-Most are terrestrial
-Reproduce asexually and sexually
Animals
-Eukaryotic
-All are multicellular
-Cells have no walls or chloroplasts
-All are heterotrophic
-Most reproduce sexually
-Live in terrestrial and aquatic environments
Three Domains of Life
Eubacteria, Archaea, Eukaryotes
Six Major Groups of Bacteria
Proteobacteria (purple bacteria), green bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), gram-positive bacteria, spirochetes, chlamydias
Proteobacteria (purple bacteria)
-Some are photosynthetic with a form of photosynthesis different from plants
-Ancient forms of these bacteria were the likely ancestors of eukaryotic mitochondria
-Some are nitrogen fixing
-Are responsible for many diseases including bubonic plague, gonorrhea, dysentery, and some ulcers
Green bacteria
-Use a form of photosynthesis that differs from plants
-Are usually found in salt water environments or hot springs
Cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria)
-Use a form of photosynthesis similar to plants and other eukaryotes
-Ancient forms of these bacteria were likely the ancestors of eukaryotic chloroplasts
-Play major roles as produces and nitrogen fixers in aquatic ecosystems
-Form symbiotic relationships with fungi
Gram-positive bacteria
-They cause many disorders (anthrax, strep throat, bacterial pneumonia, and meningitis)
-Used in food production
-Some lost their cell wall
-One type -- mycoplasms -- are smallest known cells
Spriochetes
-Spiral-shaped flagellum is embedded in their cytoplasm
-Move with corkscrew motion
-Cause syphilis
Chlamydias
-All are parasite that live within other cells
-Cause chlamydia, one of the most common STIs
-Cause trachoma, leading cause of blindness in humans
Plasmid
A small loop of DNA often found in prokaryotic cells; usually contains a small number of genes
Capsule
An outer layer on some bacteria; provides some protection for the cell
Coccus
Round bacterial cell
Bacillus
Rod-shaped bacterial cell
Spirillum
Spiral or corkscrew-shaped bacterial cell
Diplo
Pairs
Staphylo
Clumps
Strepto
Strings
Obligate aerobe
A organism that cannot survive without oxygen
Facultative aerobe
An organism that can live with or without oxygen
Fermentation
An anaerobic process that releases chemical energy from food
Obligate anaerobe
An organism that cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
Binary fission
The division of one parent cell into two genetically identical daughter cells; a form of asexual reproduction
Conjugation
A form of sexual reproduction in which two cells join to exchange genetic information
Transformation
A process in which a bacterial cell takes in and uses pieces of DNA from its environment
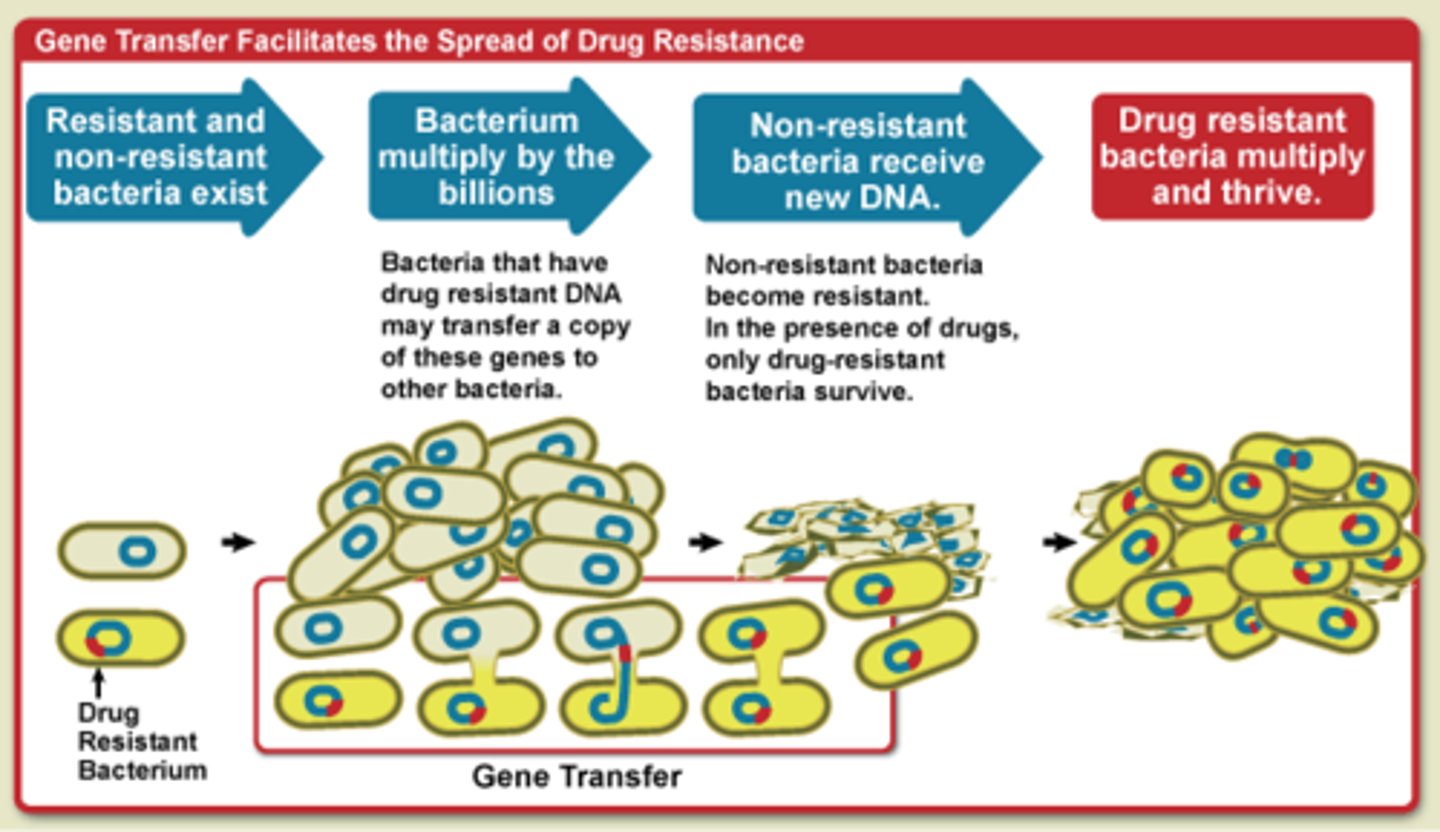
Horizontal gene transfer
Any process in which one species gets DNA from a different species
Endospore
A dormant structure that forms inside certain bacteria in response stress; protects the cell's chromosome from damage
Importance of bacteria
-Play key roles in ecosystems, many are decomposers and producers
-Recycle nutrients and are vital to biogeochemical cycles
-Fix, or convert, atmospheric nitrogen into chemical compounds
-Essential residents in the intestines of animals
-Essential in production of foods
-Produce antibiotics
Meningococcal disease
Caused by bacterium Neisseria meningitidis
Carried by humans in the nose and throat and are spread into the air by coughing and/or sneezing.
Can resemble symptoms of other diseases, such as flu. They include fever, headache, stiff neck, irritability, and nausea and vomiting. Can develop rapidly and dramatically, within minutes to hours. Fever can be very high and the headache can be intense.
A vaccine to prevent meningococcal disease is available for children and certain persons at risk for the disease
Treatment includes hospitalization, generally ICU, and immediate administration of IV antibiotics. Complications, such as brain swelling, seizures, and coma will also need aggressive intensive care treatment.
Antibiotic resistance
Groups of Archaea
Methanogens, halophiles, extreme thermophiles, psychrophiles
Methanogens
-Live in low oxygen environments (swamps, lakes, marshes, sewage lagoons, digestive tracts and insects)
-They generate energy by converting chemical compounds into methane
Halophiles
-They are salt-loving organisms that can live in highly saline environments
-Most are aerobic and get energy from organic food molecules
-Some use light as a secondary energy source
Extreme thermophiles
-They live in extremely hot environments (hot springs, hydrothermal vents)
-Optimal temperature range for growth is 70-90 degrees C
Psychrophiles
-They are cold-loving organisms fond mostly in the Antarctic and Arctic oceans
-Optimal temperature range for growth is -10 - -20 degrees C
Virus
A small infectious particle containing genetic material in the form of DNA or RNA within a protein capsule
Capsid
A protein coat that surrounds the DNA or RNA of a virus
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
A nucleic acid found in all cells and some viruses; usually carries genetic information that provides instructions for synthesizing protein
Bacteriophages
A virus that infects bacteria
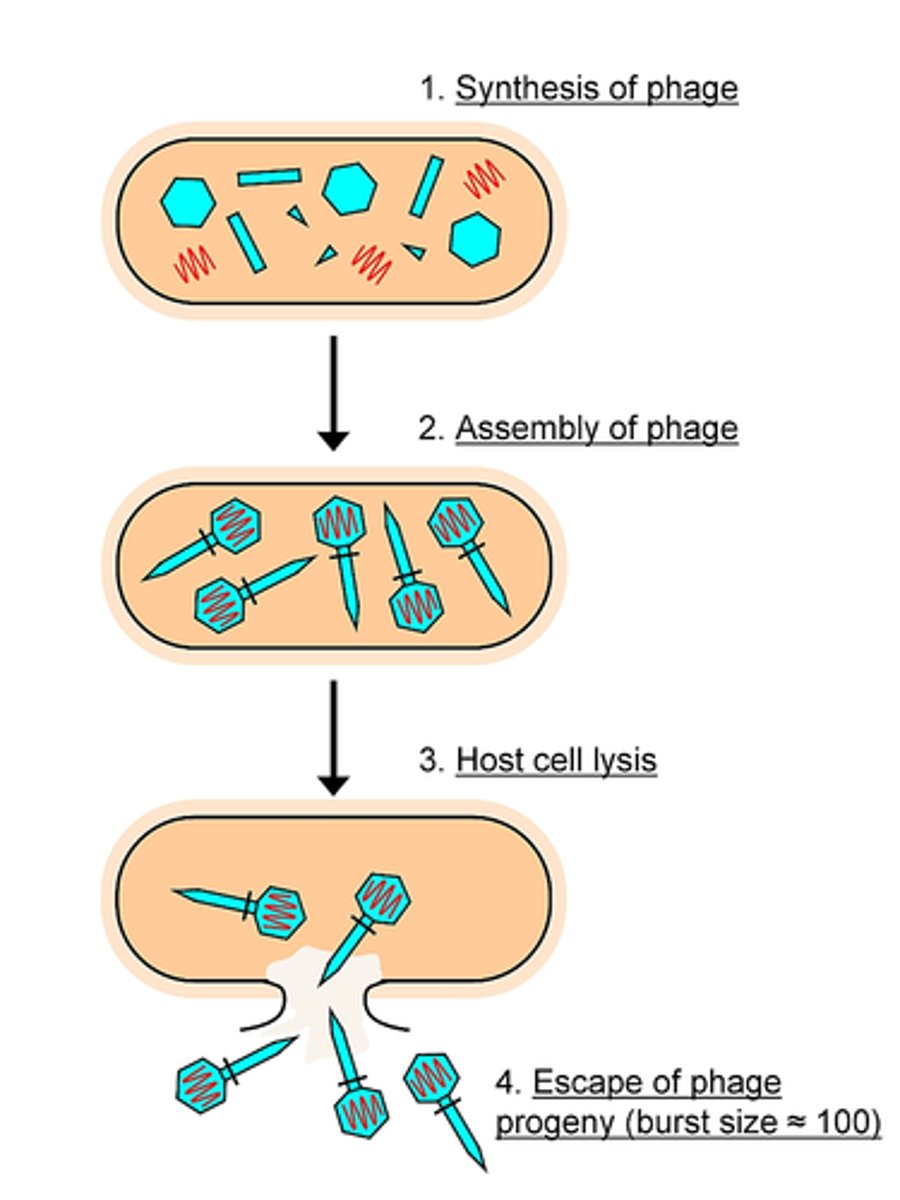
Lytic cycle
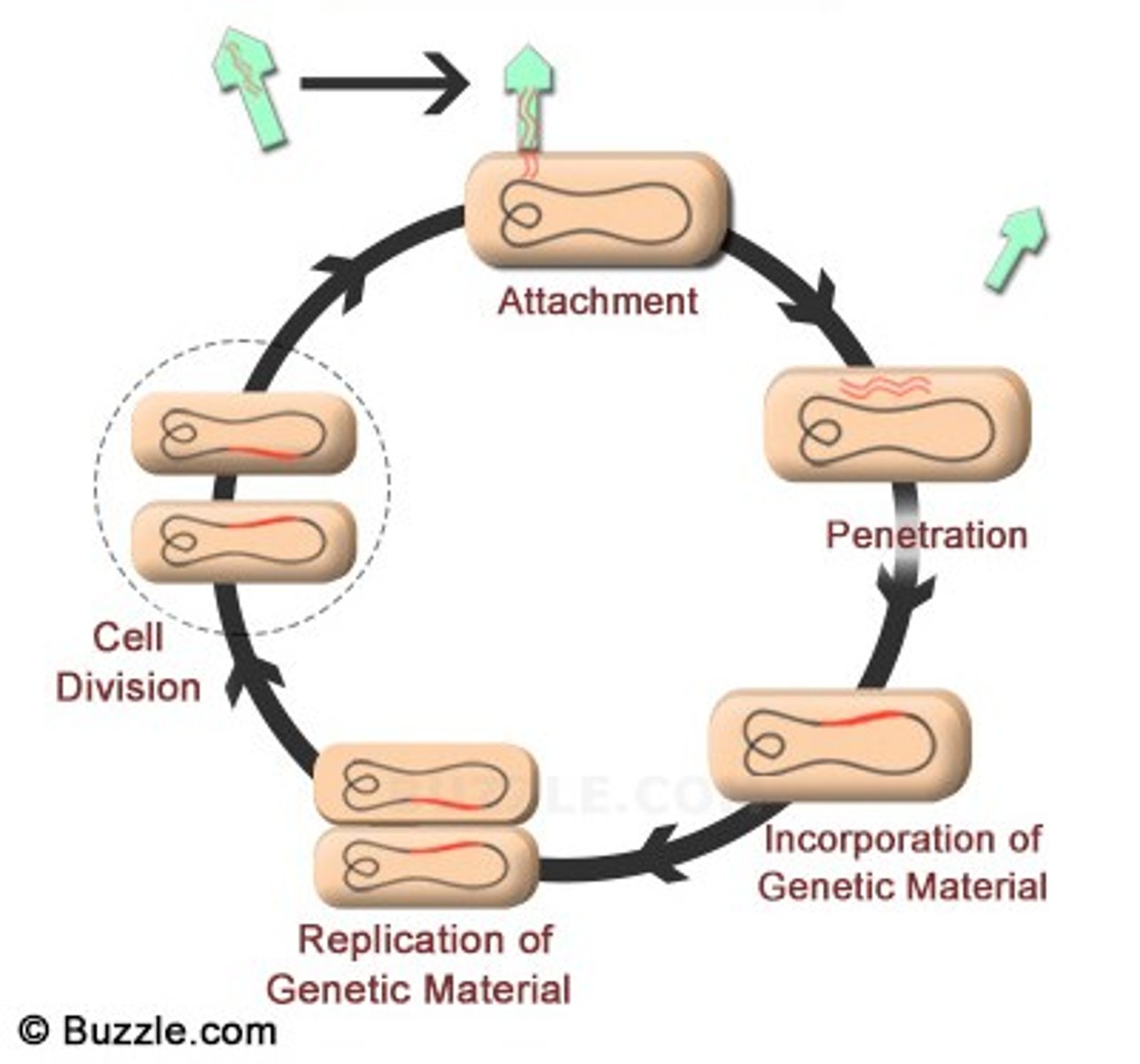
Lysogenic cycle
Lysis
The rupturing of a cell; can occur when newly made viruses are released from a host cell
Lysogeny
A state of dormancy in which viral DNA may remain within a host cell's chromosome for many cell cycle generations
Transduction
A type of gene transfer in which a virus transfers DNA from one bacterium to another
Vaccines
Mixtures that contain weakened forms or parts of a dangerous virus
Gene therapy
A method of treating disease in which genes are introduced into cells to replace, supplement, or repair a defective gene
Viroid
Very small infectious piece of RNA for some serious diseases in plants (smaller than viruses and do not have capsids)
Prion
Abnormally shaped infectious protein responsible for some brain diseases of mammals, including humans
Endosymbiosis
Relationship in which a single-celled organism lives within the cell(s) of another organism
Origins of Eukaryotes
Protists were the first. Membrane of ancestral prokaryotic cell folded developing internal membranes bounding organelles. Later endosymbiosis occured
Seven Groups of Protists
Euglenoids, ciliates, apicomplexa, diatoms, amoebas, slime moulds, red algae
Euglenoids
-Autotrophs, photosynthetic
-Unicellular
-Usually have two flagella
-Outer surface covering consists of stiff proteins
Ciliates
-Heterotrophs
-Unicellular
-Have very complex internal structures
-Have many cilia and no cell walls
Apicomplexa
-Heterotrophs
-Unicellular
-No cell wall
-All are parasites of animals
Diatoms
-Autotrophs, photosynthetic
-Unicellular
-Move by gliding
-Covered by glass like silica shells
Amoebas
-Heterotrophs
-Some have hard outer skeletons
-Move by extensions of the cytoplasm called pseudopods
Slime moulds
-Heterotrophs
-Life cycles have unicellular and multicellular stages
-Move with flagella or pseudopods
Red algae
-Autotrophs, photosynthetic
-Almost all are multicellular
-Have no cilia or flagella
-Cell walls are made of cellulose
Haploid
A cell containing half the usual complement of chromosomes (n)
Diploid
A cell containing two copies of each chromosome (2n)
Zygote
A cell formed by the fusion of two sex cells; is diploid
Life cycle of brown algae
Zygote (diploid)
Young sporophyte
Mature sporophyte
Haploid spores released
Male gametophyte and female gametophytes release gametes
Sperm fertilizes egg
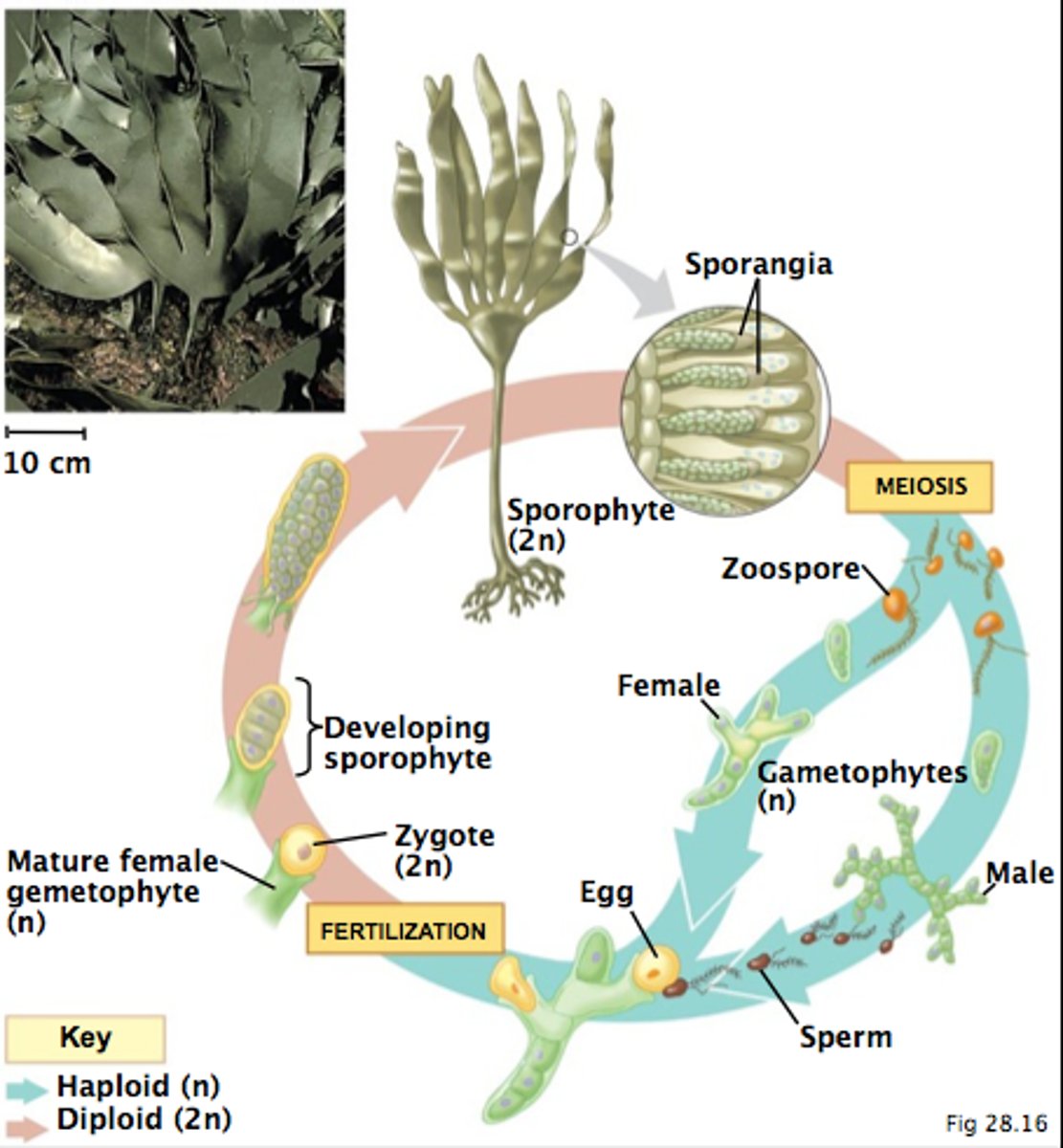
Sporophyte
A diploid organism that produces haploid spores in an alteration of generations life cycle
Spore
A haploid reproductive structure; usually a single cell; capable of growing into a new individual
Gametophyte
A haploid organism that produces haploid sex cells in an alteration of generations life cycle
Alteration of generations
A life cycle in which diploid individuals produce spores that create haploid individuals; the haploid individuals produce sexually, producing sporophyte individuals and completing the cycle
Why Fungi Are Important
-Along with bacteria, major decomposers of the Earth
-Responsible for much of the cycling of nutrients
-Engage in important symbiotic relationships
-Serve as food and alcohol
Five Major Phyla of Fungi
Chytrids, zygomycetes, glomeromycetes, ascomycetes, basidiomycetes
Chytrids
-Only phylum with swimming spores
-Most are saprophytes
-Can be unicellular or multicellular
Zygomycetes
-Include some familiar bread and fruit moulds
-Most are in soil environments
-Many used commercially
-Many parasites of insects
Glomeromycetes
-All form symbiotic relationships with plant roots
Ascomycetes
-Many, such as yeast, useful to humans
-Some cause serious plant diseases (like cordyceps)
Basidiomycetes
-Include mushrooms, puffballs, and bracket
-Most are decomposers
-Some form symbiotic relationships with plants
Mycelium
A branched mass of hyphae (that make up the bodies of most fungi)